Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas Fisdas Optik
Uploaded by
Fevy D. Kartikarini0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views2 pagestugas fisika
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenttugas fisika
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views2 pagesTugas Fisdas Optik
Uploaded by
Fevy D. Kartikarinitugas fisika
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
TUGAS FISDAS OPTIK:
4. Two flat mirrors have their reflecting surfaces
facing each other, with an edge of one mirror in
contact with an edge of the other, so that the
angle between the mirrors is . When an object
is placed between the mirrors,a number of
images are formed. In general, if the angle is
such that n=360, where n is an integer, the
number of images formed is n -1 . Graphically,
find all the image positions for the case n=6
when a point object is between the mirrors (but
not on the angle bisector).
13. A spherical mirror is to be used to form, on
a screen 5.00 m from the object, an image five
times the size of
the object. (a) Describe the type of mirror
required. (b) Where should the mirror be
positioned relative to the object?
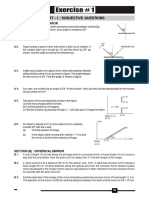
14. A rectangle 10.0 cm x 20.0 cm is placed so
that its right edge is 40.0 cm to the left of a
concave spherical mirror, as in Figure P36.14.
The radius of curvature of the mirror is 20.0 cm.
(a) Draw the image formed by this mirror. (b)
What is the area of the image?
20 cm
10 cm
C
40 cm
15. A dedicated sports-car enthusiast polishes
the inside
and outside surfaces of a hubcap that is a
section of a
sphere. When she looks into one side of the
hubcap,
she sees an image of her face 30.0 cm in back
of the
hubcap. She then flips the hubcap over and
sees another
image of her face 10.0 cm in back of the
hubcap.
(a) How far is her face from the hubcap? (b)
What is
the radius of curvature of the hubcap?
17. A ball is dropped from rest 3.00 m directly
above the
vertex of a concave mirror that has a radius of
1.00 m
and lies in a horizontal plane. (a) Describe the
motion
of the balls image in the mirror. (b) At what
time do
the ball and its image coincide?
18. A flint-glass plate (n = 1.66)rests on the
bottom of an
aquarium tank. The plate is 8.00 cm thick
(vertical dimension)
and covered with water (n = 1.33) to a depth
of 12.0 cm. Calculate the apparent thickness of
the
plate as viewed from above the water. (Assume
nearly
normal incidence.)
20. A simple model of the human eye ignores
its lens entirely.
Most of what the eye does to light happens at
the
transparent cornea. Assume that this outer
surface has a
6.00-mm radius of curvature, and assume that
the eyeball
contains just one fluid with an index of
refraction
of 1.40. Prove that a very distant object will be
imaged
on the retina, 21.0 mm behind the cornea.
Describe the
image.
21. A glass sphere (n =1.50) with a radius of
15.0 cm has a
tiny air bubble 5.00 cm above its center. The
sphere is
viewed looking down along the extended radius
containing
the bubble. What is the apparent depth of the
bubble below the surface of the sphere?
22. A transparent sphere of unknown
composition is observed
to form an image of the Sun on the surface of
the sphere opposite the Sun. What is the
refractive index
of the sphere material?
24. A goldfish is swimming at 2.00 cm/s toward
the front
wall of a rectangular aquarium. What is the
apparent
speed of the fish as measured by an observer
looking in
from outside the front wall of the tank? The
index of refraction
of water is 1.33.
25. A goldfish is swimming inside a spherical
plastic bowl of
water, with an index of refraction of 1.33. If the
goldfish
is 10.0 cm from the wall of the 15.0-cm-radius
bowl,
where does it appear to an observer outside the
bowl?
27. The left face of a biconvex lens has a radius
of curvature
of magnitude 12.0 cm, and the right face has a
radius of
curvature of magnitude 18.0 cm. The index of
refraction
of the glass is 1.44. (a) Calculate the focal
length of
the lens. (b) Calculate the focal length if the
radii of
curvature of the two faces are interchanged.
38. Figure P36.38 shows a thin glass (n
=1.50)converging
lens for which the radii of curvature are R1 =
15.0 cm
and R2 = -12.0cm. To the left of the lens is a
cube
with a face area of 100 cm2. The base of the
cube is on
the axis of the lens, and the right face is 20.0
cm to the
left of the lens. (a) Determine the focal length of
the
lens. (b) Draw the image of the square face
formed by
the lens. What type of geometric figure is this?
(c) Determine the area of the image.
You might also like
- Tugas Fisdas OptikDocument1 pageTugas Fisdas OptikhaikalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 1EDENINo ratings yet
- Assignment OpticsDocument36 pagesAssignment OpticsYash AkhauriNo ratings yet
- Refraction AssignmentDocument2 pagesRefraction AssignmentSai Viswanath BommakantiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Phy250Document9 pagesTutorial 1 Phy250Muhammad AziziNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Geometrical OpticsDocument27 pagesExercise On Geometrical OpticssakshamamitagarwalNo ratings yet
- 02 ExerciseDocument45 pages02 ExercisesocooltrishamNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssgnDocument3 pagesRay Optics AssgnHimanshi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceDocument20 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceVivaan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Assignment3Document3 pagesRay Optics Assignment3hsofficial910No ratings yet
- Optics 1Document3 pagesOptics 1Pubg AppleNo ratings yet
- Optics SheetDocument37 pagesOptics SheetSindhuNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Optics 3Document1 pageWorksheet Optics 3Anagha Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Critical ThinkingDocument9 pagesRay Optics Critical Thinkingvishal_kalraNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions Set1-OpticsDocument5 pagesRevision Questions Set1-OpticsWilberforce JakiraNo ratings yet
- Optics RepDocument29 pagesOptics RepNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Me CB Problems 4Document1 pageMe CB Problems 4ddcvNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentVelu ManiNo ratings yet
- RANKUP NEET (2019) DAY -1 (DPP) Geometrical Optics and Stoichiometry QuestionsDocument32 pagesRANKUP NEET (2019) DAY -1 (DPP) Geometrical Optics and Stoichiometry QuestionsYash bhartiNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument27 pagesOpticsSiddharth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- LightDocument2 pagesLightAmit Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWDocument5 pagesRay Optics Questions STD Xii Holiday HWamritmohanty1000No ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics Type 2 PART 2 of 2 ENGDocument27 pagesGeometrical Optics Type 2 PART 2 of 2 ENGRenu SinhaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Class X Test - CH - LightDocument4 pagesPHYSICS Class X Test - CH - Lightvidhan tiwariNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet - LightDocument3 pagesPhysics Worksheet - Lightcartooncompany73No ratings yet
- Light Reflection and Refraction WorksheetDocument2 pagesLight Reflection and Refraction Worksheetdayanandan167% (6)
- Worksheet-1 (Ray Optics)Document4 pagesWorksheet-1 (Ray Optics)Ritika SunilNo ratings yet
- 2224 - Physics (IIT 4)Document4 pages2224 - Physics (IIT 4)1harshikaNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument1 pageRay OpticsPornachandraRaoNo ratings yet
- Sine of angle of incidence vs transmission angle for dense mediumDocument3 pagesSine of angle of incidence vs transmission angle for dense mediumImro'atus SyarifaNo ratings yet
- CP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionDocument4 pagesCP Physics - Test CH 15 RefractionRashed AlawaishehNo ratings yet
- QB 10Document12 pagesQB 10Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Optics Reflection and RefractionDocument20 pagesOptics Reflection and Refractionkabir ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- BAL BHAVAN PUBLIC SCHOOL PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT RAY OPTICSDocument9 pagesBAL BHAVAN PUBLIC SCHOOL PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT RAY OPTICSKaran RanaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument14 pagesGeometric Optics Multiple Choice QuestionsqvrlenarasegtNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument5 pagesOPTICSNandan vadiNo ratings yet
- Light QBDocument3 pagesLight QBAngad SinghNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Entrance Questions HannDocument4 pagesRay Optics Entrance Questions HannPHYSCO BOT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesICSE Class 9 Physics Important QuestionsSagnik MajumderNo ratings yet
- Assignment CH-9Document2 pagesAssignment CH-9ALFRED STANSLAUSNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Optics F 1 Ass 1Document11 pagesOptics F 1 Ass 1NikhilPrakashNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssignmentDocument20 pagesRay Optics AssignmentApex Institute100% (1)
- PHY11-2 /A1 Casticimo, Milicah M. AR-2 DECEMBER 17, 2013 HW#6Document10 pagesPHY11-2 /A1 Casticimo, Milicah M. AR-2 DECEMBER 17, 2013 HW#6Higashi RyujiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions Only (3 Marks) of OPTICSPramit RanjanNo ratings yet
- 2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCDocument59 pages2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCazamchishty796No ratings yet
- Excellence Is Created HereDocument3 pagesExcellence Is Created HereLunactic ThanosNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument1 pageRay OpticsAryaNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument31 pagesQuizRendon AndrinoNo ratings yet
- 10 LightDocument50 pages10 LightNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- MCQ CH - 10 CLASS 10 PHYSICSDocument8 pagesMCQ CH - 10 CLASS 10 PHYSICSRithika GoruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Light Exercise QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 16 Light Exercise Questionskalash iyerNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ray OpticsDocument2 pagesAssignment-Ray OpticstejvanshsandhuNo ratings yet
- Self Evalution Test-OpticsDocument5 pagesSelf Evalution Test-OpticsBHAAJI0001No ratings yet
- Viewing the Constellations with Binoculars: 250+ Wonderful Sky Objects to See and ExploreFrom EverandViewing the Constellations with Binoculars: 250+ Wonderful Sky Objects to See and ExploreNo ratings yet
- Optics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionFrom EverandOptics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Experimental Determination of the Velocity of Light: Made at the U.S. Naval Academy, AnnapolisFrom EverandExperimental Determination of the Velocity of Light: Made at the U.S. Naval Academy, AnnapolisNo ratings yet
- ER DiagramDocument23 pagesER Diagramapi-2757091480% (20)
- MORTGAGE Short NotesDocument11 pagesMORTGAGE Short Noteshamzatariq015No ratings yet
- Fiera Foods - Production SupervisorDocument1 pageFiera Foods - Production SupervisorRutul PatelNo ratings yet
- PC November 2012Document50 pagesPC November 2012bartekdidNo ratings yet
- VEGA MX CMP12HP Data SheetDocument2 pagesVEGA MX CMP12HP Data SheetLuis Diaz ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Tygon S3 E-3603: The Only Choice For Phthalate-Free Flexible TubingDocument4 pagesTygon S3 E-3603: The Only Choice For Phthalate-Free Flexible TubingAluizioNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual: Auto Lensmeter Plm-8000Document39 pagesOperation Manual: Auto Lensmeter Plm-8000Wilson CepedaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Assessment of Sewer ConstructionDocument32 pagesEnvironmental Assessment of Sewer ConstructionKaleab TadesseNo ratings yet
- Scharlau Chemie: Material Safety Data Sheet - MsdsDocument4 pagesScharlau Chemie: Material Safety Data Sheet - MsdsTapioriusNo ratings yet
- Timely characters and creatorsDocument4 pagesTimely characters and creatorsnschober3No ratings yet
- Time Table For Winter 2023 Theory ExaminationDocument1 pageTime Table For Winter 2023 Theory ExaminationSushant kakadeNo ratings yet
- April 2017 Jacksonville ReviewDocument40 pagesApril 2017 Jacksonville ReviewThe Jacksonville ReviewNo ratings yet
- WWW - Istructe.pdf FIP UKDocument4 pagesWWW - Istructe.pdf FIP UKBunkun15No ratings yet
- Janome DC6030 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument56 pagesJanome DC6030 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- Modified Release Drug ProductsDocument58 pagesModified Release Drug Productsmailtorubal2573100% (2)
- Living Nonliving DeadDocument11 pagesLiving Nonliving DeadArun AcharyaNo ratings yet
- DSE61xx Configuration Suite Software Manual PDFDocument60 pagesDSE61xx Configuration Suite Software Manual PDFluisNo ratings yet
- SOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS (40 CHARACTERSDocument3 pagesSOLVING LINEAR SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS (40 CHARACTERSwaleedNo ratings yet
- Testbanks ch24Document12 pagesTestbanks ch24Hassan ArafatNo ratings yet
- The Singular Mind of Terry Tao - The New York TimesDocument13 pagesThe Singular Mind of Terry Tao - The New York TimesX FlaneurNo ratings yet
- Basf Masterseal 725hc TdsDocument2 pagesBasf Masterseal 725hc TdsshashiNo ratings yet
- Insize Catalogue 2183,2392Document1 pageInsize Catalogue 2183,2392calidadcdokepNo ratings yet
- Impact of Bap and Iaa in Various Media Concentrations and Growth Analysis of Eucalyptus CamaldulensisDocument5 pagesImpact of Bap and Iaa in Various Media Concentrations and Growth Analysis of Eucalyptus CamaldulensisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods: Jeffrey R. ChasnovDocument60 pagesNumerical Methods: Jeffrey R. Chasnov2120 sanika GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Waves and Thermodynamics, PDFDocument464 pagesWaves and Thermodynamics, PDFamitNo ratings yet
- School Quality Improvement System PowerpointDocument95 pagesSchool Quality Improvement System PowerpointLong Beach PostNo ratings yet
- Cianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogDocument1 pageCianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogMaier MariaNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of The DronesDocument43 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of The DronesVysual ScapeNo ratings yet
- GIS Arrester PDFDocument0 pagesGIS Arrester PDFMrC03No ratings yet
- Robocon 2010 ReportDocument46 pagesRobocon 2010 ReportDebal Saha100% (1)