Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hydraulic 2 post car elevator project
Uploaded by
Adrian SbarceaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hydraulic 2 post car elevator project
Uploaded by
Adrian SbarceaCopyright:
Available Formats
TRANSILVANIA UNIVERSITY OF BRASOV
FACULTY OF MECHANICAL EGINEERING
PROJECT: 2 POST CAR ELEVATOR
SPECIALISATION: Automotive Engineering
YEAR: III
GROUP: 1721
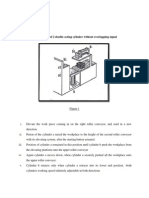
2 POST CAR ELEVATOR
I. General information
Hydraulic Elevators utilize an oil pump located in a machine room to provide the lifting power.
The machine room is preferred to be adjacent to the hoistway. A hydraulic piston is located in the
hoistway between the rails, next to the moving car. As hydraulic fluid is pumped into the piston, the car
moves upward. As hydraulic fluid is released back to the reservoir in the machine room, the car moves
downward. The benefits include smooth operation, quiet operation, and easy emergency lowering.
The hydraulic elevator is nearly silent in the down direction as the pump is not running. If the elevator
stopped between levels for any reason, it is easy to manually lower it. Every hydraulic elevator has an
emergency lowering valve. By pressing and holding a button, the elevator will slowly lower to floor
level.
Legend:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Electric Engine (EE)
Oil tank
Electric actuator
Arms
Posts
Cylinders
Working principle:
This elevator will be
used to lift a weight up to 4
tonnes (which represents a
weight of a big van, small class
cars being also included in this
domain), at a maximum height
of 1900 mm and a minimum
height of 98 mm. The
necessary time for lifting at
maximum height is 50 seconds,
while lowering time is about 55
seconds.
By acting start
button from the switch, the
electric engine starts and
actuate the oil pump, which
takes oil from the oil tank and
pushes it inside the cylinders
through the hydraulic pipes.
The car will be lifted by the
arms of the elevator which are
mounted on posts and actuated
by the cylinders.
II.Hydraulic scheme of the elevator
III. Functioning description. Dimensioning of the cylinders
Positions of functioning:
1. First position Lift
In the first position, the electric engine will actuate the hydraulic pump and with the control system, the
actuator will start, lifting the cylinders (also the vehicle).
2. Second position Neutral
In the second case, the oil that is inside the cylinders will be blocked there, and the elevator will stay at
rest, in a specific position.
3. Third position Lowering
In the third position, the oil that in the second position was blocked inside the cylinder, the pressure
will be released and the oil will enter into the upper side of the cylinders, lowering the arms of the
elevator.
where
= = 4000 9.81 = 39240 40000
= 4000
G = force
P = pressure
S = area
It is chosen a pressure of 35 bar.
20000
2
= =
=
= 5.71 103 2 = 57.1 2
5
35 10
35 105
= 2 => = = 4.26 = 42.6
= 2 = 2 42.6 = 85.2
For the hydraulic pump we have:
= => =
n = 500 rpm; Q = 7.9 lpm;
7.9
= 0.0158 3
500
IV. Choosing the cylinder
It is chosen from standard ISO 15552 a cylinder DSBG 100 PPSA with the following
specifications:
Diameter of piston: 100 mm
Stroke: 1900 mm
Volume: = = 190000 3
You might also like
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesFrom EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assign 1Document15 pagesAssign 1Aakarshit JainNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 HydraulicsDocument9 pagesExperiment 1 Hydraulicsmon patrick pradoNo ratings yet
- ME Elective (Hydraulics)Document19 pagesME Elective (Hydraulics)Lee Anthony ChingNo ratings yet
- The Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineFrom EverandThe Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Elevators Basic ComponentsDocument16 pagesHydraulic Elevators Basic ComponentsIkhwan Nasir100% (2)
- ELEVATORSDocument24 pagesELEVATORSAyesha SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- How Hydraulic Cranes Lift Heavy LoadsDocument9 pagesHow Hydraulic Cranes Lift Heavy Loadssunil481No ratings yet
- Ar 307: Building Services-Ii: Assignment IiiDocument21 pagesAr 307: Building Services-Ii: Assignment IiiAakarshit JainNo ratings yet
- ZXK 1200 Ascensor Hidrocableado Chino - ManualDocument25 pagesZXK 1200 Ascensor Hidrocableado Chino - ManualBrianEstebanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic SystemDocument16 pagesHydraulic Systemluis tocoraNo ratings yet
- Elevator TechnologiesDocument26 pagesElevator Technologiesaileen eustaquioNo ratings yet
- HYDRO POWER ELECTRIC MECHANICAL JACKDocument6 pagesHYDRO POWER ELECTRIC MECHANICAL JACKHàrđik ĶharkhandiNo ratings yet
- Project ElevatorDocument45 pagesProject ElevatorTun TunNo ratings yet
- Elevators Explained: Types, Components & How They WorkDocument11 pagesElevators Explained: Types, Components & How They Worksaad ElsheikhNo ratings yet
- So How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkDocument12 pagesSo How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkAyesha MAhmoodNo ratings yet
- System Pressure - Release: Shutdown SISDocument7 pagesSystem Pressure - Release: Shutdown SISeshopmanual TigaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Hydraulic Car Jack DesignDocument44 pagesAutomatic Hydraulic Car Jack Designinfo svmelectromechNo ratings yet
- Design and Working of Automatic Electro Hydraulic JackDocument13 pagesDesign and Working of Automatic Electro Hydraulic JackVandana VanuNo ratings yet
- 2.0 JacksDocument7 pages2.0 JacksHellena VivianNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic Mechanism of Acme Cutting MachineDocument21 pagesHydraulic Systems: Hydraulic Mechanism of Acme Cutting MachineSantha PriyaNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear SystemDocument7 pagesLanding Gear SystemKuha ManoNo ratings yet
- Convertible Top - Power: 1988 Chrysler Lebaron Convert/CoupeDocument4 pagesConvertible Top - Power: 1988 Chrysler Lebaron Convert/CoupeJames PonzoNo ratings yet
- Unitrigmt6500 Hyd Dump SysDocument19 pagesUnitrigmt6500 Hyd Dump Sysnikbeam0% (1)
- Oil Hydraulics and Pneumatics ApplicationsDocument25 pagesOil Hydraulics and Pneumatics ApplicationsAdeoti OladapoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System SpecificationsDocument38 pagesHydraulic System SpecificationsTrường NguyenNo ratings yet
- Arel Guna PneumaticDocument8 pagesArel Guna PneumaticKhairul SyahreelNo ratings yet
- Vertical Transportation SystemDocument14 pagesVertical Transportation Systempassionpropel100% (3)
- Thermo Lab ReportDocument18 pagesThermo Lab Reportanon_285098975100% (1)
- Guide to the Hydraulic System of the LG56L LoaderDocument82 pagesGuide to the Hydraulic System of the LG56L LoaderGeorge Jhonson100% (2)
- ExplainDocument2 pagesExplainmalikjawaduetNo ratings yet
- Section 31 - Power Take-Off - Chapter 2Document28 pagesSection 31 - Power Take-Off - Chapter 2احمد الشبراوى الشبراوىNo ratings yet
- Assignment On PLCDocument4 pagesAssignment On PLCNirman ParasharNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System Hydraulics: An Area of Engineering Science That Deals With andDocument19 pagesHydraulic System Hydraulics: An Area of Engineering Science That Deals With andArun Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- MEM 341 - Chapter 9 Hydraulic CircuitDocument22 pagesMEM 341 - Chapter 9 Hydraulic CircuitMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- TM 9-1750H Hydraulic Traversing Mechanism (Logansport) For Medium Tank M3 and Modifications 1943Document152 pagesTM 9-1750H Hydraulic Traversing Mechanism (Logansport) For Medium Tank M3 and Modifications 1943RobertLockieNo ratings yet
- Topic4b Building TransportationDocument71 pagesTopic4b Building Transportationelleyashahari100% (2)
- Emergency Evacuation (MRL)Document3 pagesEmergency Evacuation (MRL)王帅No ratings yet
- 400 RearlinkageDocument27 pages400 RearlinkageMrAlbert2009No ratings yet
- Automobile Engg (Unit-02)Document20 pagesAutomobile Engg (Unit-02)SUDHARSHAN REDDYNo ratings yet
- Truckcrn PDFDocument6 pagesTruckcrn PDFDusan VeljkovicNo ratings yet
- CRANE Hyd SymbolsDocument26 pagesCRANE Hyd SymbolsNiko Bintang LautNo ratings yet
- 2.steering GearDocument15 pages2.steering GearMehedy Masud100% (1)
- Mechanism On Scissor Lift Operation Report PDFDocument4 pagesMechanism On Scissor Lift Operation Report PDFAMY SHAKYLLA BINTI ADEHAM / UPMNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic System of TractorDocument53 pagesHydraulic System of Tractorsln_rj100% (4)
- Pneumatics ProblemsDocument22 pagesPneumatics ProblemsMatthew Laureano ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Mini Weighing CraneDocument12 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Mini Weighing CraneBalasubramani SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- JKR Basic Lift ComponentsDocument47 pagesJKR Basic Lift ComponentsKayrol Amry0% (1)
- Project 1-1Document9 pagesProject 1-1tcode94No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Power Basics GuideDocument53 pagesHydraulic Power Basics GuideMohit Kumar100% (2)
- ElevatorsDocument11 pagesElevatorsDalia M-aNo ratings yet
- Design sequential control circuit for industrial robotDocument5 pagesDesign sequential control circuit for industrial robotrt_srv08No ratings yet
- DOUBLE-DECK SCISSOR LIFT LS707 ManualDocument20 pagesDOUBLE-DECK SCISSOR LIFT LS707 ManualOk PalaceNo ratings yet
- Industrial Hydraulic Circuit Design and AnalysisDocument9 pagesIndustrial Hydraulic Circuit Design and AnalysisSUMEET SINGHNo ratings yet
- Elevators and Escalators DesignDocument10 pagesElevators and Escalators DesignNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Electrohydraulic Steering GearDocument6 pagesElectrohydraulic Steering Gearyoarun5100% (2)
- OPERATION OF TITANIC'S CARGO CRANESDocument8 pagesOPERATION OF TITANIC'S CARGO CRANESAlen BajrovicNo ratings yet
- Operate Tractor SafelyDocument23 pagesOperate Tractor Safelylulu323283% (6)
- D352004054 MKT 001Document32 pagesD352004054 MKT 001Cesar MoraNo ratings yet
- Weight Management: Aviation Operational Measures For Fuel and Emissions Reduction WorkshopDocument12 pagesWeight Management: Aviation Operational Measures For Fuel and Emissions Reduction WorkshopalkhaldyNo ratings yet
- WB146 Revised 03 13 06 PDFDocument10 pagesWB146 Revised 03 13 06 PDFLuisAlbertoVerdejoTapiaNo ratings yet
- HMDocument2 pagesHMapi-279049687No ratings yet
- Scania SOPS ParametersDocument32 pagesScania SOPS Parametersjose breno vieira silva89% (19)
- Explosion Deep Oil WellDocument375 pagesExplosion Deep Oil WellVincent J. CataldiNo ratings yet
- Technical English Aircraft WorksheetDocument3 pagesTechnical English Aircraft WorksheetMHLS68No ratings yet
- Hinomoto OEM 2020Document68 pagesHinomoto OEM 2020Piesemasini MasinieuNo ratings yet
- TM 9-1727B Engine Cooling, Engine Electrical and Engine Fuel Systems For Light Tank M5, Etc 1943Document252 pagesTM 9-1727B Engine Cooling, Engine Electrical and Engine Fuel Systems For Light Tank M5, Etc 1943RobertLockieNo ratings yet
- Light Running Margin CyprusDocument25 pagesLight Running Margin Cyprusstopless_dalian685No ratings yet
- MEO Class 4B Examinations Oral Question Bank For Electro Technology and Control EngineeringDocument8 pagesMEO Class 4B Examinations Oral Question Bank For Electro Technology and Control EngineeringShriram AryanNo ratings yet
- Basic CylinderDocument24 pagesBasic CylinderSamik MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- MR - Engine 1104D Assembly & Disasembly PDFDocument138 pagesMR - Engine 1104D Assembly & Disasembly PDFmliugongNo ratings yet
- Bendix D-2 GovernorDocument4 pagesBendix D-2 GovernormarcrunnerNo ratings yet
- IPM Production ProgrammeDocument55 pagesIPM Production ProgrammeSlobodan AleksovNo ratings yet
- Sanden Compressor ListDocument28 pagesSanden Compressor ListSIVARAMANJAGANATHANNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Crude Glycerol to BiodieselDocument12 pagesConversion of Crude Glycerol to BiodieselIngJesusGutierrezZenilNo ratings yet
- History of Electric CarsDocument8 pagesHistory of Electric CarsInstalatiiGeneraleNo ratings yet
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics: BlankDocument9 pagesThe Second Law of Thermodynamics: Blankbarry6688No ratings yet
- Iveco Daily F1A Engine Troubleshooting and Repair ManualDocument266 pagesIveco Daily F1A Engine Troubleshooting and Repair ManualAntonio GasparNo ratings yet
- DM-PH&SD-P4-TG18 - (Guidelines For Safety in Vehicle Repair and Servicing Shops) PDFDocument6 pagesDM-PH&SD-P4-TG18 - (Guidelines For Safety in Vehicle Repair and Servicing Shops) PDFdemie figueroaNo ratings yet
- Coal Briquetting Technology GuideDocument10 pagesCoal Briquetting Technology GuideAgrim KhatryNo ratings yet
- Bio-Batteries: An Eco-Friendly Energy AlternativeDocument25 pagesBio-Batteries: An Eco-Friendly Energy AlternativeShahid FarooqiNo ratings yet
- School of Maritime Studies Vels University Thalambur The Fuel Oil System For A Diesel Engine Internal Combustion Engine ProcedureDocument2 pagesSchool of Maritime Studies Vels University Thalambur The Fuel Oil System For A Diesel Engine Internal Combustion Engine ProcedureAayush Agrawal100% (2)
- DoosanDocument186 pagesDoosanAriadny Coelho100% (12)
- Gas Turbine - For Migas IndonesiaDocument31 pagesGas Turbine - For Migas IndonesiaGopi NathNo ratings yet
- Residencial Backup SolutionDocument20 pagesResidencial Backup SolutionOSCAR SIRIAS AGUILARNo ratings yet
- Varaschin Julian A 201609 MASCDocument151 pagesVaraschin Julian A 201609 MASCDiegoNo ratings yet
- Thermal Oil BoilerDocument4 pagesThermal Oil Boilerarjmandquest100% (1)
- SCR System and Performance Innovation (Part 2)Document2 pagesSCR System and Performance Innovation (Part 2)IQPC GmbHNo ratings yet