Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Virus Notes
Uploaded by
Tiffany Gallina100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views7 pagesOriginal Title
biology Virus Notes
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(3)100% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views7 pagesBiology Virus Notes
Uploaded by
Tiffany GallinaCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
VIRUSES
- Viruses are nonliving particles: They are not cells and
do not exhibit all the criteria for life.
- Very small: ½ to 1/100 the size of the smallest
bacterium can only been seen with an electron
microscope
- All viruses can do is replicate and they can’t do that
without the help of a host cell.
- Naming Viruses
o After the disease they cause (ex: Rabies virus)
o For the organ or tissue they infect
o Today, they are given a genus name enduing in the
word “virus” and a species name. Code numbers
are used to distinguish among similar viruses that
infect the same host.
- Viral Structure
o Inner core of nucleic acid (either DNA or RNA) and
an outer coat of protein called a capsid.
o Some viruses have an envelope surrounding their
capsid. They are composed of the same materials of
a cell’s plasma membrane.
o Four Different Viral Shapes:
Polyhedral Viruses (ex: Papilloma viruses that
causes worts)
Helical Shape (ex: Tobacco Mosaic Virus)
An envelope studded with projections (ex:
AIDS)
Bacteriophage- virus that infects a bacterium;
polyhedral-shaped head attached to a
cylindrical tail with leglike fibers (ex: T4 virus
that infects E. coli)
- Attachment- A virus attached to a host cell when one of
its proteins interlocks with a receptor site on the host
cell’s plasma membrane.
o Viruses are species specific and some are also cell-
type specific (ex: polio infects only human
intestinal and nerve cells)
o Significant for controlling the spread of viral
diseases
- Viral Replication Cycles
o Once a virus has attached to the host cell, it has 2
ways of getting in:
The virus can inject its nucleic acid into the
host cell like a syringe
Enveloped virus: The plasma membrane of the
host cell surrounds the virus and produces a
virus-filled vacuole inside the host cell’s
cytoplasm. The vacuole then burst and releases
its nucleic acid into the cell.
o Lytic Cycle: A virus uses the host cell’s energy and
raw materials to make new viruses.
Takes about 30 minutes and produces 200
new viruses
Host cell then bursts, killing it, and the new
viruses can then inject and kill other host cells
o Lysogenic Cycle: Virus’s nucleic acid is integrated
into the host cell’s chromosomes
Viral DNA that is integrated into the
chromosome is called a provirus.
• May not affect the functioning of its host
cell, but everytime the host cell
reproduces, the provirus is replicated
along with the host cell’s chromosome.
• At any time, the provirus can be activated
and enter a lytic cycle. Scientists do not
know what causes them to become
activate- could be physical or emotional
stress
- Retroviruses
o Viruses that contain RNA as their nucleic acid
o Once inside a host cell, the retrovirus makes DNA
from its RNA
o Use reverse transcriptase (enzyme) to do this-
located inside capsid
o The double-stranded DNA is then inserted into the
host cell’s chromosome and becomes a provirus
o Example: HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus)
Infects white blood cells, which are used in
fighting off infections and disease
AIDS patients usually die of infections that a
healthy person would normally resist
Transmitting in body fluids
- Some viruses can cause cancer
- Plant Viruses
o First plant virus to be identified was the tobacco
mosaic virus
o 400 viruses that infect plants, causing as many as
1000 diseases
o Can be beneficial- cause striking patterns of color
in the flowers of plants (tulips, gladioli, and
pansies)
- Prions: Particles composed of proteins and have no
nucleic acids (still infectious)
o Influence how proteins fold into their active shape
o Example: Mad cow disease (destroys brain)
- Viroid: single strand of RNA that has no capsid
o Infectious disease agents in plants (affects
cucumbers, potatoes, oranges)
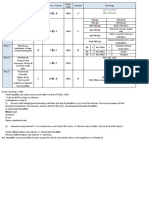
Important Viral Diseases
How the disease
Disease Symptoms
is transmitted
Blisters, rash, muscle soreness,
Chickenpox Inhalation
fever
Fever, chills, fatigue, sore throat,
Influenza Inhalation
muscle aches, weakness, headache
Rash, swollen glands, fever, fatal to
Rubella developing infant in pregnant Inhalation
woman
Mumps Painful swelling in salivary glands Inhalation
Blisters, lesions, fever, malaise,
Smallpox blindness, disfiguring scars; often Inhalation
fatal
Fever, chills, nausea, swollen liver,
Contaminated blood,
Hepatitis A and B yellow skin, painful joints, liver
food, or water
cancer
Fever, headache, stiff neck, Contaminated food
Polio
possible paralysis or water
Sexual contact,
contaminated blood,
AIDS Immune system failure; fatal
or contaminated
needles
Sinus congestion, muscle aches, Inhalation, direct
Cold
cough, fever contact
Mental depression, fever,
Bite of infected
Rabies restlessness, difficulty swallowing,
animal
paralysis, convulsions; fatal
You might also like
- APUSH AP US History Glossary - IDSDocument47 pagesAPUSH AP US History Glossary - IDSTiffany Gallina88% (8)
- APUSH Review ChartDocument22 pagesAPUSH Review ChartTiffany Gallina100% (1)
- VirologyDocument183 pagesVirologyVeronica KatigbakNo ratings yet
- Virus (Hiv)Document14 pagesVirus (Hiv)Thania WazintaNo ratings yet
- Disha Publication Chapter With Exercises BiologyDocument32 pagesDisha Publication Chapter With Exercises BiologyAnuj TripathiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ion Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesChemistry Ion Cheat SheetTiffany Gallina100% (4)
- Virus, Viroids and PrionsDocument29 pagesVirus, Viroids and PrionscatherinejoaquinNo ratings yet
- VirusesDocument40 pagesVirusesRimayaniNo ratings yet
- RhabdovirusDocument74 pagesRhabdovirustummalapalli venkateswara raoNo ratings yet
- AP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersDocument2 pagesAP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Anatomy The Brain - Coloring Worksheet - Visual MapDocument2 pagesAP Psych Anatomy The Brain - Coloring Worksheet - Visual MapTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project - Viral DiseasesDocument14 pagesBiology Investigatory Project - Viral DiseasesSamiha Antara81% (127)
- Viruses Viroids and Prions 18 2Document59 pagesViruses Viroids and Prions 18 2claudetteNo ratings yet
- Types of Diseases and Pathogens ExplainedDocument4 pagesTypes of Diseases and Pathogens ExplainedCarlos WebsterNo ratings yet
- Viruses and Other Acellular Microorganisms: DNA, RNA, PrionsDocument28 pagesViruses and Other Acellular Microorganisms: DNA, RNA, PrionscabralmdNo ratings yet
- Curs 9 - GripaDocument22 pagesCurs 9 - Gripajhonny12321No ratings yet
- Microbiology (Midterms)Document37 pagesMicrobiology (Midterms)Veloria AbegailNo ratings yet
- CNS Infectious Diseases: Meningitis, Encephalitis, Rabies, PolioDocument28 pagesCNS Infectious Diseases: Meningitis, Encephalitis, Rabies, PolioMoh A AlsalamNo ratings yet
- Diseases and VaccinesDocument22 pagesDiseases and VaccineslakshNo ratings yet
- Virus PowerpointDocument10 pagesVirus Powerpointchandrika kumariNo ratings yet
- (16b) Togaviridae, FlaviviridaeDocument44 pages(16b) Togaviridae, FlaviviridaeFarrah BenoitNo ratings yet
- Chapter-8 Human Health and DiseasesDocument10 pagesChapter-8 Human Health and DiseasesbpmbhamoraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Virus Morphology and InfectionDocument100 pagesLecture 6 Virus Morphology and InfectionArcee Feb Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Bio111 2017 Lec28 VirusesDocument12 pagesBio111 2017 Lec28 VirusesBoitumeloNo ratings yet
- Diseases and VaccinesDocument37 pagesDiseases and Vaccinesraghu ramNo ratings yet
- The infectious element that causes Mad Cow Disease is prionsDocument59 pagesThe infectious element that causes Mad Cow Disease is prionslearn bioNo ratings yet
- Viruses:: The Non-Living EntityDocument48 pagesViruses:: The Non-Living EntityhannNo ratings yet
- Kul VirusDocument48 pagesKul VirusMOCHILNo ratings yet
- Virology: Characteristics of Viruses Are Viruses Living or Non-Living?Document6 pagesVirology: Characteristics of Viruses Are Viruses Living or Non-Living?Castiel NguyenNo ratings yet
- What Are Viruses?Document5 pagesWhat Are Viruses?ZJC 2333No ratings yet
- Introduction To VirologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Virologyyezan27No ratings yet
- How Viruses Replicate Inside CellsDocument26 pagesHow Viruses Replicate Inside CellsCrystal Ann TadiamonNo ratings yet
- 2 10 VirusesDocument10 pages2 10 Virusesapi-212901753No ratings yet
- Bot 111 Module 1Document16 pagesBot 111 Module 1Jericho whiteNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Viruses Bacteria Protist FungiDocument52 pagesScience 7 Viruses Bacteria Protist FungiWelfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- West Nile FeverDocument24 pagesWest Nile Feveraliabh2006No ratings yet
- VirusDocument13 pagesVirusMaharani Putri ChaniaNo ratings yet
- Virus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCDocument33 pagesVirus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCAyu Roossea MustikaNo ratings yet
- Discoveries in BiologyDocument20 pagesDiscoveries in BiologyShifatNo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Infectious DiseaseDocument50 pagesModule 7 - Infectious Diseaseshwetlana rampureNo ratings yet
- PNVL Biological Science Lecture on VirusesDocument3 pagesPNVL Biological Science Lecture on VirusesJenny MendozaNo ratings yet
- Virus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCDocument33 pagesVirus Vs Cells Notes PPT IPCJulia NepoNo ratings yet
- DNA Viruses Causing Human DiseasesDocument43 pagesDNA Viruses Causing Human DiseasesMichelle RotairoNo ratings yet
- Virus IntroductionDocument22 pagesVirus Introductionliyana_amerNo ratings yet
- VirusDocument31 pagesVirusAmelia LimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids and Prions-2Document31 pagesChapter 13 Viruses, Viroids and Prions-2Hillani TadesseNo ratings yet
- Viruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi: Module Two: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue Level Paper OneDocument52 pagesViruses, Bacteria, Protists and Fungi: Module Two: Life at A Molecular, Cellular and Tissue Level Paper Oneapi-279296553No ratings yet
- Virusesmbft451 210328135532Document50 pagesVirusesmbft451 210328135532DELLA BLATAMANo ratings yet
- NCM 112-Mod5Document6 pagesNCM 112-Mod5Samantha BolanteNo ratings yet
- LBHS Yr 12 Biology Assessment Task The Search For Better Health by Tyrone WestwoodDocument7 pagesLBHS Yr 12 Biology Assessment Task The Search For Better Health by Tyrone WestwoodtyronewestwoodNo ratings yet
- Viruses - GoodDocument50 pagesViruses - GoodMohammed Faraaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- Lectures On VirusesDocument72 pagesLectures On Virusesvinay guptaNo ratings yet
- Bio and Images Phy Edcn Class XIIDocument35 pagesBio and Images Phy Edcn Class XIIoREpTiONNo ratings yet
- Blood InfectionsDocument3 pagesBlood InfectionsSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Hsslive XII Zoology CH 8 Human Health and Disease SlideDocument48 pagesHsslive XII Zoology CH 8 Human Health and Disease SlideAaron FelixNo ratings yet
- "Germ Theory" Pasteur Associates Rabies As A Viral InfectionDocument2 pages"Germ Theory" Pasteur Associates Rabies As A Viral InfectionpikachuNo ratings yet
- Chap4 UpdatedDocument35 pagesChap4 UpdatedROZZANE LOVELY RODNEY MoeNo ratings yet
- Viruses NotesDocument18 pagesViruses NotesAdam GlassnerNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Obligate Intracellular ParasitesDocument43 pagesViruses: Obligate Intracellular Parasitesراما عصفورNo ratings yet
- Microbiology in A Nutshell: Yes, You Will Need To Know ThisDocument19 pagesMicrobiology in A Nutshell: Yes, You Will Need To Know Thisdterrence9240100% (4)
- VirusesDocument13 pagesVirusesblakeNo ratings yet
- Pox VirusesDocument11 pagesPox VirusesSarah PavuNo ratings yet
- Rhabdoviruses by KennedyDocument36 pagesRhabdoviruses by KennedyIGA ABRAHAMNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document9 pagesPart 3api-235085390No ratings yet
- Eng - VirusesDocument27 pagesEng - VirusesMuhammad SidikNo ratings yet
- Biology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseFrom EverandBiology for Students: The Only Biology Study Guide You'll Ever Need to Ace Your CourseNo ratings yet
- Geometry ReviewDocument6 pagesGeometry ReviewTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Tiffs GA EOCT 9th Grade Lit CondensedDocument13 pagesTiffs GA EOCT 9th Grade Lit CondensedTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Fill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Document9 pagesFill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Tiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Fill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Document9 pagesFill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Tiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Tiffs GA EOCT American Lit CondensedDocument16 pagesTiffs GA EOCT American Lit CondensedTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Tiff's GA EOCT Condensed US HistoryDocument26 pagesTiff's GA EOCT Condensed US HistoryTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Chart To ID CompoundsDocument1 pageChemistry - Chart To ID CompoundsTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Naming Hydrocarbons NotesDocument1 pageChemistry - Naming Hydrocarbons NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeDocument2 pagesChemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Nuclear Chemistry NotesDocument4 pagesChemistry - Nuclear Chemistry NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Writing Ionic Formulas For CompoundsDocument5 pagesChemistry: Writing Ionic Formulas For CompoundsTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeDocument2 pagesChemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Single Replacement Reactions NotesDocument1 pageChemistry - Single Replacement Reactions NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Significant Number NotesDocument1 pageChemistry - Significant Number NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Half-Life NotesDocument1 pageChemistry - Half-Life NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Summary Unit Circle RatiosDocument1 pageTrigonometry Summary Unit Circle Ratiosteachopensource100% (2)
- Chemistry - Atomic Structure NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry - Atomic Structure NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Trig Properties of Sine and Cosine - Graphing NotesDocument2 pagesTrig Properties of Sine and Cosine - Graphing NotesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Chart of Freud's Stages Psychology MyersDocument1 pageAP Psych Chart of Freud's Stages Psychology MyersTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Myers AP Psych Important Psychologists CondensedDocument1 pageMyers AP Psych Important Psychologists CondensedTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- AP Psych Myers Chapter 7 Review Chart of DrugsDocument1 pageAP Psych Myers Chapter 7 Review Chart of DrugsTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Apush Supreme Court Cases / Decisions US HistoryDocument5 pagesApush Supreme Court Cases / Decisions US HistoryTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- APWH Gender Difference Chart by CultureDocument1 pageAPWH Gender Difference Chart by CultureTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Trig The Unit Circle in Radian and DegreesDocument1 pageTrig The Unit Circle in Radian and DegreesTiffany GallinaNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases: CowpoxDocument3 pagesInfectious Diseases: CowpoxMohammedNo ratings yet
- DNA/RNA Hepatitis Viruses Route, Acute, Chronic, Cancer, Vaccine, SerologyDocument1 pageDNA/RNA Hepatitis Viruses Route, Acute, Chronic, Cancer, Vaccine, SerologyMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Idexx Introduces CDV Quant RealpcrDocument2 pagesIdexx Introduces CDV Quant RealpcrPankaj BeniwalNo ratings yet
- DNA VIRUSES-handout PDFDocument11 pagesDNA VIRUSES-handout PDFROTHESSA MARY CARINGALNo ratings yet
- Virologi Bronkitis-BronkiolitisDocument28 pagesVirologi Bronkitis-BronkiolitisVia EkawatiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Biology Behind COVID19 VaccinesDocument6 pagesAn Introduction To The Biology Behind COVID19 VaccinesKhương KhoaNo ratings yet
- Sarjiyati, Mudji Rahardjo, Taufik Nur Pramudya Ananta, Susani TriwahyuningsihDocument5 pagesSarjiyati, Mudji Rahardjo, Taufik Nur Pramudya Ananta, Susani TriwahyuningsihLisa FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document42 pagesCovid 19ok100% (3)
- Almustaqbal University Collage Department Semester Exam./ 1 Attempt Sample: Subject: Human Biology Code: Max. Time: 2 H. Class: First DateDocument3 pagesAlmustaqbal University Collage Department Semester Exam./ 1 Attempt Sample: Subject: Human Biology Code: Max. Time: 2 H. Class: First DateZainab HasanNo ratings yet
- 2 VirologiDocument32 pages2 VirologiVanesa MuntuanNo ratings yet
- BIO 205 Chapter 8 PowerpointDocument16 pagesBIO 205 Chapter 8 PowerpointDrPearcyNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument8 pagesVirologyMello DiaxNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - VirusesDocument61 pagesModule 6 - VirusesReginaNo ratings yet
- Vaccines 11 00578 v2Document17 pagesVaccines 11 00578 v2Tari JogjaNo ratings yet
- ™ Novel Coronavirus (2019-Ncov) Detection Kit Diaplexq: Process Sample Collection Nucleic Acid Isolation Data AnalysisDocument2 pages™ Novel Coronavirus (2019-Ncov) Detection Kit Diaplexq: Process Sample Collection Nucleic Acid Isolation Data AnalysisJunior NurahmanNo ratings yet
- Monodnaviria: Virus ClassificationDocument7 pagesMonodnaviria: Virus ClassificationMiguel CarreraNo ratings yet
- ArbomapDocument1 pageArbomapNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- ViruzhinkiDocument20 pagesViruzhinkiЕгор ЧудовскийNo ratings yet
- Pox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationDocument5 pagesPox Viruses: Structure and ReplicationIDRAAK HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- Geentic Transformation in BacteriaDocument4 pagesGeentic Transformation in Bacteriahimanshi singhNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY PART 9 THE VIRUSES and PRIONSDocument13 pagesMICROBIOLOGY PART 9 THE VIRUSES and PRIONSPHAMAE JOY MEMBREVENo ratings yet
- Descriptive Text Tentang Virus CoronaDocument2 pagesDescriptive Text Tentang Virus CoronaDinda Fajhria UmmahNo ratings yet
- Nama: Khoirus Viestaria NIM: 135130101111035 Kelas: 2013/CDocument2 pagesNama: Khoirus Viestaria NIM: 135130101111035 Kelas: 2013/CDina SahmirandaNo ratings yet
- Spain Visa Application CenterDocument2 pagesSpain Visa Application CenterMansoor AliNo ratings yet
- Sasaran BIAN Ds. JuntiDocument45 pagesSasaran BIAN Ds. JuntifebriNo ratings yet
- Angine Difteria: Dr. Cristiana OpreaDocument39 pagesAngine Difteria: Dr. Cristiana OpreaAlexandra Andreea100% (1)
- Lista N de La EPADocument146 pagesLista N de La EPAPedro José Torres FernándezNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis Dan HPV (Human Papilloma Virus)Document15 pagesVirus Hepatitis Dan HPV (Human Papilloma Virus)TresaNo ratings yet