Professional Documents
Culture Documents
45 - 6575 - EE328 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - EE 328 - Lect - 01
Uploaded by
G00GLROriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
45 - 6575 - EE328 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - EE 328 - Lect - 01
Uploaded by
G00GLRCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Power & Machines Dr.
Ahmed El-Shenawy
Electrical Power and Machines
Lecture 1
<Dr Ahmed El-Shenawy>
<Dr Hadi El Helw>
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Course Contents
Review on electric circuits & Magnetic circuits.
The law of motor and generator action.
DC Motors and DC Generator.
Core Loss, transformer model and regulation.
AC rotating field.
3-phase induction motor.
Synchronous machines.
Single phase and small motors.
Electric power system.
Plant distribution system.
Protective devices and distribution of electricity in
buildings.
System protection & PF correction.
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Power System Objectives?
Provide energy services
System criteria
Safe
Reliable
Cheap
Clean
any more?
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Major Elements of Power Systems
Power Plant
Fossil fuel powered
Renewable energy
Transformers
Transmission Lines
Distribution Lines
Protection and Control
Customers
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Power Systems Components
electric generator
is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy In a
generator, moving a conductor through a stationary magnetic field generates
voltage. If a coil is rotated through a magnetic field as shown, an alternating
voltage will be produced.
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another
through inductively coupled conductorsthe transformer's coils. A varying current in
the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core,
and thus a varying magnetic field through the secondary winding. This varying
magnetic field induces a varying electromotive force (EMF) or "voltage" in the
secondary winding. This effect is called mutual induction.
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
An electric motor uses electrical energy to produce mechanical energy, very typically
through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors.
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
A power cable is an assembly of two or more electrical conductors, usually held
together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical
power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in
the ground, or run overhead.
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Introduction
The present day machines are based on the electro-magnetic
principles. Though one sees a variety of electrical machines in the
market, the basic fundamental principles of all these are the same. To
understand, design and use these machines the following laws must be
studied.
1. Electric circuit laws - Kirchoffs Laws
2. Magnetic circuit law - Amperes Law
3. Law of electromagnetic induction - Faradays Law
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Review on electric circuits &
Magnetic circuits
Kirchhoffs Current Law
at every instant of time the sum of the currents flowing into any node of a
circuit must equal the sum of the currents leaving the node,
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Example: Using Kirchhoffs Current Law. A node of a circuit is shown
with current direction arrows chosen arbitrarily.
Having picked those directions, i1 = 5 A, i2 = 3 A, and i3 = 1 A. Write an
expression for Kirchhoffs current law and solve for i4.
so that
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Kirchhoffs Voltage Law
the sum of the voltages around any loop of a circuit at any instant is zero.
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Power
Time rate of expending or absorbing energy
Energy
is the total amount of work done, energy is just the integral of power:
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Series connection
R1
R3
R2
Req
Req R1 R2 R3 RN
i
+
Voltage division:
+
v1
R1
R1
R1 R2
R2
v2 v
R1 R2
v1 v
v
R2
v2
-
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Parallel connection
R eq
R1R 2
R1 R 2
Current division:
i
+
i1
R1
i2
R2
R2
R1 R2
R1
i2 i
R1 R2
i1 i
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Three-Phase Circuit
Three sinusoidal voltages form a set of balanced voltages when they have the same
amplitudes and frequency.
These voltages are shifted in phase by 120o with each other
The standard practice is to name those phases by a, b and c and use phase a as
reference.
These voltages represent phase a voltage, phase b voltage and phase voltage.
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Three-Phase Circuit
Y-connected source
-connected source
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Three-Phase Circuit
a) a wye-connected load
b) a delta-connected load
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Three-Phase Circuit
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Phasor Representation of R,L and C Circuits
Resistance
Both the current and voltage vary sinusoidally, and are in
phase with each other.
The root-meansquare
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Phasor Representation of R,L and C Circuits
Inductive Reactance
Capacitive Reactance
Electric Power & Machines Dr. Ahmed El-Shenawy
Impedance: RLC Circuits
You might also like
- 1 s2.0 S0924013696027422 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0924013696027422 MainG00GLRNo ratings yet
- Vibration Measurement Techniques BasicsDocument11 pagesVibration Measurement Techniques BasicsAshokNo ratings yet
- 11 Chapter 1Document32 pages11 Chapter 1G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Logic Modelling, Simulation and Control: A Review: Rahul Malhotra, Narinder Singh, Yaduvir SinghDocument6 pagesFuzzy Logic Modelling, Simulation and Control: A Review: Rahul Malhotra, Narinder Singh, Yaduvir SinghG00GLRNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785317302365 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2214785317302365 MainG00GLRNo ratings yet
- MPU3343 SyllabusDocument4 pagesMPU3343 SyllabusG00GLR100% (1)
- Eme3056 Industrial Management: TRIMESTER#1 (2017-2018) Assignment#1Document8 pagesEme3056 Industrial Management: TRIMESTER#1 (2017-2018) Assignment#1G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Assignment1-Group Topics & Presentation ScheduleDocument1 pageAssignment1-Group Topics & Presentation ScheduleG00GLRNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation To Study The Effect of Solid Lubricants On Cutting Forces and Surface Quality in End MillingDocument10 pagesExperimental Investigation To Study The Effect of Solid Lubricants On Cutting Forces and Surface Quality in End MillingBro EdwinNo ratings yet
- Smith Chart From Black Magic DesignDocument1 pageSmith Chart From Black Magic DesignkgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- Full Assignment OSHDocument15 pagesFull Assignment OSHG00GLRNo ratings yet
- 3066 AssignDocument24 pages3066 AssignG00GLRNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3: EME2056 Theory of MachinesDocument7 pagesTutorial 3: EME2056 Theory of MachinesG00GLRNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785317302365 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2214785317302365 MainG00GLRNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ME26654Document1 pageTutorial ME26654G00GLRNo ratings yet
- N 9566Document1 pageN 9566G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Writing A Literature Review: G.Perkin@lboro - Ac.ukDocument15 pagesWriting A Literature Review: G.Perkin@lboro - Ac.ukG00GLRNo ratings yet
- T2 2016-17Document3 pagesT2 2016-17G00GLRNo ratings yet
- YbryrfdggDocument2 pagesYbryrfdggG00GLRNo ratings yet
- 342 11 July 25Document1 page342 11 July 25G00GLRNo ratings yet
- 6750 1Document2 pages6750 1G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ME279502Document1 pageTutorial ME279502G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Hifink Oias ''1Document1 pageHifink Oias ''1G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Beams For Bending: Concentrated Loads or Distributed LoadsDocument21 pagesAnalysis and Design of Beams For Bending: Concentrated Loads or Distributed LoadsG00GLRNo ratings yet
- EME21461Document3 pagesEME21461G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Flow Rate and Its Relation To Velocity 4Document9 pagesFlow Rate and Its Relation To Velocity 4G00GLRNo ratings yet
- Draw A Front, Top and Side Orthographic Views of Each of The Following Objects. UseDocument4 pagesDraw A Front, Top and Side Orthographic Views of Each of The Following Objects. UseG00GLRNo ratings yet
- PS1 Soln Summer2013Document6 pagesPS1 Soln Summer2013G00GLRNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
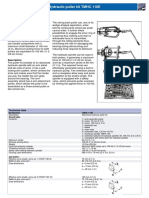
- Hydraulic Puller Kit TMHC 110E: ApplicationDocument2 pagesHydraulic Puller Kit TMHC 110E: Applicationsbosch54No ratings yet
- Desenllantadora Marca Coseng Modelo Cd540aDocument42 pagesDesenllantadora Marca Coseng Modelo Cd540ajhan123j100% (1)
- EC135 Classic B1 R06EN 02 - Lifting System.22911.2020 11 03.printableDocument72 pagesEC135 Classic B1 R06EN 02 - Lifting System.22911.2020 11 03.printableTitou GoltzNo ratings yet
- PSV PDFDocument3 pagesPSV PDFKasnowo DiponegoroNo ratings yet
- 37xr MetermanDocument2 pages37xr MetermanGatoBeckerNo ratings yet
- The Pipe Crawler: Eiki Martinson Mark Miller Sheraz WasiDocument39 pagesThe Pipe Crawler: Eiki Martinson Mark Miller Sheraz WasiMuhammed Abo-FandoodNo ratings yet
- Pz-7 КаталогDocument25 pagesPz-7 КаталогlionelNo ratings yet
- Manual SD100Document167 pagesManual SD100MiguelEnriqueCastillo91% (34)
- DIGITAL Countdown TimerDocument3 pagesDIGITAL Countdown TimerAmirul Shamir AmirShariffudinNo ratings yet
- Making Large Ups Systems More EfficientDocument21 pagesMaking Large Ups Systems More EfficientJohn CollinsNo ratings yet
- T/LL140 Series Fuel Level Sensor: Technical DataDocument1 pageT/LL140 Series Fuel Level Sensor: Technical Datacarlos andres mendezNo ratings yet
- Minisonic Assembly HeadDocument70 pagesMinisonic Assembly Headcesar cabezas rojasNo ratings yet
- A1 Template KensingtonDocument1 pageA1 Template KensingtonMuhammad TalhaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Management Procedure May 2013Document35 pagesElectrical Safety Management Procedure May 2013Roni Enjelani100% (2)
- Preventive Maintenance Checklist - KR150Document7 pagesPreventive Maintenance Checklist - KR150Juan c sanchezNo ratings yet
- Mobilisation Schedule - Periodic Maintenance of 110km Road in LufwnyamaDocument1 pageMobilisation Schedule - Periodic Maintenance of 110km Road in LufwnyamaWoodlock Limited67% (6)
- Certificate of Motor Solo RunDocument1 pageCertificate of Motor Solo RuntalhaNo ratings yet
- SIMATIC - Cabling TechnologyDocument24 pagesSIMATIC - Cabling TechnologyJorge_Andril_5370No ratings yet
- DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF 1.5kVA PURE SINEWAVE INVERTERDocument49 pagesDESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF 1.5kVA PURE SINEWAVE INVERTERemmanuel akojiNo ratings yet
- Konka KLC-2011US LCD TV Service ManualDocument9 pagesKonka KLC-2011US LCD TV Service ManualpasantitoNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Design of Auxiliary Systems and Selection of Equipments PDFDocument116 pages3.5 Design of Auxiliary Systems and Selection of Equipments PDFNARENDER KUMARNo ratings yet
- V0lvo &scaniaDocument41 pagesV0lvo &scaniairawan budi santosaNo ratings yet
- DGS-MN-001 - Rev-3 Insulation BoxesDocument2 pagesDGS-MN-001 - Rev-3 Insulation BoxesHabibur Rehman MNo ratings yet
- Wheel Bearing Notes-Mr. BootheDocument9 pagesWheel Bearing Notes-Mr. BootheJordon LewisNo ratings yet
- CAMA HILLROOM Service ManualDocument355 pagesCAMA HILLROOM Service ManualOrlando Contreras Muñoz100% (1)
- Am2020 FacpDocument268 pagesAm2020 Facpaubz20No ratings yet
- Task 53-10-00-252 16. Fuselage To Wing Attach Fitting Lugs Special Detailed InspectionDocument4 pagesTask 53-10-00-252 16. Fuselage To Wing Attach Fitting Lugs Special Detailed Inspectionworm_stellNo ratings yet
- DSK ELEV Installation ManualDocument64 pagesDSK ELEV Installation ManualAjay GrinduloNo ratings yet
- Travel Systems - 7Document59 pagesTravel Systems - 7اياد القباطيNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25 Equipment - FurnishingDocument63 pagesChapter 25 Equipment - FurnishingHartomo DK.No ratings yet