Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ap7102 Adsd Syllabi
Uploaded by
shankarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ap7102 Adsd Syllabi
Uploaded by
shankarCopyright:
Available Formats
KONGUNADU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THOTTIAM.
AP 7102 ADVANCED DIGITAL LOGIC SYSTEM DESIGN
OBJECTIVES:
To analyze synchronous and asynchronous sequential circuits
To realize and design hazard free circuits
To familiarize the practical issues of sequential circuit design
To gain knowledge about different fault diagnosis and testing methods
To estimate the performance of digital systems
To know about timing analysis of memory and PLD
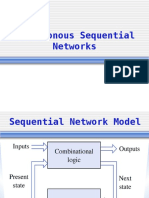
UNIT I SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT DESIGN
9
Analysis of Clocked Synchronous Sequential Networks (CSSN) - Modeling of CSSN State Assignment and Reduction Design of CSSN Design of Iterative Circuits
ASM Chart ASM Realization, Design of Arithmetic circuits for Fast adder- Array Multiplier.
UNIT II ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT DESIGN
9
Analysis of Asynchronous Sequential Circuit (ASC) Flow Table Reduction Races in ASC State Assignment Problem and the Transition Table Design of ASC
Static and Dynamic Hazards Essential Hazards Design of Hazard free circuits - Data Synchronizers Designing Vending Machine Controller Mixed Operating Mode
Asynchronous Circuits. Practical issues such as clock skew, synchronous and asynchronous inputs and switch bouncing.
UNIT III FAULT DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
9
Fault diagnosis: Fault Table Method Path Sensitization Method Boolean Difference Method Kohavi Algorithm Tolerance Techniques The Compact Algorithm.
Design for testability: Test Generation Masking Cycle DFT Schemes. Circuit testing fault model, specific and random faults, testing of sequential circuits, Built in Self
Test, Built in Logic Block observer (BILBO), signature analysis.
UNIT IV PERFORMANCE ESTIMATION
9
Estimating digital system reliability, transmission lines, reflections and terminations, system integrity, network issues for digital systems, formal verifications of digital
system: model-checking, binary decision, theorem proving, circuit equivalence.
UNIT V TIMING ANALYSIS
9
ROM timings, Static RAM timing, Synchronous Static RAM and its timing, Dynamic RAM timing, Complex Programmable Logic Devices, Logic Analyzer Basic
Architecture, Internal structure, Data display, Setup and Control, Clocking and Sampling.
TOTAL: 45 PERIODS
REFERENCES:
1. Charles H.Roth Jr Fundamentals of Logic Design, Thomson Learning 2004.
2. Nripendra N Biswas Logic Design Theory Prentice Hall of India, 2001.
3. Parag K.Lala An introduction to Logic Circuit Testing Morgan and claypool publishers, 2009.
4. Stephen D Brown, Fundamentals of digital logic, TMH publication, 2007.
5. Balabanian, Digital Logic Design Principles, Wiley publication, 2007.
6. Stalling, Computer Organization & Architecture, Pearson Education India, 2008.
7. J.F.Wakerly, Digital Design, Pearson Education India, 2012.
8. J.F.Wakerly, Digital Design principles and practices, PHI publications, 2005.
KNCET, TRICHY
9. Charles J. Sipil, Microcomputer Handbook McCrindle- Collins Publications 1977.
UNIT I
SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT DESIGN
Analysis of Clocked Synchronous Sequential Networks (CSSN) - Modeling of CSSN- State Assignment and Reduction- Design of CSSN- Design of
iterative circuits-ASM chart- ASM Realization, Design of arithmetic Circuits for Fast adder-Array Multiplier.
Session
No.
Topics to be covered
Ref
1.
Analysis of Clocked Synchronous Sequential Networks- Introduction.
2.
Design of a Sequential parity checker, Analysis of Moore and Mealy sequential circuit by signal
tracing and timing charts.
3.
Method of constructing state table and state graphs for Moore and Mealy machines.
4.
General Models for a clocked Mealy and Moore sequential circuits.
5.
Guidelines for state assignments and reduction of state table using state assignment.
6.
Different types of State Assignment- Shared row, Multiple row and One hot state assignment.
7.
Determination of state equivalence and circuit equivalence using an implication table.
8.
Design of iterative circuits, Design of a n-bit comparator.
9.
Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) Charts- Derivation and realization of ASM Chart.
10.
Design of Arithmetic circuits for Fast adder- Carry look ahead adder.
11.
Array Multiplier Structure of an 4 X 4 Multiplier circuit.
Page No
Material Page
No
KNCET, TRICHY
UNIT II
ASYNCHRONOUS SEQUENTIAL CIRCUIT DESIGN
Analysis of Asynchronous Sequential Circuit (ASC) - Flow Table Reduction-Races in ASC- State Assignment Problem and the Transition Table- Design of
ASC-Static and Dynamic Hazards- Essential Hazards- Design of Hazard free circuits- Data Synchronizers- Designing Vending Machine Controller- Mixed
Operating Mode Asynchronous Circuits. Practical issues such as clock skew, synchronous and asynchronous inputs and switch bouncing.
Session
No.
Topics to be covered
Ref
12.
Analysis of Asynchronous Sequential Circuit - Design of Fundamental mode sequential
circuit - Primitive state table, state table reduction and state assignment.
13.
Design of Pulse mode sequential circuit- Primitive state table, state table reduction and state
assignment.
14.
Problems in Asynchronous Sequential Circuits Cycles, Critical race and Non- Critical race.
2,5
15.
Hazards- Static, Dynamic and Essential Hazards.
2,5
16.
Design of Hazard free switching circuits- Static Hazard and Essential Hazard elimination.
2,5
17.
Working principle of Data synchronizer.
18.
Design of Vending machine controller- Description/ Specification, FSM design steps, State
diagram and state table.
19.
Design of mixed operating mode asynchronous circuit.
20.
Practical issues: Clock skew, synchronous and asynchronous inputs and switch bouncing.
Page No
Material Page
No
KNCET, TRICHY
UNIT III
FAULT DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
Fault diagnosis: Fault Table Method- Path Sensitization Method- Boolean Difference Method- Kohavi Algorithm -Tolerance Techniques- The Compact
Algorithm. Design for testability: Test Generation- Masking Cycle - DFT schemes. Circuit testing fault model, specific and random faults, testing of
sequential circuits, Built in self test, Built in Logic Block observer (BILBO), Signature analysis.
Session
No.
Topics to be covered
Ref
21.
Fault Models- Stuck-at fault, Bridging fault, stuck-open fault and Temporary faults.
22.
Fault Diagnosis of Digital systems- Test generation for combinational logic circuits- Fault
Table Method and Path Sensitization method.
23.
Boolean Difference method.
24.
Kohavi and Compact Algorithm.
25.
Tolerance techniques- Static redundancy, Dynamic redundancy
and Hybrid redundancy.
26.
Self- purging redundancy, Sift-out modular redundancy
27.
Fault in PLAs, Test generation and Masking cycle.
28.
Design for Testability (DFT), DFT schemes, Circuit testing fault model: Specific and random
faults.
29.
Testing of sequential circuits and Built In Self Test (BIST).
30.
Built In Logic Block Observer (BILBO) and Signature analysis.
Page No
Material Page
No
KNCET, TRICHY
UNIT IV
PERFORMANCE ESTIMATION
Estimating digital system reliability, transmission lines, reflections and terminations, system integrity, network issues for digital systems, formal verifications
of digital system: model- checking, binary decision diagram, theorem proving, circuit equivalence.
Session
No.
Topics to be covered
Ref
31.
Estimating Digital System Reliability- Failure rates, Reliability and MTBF, System
Reliability.
32.
Transmission lines with infinite and finite length terminated with characteristic impedance,
Logic signal terminations.
33.
Network issues for digital systems: Noise, Time margin, Parasitic inductance and
capacitances.
34.
Digital System Integrity to minimize Noise Margin, Transmission Line effects, Signal Path
Return currents and power distribution.
35.
Design and Verification of Digital Systems: Design flow and RTL Verification.
36.
Binary Decision Diagrams with an example.
37.
Model for Design Verification, Functional Validation.
38.
Formal Verification and Challenges in Symbolic Simulation.
Page No
Material Page
No
KNCET, TRICHY
UNIT V
TIMING ANALYSIS
ROM timings, Static RAM timing, Synchronous Static RAM and its timing. Dynamic RAM timing, Complex Programmable Logic devices, Logic Analyzer
Basic Architecture, Internal Structure, Data display, Setup and Control, Clocking and Sampling.
Session
No.
Topics to be covered
Ref
39.
Read Only Memory (ROM) Timing diagram.
40.
Static RAM Internal Structure and Timing parameters for Read and Write operation of
static RAM.
41.
Synchronous SRAM- Internal Structure and its read and Write operation.
42.
Dynamic RAM Structure, Write and burst read cycle Timing.
43,44
Complex Programmable Logic Devices general architecture, Function block architecture,
Input/output block architecture and Switch Matrix.
45.
Logic Analyzer- Basic Architecture and Internal Structure.
46.
Logic Analyzer- Clocking, Triggering, Acquisition and Capturing Glitches.
47.
Logic Analyzer- Data display, Setup and Control
Page No
Material
Page No
7
7
7
6
6
6
KNCET, TRICHY
You might also like
- Ap7102 AdsdDocument5 pagesAp7102 AdsdshankarNo ratings yet
- De SyllabusDocument2 pagesDe SyllabusKarthikeyan_Go_9525No ratings yet
- Regulations - 2009: Affiliated Institutions Anna University, ChennaiDocument10 pagesRegulations - 2009: Affiliated Institutions Anna University, Chennaisri_vas00074013No ratings yet
- EC6302 - de - SyllabusDocument2 pagesEC6302 - de - SyllabusNava KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization Lab Experiments ListDocument1 pageComputer Organization Lab Experiments ListHimanshu MittalNo ratings yet
- Advanced Digital System DesignDocument1 pageAdvanced Digital System Designarunecetheboss0% (3)
- Ae IIDocument27 pagesAe IIAnbu SelvanNo ratings yet
- M E EmbeddedSystemTechnologiesDocument31 pagesM E EmbeddedSystemTechnologiesRohini BabuNo ratings yet
- Vlsi Design PDFDocument22 pagesVlsi Design PDFKishore KumarNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics Combinational and Sequential Circuit DesignDocument2 pagesDigital Electronics Combinational and Sequential Circuit DesignjeevaNo ratings yet
- R 2008 M.E. Applied Electronics SyllabusDocument31 pagesR 2008 M.E. Applied Electronics SyllabusisasenthilNo ratings yet
- EC657 Digital System Design and EC661 Digital Signal Processing StructuresDocument2 pagesEC657 Digital System Design and EC661 Digital Signal Processing StructuresAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- EC1303 Digital System Design Course OverviewDocument2 pagesEC1303 Digital System Design Course OverviewMohamed Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Course 9Document2 pagesCourse 9faster123No ratings yet
- Revised Syllabus MicroelectronicsDocument19 pagesRevised Syllabus MicroelectronicsBaluvu JagadishNo ratings yet
- M.tech Vlsi Syllabus: D.A.John & K.Martin, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, Wiley, 1997Document5 pagesM.tech Vlsi Syllabus: D.A.John & K.Martin, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, Wiley, 1997Garth RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematics For Electronics EngineersDocument35 pagesApplied Mathematics For Electronics EngineersRamJiDRNo ratings yet
- Switching Theory and Logic DesignDocument2 pagesSwitching Theory and Logic DesignManjunath BadigerNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Fundamentals and Digital CircuitsDocument2 pagesVLSI Design Fundamentals and Digital Circuitsjames RNo ratings yet
- EtrxDocument16 pagesEtrxapi-236544093No ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics - Iv CODE: 10 MAT 41 IA Marks: 25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam HRS: 03 Total HRS: 52 Exam Marks:100 Part-A Unit-I: Numerical Methods - 1Document14 pagesEngineering Mathematics - Iv CODE: 10 MAT 41 IA Marks: 25 Hrs/Week: 04 Exam HRS: 03 Total HRS: 52 Exam Marks:100 Part-A Unit-I: Numerical Methods - 1HmmTell TellNo ratings yet
- VLSI SyllabusDocument13 pagesVLSI SyllabusNagabhushanam KoduriNo ratings yet
- Regulation - 2009: Affiliated Institutions Anna University, ChennaiDocument27 pagesRegulation - 2009: Affiliated Institutions Anna University, ChennaiYogeswaran SundarrajNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Course OverviewDocument1 pageVLSI Design Course OverviewRajalingam BossNo ratings yet
- M.tech Vlsi Syllabus: D.A.John & K.Martin, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, Wiley, 1997Document6 pagesM.tech Vlsi Syllabus: D.A.John & K.Martin, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, Wiley, 1997yupsup9No ratings yet
- Vit Ece 5th Year SyllabusDocument16 pagesVit Ece 5th Year Syllabuspranavateja12399No ratings yet
- (IIT Guwahati) VLSI Design Verification and TestDocument4 pages(IIT Guwahati) VLSI Design Verification and Testjitu_4No ratings yet
- Vlsi Vlsid Vlsisd Vlsi Me Ece PDFDocument18 pagesVlsi Vlsid Vlsisd Vlsi Me Ece PDFramanaidu1No ratings yet
- 401 M.E. Applied ElectronicsDocument10 pages401 M.E. Applied Electronicsd_vijay666No ratings yet
- Vlsi Mtech Jntu Kakinada II Sem SyllabusDocument16 pagesVlsi Mtech Jntu Kakinada II Sem Syllabusrv prasad50% (2)
- Vlsi Mtech 1st - Year - Jntu Kakinada SyllabusDocument8 pagesVlsi Mtech 1st - Year - Jntu Kakinada Syllabustele203No ratings yet
- Common Recruitment Examination June 2013: DeityDocument10 pagesCommon Recruitment Examination June 2013: DeitydannycbsNo ratings yet
- Es IiDocument16 pagesEs IiSivasankar YalavarthyNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design SyllabusDocument2 pagesVLSI Design SyllabusJyoti RanjanNo ratings yet
- Btech New SyllabusDocument8 pagesBtech New SyllabusDrBhoopal RaoNo ratings yet
- 6Xn1 Digital Integrated CircuitsDocument2 pages6Xn1 Digital Integrated CircuitsapbhatkarNo ratings yet
- Vlsi DesignDocument12 pagesVlsi DesignTanveer AhmedNo ratings yet
- Me SyllabusDocument3 pagesMe SyllabusPrabhu SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- B 1254789545454e CseDocument1 pageB 1254789545454e CseAnonymous a8rdyKOCNo ratings yet
- Vlsi System DesignDocument12 pagesVlsi System DesignMahender GoudNo ratings yet
- RGPV Syllabus Cbgs Ec 3 Sem All SubjectsDocument8 pagesRGPV Syllabus Cbgs Ec 3 Sem All SubjectsAyushNo ratings yet
- EmbeddedDocument9 pagesEmbeddedNanc Joy100% (1)
- Applied Mathematics and Digital Signal ProcessingDocument5 pagesApplied Mathematics and Digital Signal ProcessingvigneshkumarcNo ratings yet
- syllabusTNPSC Ase Asa SyllabusDocument9 pagessyllabusTNPSC Ase Asa SyllabusVaikunthan SNo ratings yet
- Postgraduate M E Instrumentation and ControlDocument8 pagesPostgraduate M E Instrumentation and Controljricardo019763535No ratings yet
- Vlsi Mtech Jntu Kakinada SyllabusDocument11 pagesVlsi Mtech Jntu Kakinada Syllabusaditya414No ratings yet
- Syllabus For Applied ElectronicsDocument28 pagesSyllabus For Applied ElectronicsvinayakbondNo ratings yet
- MTech VLSI Design 1st Sem SyllabusDocument5 pagesMTech VLSI Design 1st Sem SyllabusPrakash Sinha100% (1)
- Electronic Design Automation: Synthesis, Verification, and TestFrom EverandElectronic Design Automation: Synthesis, Verification, and TestNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Digital Systems: Modeling, Synthesis, and Simulation Using VHDLFrom EverandIntroduction to Digital Systems: Modeling, Synthesis, and Simulation Using VHDLNo ratings yet
- Networks on Chips: Technology and ToolsFrom EverandNetworks on Chips: Technology and ToolsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Performance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksFrom EverandPerformance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksNo ratings yet
- On-Chip Communication Architectures: System on Chip InterconnectFrom EverandOn-Chip Communication Architectures: System on Chip InterconnectNo ratings yet
- Parallel Processing for Artificial Intelligence 1From EverandParallel Processing for Artificial Intelligence 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Digital Circuit Testing: A Guide to DFT and Other TechniquesFrom EverandDigital Circuit Testing: A Guide to DFT and Other TechniquesNo ratings yet
- Analog and Hybrid Computing: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandAnalog and Hybrid Computing: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Ex05 - Question Paper Adaic - ModelDocument2 pagesEx05 - Question Paper Adaic - ModelshankarNo ratings yet
- Ex06 - Answer Key Adaic Te-2Document8 pagesEx06 - Answer Key Adaic Te-2shankarNo ratings yet
- KONGUNADU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY TERMINAL EXAMINATION-I ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUITSDocument2 pagesKONGUNADU COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY TERMINAL EXAMINATION-I ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUITSshankarNo ratings yet
- Zero Diagonal Property Symmetry Property Unitary Property Phase Shift PropertyDocument5 pagesZero Diagonal Property Symmetry Property Unitary Property Phase Shift PropertyshankarNo ratings yet
- Adaic TT 2016Document2 pagesAdaic TT 2016shankarNo ratings yet
- M.E. Applied Electronics - R2017Document47 pagesM.E. Applied Electronics - R2017Mr.R.Ragumadhavan ecestaffNo ratings yet
- KONGUNADU COLLEGE M.E ECE I/I TIME TABLE 2018-19Document1 pageKONGUNADU COLLEGE M.E ECE I/I TIME TABLE 2018-19shankarNo ratings yet
- Kongunadu College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument2 pagesKongunadu College of Engineering and TechnologyshankarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MATLABDocument36 pagesIntroduction To MATLABViju JigajinniNo ratings yet
- MATLAB BasicsDocument24 pagesMATLAB BasicsshankarNo ratings yet
- Design of Efficient Class-E Power Amplifiers For Short-Distance CommunicationsDocument11 pagesDesign of Efficient Class-E Power Amplifiers For Short-Distance CommunicationsshankarNo ratings yet
- CH 3 - FeedbackDocument54 pagesCH 3 - FeedbackshankarNo ratings yet
- Central Board of Secondary Education Secondary School Examination-2019 (Class X) DatesheetDocument4 pagesCentral Board of Secondary Education Secondary School Examination-2019 (Class X) DatesheetPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- NBA Modified RF&MW LPDocument4 pagesNBA Modified RF&MW LPshankarNo ratings yet
- Ada Syllabus 2013Document1 pageAda Syllabus 2013shankarNo ratings yet
- Kongunadu College of Engineering and Technology, ThourpattiDocument1 pageKongunadu College of Engineering and Technology, ThourpattishankarNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Introduction PartDocument13 pagesDigital Signal Processing Introduction Partshankar100% (1)
- HTTPDocument2 pagesHTTPshankarNo ratings yet
- RF&MW M 1Document2 pagesRF&MW M 1shankarNo ratings yet
- Ada Syllabus 2013Document1 pageAda Syllabus 2013shankarNo ratings yet
- Ec 6502 Principles of Digital Signal Processing - Question Bank - 2018Document17 pagesEc 6502 Principles of Digital Signal Processing - Question Bank - 2018shankarNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument2 pagesHTTPshankarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ada 2014Document22 pagesUnit 1 Ada 2014shankarNo ratings yet
- WN Unit1 and Unit5Document1 pageWN Unit1 and Unit5shankar0% (1)
- MultiplierDocument16 pagesMultipliershankarNo ratings yet
- Unit V: Time Varying Fields and Maxwell'S EquationsDocument12 pagesUnit V: Time Varying Fields and Maxwell'S EquationsshankarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Adsd KncetDocument46 pagesUnit 1 Adsd KncetshankarNo ratings yet
- Ec6802 Wireless NetworksDocument1 pageEc6802 Wireless NetworksBritto Ebrington AjayNo ratings yet
- AP9212Document7 pagesAP9212shankarNo ratings yet
- 2021.01 - Key-Findings - Green Bond Premium - ENDocument6 pages2021.01 - Key-Findings - Green Bond Premium - ENlypozNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Cyanotic Newborn Part IDocument9 pagesEvaluation of The Cyanotic Newborn Part Ijwan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Currency Exchnage FormatDocument1 pageCurrency Exchnage FormatSarvjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- ATV600 - Communication - Parameters - EAV64332 - V1.3Document46 pagesATV600 - Communication - Parameters - EAV64332 - V1.3Sugeng WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 ResearchDocument14 pagesChapter 2 ResearchabibualNo ratings yet
- 10 Questions About Independent ReadingDocument4 pages10 Questions About Independent ReadingdewiNo ratings yet
- Bank 12Document19 pagesBank 12Shivangi GuptaNo ratings yet
- Accenture Faq For New JoinersDocument4 pagesAccenture Faq For New JoinersBaazinow Hack Brainbaazi Live AnswersNo ratings yet
- (Macmillan Studies in Marketing Management) Frank Jefkins BSC (Econ), BA (Hons), MCAM, FIPR, MInstM, MAIE, ABC (Auth.) - Public Relations For Marketing Management-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1983)Document193 pages(Macmillan Studies in Marketing Management) Frank Jefkins BSC (Econ), BA (Hons), MCAM, FIPR, MInstM, MAIE, ABC (Auth.) - Public Relations For Marketing Management-Palgrave Macmillan UK (1983)Subhasis DasNo ratings yet
- Service ManualDocument14 pagesService ManualOlegNo ratings yet
- Chobani: The Falling First Mover: Jianan LiaoDocument5 pagesChobani: The Falling First Mover: Jianan Liaowofop34547No ratings yet
- E-Leadership Literature ReviewDocument36 pagesE-Leadership Literature ReviewYasser BahaaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 - Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free EnergyDocument65 pagesCH 9 - Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free EnergyCharbel RahmeNo ratings yet
- Newman News January 2017 EditionDocument12 pagesNewman News January 2017 EditionSonya MathesonNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument7 pagesSciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectMohamed Amine NZNo ratings yet
- Teamcenter 10.1 Business Modeler IDE Guide PLM00071 J PDFDocument1,062 pagesTeamcenter 10.1 Business Modeler IDE Guide PLM00071 J PDFcad cad100% (1)
- Responsibility Matrix D&B Rev 3 22 - Sep - 2014Document10 pagesResponsibility Matrix D&B Rev 3 22 - Sep - 2014hatemsharkNo ratings yet
- Alpacon Degreaser BIO GENDocument2 pagesAlpacon Degreaser BIO GENFahmi Ali100% (1)
- SSC CGL 13th Dec 2022 Shift-4 by CrackuDocument29 pagesSSC CGL 13th Dec 2022 Shift-4 by CrackuyuviNo ratings yet
- Geography Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesGeography Lesson Planapi-204977805100% (3)
- What Is InterpolDocument5 pagesWhat Is InterpolJimmy Jr Comahig LapeNo ratings yet
- Vào 10 - Sở L NG Sơn 2022-2023Document5 pagesVào 10 - Sở L NG Sơn 2022-2023Lan HuongNo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary Surgery BlumgartDocument301 pagesHepatobiliary Surgery Blumgartaejazahsan100% (7)
- List of RelaysDocument26 pagesList of RelaysadhyarthaNo ratings yet
- Salting-Out Crystallisation Using NH Ina Laboratory-Scale Gas Lift ReactorDocument10 pagesSalting-Out Crystallisation Using NH Ina Laboratory-Scale Gas Lift ReactorChester LowreyNo ratings yet
- LAB-Histopath Midterms 01Document5 pagesLAB-Histopath Midterms 01Jashmine May TadinaNo ratings yet
- Project Close OutDocument12 pagesProject Close OutWeel HiaNo ratings yet
- Wheatstone Bridge Circuit and Theory of OperationDocument7 pagesWheatstone Bridge Circuit and Theory of OperationAminullah SharifNo ratings yet
- GCAF Online Inspector Practice ExamDocument5 pagesGCAF Online Inspector Practice Examcamwills2100% (1)
- J S S 1 Maths 1st Term E-Note 2017Document39 pagesJ S S 1 Maths 1st Term E-Note 2017preciousNo ratings yet