Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Casting Elwany Full
Uploaded by
Anonymous mKdAfWifCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Casting Elwany Full
Uploaded by
Anonymous mKdAfWifCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11
Metal-Casting Processes
3/20/2006
56:032 Design for Manufacturing
Manufacturing Processes Alternatives
Material Removal Processes
Forming Processes
Assembly
Similar to?
Examples?
And..
Casting Processes
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
Metal Casting Processes
The process involves:
Advantages of Metal Casting Processes:
Pour molten metal into a mold patterned after the part to be
manufactured
Allow it to solidify
Remove the part from the mold
Produce part in single step (near-net shape)
Produce large parts
Can produce a wide variety of shapes and sizes
Complex shapes are possible
Internal cavities are possible
Any Disadvantages?
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
Examples of Cast Products
Note how difficult it might get to produce these parts using
other manufacturing processes
Fig.
11.1
Fig.
Fig.11.1
11.1dbac
Fig.
11.1
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
Categories of Metal-Casting Processes
Expendable Molds:
Typically made out of sand, plaster, ceramics and similar
material
Such material are refractory i.e., capable of withstanding high
temperatures.
After casting the mold is broken up to remove the casting
Permanent Molds:
3/20/2006
Made of metals that maintain their strength at high
temperatures.
Are used repeatedly
Designed in such a way that the casting can be removed
easily
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
Categories of Metal-Casting Processes
Composite Molds:
3/20/2006
Made of two or more materials (sand, graphite, and metal) in
order to combine the advantages of each
Have both permanent and expendable portions
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
First: Expendable Mold Casting
Theres a variety of casting processes that use
expendable molds.
We will focus on discussing 2 of them in detail:
3/20/2006
Sand Casting
Investment Casting
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
Sand Casting
Process outline:
Place a pattern (having the shape of the desired casting) in
sand to make an imprint
Incorporate a gating system
Remove the pattern and filling the mold cavity with molten
metal
Allow the metal to cool until it solidifies
Break away the sand metal
Remove the casting
Example
Can we make hollow parts or parts with internal
cavities? How?
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
Sand Casting (contd.)
Sands
Silica sands (SiO2) is widely used as the mold material
High melting point
Factors affecting sand selection
3/20/2006
Fine round grains can be closely packed
Fine grained sand has lower permeability
Mold should have good collapsibility
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
Sand Mold Terminology
Figure 11.3 Schematic illustration of a sand mold, showing various features.
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
10
Finished Casting
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
11
Sand Mold Preparation
(a) Mechanical drawing of part
(b & c) Pattern Mounting
(d) Core Production
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
12
Sand Mold Preparation (Contd.)
(e) Cores are pasted
(f ) Assembly of the cope half of the mold
(g) The flask is rammed with sand
(h) The drag half is produced in a similar manner
(i) The pattern , flask, and bottom board are inverted; and
the pattern is withdrawn
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
13
Pattern Plate
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
14
Pattern Considerations/Allowances
Shrinkage Allowance (Why?)
Machining Allowance (?)
Draft Allowance (?)
Round corners (?)
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
15
Demonstration of the Draft Allowance
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
16
Sand Cores
Cores are used for internal cavities and passages
Removed from the finished part during shakeout
Must be strong, collapsible, permeable, heat resistant
Made in a similar manner to mold making
Figure 11.6 Examples of sand cores showing core prints and chaplets to support cores.
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
17
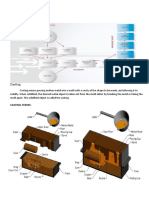
Investment Casting Process
Another common casting process with expendable
molds.
Also known as lost-wax process
Advantages
The mold material and labor is costly
Suitable for high-melting-point alloys
Good surface finish
Few or no finishing operations thus reducing cost
Typical parts
3/20/2006
Mechanical components such as gears, cams, valves.
Lately, titanium aircraft-engine
Parts up to 2500 lbs were successfully produced
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
18
Investment Casting Process (Contd)
Figure 11.13 Schematic illustration of investment casting (lost-wax) process. Castings
by this method can be made with very fine detail and from a variety of metals.
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
19
Disadvantages of Metal Casting
Depending on the casting process used, and specially
for expendable mold casting processes discussed in this
lecture:
Production rate can be slow
Finished Casting usually needs finishing operations
Casting Defects
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
20
Casting Defects and How to Avoid them
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
21
Next Time
Permanent Molds Casting Processes
Other Technicalities in various casting processes
3/20/2006
56:032 :Design for Manufacturing
22
You might also like
- FKM Lab - Metal Casting Process Lab ReportDocument20 pagesFKM Lab - Metal Casting Process Lab Reportzazaeureka0% (1)
- Non-Ferrous Metals Casting QuizDocument7 pagesNon-Ferrous Metals Casting Quizabhi100% (10)
- Summer Training Report CastingDocument29 pagesSummer Training Report CastingFaisal Bin Shabbir100% (1)
- Ch11metalcastingprocDocument74 pagesCh11metalcastingprocCharurat KongyangNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document77 pagesCH 11Davinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting ProcessesDocument98 pagesMetal Casting ProcessestmcoachingcentreNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting ProcessesDocument87 pagesMetal Casting ProcessesgggNo ratings yet
- ME364 Casting ProcessesDocument5 pagesME364 Casting Processesjegan_tamilNo ratings yet
- METAL CASTING GUIDEDocument18 pagesMETAL CASTING GUIDEvelavansuNo ratings yet
- 4 Various Types of Expendable Mold and Permanent Mold CastingDocument45 pages4 Various Types of Expendable Mold and Permanent Mold CastingLiaquat AliNo ratings yet
- MCW!!!Document9 pagesMCW!!!badshahsaadNo ratings yet
- MM Experiment ReportDocument10 pagesMM Experiment ReportAbdullah ArshadNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Advanced Workshop PracticeDocument28 pagesWeek 2 Advanced Workshop PracticeBasit AliNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Lecture 2 FinalDocument22 pagesModule 3 Lecture 2 Finaltejap314No ratings yet
- Metal Casting ProcessesDocument169 pagesMetal Casting ProcessesSajeed Shaik100% (1)
- Casting Process GuideDocument74 pagesCasting Process Guidevinu1977No ratings yet
- DFM ch-2Document114 pagesDFM ch-2Trâp A NâtïøñNo ratings yet
- Found AryDocument14 pagesFound Aryluv_leo007No ratings yet
- ME364 - Casting - Processes Nptel PDFDocument8 pagesME364 - Casting - Processes Nptel PDFvijaykumarNo ratings yet
- Sand CastingDocument5 pagesSand CastingEfy BellaNo ratings yet
- EIN 3390 Chap 12 Expendable-Mold Cast B Spring - 2012Document51 pagesEIN 3390 Chap 12 Expendable-Mold Cast B Spring - 2012Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting and Welding 15Me35ADocument29 pagesMetal Casting and Welding 15Me35A01061975No ratings yet
- Metal casting processes and design considerationsDocument78 pagesMetal casting processes and design considerationstvishal8No ratings yet
- Casting and Welding GuideDocument27 pagesCasting and Welding GuidePavaniNo ratings yet
- A402072949 - 17676 - 17 - 2018 - Casting 2Document39 pagesA402072949 - 17676 - 17 - 2018 - Casting 2KushNo ratings yet
- Ssignment Topic: Casting Process, Material & Technique Course Title: Moulding and Casting Course No. F-ART-S 3204Document16 pagesSsignment Topic: Casting Process, Material & Technique Course Title: Moulding and Casting Course No. F-ART-S 3204muntasir id1No ratings yet
- MT Merged PDFDocument273 pagesMT Merged PDFavcNo ratings yet
- Casting Process: Steps of Casting AreDocument10 pagesCasting Process: Steps of Casting AreReham Emad Ezzat MohamedNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ProcessesDocument134 pagesManufacturing ProcessesB J ISAC ABRAHAM PAULNo ratings yet
- 15ume302 - MT - I BankDocument17 pages15ume302 - MT - I BankKARTHICK MNo ratings yet
- NPTL CompressedDocument228 pagesNPTL CompressedAniketan kumar Singh - EC-32No ratings yet
- MME 512 Note 1Document36 pagesMME 512 Note 1faithNo ratings yet
- Casting ProcessesDocument20 pagesCasting ProcessesVv4HNo ratings yet
- Special CastingDocument24 pagesSpecial CastingManohara ErlaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Sand CastingDocument36 pagesUnit I Sand CastingSrinivas Gowda100% (1)
- Casting LabDocument11 pagesCasting Labfawad naeemNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - LECTURE3Document36 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - LECTURE3Sugumar MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- EAT227-Lecture 2.1 - Metal CastingDocument42 pagesEAT227-Lecture 2.1 - Metal CastingQim SvNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document42 pagesUnit 3Anup M UpadhyayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document43 pagesChapter 7Bairoju Shiva KumarNo ratings yet
- METAL CASTING PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONDocument10 pagesMETAL CASTING PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONcarrespmNo ratings yet
- Adama Science and Technology University: School of Mechanical, Chemical & Materials EngineeringDocument12 pagesAdama Science and Technology University: School of Mechanical, Chemical & Materials EngineeringAbel MeketaNo ratings yet
- Steps Involved in Sand Casting Process: BY Aravindkumar BDocument39 pagesSteps Involved in Sand Casting Process: BY Aravindkumar BanilNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Sand CastingDocument25 pagesRecent Advances in Sand Casting9591007896No ratings yet
- Basics of Metal Casting Methods and ProcessesDocument14 pagesBasics of Metal Casting Methods and ProcessesMathew Joel MathewNo ratings yet
- Mft-I Two & 13 Marks QuestionDocument16 pagesMft-I Two & 13 Marks QuestionrahulNo ratings yet
- Ch11 More Metal CastingDocument87 pagesCh11 More Metal CastingNaresh N BabuNo ratings yet
- UNit 3 Part A RevisedDocument76 pagesUNit 3 Part A Revisedraymon sharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Expendable and Permanent Moulding ProcessesDocument275 pages1 Expendable and Permanent Moulding Processesvasanthakumarsk17No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Metal Casting ProcessesDocument115 pagesUnit 1 Metal Casting ProcessesMadhav MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Foundry Asguest57564 Download: Share Add To Flagembed Views: 5846 Category: EducationDocument9 pagesFoundry Asguest57564 Download: Share Add To Flagembed Views: 5846 Category: EducationGurjinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Methods and ApplicationsDocument31 pagesMetal Casting Methods and ApplicationsKelvin KVNo ratings yet
- Casting ProcessDocument30 pagesCasting ProcessParas ThakurNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting Processes Lecture on Shell Molding, Vacuum Molding and Other Expendable Mold TechniquesDocument18 pagesMetal Casting Processes Lecture on Shell Molding, Vacuum Molding and Other Expendable Mold TechniquesSports GloballyNo ratings yet
- CastingDocument30 pagesCastingwatcharpNo ratings yet
- Learn Critical Aspects of Pattern and Mould Making in FoundryFrom EverandLearn Critical Aspects of Pattern and Mould Making in FoundryNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- Concrete-Block Manufacture - Processes and MachinesFrom EverandConcrete-Block Manufacture - Processes and MachinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Manufacturing Technology for Aerospace Structural MaterialsFrom EverandManufacturing Technology for Aerospace Structural MaterialsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Prison Camp LatheDocument6 pagesPrison Camp LatheChukwuRapNo ratings yet
- ZlatarstvoDocument1 pageZlatarstvokosinNo ratings yet
- DemoDocument4 pagesDemoAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- Prison Camp LatheDocument6 pagesPrison Camp LatheChukwuRapNo ratings yet
- Solidworks:: Lesson 1 - Basics and Modeling FundamentalsDocument48 pagesSolidworks:: Lesson 1 - Basics and Modeling FundamentalsmekoxxxNo ratings yet
- Primena 3D Stampe U ObrazovanjuDocument4 pagesPrimena 3D Stampe U ObrazovanjuAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- S.E Mechanical EngineeringDocument35 pagesS.E Mechanical EngineeringRahul KalathilNo ratings yet
- Taper Basics PDFDocument3 pagesTaper Basics PDFAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- Pear Orchard Engineers: Do Not Scale Drawing Part Used OnDocument4 pagesPear Orchard Engineers: Do Not Scale Drawing Part Used OnAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- Home Shop Machinist's Gears GuideDocument8 pagesHome Shop Machinist's Gears Guidegaragepunkfan100% (1)
- En Metalwork General Metal WorkDocument90 pagesEn Metalwork General Metal WorkAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- Owners Manual 4 The Human BodyDocument184 pagesOwners Manual 4 The Human BodyAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- Three Wire MethodDocument4 pagesThree Wire MethodmaivizhiNo ratings yet
- Machining Operations and Machine ToolsDocument18 pagesMachining Operations and Machine ToolsAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument4 pagesGearsR@XNo ratings yet
- Zadatak 1a Vitlo SkidDocument2,018 pagesZadatak 1a Vitlo SkidAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- 01 MaterialsDocument6 pages01 MaterialsAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- A Few Project Images: Tool Posts Lathe Cutting ToolsDocument4 pagesA Few Project Images: Tool Posts Lathe Cutting ToolsAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- Workshop Practice Series - BooksDocument8 pagesWorkshop Practice Series - Bookscatapix100% (5)
- 08 Milling Full SlidesDocument35 pages08 Milling Full SlidesAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- FertDocument7 pagesFertBibi NiniNo ratings yet
- Testing Lathe For AccuracyDocument4 pagesTesting Lathe For AccuracyArnieTNo ratings yet
- Machining Processes Used To Produce Round Shapes: Turning and Hole MakingDocument36 pagesMachining Processes Used To Produce Round Shapes: Turning and Hole MakingAnonymous mKdAfWif0% (1)
- Atlas Cut-Off Tools PDFDocument2 pagesAtlas Cut-Off Tools PDFhugo@wideas.comNo ratings yet
- 11-Turning Equations FullDocument21 pages11-Turning Equations FullmagzigioNo ratings yet
- Working Drawings-Full SlidesDocument14 pagesWorking Drawings-Full SlidesAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- Prison Camp LatheDocument6 pagesPrison Camp LatheChukwuRapNo ratings yet
- IC Learning Series 2012 - Metal Cutting Processes - TurningDocument15 pagesIC Learning Series 2012 - Metal Cutting Processes - TurningSorin FrentoniNo ratings yet
- Machining Operations and Machine ToolsDocument18 pagesMachining Operations and Machine ToolsAnonymous mKdAfWifNo ratings yet
- GATE MFG LatestDocument210 pagesGATE MFG LatestRanjan Kumar PathakNo ratings yet
- Casting NotesDocument32 pagesCasting NotesGanesh MandpeNo ratings yet
- Emm 315 Materials Forming Processes - CastingDocument40 pagesEmm 315 Materials Forming Processes - CastingNehemiah LemombianNo ratings yet
- Sand Casting and Other Casting ProcessesDocument74 pagesSand Casting and Other Casting ProcessesRashid KareemNo ratings yet
- Metal CastingDocument93 pagesMetal CastinghashimtkmceNo ratings yet
- Metal Casting TechniquesDocument81 pagesMetal Casting TechniquesAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Metal Casting 2018Document69 pagesFundamental of Metal Casting 2018Mohd MuhaiminNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Casting and Molding ProcessDocument18 pagesLec 1 - Casting and Molding ProcessEslam MansourNo ratings yet
- India Foundry Best Practice GuideDocument325 pagesIndia Foundry Best Practice GuideSiddharth Gupta100% (2)
- Carpentry Joints & Pattern MakingDocument2 pagesCarpentry Joints & Pattern MakingKunalNo ratings yet
- Expendable Mold CastingDocument18 pagesExpendable Mold CastingCheeragNo ratings yet
- Imp ExamDocument15 pagesImp ExamMalvin Roix OrenseNo ratings yet
- Slide Manufacturing Process Week 5 UTHMDocument37 pagesSlide Manufacturing Process Week 5 UTHMwhosamiruladliNo ratings yet
- Casting Process GuideDocument25 pagesCasting Process GuiderahulNo ratings yet
- Foundry Notes by ShiftyDocument22 pagesFoundry Notes by ShiftyRaiyan Shifty100% (1)
- CAD System in Pattern Production 2Document65 pagesCAD System in Pattern Production 2Lengamo L AppostilicNo ratings yet
- Sand CastingDocument81 pagesSand Castingkumarrohit91100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting Processes and Mold DesignDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Metal Casting Processes and Mold DesignVignesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Casting Technology'Document40 pagesCasting Technology'yakarim0% (1)
- 7 Nptel CastingDocument26 pages7 Nptel CastingmayilsvhecNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument38 pagesReportManojMeenaNo ratings yet
- Appendix I - Pattern Making ProceduresDocument6 pagesAppendix I - Pattern Making ProceduresRafiah N Kamal100% (2)
- Foundry LabDocument50 pagesFoundry Labanon-76437486% (21)
- FW Taylor - Bio Timeline - 010611Document3 pagesFW Taylor - Bio Timeline - 010611Jeffrey Endaya100% (1)
- Pattern CastingDocument17 pagesPattern CastingKishor kumar Bhatia100% (1)
- CastingDocument10 pagesCastingAkshay GargNo ratings yet
- Foundry Process:: Casting TermsDocument23 pagesFoundry Process:: Casting TermskalaivananmekNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual SM Ch11-20Document88 pagesSolutions Manual SM Ch11-20محمد فطري فيك نظام25% (4)