Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)
Uploaded by
Joanna Duapa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
134 views5 pagesDM1 & THYROOID STORM
Original Title
Anatomy & Physiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDM1 & THYROOID STORM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
134 views5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Endocrine System (Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)
Uploaded by
Joanna DuapaDM1 & THYROOID STORM
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Anatomy & Physiology of the Endocrine system
(Pancreas & Thyroid Gland)
Maintains homeostasis by releasing chemicals called HORMONES.
Controls prolonged or continuous processes such as growth and development,
reproduction and metabolism.
Power of the second great controlling system of the body.
Small and unimpressive
Bits and pieces of endocrine tissue are tuck away in widely separated regions of
the body.
Endocrine are true GIANTS.
The key to the incredible power of the Endocrine Gland is
HORMONE A chemical substance that are secreted by cells into the
Extracellular fluid and regulate the metabolic activity of other cells in the body.
Mechanism of Hormone Action
A given hormone affects only certain tissue cells or organs
TARGET CELLS or TARGET ORGANS
Specific protein receptor must be present.
In order for that hormone to ATTACH or BIND.
If bindings occurs HORMONE influence the WORKINGS of a cell.
HORMONE
Hormone is from the Greek word meaning to arouse
They arouse or bring about their effects on the bodys cells primarily by altering
cellular activity.
That is by releasing increase or decrease the rate of a normal or usual, metabolic
process rather than stimulating a new one.
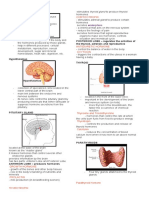
PITUITARY GLAND
It is approximately the size of a grape.
It has two functional lobes
Anterior Pituitary
Several Anterior Pituitary hormones that affect many body
organs.
Growth & prolactin hormone
Thyrotrophic, Adrenocorticotropic and two gonadotropic
hormones.
Posterior Pituitary
The Anterior Pituitary gland controls the activity of so many other endocrine
glands that it has often been called Master Endocrine Gland.
With the help of releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the
hypothalamus.
PANCREAS
It is about 15cm (6in) long.
Widest section is called the head.
The narrowest is called tail.
The middle section is called the body.
The pancreas is made up of exocrine cells endocrine cells.
Aids for digestion Exocrine cells
Islets/ Islets of Langerhans
There are 3 cells ALPHA,BETA,DELTA cells
Alpha cells secrets Glucagon
Beta cells secretes Insulin
Insulin lowers the amount of sugar in the blood when blood sugar is high.
Glucagon Increases the amount of sugar in the blood when the blood sugar is
low.
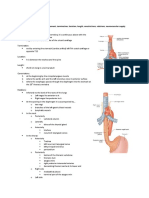
THYROID GLAND
Located base of the throat, just inferior to the Adams apple.
It is easily palpated during a physical examination.
It consist of two lobes joined by a central mass or isthmus.
Thyroid Gland produces two hormones Thyroid hormone and calcitonin.
THYROID HORMONE
Referred to as the bodys major metabolic hormone.
An active iodine-containing hormones.
Thyroxine or T4 and tri-iodothyronine or T3.
THYROXINE Is the major hormone secreted by the thyroid follicles.
Controls the rate at which glucose is burned or iodized.
And converted to body heat and chemical energy.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology-Endocrine SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-Endocrine SystemEixid Enna YeLikNo ratings yet
- (Sep. 6) CPR RationalizationDocument21 pages(Sep. 6) CPR RationalizationJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument11 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyAmanda WildeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Endocrine SystemJumaimah BauloNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2Document4 pagesNCM 106 Pharmacology Lec 1 and 2christyl necesitoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Respiratory System: Chapter 20Document4 pagesStructure and Function of The Respiratory System: Chapter 20Shari TernolaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Seventh EditionDocument40 pagesThe Endocrine System: Seventh EditionAngelaNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System PharmacologyDocument13 pagesAutonomic Nervous System PharmacologySam BotNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of BiologyDocument28 pagesCentral Dogma of BiologyJabin Sta. TeresaNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Part BDocument38 pagesThe Endocrine System: Part BKaly RieNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System in 40 CharactersDocument5 pagesEndocrine System in 40 CharactersJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemDara BMNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes #1 DRUG ACTIONDocument4 pagesPharmacology Notes #1 DRUG ACTIONAyumi StarNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument30 pagesBiologyChristel Ramos100% (1)
- Hormones and Coordinating System of AnimalsDocument2 pagesHormones and Coordinating System of AnimalsLin ManahanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Endocrine SystemDocument45 pagesIntroduction To The Endocrine Systemវ៉ុន ដាលីន Von DalinNo ratings yet
- Flowers and reproduction life cyclesDocument16 pagesFlowers and reproduction life cyclesCat100% (1)
- Skeletal Muscle Physiology LectureDocument65 pagesSkeletal Muscle Physiology Lectureanon_737973908No ratings yet
- Endocrine System GuideDocument6 pagesEndocrine System GuideChechan AmbaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesDrugs Affecting The Autonomic Nervous SystemJs BaldomaroNo ratings yet
- General Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyDocument4 pagesGeneral Chapter 4: The Physiological Basis of Behavior PsychologyChristine Rose EmNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument163 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyColor BlackNo ratings yet
- Anatomic and Physiologic OverviewDocument8 pagesAnatomic and Physiologic OverviewJoseph King MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Property. Nuguid V Ca. Full CaseDocument7 pagesProperty. Nuguid V Ca. Full CaseAnonymous XduaVMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-SensesDocument74 pagesChapter 9-SensesMaiah DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The StomachDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The StomachEmmi Maliza HutagaolNo ratings yet
- Pulse sites for upper limb, lower limb, head, neck and torso assessmentDocument1 pagePulse sites for upper limb, lower limb, head, neck and torso assessmentArnel AlmazanNo ratings yet
- Ra 9003Document20 pagesRa 9003Marc Robin RejasNo ratings yet
- Sheehan Syndrome Lancet Eponym 2003Document3 pagesSheehan Syndrome Lancet Eponym 2003Alejandro GuillenNo ratings yet
- Blood physiology components and functionsDocument39 pagesBlood physiology components and functionsSarmad Laith MortadaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMODULE 1FEMALE Reproductive SystemHoney Lou SemblanteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Urinary System (JOse Reyes)Document2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Urinary System (JOse Reyes)Bryan Baynosa ArabianaNo ratings yet
- Obstetirc NursingDocument36 pagesObstetirc NursingGlenn Daryll SantosNo ratings yet
- Court of Appeals decision overturned in land dispute caseDocument12 pagesCourt of Appeals decision overturned in land dispute caseKyle CroodsNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEW QUESTIONSDocument15 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEW QUESTIONSMarcoNo ratings yet
- A&P 302 Endocrine ChartDocument7 pagesA&P 302 Endocrine ChartBethanyNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology: Clarito F. Concepcion Associate Professor 5 CSM, WmsuDocument48 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology: Clarito F. Concepcion Associate Professor 5 CSM, WmsuScar Shadow100% (1)
- Endocrine System QuizDocument2 pagesEndocrine System QuizDr. Atif Hassan KhirelsiedNo ratings yet
- CATS & DOGS Nutrition PDFDocument71 pagesCATS & DOGS Nutrition PDFErald Renz LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Esphagus Stomach Duodenum Gross AnatomyDocument9 pagesEsphagus Stomach Duodenum Gross AnatomyWinchester LoapedNo ratings yet
- Phases of Drug Therapy and PharmacokineticsDocument3 pagesPhases of Drug Therapy and PharmacokineticsLae DujonNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System: Glands and HormonesDocument213 pagesThe Endocrine System: Glands and HormonesRosita Antiquina Elopre100% (1)
- The Human Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemsDocument51 pagesThe Human Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemsAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes Chapter 1 IntroDocument4 pagesPharmacology Notes Chapter 1 Introridley45No ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous System Spinal CordDocument41 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous System Spinal CordAleksandarTrenovskiNo ratings yet
- 1 Rallos v. Felix Go ChanDocument7 pages1 Rallos v. Felix Go ChansdfoisaiofasNo ratings yet
- Spouses Nuguid vs Court of Appeals and PecsonDocument2 pagesSpouses Nuguid vs Court of Appeals and PecsonJohn Paul Pagala AbatNo ratings yet
- New SasDocument133 pagesNew SasUNKNOWN ANGELNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Document47 pages02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Document55 pagesANAPHY LEC PRELIMS NOTES by NOVERO KEN BMLS2 1Marcus Randielle FloresNo ratings yet
- The Heart: Sources: Google Images, Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 10 EditionDocument4 pagesThe Heart: Sources: Google Images, Seeley's Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 10 EditionShane Aileen AngelesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemMaricris GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument8 pagesEndocrine System NotesShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System OutlineDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System OutlineRogie P. BacosaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Glands and Hormones (39Document8 pagesEndocrine System Glands and Hormones (39Criscia Lene OlatNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument10 pagesEndocrine System13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: RespirationDocument2 pagesBiology Notes: RespirationDaniel Baluris100% (1)
- Ymphatic Ystem: Natomy AND HysiologyDocument7 pagesYmphatic Ystem: Natomy AND Hysiologydlneisha61No ratings yet
- Grow Taller: © Dr. Laura de Giorgio All Rights ReservedDocument12 pagesGrow Taller: © Dr. Laura de Giorgio All Rights ReservednepplutoNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument19 pagesEndocrine Systemethel roseNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis WS1Document3 pagesHomeostasis WS1firas Abdel-Kareem100% (1)
- Harmening QuestionsDocument19 pagesHarmening QuestionsJeremiah Gatchalian100% (1)
- Blood Evidence Techniques: Locating, Collecting & Preserving Blood SamplesDocument21 pagesBlood Evidence Techniques: Locating, Collecting & Preserving Blood SamplesEmelie TipayNo ratings yet
- Digestive System by Dr. Tehreem FatimaDocument9 pagesDigestive System by Dr. Tehreem FatimaTehreem FatimaNo ratings yet
- The Boxing Debate by The British Medical AssociationDocument132 pagesThe Boxing Debate by The British Medical AssociationTheRealBarrettNo ratings yet
- Nephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Document42 pagesNephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Alokh Saha RajNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science GradeDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science GradeninaNo ratings yet
- Modern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionsDocument11 pagesModern Treatment Planning Approach Facing A Failure of Conventional Treatment. Part I: Analysis of Treatment OptionscdoskarNo ratings yet
- Krok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationDocument24 pagesKrok 1 Stomatology: Test Items For Licensing ExaminationhelloNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Placement: First YearJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- PIH CASE FinalDocument35 pagesPIH CASE FinalrJ67% (3)
- MCQ - Cardiovasuclar SystemDocument3 pagesMCQ - Cardiovasuclar SystemAmacus NirvanaNo ratings yet
- Blood Types Transfusion Tissue and Organ Transplantation NotesDocument7 pagesBlood Types Transfusion Tissue and Organ Transplantation NotesRama JoshiNo ratings yet
- Materi Digestive SystemDocument13 pagesMateri Digestive Systembetta putriNo ratings yet
- Otalgia & TinnitusDocument19 pagesOtalgia & Tinnitushonda matizNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Q3Document188 pagesScience 10 Q3mariacayeneNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1571800842460Document27 pagesOrca Share Media1571800842460Reniel De MesaNo ratings yet
- Craniofacial Changes in Patients With Class III Malocclusion Treated With The Rampa SystemDocument7 pagesCraniofacial Changes in Patients With Class III Malocclusion Treated With The Rampa Systemapi-192260741100% (1)
- Regulation of Heart RateDocument27 pagesRegulation of Heart RateGaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- DR - Asdala TransDocument8 pagesDR - Asdala TransthorheavenNo ratings yet
- 1000 MCQ Bank for Palestine Faculty of MedicineDocument161 pages1000 MCQ Bank for Palestine Faculty of MedicineMuhsen Muneer89% (9)
- Lecture10 - Blood Groups and TransfusionDocument28 pagesLecture10 - Blood Groups and Transfusionmohapatrarashmi050No ratings yet
- Clitoral SensationDocument36 pagesClitoral Sensationjariyaz50% (6)
- Neurogenic and Myogenic HeartsDocument14 pagesNeurogenic and Myogenic HeartsSantanu100% (1)
- Pragyan College of Nursing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Sense of Taste/TongueDocument3 pagesPragyan College of Nursing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Sense of Taste/TongueNeelofur Ibran AliNo ratings yet
- WL-ES700 Manual Preso en InglesDocument10 pagesWL-ES700 Manual Preso en InglesVerónica Barría JerezNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesReproductive SystemCamille Ann Faigao FamisanNo ratings yet
- Accordion Sign-Appearance (C. Difficile)Document41 pagesAccordion Sign-Appearance (C. Difficile)Andra HijratulNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing 1Document43 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing 1Tifanny Shaine Tomas100% (2)
- The Excretory System BiologyDocument6 pagesThe Excretory System BiologyCamille ComasNo ratings yet