Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sop Onshore PDF
Uploaded by
Vivek MishraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sop Onshore PDF
Uploaded by
Vivek MishraCopyright:
Available Formats
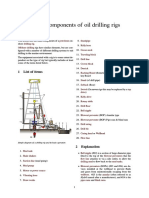
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
Table of Contents
1. Preface .......................................................................................................................................... 3
2. Introduction ................................................................................................................................ 4
3. Standard Operating Practices SOPs .............................................................................. 6
3.1 Components ........................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 References .............................................................................................................................. 7
4. Risk Management ..................................................................................................................... 8
5. Work Over Rig Summary................................................................................................. 11
6. Equipment ................................................................................................................................. 13
6.1 Rig Carrier Chassis ......................................................................................................... 13
6.2 Diesel Engine........................................................................................................................ 16
6.3 Mud / Slush Pump .............................................................................................................. 20
6.4 Draw Works .......................................................................................................................... 23
6.5 Crown Block .......................................................................................................................... 25
6.6 Travelling Block ................................................................................................................... 27
6.7 Hook Assembly .................................................................................................................... 29
6.8 Swivel...................................................................................................................................... 31
6.9 Rotary Table ......................................................................................................................... 33
6.10 Mud Agitator ...................................................................................................................... 35
6.11 Air Compressor ................................................................................................................. 37
6.12 Centrifugal Pumps ........................................................................................................... 40
6.13 Transmission (Allison) .................................................................................................... 42
6.14 Hydro-Matic Brake ........................................................................................................... 44
6.15 AC Generator ..................................................................................................................... 46
6.16 Electric AC Motors............................................................................................................ 50
6.17 Pneumatic / Hydraulic Winch ...................................................................................... 54
7. Annexures ................................................................................................................................. 56
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 1
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
7.1 Norms and Policies Issued by Technical Services.................................................. 56
7.2 OISD references Relevant for Work Over Rigs .................................................... 57
7.3 DGMS References Details of regulations / guidelines ...................................... 59
7.4 Central Pollution Control Board .................................................................................... 59
7.5 Electrical Related Standards A Reference ............................................................. 59
7.6 Selected Applicable Standards Drilling Rig Equipment .................................... 60
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 2
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
1. Preface
ONGC is a capital intensive organization having Plant and Machinery Assets of more than
Rs.67000 Crores. ONGC stands as No.1 E&P Company of India with its operation in various
parts of the country and in other countries through OVL. The management of this large
volume of capital asset demands an effective and efficient Equipment Management System
in place. The Equipment Management includes planning, procurement, operation,
maintenance, overhaul, health, performance and finally its reliability, safety and discards of
equipment. A systematic approach to equipment management (Inception to Discard) finally
results in an effective equipment life cycle management.
ONGC a MAHARATNA has been managing a large number of equipment at its installation
spread across various parts of India with qualified executives managing operation and
maintenance to a global level. ONGC with its foresight to effectively manage its equipment
set up Directorate of Equipment Management in the year 1982 and presently being
referred as Technical Services since 2004.
Technical Services as a service provider, is responsible for the effective Equipment Life
Cycle Management by framing norms, policies and guidelines for equipment maintenance &
replacement. Primarily, these include Technical & Energy Audit, up-gradation of technical
skills, and standardization of specifications, quality assurance services, failure analysis and
promotion of creative and innovative skills.
A step forward with objective to meet global standards, Technical Services is introducing
Standard Operating Practices (SOP) to upgrade present equipment management system.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 3
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
2. Introduction
EQUIPMENT MANAGEMENT was instituted in the year 1982 and has been instrumental in
bringing out approved norms, policies and guidelines for equipment operation, maintenance,
overhaul, replacement and numbers of equipment requirement as stand by for
uninterrupted operation. The equipment management in any organization starts from
purchase equipment to its disposal, the period in between includes its operation &
maintenance. The function in brief is projected by the sequence as under.
ONGC being a large organization with work centres referred as Assets, Basins & Plants,
located across various parts of the country, the function of equipment life cycle
management also becomes part of Work Centres. Technical Services, being a service
provider in the organization, is assigned with role of providing guidelines for primarily
managing equipment life. This function is achieved by different arms of Technical Services.
As per image above, all the functions are part of Work Centres operating the equipment. At
organization level, the preventive maintenance and overhauling requirement are centralized
through application of SAP Module. The SAP Module has been updated with equipment
preventive maintenance program and overhaul program based on fixed periodicity &
operating hours. The details of spares of equipment (Bill of Material), consumption for
preventive maintenance & overhauling are also part of this module to provide support for
the installations and Work Centres to monitor actions carried out and to be carried out.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 4
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
The focus of technical services is, therefore, aligned with monitoring function of repairs and
reliability analysis. The details of availability at installations, performance, maintenance
compliance etc. are being monitored by the departmental audits in the form of technical and
energy audits.
Department of Equipment Management, Technical Services, Dehradun has already issued
norms, policies and guidelines and the details are produced below for reference.
1. Life cycle period of major equipment for LCC based equipment purchases.
2. Norms for Noise and Exhaust emissions for rotating equipment.
3. Policy for revamping of onshore work over rig.
4. Policy for equipment health check-up for drilling & work over rig.
5. Policy for discard of onshore work over rigs.
6. Revised equipment replacement policy for drilling rigs and work over rigs.
7. Capitals overhaul norms for onshore work over rig equipment.
8. Standby equipment norms for onshore work over rig equipment.
9. Storage, handling and disposal of lubricants.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 5
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
3. Standard Operating Practices SOPs
SOPs are written instructions that document a routine or repetitive activity for equipment in
use by an organization. It addresses all requirements to be safely performed as
recommended. For effective equipment management SOPs need to be enforced and also
reviewed periodically.
The abbreviation SOPs stands for
Safe Operating Procedures / Practices
Standard Operating Procedures / Practices
SOPs ensure Equipment and personnel safety through compliance with recommended
procedures, guidelines issued for
1. Equipment installation as recommended by manufactures / suppliers.
2. Equipment start-up checks / steps for starting.
3. Equipment Operations including monitoring of operating parameters and taking
corrective action in case of deviations.
4. Preventive maintenance activities as per approved/ recommended schedule.
5. Equipment Overhaul to restore/ maintain equipment health, efficiency, reliability
and performance.
The equipment health, efficiency, reliability, safety and performance depend on its
condition. If equipment is operated within recommended limits of load and operating
parameters, it shall result in higher availability & reliability during its complete lifecycle.
The scope of this manual is to issue STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES for equipment
and personnel safety covering all aspects of equipment lifecycle, from its installation to
disposal.
For all equipment, however big or small, the OEM/ OES issues a manual covering guidelines
and procedures for equipment pre start checks, operation and maintenance. In a single
document, the Operating Practices shall cover all areas of equipment management including
equipment installation, pre-start, operation, preventive maintenance, overhaul, safety and
regulatory requirements.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 6
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
3.1 Components
a.
Identification of equipment being used.
b.
Identification of its operational, maintenance and overhauling requirements.
c. Engineering control to include work environment, stores and spares management at
installation, compliance to preventive & overhauling program, restrictions and
approvals for deviations
d. Administrative control to include issue of guidelines / norms for equipment
maintenance, overhaul, replacement and requirement.
e.
Safe practices to include use of PPE as per field operations / requirements.
3.2 References
a. ONGC Norms, Policies and Guidelines circulated by Technical Services or any other
authority /agency.
b. Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) manual / guidelines of operation,
maintenance & overhauling and safety requirement during equipment maintenance.
c.
OISD Oil Industry Safety Directorate (Safety & Inspection Practices).
d.
DGMS Directorate General of Mines and Safety Regulations.
e.
OMR Oil Mines Regulations.
f.
SOP Work Over Operations Issued January 2012.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 7
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
4. Risk Management
ONGC has rolled out a structured risk management process across the organization. All
SBUs (Assets, Basins, Plants, Institutes and Select Services) are aware of the risk
management process. Risk owners, risk controllers and risk coordinators have already been
nominated at all SBUs and risk register is being filled up on quarterly basis.
The risk identification, categorization, assessment and mitigation plan across the life cycle
of all equipment has to be worked out for every installation, i.e. drilling rig/ work-over rig in
association with identified stakeholders. The risks so identified must then be maintained as
a risk register for "Onshore drilling rig/ work over rig equipment".
The risk can arise from:
OIL & NATURAL GAS CORPORATION LIMITED
RISK REGISTER - SERVICES
Work Centre
Asset, Basins
Risk Description
Equipment failure
Root causes
Wrong
Selection
equipment
Mitigating Factors
of
The desired rating, capacity and application should
be as per standards API/ASTM/BIS.
Statutory requirements
not met
Equipment should meet all prevailing standards and
regulations.
Improper
equipment
specification
and
operating instructions
Manufacturer should provide complete specifications,
instructions for installation; start-up, maintenance
and storage for efficient, optimum life and safe
equipment operation.
Improper
installation
Equipment shall be installed as per recommended
instructions for space above and around equipment
for maintenance activities.
equipment
Inadequate preventive
maintenance
Preventive maintenance will be carried out as per
manufacturers recommendation.
Delayed
Overhaul
Overhauling will be carried out as per manufacturers
recommendation.
Equipment
Inadequate Equipment
Protection
Proper Instruments for Safety of Equipment.
Failure to comply with
Equipment Safety
All safety requirements as per equipment design, its
checking,
calibration
and
testing
and
as
recommended by OEM should be strictly adhered to.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Remarks
Page : 8
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
Risk management, just like safety requires active participation of employees. The above
table provides some known risks for which mitigating factors have been mentioned. The
mitigating factors should be strictly adhered to. Risk is a dynamic process and every
employee is requested to participate in this process and any risk perception may please be
brought to the notice of Head Maintenance / HDS/ HWS. The block diagram shown below
will be the communication protocol to be followed in the event of risk being perceived by the
employee:
RISK PROTOCOL (COMMUNICATION):
CHIEF RISK OFFICER
HEAD SBU (AM/BM/PH/HOI)
RISK CONTROLLER
HEAD MAINTENANCE / DRIL SERV/
WELL SERV
RISK OWNER
ASSET / BASIN (SBU)
RISK ORIGIN
CHIEF RISK OFFICER:
COMPANY SECRETARY, NEW DELHI
HEAD - SBU:
UNIT LEVEL
HEAD MAINTENANCE (RISK OWNER):
UNIT LEVEL
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN:
RISK OWNER
Action plan for the perceived risk reported will be
formulated by the risk owner. He will categorize and
validate risk and state the risk in the Governance, Risk
Management and Compliance (GRC) module of SAP.
Monitoring of action plan and mitigating factors.
RISK CONTROLLER
Version 1, June-2014
He will report the risk, root causes and mitigating factors
to the CRO for updating of risk register of ONGC.
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 9
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
The risk to equipment operation and maintenance can be minimized if parameters defined in
SOP are complied. The SOP document is issued so that the recommended practices of OEM,
OES, norms and policies of ONGC, statutory requirements and OISD guidelines are followed.
SOPs are a very vital part of risk management process where in many of the O & M
parameters are standardized and provide a uniform O & M template to personnel working in
field and offices across the organization. Work performed in line with the indicated SOP for
respective equipment shall result in not only an effective equipment life cycle management
but also minimize the risk of equipment failure.
Non-compliance to indicated SOP may result in:
1. Time and Cost Over-run The planned maintenance program by manufacturers are
indicated in the equipment manuals depending on operating hours, rate of component
wear and change in component performance due to variable thermal cycles. The action
taken and components replaced are to keep the equipment performance to its designed
level. Any delay in attending to the indicated maintenance activity may result in
increased cost of repairs and longer stoppage than planned. The risk is decreased
output & performance.
2. Equipment Failure There may be unscheduled equipment stoppages, breakdowns that
may force decreased output or even shut down of complete installation.
3. Failure to deliver services Health of the equipment is important to meet its designed
capacity. The capacity of equipment decreases if planned maintenance and overhauls
are not carried out.
4. Failure to meet expected quality There may be the cases where maintenance is
carried out in parts or by use of non-recommended spares to meet operational
contingencies. This directly affects the quality of maintenance and may result in
decrease in output availability and efficiency.
5. Obsolescence The document is primarily focussed on equipment life cycle
management. If equipment has completed its life, it may not be feasible to carry out
expected maintenance activities if OEM/ market support for spares and services are not
available. In such case, the equipment shall be planned for replacement at the earliest
opportunity.
SOP provides a standard template for practices to be followed, to establish a robust
Operation and Maintenance of rig equipment. Compliance to SOP shall result in enhanced
equipment reliability, efficiency, output and overall performance and shall prevent any
operational complications in operation. Non-compliance can in turn cause increased cost of
operations and reduced profitability to the company.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 10
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
5. Work Over Rig Summary
Work Over Rigs are mobile rigs, mounted on wheeled carrier, with or without prime mover,
which can be driven to the well site with all necessary hoisting equipment, engines and
special telescopic mast as one of the complete unit.
The operations to be performed by a work-over rig are different in nature depending on
process and well requirement. To meet these requirements, Rigs of different make,
capacities are provided with various equipment to carryout operation of different
characteristics.
In the work over operations, if process requires drilling of cement, sand plug, milling of
bridge plug, packers and fishing activity etc. the rig is provided with rotary table for rotation
of work string. In addition the rig may also be provided with air compressor package and
well control systems like Kommey Control Units. Some of the rigs are provided with brine /
mud tanks and screen to separate any solids during circulation.
If Work over rig is not provided with rotary table, the string rotation can be achieved by
power swivel, dyna-drill system and special tools where rotation is accomplished by working
fluid.
The work-over rig, as per requirement, is brought to the location, rig carrier is correctly
positioned, the sub-structure is aligned to the centre of well and levelled. The rig is placed
on foundation and levelled before rigging up mast structure. The recommended process of
rigging up the mast shall be followed as per issued guidelines.
The equipment are deployed, connected and made ready for operational requirement. Care
shall be taken to properly secure the cables, hoses, lines and routed correctly to prevent
any damage and safety of personnel.
The STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES (SOP) Work-over Operations Onshore, cover the
practices to be complied with for rig deployment, movement and other operations.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 11
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
ROM-UPET 100
A 50
10
IR 750
ROM-UPET - 50
Total
15
Version 1, June-2014
1
7
10
IR 500
BHEL - 120
8
1
8
1
10
Total
Tripura Asset
A&AA Basin Jorhat
MBA / CBM Kolkata
Assam Asset
Karaikal Asset
CW 50
Cambay Sub-Asset
Ankleshwar Asset
CW 100
Mehsana Asset
Type of Work
Over Rig / Work
Centre
Ahmedabad Asset
A summary of the work-over rigs in use is tabulated for reference only.
5
1
1
11
SOP Work Over Rigs
9
1
53
Page : 12
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6. Equipment
6.1 Rig Carrier Chassis
The Work-over Rigs are carrier / chassis mounted for easy mobility so that it can be
deployed at any location as per operational requirement. For smooth operation as well as
relocation, maintaining rig carrier is equally important. A rig carrier may have the complete
chassis, suspension, transmission, power take-off, gear box and engine to drive.
INSTALLATION
The Work-over Rig unit is completely made ready for use by the rig manufacturer. The
chassis is mounted with desired equipment and other systems as per rig make, design and
capacity. There is no separate installation of the unit except as under
1. The rig carrier is deployed at the location to carry out work over operation.
2. It shall be correctly aligned with the oil well to be used for carrying out the operational
process.
3. The correct positioning, jacking up the carrier, levelling, raising the rig mast and
making the rig ready for operation shall be carried out as per manufacturer
recommendations and procedure outlined.
START UP CHECKS
Start-up checks are required to be carried out when the carrier is to be relocated. Before it
is moved the desired checks are
1. Carrier engine instruments are functional.
2. Air system pressure maintained as per recommendations.
3. Lube oil in power steering system.
4. Lube / brake oil up to indicated level.
5. Lube oil level and condition in Gear box.
6. Lube oil level and condition in transmission system, if applicable.
7. Radiator water level / coolant if recommended.
8. Fuel level in fuel tank.
9. Greasing of suspension bearings / pins / springs.
10. Greasing of wheel bearings, if applicable.
11. Checking of air pressure in wheels.
12. Checking and greasing of steering system.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 13
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
13. Checking up hydraulic system for oil level, condition of filters, pumps and operational
levers.
14. Checking that equipment at the carrier are secured and tied.
15. Availability of carrier and mast pads for positioning and levelling.
OPERATION
There is no specific operational requirement for rig carrier / chassis, since once it is located
for operational requirement, the activities are carried out by the crew with the equipment
deployed at the carrier and provided with the rig.
The inspection of carrier shall be carried out during operation for any abnormal noise,
vibration, status of alignment, levelling of structure, leakages or oil & air and cleanliness of
the complete unit.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Being common for all the work over rigs, the preventive maintenance is equally important.
The general preventive maintenance activities that may be / need to be carried out are;
a. Greasing of wheel bearings, suspension links, transmission system and other
assemblies as required.
b. Inspection of chassis and suspension for any damage, crack, wear to prevent
breakdown to rig.
c. Lube oil change / top up as required for gear box and suspension.
d. Lube oil change / top up as required for Hydraulic system.
e. Lube oil change / top up as required for transmission.
f.
In case of hydraulic or nitrogen suspension system, recommended preventive
maintenance activities suggested by manufacturer.
g. Greasing of the pins / bearing of mast structure.
OVERHAUL
There may not be any specific overhaul to be carried out at chassis and its components. The
abnormality observed during inspection shall be attended and recommended components
replaced with original to prevent any unscheduled breakdown of unit.
SAFETY
The rig / carrier / chassis are moved from one location to other through the main roads as
well rural roads. The person driving shall ensure safety guidelines during the movement for
safety of rig units as well of other moving vehicles on the roads. The rig carrier consists of
some equipment in addition to the mast structure. The structure and equipment shall be
properly secured on the carrier. There shall not be any loose components that may cause
damage or injury during the movement.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 14
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
ENVIRONMENT & EMISSION CONTROL
1. The carrier engine shall be checked for exhaust emission as per prevailing vehicle
standards of POLLUTION UNDER CONTROL ((PUC) CERTIFICATE. In case of
deviations, engine shall be checked and tuned to operate within prescribed limits.
2. Used lube oil, filters and other components if not disposed properly may damage the
environment. The guideline has been provided to return these items to designated
locations (Stores) for further disposal action. (Refer guidelines for storage, Handling
and Disposal of Lubricants issued by Technical service).
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Since the rig unit is moved on roads, the recommended documents / certificates shall be
taken from the appropriate state agencies. Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation,
maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of
the guidelines / regulations issued by statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 15
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.2 Diesel Engine
Diesel Engine is used as prime-mover for various applications such as generation of electric
power, operating other equipment directly coupled to engine like draw work. As per need of
power, engines are of different capacity, types and make, being used in organization. In
work over rigs, engines are used as prime-mover for equipment at rig such as carrier
engine, mud pump engine and DG engine. It drives rig chassis, draw works, mud pump and
other equipment. It is installed along with driven equipment on a sturdy skid for easy
transportation and movement from one location to other.
The Diesel Engine basics includes various systems such as starting system, air intake
system, exhaust system, fuel system, lube oil system cooling system and safety system.
INSTALLATION
1. Skid Mounted along with driven equipment and secured with recommended size of
hardware.
2. Skid mounted with vibration mounts for smaller applications.
3. Permanently secured with grouted hardware for a fixed location.
START UP CHECKS
Start-up checks are carried out to verify that engine can be operated without any problem,
it may include
1. Lube oil level and/or draining of water from water separator (If provided).
2. Water / coolant level in radiator system.
3. Status / working of cooling system in case of heat-exchanger system.
4. Fuel level in case of day tank system.
5. Leakages from fuel, lube oil, air & cooling water piping and cylinder head.
6. Belt tension for radiator pulley, cooling water pump.
7. Proper & smooth movement of throttle linkage.
8. Condition and indication status for fuel, oil and & intake filters and fuel tank
breather.
9. Operating status of engine safety system.
10. Operation of pre-lube (If provided) & pre-fuel pumps to indicated pressure for
distribution.
11. Air starting system lubrication including starter.
12. Hydraulic start system level of hydraulic oil, pump and filters.
13. Electric start system (If available) condition of battery, terminals and its charging
indicators.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 16
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
OPERATION
Engine should be initially run at idle rpm to warm up and to allow its operating parameters
to stabilize. The engine shall be subjected to its rated load only after it attains stabilized
operating parameters. The parameters as per its display panel shall be recorded in log book.
These parameters include;
1. Lube oil pressure.
2. Lube oil temperature.
3. Fuel pressure.
4. Cooling water / coolant circulation pressure.
5. Cooling water / coolant temperature.
6. Engine RPM.
7. Engine run hour meter.
8. Differential pressure gauge of air intake filter.
9. Differential pressure gauge or indicators for lube oil filter (If available).
10. Engine is provided with emergency shutdown system to manually stop the engine in
cases of emergency. In general, for stopping an engine, it shall be allowed to
operate on without load for some duration so that its temperature parameter is
stabilized by circulation of oil / coolant across engine system. It helps prevent
formation of hot spots that may cause damage to engine.
11. Battery for starter Voltage & ampere
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance may include daily, weekly, fortnightly, monthly, quarterly, halfyearly and annual program. The activities to be carried out are indicated by the
manufacturer in its operation and maintenance manual. It may be
1. Engine servicing that include lube oil replacement, filters (lube oil & fuel)
replacement, cleaning or replacement of air intake filters, topping up or changing of
cooling system with de-mineralized water and inhibitors (If recommended), cleaning
of engine radiators fins & tubes, checking operation of thermostatic valves in cooling
system, checking/calibration of shut off switches for low lube oil pressure, high
cooling water temperature, air system and over speed.
2. Run-hour based
a.
Lube oil analysis including wear debris analysis. (Refer Equipment Health checkup for drilling & work over rigs issued by Technical service).
b. Tappet clearance checking and adjustment to recommended clearance.
c.
Measurement of turbocharger axial movement.
d. Calibration of fuel injectors
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 17
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
e.
Crankcase inspection for any abnormality or looseness.
OVERHAUL
Engine is subjected to deterioration of its components during operation and need to be
replaced at scheduled interval. Engine health and performance can be restored by overhauls
that depend on operating hours. It may be
1. Top Overhaul It may include replacement of cylinder head components such as
valves, valve inserts, piston rings, cleaning of radiator/Heat exchanger, testing and
calibration of injectors etc.
2. Average Overhaul It includes top overhaul and additionally piston, cylinder heads,
bearing and other components of cooling water pump, lube oil pump and inspection
of bearings.
3. Capital Overhaul It includes average overhaul and additionally replacement of all
bearings, inspection of crankshaft & resize of bearing to next size if required,
cleaning / replacement of heat-exchangers, replacement of injectors, replacement of
lube oil and water pump components.
SAFETY SYSTEM
Safety system on an engine is provided to caution operation to take corrective measures in
case of deviation in its operating parameters and to protect engine from damage & failure.
The safety system is provided with alarm system and engine shut down system. The
parameters monitored and included in system are 1. Lube oil: - Low pressure alarm & shut down.
2. Lube oil temperature: - High temperature Alarm & shut down.
3. Cooling system pressure: - Alarm & shut down.
4. Cooling system temperature: - High temperature Alarm & shut down.
5. Engine high Vibration alarm.
6. Lube oil low level alarm.
7. Engine over speed alarm & shut down.
8. To carry out any maintenance activity the work permit shall always be taken as per
organization policy / guidelines.
ENVIRONMENT & EMISSION CONTROL
1. Used lube oil, filters and other components if not disposed properly may damage the
environment. The guideline has been provided to return these items to designated
locations (Stores) for further disposal action. (Refer guidelines for storage, Handling
and Disposal of Lubricants issued by Technical service).
2. Similarly measurement of engine exhaust is to be carried out for complete burning of
fuel and to monitor contents of CO, CO2, SO2, NO2 etc. The central pollution control
board (CPCB) has issued guidelines for emission parameters depending on the
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 18
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
engine rating, location and application. Such guidelines if applicable shall be
followed. (Refer guideline for Noise and Exhaust emissions for rotating equipment
issued by Technical service).
3. In case of deviations from prescribed limits of exhaust, corrective maintenance
actions shall be taken to correct the emission of gases.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 19
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.3 Mud / Slush Pump
The Standard Operating Practices covers all the mud / slush pumps irrespective of make,
size and their application. These are reciprocating high pressure pumps used for circulation
of fluid called mud during oil well drilling operation or work over jobs. The pump is divided
among drive system, power end, fluid end, lubrication system, cooling system. In work over
rigs mud pumps are of smaller volume discharge at high pressure. There may be variation
in its application as the mud pumps are also used for injection of brine solutions, acids and
other fluids as per work over operation requirement.
INSTALLATION
Mud / Slush Pumps in a work over rig is normally skid mounted along with engine as primemover, properly aligned and secured with recommended size of hardware along with its
auxiliaries.
START UP CHECKS
Start-up checks are carried out to verify that pump can be operated without any problem, it
may include
1. Lube oil level (Crankcase).
2. Oil pressure, temperature, pumps suction & discharge pressure.
3. Condition of safety/ pressure relief valve.
4. Nitrogen charging of its discharge dampener.
5. Nitrogen charging / pre-charging of its suction side dampener, if recommended.
6. Suction and discharge connections and if flexible hoses are used, securing hoses
with metal chains to prevent injury to working personnel.
7. To ensure that suction and discharge line valves are in open status, if provided.
OPERATION
Pump operation is critical for safe activities to be carried out by work over rig. Mud flow
volume and pressure are controlled by the person assigned with operation by regulating its
RPM / strokes. Pump shall be started at low rpm and increased to desired rpm / nos. of
strokes to establish desired mud flow for safe circulation requirement. The operating
parameters of the pump shall be recorded in log book. These parameters include
1. Operating parameters.
2. Lube oil pressure.
3. Cooling water pressure, if provided.
4. Discharge pressure of pump.
5. RPM / Nos. of pump Strokes.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 20
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6. Mud pump is normally stopped from the controls at operator console / from local
pump station. Its lube oil pump / cooling water pump, is then stopped manually or in
auto-mode with recommended time delay to circulate and stabilize temperature
across bearings.
7. If mud pump is to be stopped for longer duration, its hydraulic end shall be opened
and flushed with water to prevent settling of mud in compartment.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
In normal operation of pump, regular maintenance activity is, check and inspection of its
fluid end for smooth functioning of valves and to replace consumables as required, changing
the piston and liner to meet operational requirements. Other activities to be carried out may
be
1. Cleaning of fluid end compartments, cleaning of sludge chamber to remove
deposited mud.
2. Inspection, replacement of dampener element and nitrogen charging of dampener
as required.
3. Checking & recording cross head, cross head pin, main bearing, crank pin bearing,
and pinion shaft bearing clearance.
4. Replacement of lube oil and its filters at scheduled interval.
5. Inspection and cleaning of magnetic filter.
6. Cleaning of heat-exchanger provided for lube oil cooling.
7. Inspection of oil distribution network for its distribution at provided locations.
8. Checking of gear backlash and its loading surface for cavities and damage.
9. Checking of gear and / or chain & sprockets for wear in drive system.
OVERHAUL
Mud / Slush Pump overhaul is carried out to replace its worn out components. The overhaul
may include replacement of bearings, shafts and gears as per its condition and damage.
Generally the overhaul is based on run hours, OEM recommendations, norms / policies
issued by Technical Services.
SAFETY SYSTEM
Safe operation of mud pump is as important as the safety of an oil-well either during drilling
or work over operation. The safety includes
1. Operating pump as desired RPM / within recommended operating pressure.
2. Maintaining dampener
maintenance.
performance
by
timely
inspection
and
preventive
3. Securing discharge hose connections with metallic chain / wire to prevent injury in
case of hose failure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 21
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
4. Scheduled check and calibration of pump discharge pressure safety valve.
5. Any other safety features provided at the pump.
6. To carry out any maintenance activity the work permit shall always be taken as per
organization policy / guidelines.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 22
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.4 Draw Works
The Standard Operating Practices covers all sizes of Draw Works deployed at work over rigs
of different make and capacity.
INSTALLATION
Draw Works is installed at work over rig chassis. It is a major equipment of hoisting system
and controls all the string movement during work over jobs. Correctly positioning the draw
works at chassis and using correct size of hardware to secure in position shall be ensured.
The control system is pneumatic hence air connections and their condition shall be healthy
while installation as well as the direction of rotation of input shaft / power take-off system
and cooling water connections shall be correct and checked.
The wire rope used shall be of correct size, configuration and load rating. Wire rope test
certificate shall be checked and record maintained.
OPERATION
Draw Works is a primary unit for operation of all the hoisting equipment. The operational
control is obtained by operation of engine as prime-mover at different RPM along with
Allison Transmission, application of pneumatic clutches, manual brake, disc brake and
Hydro-Matic brake as and when required and controlling the movement and function of all
hoisting equipment. Reeving of wire rope shall be in correct order and provision made for
greasing of wire rope shall also be checked and greased filled. Any mal-function in operation
shall be attended at priority for smooth operation as well as rig safety.
Draw-works is stopped by operator from its control system. Its lube oil pump / cooling
system, is then stopped manually or in auto-mode with time delay to circulate and stabilize
temperature across bearings.
Joy Stick Control In some of the Work-over Rigs, the control system for operational
activities at the rig are managed by a joystick control system. The joystick control is for
operation of hoisting equipment and other rig activities. For the rigs provided with this
control / operational feature need to attend to the recommended checks / preventive
maintenance program and replacement as per manufacturer recommendations.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
In normal operation of Draw Works, regular maintenance activity is 1. Inspection, adjustment and replacement of brake, rim, band, pin, clutch shoes,
Pneumatic Valves and Controls (Refer equipment health check-up for drilling & work
over rig issued by Technical Services).
2. Check for corrosion on inside of brake band/thickness of brake band.
3. Inspection for proper water circulation for brake drum and adjustment of various
linkages.
4. Inspection, cleaning and servicing of pneumatic valves.
5. Greasing of bearings at scheduled interval.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 23
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6. Replacement of lube oil.
7. Inspection of sprocket & chains for wear, damage and replacement.
8. Inspection and replacement of air & water line hoses.
9. Check and tighten all the foundation bolts.
10. Inspection of wire rope for greasing and deformity/looseness in wire strands,
11. Any abnormal sound in operation of draw works.
OVERHAUL
Overhaul is carried out to maintain equipment health and performance during its life cycle
and is carried out to replace its worn out components. It may include replacement of
bearings, shafts, chains, sprockets, components of brake and clutch assemblies depending
on their condition and damage. Generally the overhaul is based on run hours or as per
norms / policies issued by Technical Services.
SAFETY SYSTEM
Safe operation of draw works is as important as the safe work-over operation of an oil-well.
The safety includes
1.
Operating within specified load rating.
2.
Timely inspection and adjustment of brake, clutch assemblies & Equalizer beam.
3.
Proper Adjustment and functioning of Twin Stop System.
4.
Replacement of wire rope as per usage / ton-mile indicator guidelines.
5.
Wire rope used for draw works shall be of correct size and configuration.
6. Wire ropes / manila ropes used for other applications such as material handling,
connection / de-connection of string assembly using cathead system shall be of
recommended size and shall be replaced if found damaged.
7.
Any other safety features provided / recommended for draw works.
8. To carry out any maintenance activity the work permit shall always be taken as per
organization policy / guidelines.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 24
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.5 Crown Block
As the name specifies, the crown block is installed at top end of rig mast structure and is
part of hoisting equipment. Wire rope from draw works is routed through crown block
pulleys and the complete string weight is supported on mast through crown block.
INSTALLATION
Crown block is installed at the top end of mast structure. The position of fast pulley shall be
in line with draw works wire rope position. Since the equipment cannot be repaired at its
location, the health of equipment shall be ensured at the time of installation.
START UP
1. Greasing of pulley bearings is the top most priority at start up.
2. Wear of Sheaves to be checked with Go No Go gauge for its profile to prevent
damage to wire rope and to get recommended life.
OPERATION
The crown block is not provided with any driving equipment as it is one of hoisting
equipment and operated by draw works only.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Periodic greasing of bearings as per schedule.
2. Checking of pulley profile for wear as uneven profile may damage the wire rope.
3. Checking for wear, damage and misalignment.
4. Block shall be free of projecting bolts, nuts, pins or parts.
5. Interchanging pulleys (fast end to dead end) for ensuring maximum life & even wear
of sheaves at intervals recommended by OEM.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of pulleys and bearings, it may be depending on condition /
operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms / guidelines issued by Technical
Services. (Also refer equipment health check-up for drilling & work over rig issued by
technical services).
SAFETY
Crown block is provided with safety brackets at pulleys to prevent bumping of wire rope. It
shall be properly secured at the time of installation.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 25
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 26
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.6 Travelling Block
As the name specifies, the travelling block is a moving block to lift up and lower down the
drill string assembly through wire ropes and support of crown block. It is a part of hoisting
equipment. Wire rope from draw works is routed through clown block pulleys to the
travelling block pulleys and the block is connected to further string assembly equipment.
INSTALLATION
Travelling block is not rigidly installed and is one of the moving hoisting equipment. Since
the equipment cannot be repaired at its location, the health of equipment shall be ensured
at the time of installation.
START UP
Greasing of pulley bearings is the top most priority at start up.
OPERATION
The travelling block is not provided with any driving equipment as it is one of hoisting
equipment and operated by draw works only.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Periodic greasing of bearings as per schedule.
2. Checking of pulley profile for wear as uneven profile may damage the wire rope.
3. Checking for wear, damage and misalignment.
4. Block shall be free of projecting bolts, nuts, pins or parts
5. Interchanging pulleys (fast end to slow end) for ensuring maximum life & even wear
of sheaves at intervals recommended by OEM.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of pulleys and bearings; it may be depending on condition /
operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms / guidelines issued by Technical
Services. (Also refer equipment health check-up for drilling & work over rig issued by
technical services)
SAFETY
Travelling block is provided with safety guard at pulleys to prevent bumping of wire rope,
spillage of wire rope grease & loose particles and safety of persons in case of wire rope
damage. It shall be properly secured at the time of installation.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 27
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 28
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.7 Hook Assembly
As the name specifies, the hook is connected to travelling block and is an equipment to
provide flexibility of different connections for string assembly as required during work over
operation and to compensate the sudden loading of components. It is an equipment of
hoisting equipment.
INSTALLATION
Hook is not rigidly installed and is one of the moving hoisting equipment. Since the
equipment cannot be repaired at its location, the health of equipment shall be ensured at
the time of installation.
START UP
Replacement of lube oil of appropriate grade and greasing of its moving joints / connections
shall be carried out before start up at new location.
OPERATION
The hook is not provided with any driving equipment as it is one of hoisting equipment and
is used for providing connections between travelling block and string assembly.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Periodic replacement of lube oil/oil seals as per schedule.
2. Checking for wear, damage and misalignment.
3. Hook shall be free of projecting bolts, nuts, pins or parts.
4. Greasing of hook hinge / moving connections.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings and other components as required. It may be
depending on condition / operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms /
guidelines issued by Technical Services. (Also refer equipment health check up for drilling &
work over rig issued by technical services).
SAFETY
Hook is provided with lock system to prevent opening of hook jaws during operation. It shall
be ensured that jaws are locked after hooking up swivel, top drive system or elevator
assembly.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 29
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 30
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.8 Swivel
The swivel is connected to hook and facilitates rotation of string assembly during work-over
operation. The high pressure hose to circulate mud is also connected through the swivel. It
is an equipment of hoisting system.
INSTALLATION
Swivel is not rigidly installed and is one of the moving hoisting equipment. Since the
equipment cannot be repaired at its location, the health of equipment shall be ensured at
the time of installation. It is stacked at derrick floor after connection with mud pump hose
and Kelley and is connected to hook as required for carrying out work-over operation on the
well.
START UP
Replacement of lube oil of appropriate grade and greasing of its moving joints / connections
shall be carried out before start up at new location. The wash pipe assembly provided in
swivel to support mud connection and to allow rotation without any mud leakage shall be
checked greased and components replaced before start up. The condition of oil seals at top
& bottom shall also be checked for any leakage.
OPERATION
The swivel is not provided with any driving equipment as it is one of hoisting equipment and
is used for providing rotation support and mud flow support of string assembly.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Periodic replacement of lube oil/oil seals (both at Top & Bottom) as per schedule.
2. Greasing of hook hinge / moving connections.
3. Check wash pipe integrity for swivel.
4. Greasing of wash pipe seal / packing assembly.
5. Replacement of wash pipe assembly and its seal assembly.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings and other components as required. It may be
depending on condition / operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms /
guidelines issued by Technical Services. (Also refer equipment health check-up for drilling &
work over rig issued by technical services).
SAFETY
Swivel is connected with mud pump high pressure hose connections and the hose is secured
through its length by chain/suitable mechanism to swivel to prevent injury in case of hose
failure. It shall be properly secured at the time of installation. Swivel is used during string
rotation and is stacked at derrick floor and care shall be taken while stacking or
reconnecting to the drill string assembly.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 31
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 32
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.9 Rotary Table
The rotary table is not used at all Work-over Rigs. It is used only as per work-over
operational requirement at the rig. It is installed at a separate structure mounted at well
location and is powered through PTO (Power Take Off) system of carrier engine, connecting
rotary table by chain & sprocket and Gear Box.
INSTALLATION
Rotary table is rigidly installed at a separate structure fixed as per location requirement and
well location and is connected to carrier engine through PTO, GB and chain / sprocket. Since
the equipment cannot be repaired at its location, the health of equipment shall be ensured
at the time of installation.
START UP
Replacement of lube oil of appropriate grade and greasing of bearings (if provision exists)
shall be carried out before start up at new location. The rotary lock system to prevent
reverse rotation shall be checked for its effectiveness and rectified / replaced if required.
OPERATION
The rotary table is used to provide rotating movement to string assembly and facilitates
lowering / lifting up through adaptors / accessories. In case of power from draw works, the
rotation speed is controlled through draw works and in case of other drive mechanism, the
speed is controlled as per design and requirement.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Periodic replacement of lube oil as per schedule.
2. Greasing of bearings as per the recommendations.
3. Inspection for any looseness of rotary table installation system and corrective
action.
4. Periodic top up / replacement of lube oil for chain & sprocket system for its power.
5. Periodic replacement of lube oil of gear box provided in independent drive system.
6. Periodic inspection of rotary drive clutch in case of drive by draw works.
7. Repair and replacement of components of rotary table drive clutch assembly.
8. Replacement / repair of rotary table lock assembly.
9. Cleaning to remove mud splashes.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings and other components as required. It may be
depending on condition / operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms /
guidelines issued by Technical Services. (Also refer equipment health check-up for drilling &
work over rig issued by technical services).
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 33
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
SAFETY
The rotary table is provided with lock system to prevent reverse rotation. It is to prevent
opening of string assembly connections and safety of well in emergency situations. The
condition & performance of lock system shall always be checked and kept in working
condition.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 34
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.10 Mud Agitator
Mud is a fluid chemically prepared and is used during drilling / work-over operation, well
control activities and work over operations. Mud tank is used for preparation and storage of
mud. It is also named as brine solution tank for work over operations. To prevent deposit /
settling of deposits, a mud agitator assembly is used for keeping it in agitation / continues
movement. A mud agitator consists of agitator (shaft, bearings and blades) gear box and
drive motor.
INSTALLATION
The agitator is installed as per size / requirement of tank system. The moving blades / rotor
keep the mud active by centrifugal / axial action on mud and are driven by gear box
mounted at the top of mud tank.
START UP
Before start up if the condition of mud/ brine solution is unknown, a manual rotation shall
be given to the agitator to ensure its freeness. Other start up checks is
1. Lube oil level and condition in gear box.
2. Condition of couplings and shaft/Guide of rotor & shaft.
3. Direction of rotation of agitator.
4. Current drawn by motors
OPERATION
During operation of mud agitator observe for effective agitation or movement of solution in
tank. Observe for any abnormal sound from agitating blades or gear box and check drive
motor current.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Replacement of lube oil and greasing of bearings on gear box as per recommended
schedule.
2. Replacement of lube oil / greasing of bearings of agitator blade shaft.
3. Inspection and replacement of agitator blades and shaft if required.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings and other components as required. It may be
depending on condition / operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms /
guidelines issued by Technical Services.
SAFETY
Safety of mud agitator is compliance of recommended operating & maintenance practices,
inspection of coupling, coupling guards, bearing housings of agitator shaft assembly and
electrical motors.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 35
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 36
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.11 Air Compressor
Various functions & operation of Work over rig chassis and draw works are pneumatically
operated. High pressure air is also used for starting of engines and operation of air winch.
Air compressors are installed to keep pneumatic system pressurised at desired pressure for
different application. In some of work over rigs, air compressor is connected with carrier
engine and for others as a separate air compressor package. The SOP shall be applicable as
per the rig design.
INSTALLATION
Air compressors are either skid mounted or coupled directly with main diesel engine in an
enclosure along with air tank and moisture separation system (Air dryer If applicable).
Correct installation as per OEM recommendations, alignment and use of correct size of
hardware is to be ensured.
START UP
Air compressor start up requires pre-checks and setting that may be manual or automatic.
The pre-start checks are 1. Direction of rotation.
2. Condition of drive system that may be direct driven, belt driven or through gear
box.
3. Condition and lube oil level.
4. Cooling system that may be water cooled or air cooled.
5. Check that discharge valves are open.
6. Condition of air intake filter.
7. Status of air pressure safety valves for interstate pressure and discharge pressure.
8. Status of blow down valve.
9. Operation of no-load / auto load system.
10. Status of compressor safety system for alarm and shut down.
11. Condition of cooling tubes, fins and heat exchanger.
OPERATION
Air compressor operation depends on the air pressure that is to be maintained in air vessel.
The operation is carried out by setting the operating limits of minimum and maximum air
pressure. There are several parameters to be checked and monitored such as
1. Drive motor current.
2. Air discharge pressure.
3. Inter-stage air pressure.
4. Air temperature at inter-stage and air discharge.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 37
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
5. Lube oil pressure & temperature.
6. Cooling water pressure and temperature if system exists.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Replacement of lube oil as per recommended schedule.
2. Servicing and replacement of suction and discharge valves and its components.
3. Servicing/replacement of air end (In case screw air compressor)
4. Servicing of air intake filters (Primary & secondary)
5. Servicing / Calibration of discharge pressure control for maintaining air pressure in
the receiver through discharge check valve and pressure regulator valve.
6. Servicing/ Replacement of crankcase and bearing filters.
7. Servicing of compressor loader / un-loader valve.
8. Draining of moisture from moisture trap of cooler/ heat exchanger
9. Servicing of Oil stop valve for preventing back flow.
10. Servicing of blow down valve, butterfly type inlet valve.
11. Cleaning of coolers / heat exchangers as exist in air compressor.
12. Oil carry over through discharge air of the air-oil separator system should not
exceed recommended limit.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings, piston, cylinder liners, cross-head liners (Or
compressor block Air end including rotor screw in case screw air compressor) and other
components as required. It may be depending on condition / operating hours as per OEM
recommendations or norms / guidelines issues by Technical Services.
SAFETY SYSTEM
Safety system on air compressor is provided to prevent any damage in case of deviation in
its operating parameters. The safety system is provided with alarm and shut down system.
The parameters monitored and included in system are 1. Lube oil low pressure alarm & shut down.
2. Lube oil temperature High Alarm & shut down.
3. Cooling system pressure alarm & shut down.
4. Cooling system temperature alarm & shut down.
5. High output (Air) pressure Functioning of relief valve.
6. High Vibration alarm.
7. Lube oil low level alarm.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 38
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
8. Pressure vessel / Receiver tank shall be tested as per statutory requirement. (Refer
equipment health check-up for drilling & work over rig issued by technical services)
ENVIRONMENT & EMISSION CONTROL
1. Used lube oil, filters and other components if not disposed properly may damage the
environment. The guideline has been provided to return these items to designated
locations (Stores) for further disposal action.
2. The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory
requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 39
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.12 Centrifugal Pumps
The centrifugal pumps may be of different make and capacity but consist of basic pumps
components. Centrifugal pumps are used at work over rigs for different applications, as
under.
1. Water pump for general use and fire safety.
2. Supercharger pump as feed for mud pump, hopper pumps for preparation of mud or
brine solution.
INSTALLATION
Pumps are installed and skid mounted rigidly and drive motor connected through
flexible/rigid coupling, aligned. The suction and discharge connections are secured to
prevent any looseness. If mechanical seal is provided with water cooling system then the
cooling system connections shall be properly secured.
START UP
Centrifugal pump shall be primed (its casing filled with water/ mud as per application),
adjustment of gland packing / mechanical seal, greasing / lube oil condition of bearings and
condition of drive coupling shall be checked before start.
OPERATION
Centrifugal pumps generally have trouble free operation. The operating status can be
observed by drive motor current and any flow fluctuations affect the current. Pump
discharge pressure is indicator of any damage or increased clearance across impeller /
casing. Other parameters to be checked are condition of pump bearings, adjustment of
gland packing / mechanical seal to arrest leakage if any and direction of rotation of motor.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Replacement of lube oil (For bearing housing) at scheduled interval or greasing
of bearings.
2. Replacement/Tightening of gland packing / mechanical seal components in case
of leakage from sealing system.
3. Inspection & replacement of sealing rings of impeller / casings as desired.
4. Inspection of coupling & tightening of bolts.
5. Vibration monitoring of bearings, unbalance, misalignment and corrective action
as desired.
6. Inspection/replacement of pump skid including foundations bolts (Due to
environment/mud)
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 40
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings, impeller, and other components as required. Pump
skid may also be taken up repair/replacement during over haul (Condition based). It may be
depending on condition / operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms /
guidelines issues by Technical Services /OISD.
SAFETY
Safety of centrifugal pump is compliance of recommended operating & maintenance
practices, gland seal system, inspection of coupling, coupling guards, bearing housings,
pump casing for any abnormality / damage.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 41
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.13 Transmission (Allison)
As the name specify, Allison Transmission is used in draw works of some rigs. It is
connected between drive motor /diesel engine and draw works to provide desired direction
of rotation and speed as per rig operation. The control for Allison transmission is hydraulic
and hence a hydraulic power unit is associated with Allison transmission. It is also for other
applications such as mud / slush pumps and other pumping units deployed at work over
rigs.
INSTALLATION
Allison transmission is installed between drive motor/ diesel engine and draw works and
connected to both ends as per recommended procedure. The control system is hydraulic and
the hydraulic power unit, hose connections and control cables shall be properly secured and
checked.
START UP
Allison transmission is used at rig to provide variable speed & rotation in both directions.
These actions are managed by hydraulically operated actuators. The high pressure hydraulic
system shall be checked for hydraulic oil, filters, pressure gauges and other functions. The
cooling system (air or water) shall be operational.
OPERATION
The operation of Allison transmission is carried out by rig operator from its control as per
operational requirement. The working of transmission, function of its actuators and
hydraulic system shall be checked for reliability and performance.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Replacement of hydraulic oil and filters as required.
2. Greasing of actuators, control levers and other components need greasing.
3. Condition of couplings.
4. Inspection of hydraulic hose (Leakages, deformation, cracks) and its connections
and replacement if required.
5. Tightness of hardware.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings, gears, shafts, valves, piston & cylinder and other
components as required. The overhauling may be required depending upon severity of
operation, run hours, observations during preventive maintenance activities. (Refer
equipment health check-up for drilling & work over rig issued by technical services).
SAFETY
Allison Transmission is used for operating equipment at variable speed. To ensure safety
during operation, it shall be correctly secured both with driver and driven equipment. To
change the speed, recommended procedure shall be followed for safety of equipment itself.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 42
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 43
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.14 Hydro-Matic Brake
The Hydromatic is a hydro-dynamic device that absorbs power by converting mechanical
energy into heat in its working fluid which is normally water. Resistance is created
exclusively by fluid friction and agitation of the fluid circulated between the vaned pockets
of the rotor and stator elements with the conversion of mechanical energy to heat taking
place directly within the fluid itself. The amount of mechanical energy that can be absorbed
in this manner is dependent upon the quantity and velocity of the fluid in the working
chamber.
The weight of string assembly is high and its movement is controlled by braking action. In
normal operation, braking action is taken care by draw works brake depending on string
load. In case of run in and pull out process, while lowering string assembly, additional
braking action is managed by use of hydromatic brake, for smooth & effective braking
action.
INSTALLATION
The hydro-matic brake assembly is installed, coupled to draw works shaft. It is circulated
with water to provide braking action and to remove heat generated in braking action.
Further installation practice include
1. While installing, required clearances should be maintained for working space and
piping connections.
2. The areas and surfaces to mount hydro-matic brake should comply with
requirements and installation tolerances recommended by manufacturer. Installation
should be carried out only when all conditions are satisfactory.
3. Water line connections should be of recommended size and secured, routed correctly
for smooth operation.
4. All installation checks should be completed according to manufacturers written
instructions.
START UP
The cooling water inlet and outlet connections shall be checked. The quality of water being
used (if required inhibitors to be added to prevent corrosion of brake drum) shall be as
recommended by OEM. The braking action shall be checked at no load condition. In case of
provision of heat exchanger, same shall be installed as per recommendations.
OPERATION
The desired braking action is achieved by varying position of vanes in brake system and
regulated by operator as per operational requirement. The quantity/ flow of water shall be
checked for removing heat and effective braking action.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 44
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1.
A Hydromatic Brake must have an adequate circulating system that will provide cool
water at all times for the loads that it will be required to handle. It is imperative that
the water used in the circulating system be fresh and free of all foreign substance.
Brackish or corrosive water, when used in the circulating system, causes corrosion that
accelerates cavitation and erosion within a brake.
2.
When a Hydromatic Brake has been properly installed, it requires no special care. It
should be inspected at regular periods, such as should be done with the entire rig. Each
grease fitting on the brake should be lubricated with a good grade of No. 2 waterproof
grease equivalent on each round trip. It is recommended that same type waterproof
grease be used consistently, as some types are not compatible with others.
3.
The rotor in a Hydromatic Brake is also designed to serve as an impeller for discharging
heated water at the discharge ports. The rate of discharge is approximately the same as
the rate at which cool water enters the brake, provided the discharge line from the
brake is not restricted. During the running in of a stand of pipe with a Hydromatic Brake
revolving in the direction to create resistance, a sufficient volume of cool water must be
available at the brake inlet, at pressures between the minimum and maximum
recommended, to displace the water in the brake as it is heated.
4.
Inspection and condition of coupling.
5.
Greasing of bearings or lube oil replacement as per provision.
6.
Adjustment of any water sealing / gland system to arrest leakages.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings and other components as required. It may be
depending on condition / operating hours as per OEM recommendations or norms /
guidelines issues by Technical Services.
SAFETY
Hydro-matic Brake is installed for safe operation of rig and for its expected performance,
compliance to recommended safety practices is essential.
ENVIRONMENT
Equipment grounding and noise attenuation practices for electrical and electromagnetic
interference should be properly followed and should be according to manufacturers
recommendations.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 45
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.15 AC Generator
The Alternating Current Generators on Work-over rigs of ONGC are cooled by the flow of air
through the machine.
The machine armature (stator) comprises low-loss steel laminations assembled under
pressure. The steel laminations are blocked axially by a welded ring. The stator coils are
inserted and blocked in the slots, then impregnated with varnish, and polymerised to ensure
maximum resistance to mould, excellent dielectric rigidity and perfect mechanical linking.
The revolving field coil (rotor) comprises a stack of steel laminations, stamped and cut to
reproduce the indentation of the projecting poles. The steel lamination stack-up is
terminated at each end with high-conductivity electrical plates. To enable parallel operation
between machines, and in order to ensure stability, high electrical conductivity bars are
inserted in holes crossing the poles from one side to the other. These bars are welded with
the stack end laminations in order to obtain a complete cage winding.
The SOP for alternators is expected to ensure:
1. Safe operation
2. High efficiency and reliability
3. Low maintenance cost
4. Improved life cycle
5. Low noise pollution
Following documents should be diligently maintained at site:
1. Manufacturers instruction sheets
2. Manufacturers installation instructions
3. Manufacturers operating manual
INSTALLATION
Following practices should be followed with regard to installation:
1. All installation checks should be completed according to manufacturers written
instructions.
2. While accepting delivery of new alternators, it should be ensured that they are
received packed in secure cartons and covered for protection against dirt and
moisture during transit and outdoor storage.
3. Alternators should be stored in clean dry space, protected from dirt, fumes, water,
corrosive substances and physical damage.
4. Handling should be done with proper lifting equipment using lugs or eyebolts
provided by the manufacturer.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 46
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
5. While installing, required clearances should be maintained for working space, cable
terminal boxes, coupling access and alternator cooling air.
6. The areas and surfaces to mount alternators should comply with requirements and
installation tolerances recommended by manufacturer. Installation should be carried
out only when all conditions are satisfactory.
7. Fitting of coupling, alignment and electrical connections should be carried out strictly
as per manufacturers written instructions.
8. It has to be ensured that all protection devices are correctly connected and are in
good working order.
9. The power cables must not push, pull or bend the generator terminals.
10. Washers should not be added to the power supply cable terminals other than those
used by the manufacturer.
START UP CHECKS
Start-up checks are carried out to ensure that the alternators start smoothly and thereafter
operate without any problem. The start-up checks include:
1. All start up checks should be completed according to manufacturers written
instructions.
2. The commissioning checks should follow the sequence recommended by the
manufacturer.
3. Static checks include machine fixing, alignment, cooling, bearing lubrication,
electrical connections and insulation checks.
4. Rotating checks include running the alternator without excitation; running with
excitation (AVR manual and auto modes) at no load; adjustments of over voltage
relays, over current relays, differential protection relays, negative sequence relays;
running at full load. Vibration levels are recorded during the rotating checks.
5. Foundation bolts should be properly tight. Coupling to be in good condition.
6. Cable connections to be tight as per manufacturers instruction.
7. Proper earthing/ grounding of alternator for safety as per recommended statutory
code of practice.
8. Alternator bearings to be properly lubricated.
9. Personal Protective Equipment for operating personnel to be available. Use of Rubber
mats etc. should be ensured.
OPERATION
The factors to be checked and monitored are:
1. Dirt and Corrosion
2. Winding Insulation
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 47
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
3. Heat, Noise and Vibration
4. Lubrication
Written record in the form of Log Books, indicating date, items inspected, services
performed and alternator condition help in quick identification of specific problems. These in
turn provide quick solutions thereby helping in avoiding breakdowns and downtime losses.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The suggestions and recommendations of manufacturer regarding the preventive
maintenance schedule are to be followed as closely as possible in order to maintain the
machine efficiency and in order not to reduce the service life of the machine.
The Preventive Maintenance activities of alternators includes
1. Stator Checking winding temperature; Bolts tightening; Cleaning of air inlet and
outlet; checking Insulation and Polarisation index
2. Rotor Checking Insulation, cleaning diodes, diodes tightening, checking Polarisation
index
3. Terminal Box Cleaning of terminal box, maintenance of regulator assembly, bolts
tightening.
4. Bearings Re-greasing; checking bearing temperature
OVERHAUL
Alternator overhaul decision shall be either based on OEM recommendations or on the basis
of condition detected during inspection. The activities during overhaul shall be some or all of
the following:
1. Bearing replacement.
2. Servicing/ replacement of switchgear components.
3. Servicing/ replacement of rotating diodes and resistors.
4. Repair/ replacement of space heaters.
5. Cleaning/ re-varnishing of windings if required.
6. Replacement of vibration dampeners.
7. Painting of external surface of alternator.
SAFETY
For safe operation of alternator, compliance to recommended safety practices is essential.
This includes:
1. Electrical connectors and terminals should be tightened according to cable and
terminal manufacturers recommended torque values.
2. Handling should be done with proper lifting equipment using lugs or eyebolts
provided by the manufacturer.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 48
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
3. Proper earthing/ grounding of alternator for safety as per recommended statutory
code of practice.
4. Personal Protective Equipment for operating personnel to be available. Use of Rubber
mats etc. should be ensured.
ENVIRONMENT
1. The noise attenuation practices for electrical and electromagnetic interference should
be properly followed and should be according to manufacturers recommendations.
2. CPCB norms for noise and exhaust gas emission to be followed/ complied with.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines/ norms issued for safe operation and maintenance by OEM/ regulatory
agencies/ Indian Electricity Rules should be diligently followed. Reference to some of the
guidelines / regulations issued by statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 49
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.16 Electric AC Motors
On work-over rigs in ONGC, all AC motors irrespective of size are Squirrel Cage Induction
Motors. AC motors are used as drives for various applications such as pumping, lifting,
rotating etc. As per the power need, motors of different HP/ KW capacities are being used
on rigs. The following SOP covers all AC motors irrespective of make, size and their
application and is expected to ensure:
1. Safe operation
2. High efficiency and reliability
3. Low maintenance cost
4. Improved life cycle
5. Low noise pollution
Following documents should be diligently maintained at site:
1. Manufacturers instruction sheets
2. Manufacturers installation instructions
3. Manufacturers operating manual
INSTALLATION
On work-over rigs, AC motors are generally installed on the same skid as the driven
equipment.
Following practices should be followed with regard to installation:
1. While accepting delivery of new motors, it should be ensured that they are received
packed in secure cartons and covered for protection against dirt and moisture during
transit and outdoor storage.
2. Motors should be stored in clean dry space, protected from dirt, fumes, water,
corrosive substances and physical damage.
3. Handling should be done with proper lifting equipment using lugs or eyebolts
provided by the manufacturer.
4. While installing, required clearances should be maintained for working space, cable
terminal boxes, coupling access and motor cooling air.
5. The areas and surfaces to mount motors should comply with requirements and
installation tolerances recommended by manufacturer. Installation should be carried
out only when all conditions are satisfactory.
6. Technical features and parameters of AC motors like ambient conditions, duty cycle,
starting and running torque demands etc should be coordinated with the power and
control circuits to which they are connected.
7. Electrical cables should be laid, routed and covered properly. Cable connections with
motor should be done as per recommended procedure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 50
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
8. The foundation should be rigid to minimise vibration and to maintain alignment
between motor and load shaft. AC motors should be connected and aligned with
driven equipment with coupling of recommended size & capacity and according to
manufacturers written instructions. The shims and foundation bolts shall be of
proper size.
9. Flexible couplings for direct drive or belt drive alignments should be carried out as
per their respective manufacturers instructions.
10. It should be ensured that motors are designed for operation in either direction of
rotation without any physical change in the motor.
11. All installation checks should be completed according to manufacturers written
instructions.
START UP CHECKS
Start-up checks are carried out to ensure that the motors start smoothly and thereafter
operate without any problem. The start-up checks include:
1. Foundation bolts should be properly tight. Coupling to be in good condition.
2. Motor rating to match application requirements. Flame proof equipment to be used in
hazardous classified zones.
3. Cable connections to be tight as per manufacturers instruction.
4. Winding insulation integrity to be tested with a megger.
5. Proper earthing/ grounding of motor for safety as per recommended statutory code
of practice.
6. Motor bearings to be properly lubricated.
7. Personal Protective Equipment for operating personnel to be available. Use of Rubber
mats etc. should be ensured.
8. Power should be applied to verify direction of rotation. If necessary, load should be
decoupled before this test to ensure safety of load equipment in case of reverse
rotation. The direction of rotation to be changed if necessary and retested.
9. All start up checks should be completed according to manufacturers written
instructions.
OPERATION
Routine inspection and servicing can generally be done without disconnecting or
disassembling the motor during operation. The factors to be checked and monitored are:
1. Dirt and Corrosion
2. Winding Insulation
3. Heat, Noise and Vibration
4. Lubrication
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 51
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
Written record in the form of Log Books indicating date, items inspected, service performed
and motor condition, help in quickly identifying specific problems in each application. These
in turn provide quick solutions thereby helping in avoiding breakdowns and downtime
losses.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Preventive Maintenance activities of electrical motors includes
1. Greasing of bearings with periodicity and methodology as per recommendation of
manufacturer.
a.
Both over/ under greasing are detrimental to motor performance.
b. No impurity should be allowed to get inside the bearing.
c.
Only grease of recommended type and viscosity should be used.
2. Measurement of winding insulation resistance.
3. Measurement of earth resistance.
4. Checking condition of drive coupling; replacement of flexible elements if damaged/ at
scheduled intervals.
5. Condition monitoring of motors, if facility exists.
6. Testing of switchgear and calibration of protective relays.
7. Condition of electric supply cables. Proper lay of cables in trays and fixing of tray
covers.
8. Checking condition of space heaters.
OVERHAUL
Motor overhaul decision shall be either based on OEM recommendations or on the basis of
condition detected during inspection. The activities during overhaul shall be some or all of
the following:
1. Bearing replacement.
2. Replacement of cooling fan.
3. Cleaning of cooling fins / ducts.
4. Servicing/ replacement of switchgear components.
5. Repair/ replacement of space heaters.
6. Cleaning/ re-varnishing of windings if required.
7. Painting of external surface of motor.
SAFETY
For safe operation of motor, compliance to recommended safety practices is essential. This
includes:
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 52
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
1. Recommended type of cable glands should be installed according to statutory
guidelines/ instructions.
2. Correct motor cable size should be selected based on standard code of practice.
3. It should be verified that the rated voltage, frequency and full load current is
matching with drawings, specifications and application requirements.
4. It should be verified that motor overload protection devices are installed as required
by Indian Electricity Rules.
5. It should be ensured that motor power and auxiliary cabling is according to safety
and statutory requirements for electrical systems.
6. Grounding of all equipment should be proper and according to manufacturers
recommendations.
7. Electrical connectors and terminals should be tightened according to cable and
terminal manufacturers recommended torque values.
ENVIRONMENT
Equipment grounding and noise attenuation practices for electrical and electromagnetic
interference should be properly followed and should be according to manufacturers
recommendations.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines/ norms issued for safe operation and maintenance by OEM/ regulatory
agencies such as DGMS/ Indian Electricity Rules should be diligently followed. Reference to
some of the guidelines / regulations issued by statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 53
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
6.17 Pneumatic / Hydraulic Winch
Work Over Rig operation involves material handling for continuation of its activities. String
assembly that is made up of special assemblies & production tubing assembled to desired
length. Most of such material handling activities from ground to derrick level is managed
using pneumatic winch / Hydraulic winch of rated capacity. The winch may be operated
through pneumatic motor or hydraulically motor and has wire rope and braking system for
material handling operation. It can be operated in both the directions for lifting and lowering
of materials.
INSTALLATION
Winch is installed at rig carrier / chassis. It is provided with air / hydraulic connection and is
driven by a reversible motor with auxiliaries such as lubricator and strainer. Wire rope of
recommended size and configuration shall be used. The lifting shackles connected for
material handling shall be of desired load rating. Air outlet connection (silencer/muffler)
shall be directed to prevent any impact on persons operating the winch or involved with
handling of material. Winch is provided with overload sensing and shut off device for safety
and protection.
START UP
Before operation of winch, lube oil shall be filled in air lubricator or hydraulic oil in hydraulic
power system, brake shoes and throttle valve shall be checked and adjustment carried out
for effective braking action. The condition of wire ropes should also be checked for a safe
operation. The operation of winch shall be checked at no load before deploying for material
handling activities.
OPERATION
As the winch is used for material handling operation and is operated by crew deployed for
work over operation, persons operating winch shall take necessary precautions for the
material being lifted / lowered and safety of other crew members associated with.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
The preventive maintenance activities are
1. Replacement / topping up of oil in air lubricator. Replacement / topping of oil in
hydraulic tank as per winch installed.
2. Inspection of air motor or pump. (hydraulic motor / pump for hydraulic winch).
3. Cleaning / replacement of filter or strainer, if exist.
4. Greasing of actuators, throttle valve, control levers and other components need
greasing.
5. Inspection of air / hydraulic line connections and replacement if required.
6. Inspection of air silencer/muffler at exhaust port for any blockage.
7. Inspection of wire rope and replacement if found damaged/worn out/slippage.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 54
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
8. Inspection of overload sensing and shut off device.
OVERHAUL
Overhauling is replacement of bearings, shafts, clutch assemblies, actuators, valves,
filters/strainers and other components as required. The overhauling may be required
depending upon severity of operation, run hours, observations during preventive
maintenance activities.
SAFETY
Since winch is used for material handling, person operating the winch shall ensure safety of
material handled and person involved. The ropes, slings, belts, hooks, overload sensing
and shut off device etc. used shall be of approved rating and recommended for use.
ENVIRONMENT CONTROL
The consumables / used components shall be disposed at designated places only or
returned to stores for disposal as per approved guidelines / regulatory requirements.
STATUTORY / REGULATORY PROVISIONS
Any guidelines, norms issued for safe operation, maintenance by OEM and/ or regulatory
agencies shall be followed. Reference to some of the guidelines / regulations issued by
statutory agencies is enclosed as annexure.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 55
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
7. Annexures
7.1 Norms and Policies Issued by Technical Services
1. Life cycle period of major equipment for LCC based equipment purchases.
2. Norms for Noise and Exhaust emissions for rotating equipment.
3. Policy for revamping of onshore work over rig.
4. Policy for equipment health check-up for drilling & work over rig.
5. Policy for discard of onshore work over rigs.
6. Revised equipment replacement policy for drilling rigs and work over rigs.
7. Capitals overhaul norms for onshore work over rig equipment.
8. Standby equipment norms for onshore work over rig equipment.
9. Storage, handling and disposal of lubricants.
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 56
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
7.2 OISD references Relevant for Work Over Rigs
Sr.
No.
OISD
Standard/GDN/RP
No
OISD-STD-105
Work Permit System
Sep-2004
OISD-STD-106
Pressure Relief & Disposal System
Oct-2010
OISD-RP-110
Recommended Practices on Static Electricity
Aug-1999
OISD-STD-113
Classification of Area for Electrical Installations at
Hydrocarbon Processing & Handling Facilities
Oct-2013
OISD-STD-119
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of Pumps
Jul-2008
OISD-STD-120
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of
Compressors
Jul-2008
OISD-RP-122
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of Fans,
Blowers, Gear Boxes, Agitators & Mixers
Jul-2008
OISD-RP-123
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of Rotary
Equipment Components
Jul-2008
OISD-RP-126
Specific practices for installations and maintenance
of Rotating Equipment
Aug-2007
10
OISD-STD-127
Selection, Operation, Inspection & Maintenance of
Diesel Engines
Oct-2010
11
OISD-STD-132
Inspection of Pressure Relieving devices
Jul-2012
12
OISD-STD-137
Inspection of Electrical Equipment
13
OISD-RP-146
Preservation of idle electrical equipment
Aug-2000
14
OISD-RP-147
Inspection & safe practices during electrical
installations
Oct-2002
15
OISD-RP-148
Inspection & safe practices during overhauling
electrical equipment
Aug-2000
Version 1, June-2014
STANDARD NAME
SOP Work Over Rigs
CURRENT
EDITION IN
VOGUE
Oct-2010(Under
Revision)
Page : 57
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
Sr.
No.
OISD
Standard/GDN/RP
No
16
OISD-STD-171
Preservation of Idle Static & Rotary Mechanical
Equipment
Jul-1998
17
OISD-GDN-180
Lightning Protection
Jul-1999
18
OISD-STD-184
Standard on Replacement of Personal Protective
Equipment & Life Saving Appliances
Aug-2000
19
OISD-STD-187
Care And Use Of Wire Rope
Aug-2000
20
OISD-STD-189
Standard On Fire Fighting Equipment For Drilling
Rigs, Work Over Rigs And Production Installations
Jul-2012
21
OISD-STD-190
Derrick Floor Operations (Onshore Drilling /
Workover Rigs)
Aug-2000(Under
Revision)
22
OISD-GDN-202
Inspection of Drilling and Workover Rig Mast / SubStructure
Oct-2002(Under
Revision)
23
OISD-GDN-203
Operation, Maintenance & Inspection Of Hoisting
Equipment
Sep-2003
24
OISD-STD-216
Electrical Safety in Onshore Drilling & Workover Rigs
Oct-2010
25
OISD-GDN-218
Guidelines For Safe Rig- Up & Rig- Down Of Drilling
And Work-Over Rigs
Oct-2004
Version 1, June-2014
STANDARD NAME
SOP Work Over Rigs
CURRENT
EDITION IN
VOGUE
Page : 58
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
7.3 DGMS References Details of regulations / guidelines
-
OMR Oil Mines Regulation
7.4 Central Pollution Control Board
- Guidelines issued for noise and emission from Gen-sets.
7.5 Electrical Related Standards A Reference
Sr.
No.
OISD
Standard/GDN/RP
No
OISD-RP-110
OISD-STD-137
OISD-RP-146
Preservation of idle electrical equipment
Aug-2000
OISD-RP-147
Inspection & safe practices during electrical
installations
Oct-2002
OISD-RP-148
Inspection & safe practices during overhauling
electrical equipment
Aug-2000
OISD-GDN-180
Lightening Protection
July-1999
OISD-STD-216
Electrical Safety in Onshore Drilling & Work Over Rigs
Oct-2010
STANDARD NAME
Recommended Practices on Static Electricity
Inspection of Electrical Equipment
Indian Electricity Rules 1956.
OMR
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
CURRENT EDITION
IN VOGUE
Aug -1999
Oct-2010(Under
Revision)
Page : 59
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
7.6 Selected Applicable Standards Drilling Rig Equipment
Sr.
No.
Standard
Technical Services
Life cycle period of major equipment for LCC based
equipment purchases.
July-2006
Technical Services
Norms for Noise and Exhaust emissions for rotating
equipment.
Nov-2010
Technical Services
Policy for revamping of onshore work over rig,
June-2006
Technical Services
Policy for equipment health check-up for drilling and
work over rig.
Jan-2009
Technical Services
Policy for discard of onshore work over rigs
Jan-2010
Technical Services
Revised equipment replacement policy for drilling and
work over rigs.
Jan-2013
(Under Revision)
Technical Services
Capital overhauls norms for onshore work over rig
equipment.
Mar-2010
Technical Services
Stand by equipment norms for onshore work over rig
equipment.
Dec-2009
Technical Services
Storage, Handling and disposal of lubricants.
July-2011
10
OISD-STD-105
Work Permit System
Sep-2004
11
OISD-STD-119
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of Pumps
Jul-2008
12
OISD-STD-120
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of Compressors
Jul-2008
13
OISD-RP-122
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of Fans,
Blowers, Gear Boxes, Agitators & Mixers
Jul-2008
14
OISD-RP-123
Selection, Operation and Maintenance of Rotary
Equipment Components
Jul-2008
15
OISD-RP-126
Specific practices for installations and maintenance of
Rotating Equipment
Aug-2007
Version 1, June-2014
STANDARD NAME
SOP Work Over Rigs
CURRENT EDITION
IN VOGUE
Page : 60
STANDARD OPERATING PRACTICES
Equipment Management, Technical Services
16
OISD-STD-127
Selection, Operation, Inspection & Maintenance of
Diesel Engines
Oct-2010
17
OISD-STD-171
Preservation of Idle Static & Rotary Mechanical
Equipment
Jul-1998
18
OISD-STD-187
Care And Use Of Wire Rope
Aug-2000
19
OISD-GDN-203
Operation, Maintenance & Inspection Of Hoisting
Equipment
Sep-2003
20
OISD-GDN-218
Guidelines For Safe Rig- Up & Rig- Down Of Drilling
And Work-Over Rigs
Oct-2004
Version 1, June-2014
SOP Work Over Rigs
Page : 61
You might also like
- Rig Inspection & SurveyDocument102 pagesRig Inspection & SurveyhshobeyriNo ratings yet
- Mast and Dwks Lowering ChecklistDocument5 pagesMast and Dwks Lowering Checklistjinyuan74No ratings yet
- 10 Work On Mud PumpsDocument5 pages10 Work On Mud PumpsdraghiceanuNo ratings yet
- Checklist FloormanDocument4 pagesChecklist FloormansaysamajoNo ratings yet
- Rig Up and Rig Down Potential HazardDocument3 pagesRig Up and Rig Down Potential HazardRizwanButtNo ratings yet
- Drilling Rig Components GuideDocument66 pagesDrilling Rig Components Guidehardik khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Drilling HSE Audit - Base Questionnaire: 1 4.1 Well Control 2Document58 pagesDrilling HSE Audit - Base Questionnaire: 1 4.1 Well Control 2MartahanManurungNo ratings yet
- Haider Ali: Field Service Technician (Level 3)Document3 pagesHaider Ali: Field Service Technician (Level 3)Junaid Ahmed SattiNo ratings yet
- PRESPUD CHECKLISTDocument8 pagesPRESPUD CHECKLISTAgus Alexandri100% (2)
- Daily Tool Pusher ChecklistDocument2 pagesDaily Tool Pusher ChecklistKaleem UllahNo ratings yet
- RIG EQUIPMENTDocument2 pagesRIG EQUIPMENTRoger AddyNo ratings yet
- IADC DDR Codes 2 13 2019Document4 pagesIADC DDR Codes 2 13 2019txcrudeNo ratings yet
- Rig Personnel Job DescriptionsDocument6 pagesRig Personnel Job DescriptionsKachur Aleksey100% (1)
- 2017 Wellbore Customer Training CatalogDocument20 pages2017 Wellbore Customer Training CatalogAhmed ShaabanNo ratings yet
- 02 Reset Pop Off ValveDocument5 pages02 Reset Pop Off ValveShussan PrinceNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities of Rig Superintendent StudyDocument7 pagesResponsibilities of Rig Superintendent StudyAnonymous VNu3ODGavNo ratings yet
- 1000HP SpecificationDocument107 pages1000HP SpecificationAl Manar Petroleum100% (1)
- 9.1.4 Admasco Rig Move Procedure PDFDocument52 pages9.1.4 Admasco Rig Move Procedure PDFkhaled100% (2)
- Oil Rig Components ListDocument9 pagesOil Rig Components ListsamirgoranNo ratings yet
- Oil Based Rig Maintenance ReportDocument12 pagesOil Based Rig Maintenance Reportelmaadawy2002No ratings yet
- Equip ChecklistDocument65 pagesEquip Checklistkaveh-bahiraee100% (1)
- Units of Competence: Assistant Driller Level - 7Document17 pagesUnits of Competence: Assistant Driller Level - 7Ben BieberNo ratings yet
- E-Totco Electronic Drift Survey Tool FlyerDocument1 pageE-Totco Electronic Drift Survey Tool FlyerEmad JamshidiNo ratings yet
- Drilling Training ProgramDocument7 pagesDrilling Training Programbehnam197100% (1)
- Drilling Blowout PreventionDocument203 pagesDrilling Blowout PreventionLuisBlandón100% (1)
- Maintaining Rig MastsDocument14 pagesMaintaining Rig MastsVerda YunitaNo ratings yet
- Rig Components: We LL Drilling Eng Dana MohammadDocument129 pagesRig Components: We LL Drilling Eng Dana Mohammaddana mohammedNo ratings yet
- Inspection - Rig AcceptanceDocument40 pagesInspection - Rig AcceptanceSrikanth Bammidi100% (6)
- Drilling. and Casing. Check List.Document24 pagesDrilling. and Casing. Check List.Aderobaki GbengaNo ratings yet
- Rig RepairDocument30 pagesRig Repaircrown212100% (1)
- 02 Operation ManualDocument30 pages02 Operation ManualramiNo ratings yet
- Zj50d Drilling Rig PartsDocument76 pagesZj50d Drilling Rig PartsAye Kywe100% (4)
- Rigsco IADC Land Rig Equipment ListDocument42 pagesRigsco IADC Land Rig Equipment ListOmarSaid100% (1)
- Arabian Drilling Company Rig Specific Procedure AD - 32 Pick Up Drill PipeDocument4 pagesArabian Drilling Company Rig Specific Procedure AD - 32 Pick Up Drill Pipehosam aliNo ratings yet
- Attachment D Pre Rig Move ChecklistDocument2 pagesAttachment D Pre Rig Move ChecklistJennifer WangNo ratings yet
- 100027D-CRTi Running Procedure PDFDocument9 pages100027D-CRTi Running Procedure PDFAhmed Eid FarhNo ratings yet
- Draw WorksDocument3 pagesDraw WorksUsman AhmedNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Components of Drilling RigDocument81 pages2.0 Components of Drilling RigConnor Whiltshire100% (1)
- Career On A Drilling RigDocument12 pagesCareer On A Drilling RigdonivaldNo ratings yet
- Arabian Drilling Company Rig Specific Procedure AD - 32 Manriding OperationDocument5 pagesArabian Drilling Company Rig Specific Procedure AD - 32 Manriding OperationinfonexusNo ratings yet
- Triplex Drilling Mud Pump Fluid ExpendablesDocument6 pagesTriplex Drilling Mud Pump Fluid ExpendablesClevin Zhao100% (1)
- B+V Manual - CLS 100-150 - 621100-Y-BC-D Rev 005Document30 pagesB+V Manual - CLS 100-150 - 621100-Y-BC-D Rev 005Leonardo Rachen RodriguezNo ratings yet
- List of Components of Oil Drilling RigsDocument4 pagesList of Components of Oil Drilling RigsIjlal AhmadNo ratings yet
- Work Over RigDocument28 pagesWork Over RigbvkvijaiNo ratings yet
- EDC-61 Rig SurveyDocument14 pagesEDC-61 Rig SurveyMostafa Elghifary100% (1)
- Arabian Drilling Company Rig Specific Procedure AD - 32 Prepare CasingDocument6 pagesArabian Drilling Company Rig Specific Procedure AD - 32 Prepare CasinginfonexusNo ratings yet
- KPC Drilling Rig AcceptanceDocument3 pagesKPC Drilling Rig Acceptanceislam atifNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents Iadc Safety Meeting TopicsDocument4 pagesTable of Contents Iadc Safety Meeting TopicsfarisNo ratings yet
- Well Intervention Pressure Control Syllabus - Level 3 4Document52 pagesWell Intervention Pressure Control Syllabus - Level 3 4ryaneschultzhotmail.comNo ratings yet
- Flowhead: Multifunction Flow Control From The Top of The WellDocument2 pagesFlowhead: Multifunction Flow Control From The Top of The WellSandro Ha100% (1)
- SOP - 03 - Job Execution Procedure - Rev02Document9 pagesSOP - 03 - Job Execution Procedure - Rev02HasnainNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities During Drilling OperationsDocument1 pageResponsibilities During Drilling OperationsYougchu LuanNo ratings yet
- Case Study MaintenanceDocument14 pagesCase Study Maintenancenash vinNo ratings yet
- UPK 4a COMPLETEDDocument14 pagesUPK 4a COMPLETEDHannan__AhmedNo ratings yet
- Toolkit On Standard Operating Procedures March 2013Document13 pagesToolkit On Standard Operating Procedures March 2013iabureid7460No ratings yet
- VIP HandbookDocument5 pagesVIP HandbookClémentNo ratings yet
- PIP-Guidelines For Spare Parts ManagementDocument16 pagesPIP-Guidelines For Spare Parts ManagementrizaNo ratings yet
- OM Script ReportDocument8 pagesOM Script ReportThreeGee JoseNo ratings yet
- TR CMS 101:2011 Standard For Compliance Management Systems (CMS)Document22 pagesTR CMS 101:2011 Standard For Compliance Management Systems (CMS)Darshan ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Casing Data PDFDocument62 pagesCasing Data PDFVivek MishraNo ratings yet
- Mudras For MeditationDocument14 pagesMudras For Meditationdeepul_s100% (4)
- RP 174Document43 pagesRP 174Vasant Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- Casing Data PDFDocument62 pagesCasing Data PDFVivek MishraNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal PumpDocument105 pagesCentrifugal PumpVivek Mishra100% (2)
- Vivek 4 StudentsDocument62 pagesVivek 4 StudentsVivek MishraNo ratings yet
- UPSC Geography SyllabusDocument4 pagesUPSC Geography SyllabusVivek MishraNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts On Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity Risk AssessmentDocument42 pagesBasic Concepts On Laboratory Biosafety and Biosecurity Risk Assessmentpristine de guzmanNo ratings yet
- 441 - 738790 - Module 12Document2 pages441 - 738790 - Module 12Wena Mae CristobalNo ratings yet
- FitTestAdapters PDFDocument1 pageFitTestAdapters PDFStivens Marin MedinaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument5 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationWendy Christian Sihombing100% (1)
- Servo Motor Motor ManualDocument99 pagesServo Motor Motor ManualHùng ThanhNo ratings yet
- 15.1 Safety Management: Contractor Management System: 15.1.1 PurposeDocument13 pages15.1 Safety Management: Contractor Management System: 15.1.1 Purposesyedahmad39No ratings yet
- HACCP Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesHACCP Questions and AnswersAnil Kumar Singh100% (1)
- NVQ Level 5 Initial AssessmentDocument10 pagesNVQ Level 5 Initial AssessmentZubair KhanNo ratings yet
- TFS Audit Program V2.0Document29 pagesTFS Audit Program V2.0kanji63No ratings yet
- Sullube American Chemical MSDS - EnglishDocument6 pagesSullube American Chemical MSDS - EnglishMod Kaewdaeng100% (2)
- Rejection Criteriafor Lead ApparelDocument8 pagesRejection Criteriafor Lead Apparelbassem besbesNo ratings yet
- 2206F-E13TA Industrial Engine Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument118 pages2206F-E13TA Industrial Engine Operation and Maintenance ManualWeifang PowerNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet X-CIDE 207: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument7 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet X-CIDE 207: 1. Chemical Product and Company IdentificationLuis Gomez JimenezNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Preliminary Analysis of Production ProcessDocument14 pagesProcedure For Preliminary Analysis of Production ProcessNurulsakinah SailinNo ratings yet
- Driving Policy Signed ApprovedDocument1 pageDriving Policy Signed ApprovedSantos RexNo ratings yet
- Safety Manual - Bfp-A8006f PDFDocument44 pagesSafety Manual - Bfp-A8006f PDFNur ZaidanNo ratings yet
- S110 ManualDocument734 pagesS110 ManualStevie WrightNo ratings yet
- 2954 4650 00 - Qas 600 - enDocument58 pages2954 4650 00 - Qas 600 - enIlarion CiobanuNo ratings yet
- First Aid Education in 40 CharactersDocument22 pagesFirst Aid Education in 40 CharactersMelNo ratings yet
- CIVSDTUM1900Document135 pagesCIVSDTUM1900Edgar Mendoza GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Fema CertificateDocument1 pageFema Certificateapi-314439695No ratings yet
- Water Supply Temporary Bypass SpecificationDocument15 pagesWater Supply Temporary Bypass SpecificationtranquangtrungxdNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management Systems - Three Different Levels of IntegrationDocument11 pagesIntegrated Management Systems - Three Different Levels of IntegrationmohamedNo ratings yet
- Shabbir Kamran - 00741946 - 645-TWI Middle East FZ - LLC - IG-1Document14 pagesShabbir Kamran - 00741946 - 645-TWI Middle East FZ - LLC - IG-1Rashid Jamil100% (1)
- Haccp CrabDocument22 pagesHaccp CrabOlga NazarenkoNo ratings yet
- Manual Kidde ConvencionalDocument102 pagesManual Kidde ConvencionalSantiago AguilarNo ratings yet
- Nebosh: Management of Health and Safety Unit Ig1Document6 pagesNebosh: Management of Health and Safety Unit Ig1zeeshanNo ratings yet
- 1315w Nib Pre-Bid Walk Thru DirectionsDocument10 pages1315w Nib Pre-Bid Walk Thru DirectionsJAGUAR GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Proline Promass 80 Operating InstructionsDocument130 pagesProline Promass 80 Operating InstructionsOgnjen DrljanNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product IdentificationDocument4 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: 1. Product IdentificationMuhammad Wasim Shahzad0% (1)