Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Material Characteristics
Uploaded by
Exsan OthmanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Material Characteristics
Uploaded by
Exsan OthmanCopyright:
Available Formats
MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS
CONTENT
STEELS
PLASTICS
STAINLESS STEELS
OTHER METALS AND GLASS
CERAMICS
- Tl : 33 (0)1 44 29 00 00 - Fax : 33 (0)1 46 22 26 10 - www.cimap.fr
MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS
STEELS
Materials
Chrome steel
AISI 52100
Symbolic
designation
Numeric
designation
100Cr6
1.3505
Chemical analysis %
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Hardness Density
Kg/dm3
0,95 0,15 0,25 0,030 0,025 1,35
60
max max
66 HRC
1,05 0,35 0,45
1,65
7,83
Through hardened
Carbon steel (with
chrome) C65Cr2
0,65 0,15 0,70 0,025 0,025 0,35
max max
60
0,70 0,35 0,80
0,45 66 HRC
7,85
Through hardened
Carbon steel
or AISI 1055
0,50
0,60
0,60
0,030 0,050
0,60 max 0,90
58
66 HRC
7,86
0,83 0,10 0,30 0,040 0,040
max max
0,88 0,30 0,70
60
66 HRC
7,85
Case hardened
Carbon steel
AISI 1010/1015
0,06 0,10
0,2 0,60
60
66 HRC*
7,86
Soft steel F
non hardened
XC 10 or CQ 15
0,17
max
Through hardened
Carbon steel C85
or AISI 1085
C55E (1)
1.1203 (1)
D85.2 (1)
1.0616 (1)
0,3 0,045 0,045
max max
0,9
0,045 0,045
max max
Properties
Bearing steel through hardened,
fine surface finish, high hardness
and load capacity
Through hardened, used in
applications in which case
hardened carbon steel
is not sufficient
Usable when through hardened steel
is not necessary
7,86
Can be machined and welded
* Surface hardness. (1) closest reference. 740 to 900 HV10 for diameters 12,7 according DIN 5401-1993.
PLASTICS
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
DIN
Units
PA
PA6.6
POM
PP
PUR
PTFE
Standard
PAI
PEEK
(Torlon )
Density
53479
Kg/dm3
1,14
1,15
1,41
0,91
1,23
2,20
1,40
1,32
Water absorption to 23C HR 50%
53495
3,00
2,5
0,22
0,33
0,50
Hardness
53505
Kj/m2
R 100
R 118
R 120
D 73
A 90
R 15
E 86
R 120
Resilience
53453
Kj/m2
>7,00
>5
SR 10
142
Elastic modulus in tension
53457
N/mm
2 800
3 300
2 900
1 300
700
4 900
3 600
-269/+260
+260
-50/+250
49
278
160
THERMICAL PROPERTIES
52 612
T for continuous uses
2
T when deformation on load 1.85 N/mm
C
C
-40/+90 -40/+120 -50/+90 -10/+100
75
104
110
65
PA :
polyamid, Nylon 6,6, Zytel, Ultramid
POM : polyoxymethylene, polyacetal, Hostaform,
Delrin, Ultraform
PAI :
Polyamid-imide, Torlon
PP :
PUR :
PTFE :
PEEK :
polypropylene, Hostalen, Moplen
polyurethane, Vulkollan
polytetrafluorethylene, Teflon
polyetherethercetone, Ketron
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS
Low density : from 0.92 to ~ 2
Good corrosion resistance
Noiseless use
Possible use as valves
Food contact possible for POM, PP, and PTFE.
APPLICATIONS :
Valves for food industry
Pumps
Hydraulic and electrical devices
Optical application
Filters
Medical and chemical devices
Linear motion
- Tl : 33 (0)1 44 29 00 00 - Fax : 33 (0)1 46 22 26 10 - www.cimap.fr
MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS
STAINLESS STEELS
Materials
Symbolic
designation
Numeric
designation
Stainless 13 %
AISI 420 C
or Z40C13
X39Cr13
X46Cr13
X45Cr13
1.4031
1.4034
1.3541
0,36 1
1 0,04 0,03 12,5
max max max max
0,50
14,5
52
58
HRC
Good balance between corrosion
7,68 resistance and hardness; through
hardened stainless steel
Stainless 13 %
SEW 400
X65Cr13
1.4037
0,58 1
1 0,04 0,015 12,5
max max max max
0,70
14,6
58
64 HRC
7,7
X105CrMo17
1.4125
Stainless 17 %
AISI 440 C
or
Z100CD17
Stainless 17 %
AISI 430
or Z8C17
X6Cr17
Si
Chemical analysis %
Mn P
S
Cr Ni
0,40
58
64
1,2
0,80
HRC
18
1.4016
16
0,08 1
1 0,04 0,03
max max max max max 18
X14CrMoS17
1.4104
Stainless 18/10
AISI 304
or Z7CN 18-09
X5CrNi18-10
1.4301
17
8
0,07 1
2 0,045 0,03
max max max max max 19,5 10,5
X2CrNi18-09
1.4306
18
0,03 1
2 0,045 0,03
max max max max max 20
Stainless 18/12/3
AISI 316
X5CrNiMo17
or Z6CND 17-12
12.02
1.4401
16,5 10
0,07 1
2 0,045 0,03
max max max max max 18,5 13
1.4404
16,5 10
0,03 1
2 0,045 0,03
max max max max max 18,5 13
10
N:
0,11
max
Characteristics
close to
AISI 440C
Afford the advantage of maximum
7,75 hardness combined with corrosion
resisting properties. First choice
steel for stainless steel bearings
Intermediate stainless
steel quality between
420 and 304
380 HV*
7,68
Additional sulfur makes
this stainless steel
more machinable
135
7,93
0,20
0,60
Properties
7,68
135
0,10
0,15 15,5
1 1,50 0,04
0,17 max max max 0,35 17,5
Stainless 18/12/3
AISI 316L
X2CrNiMo17
or Z2CND 17-12
12.02
Hardness Density
Kg/dm3
0,95 1
1 0,04 0,03 16
max max max max
Stainless 17 %
AISI 430 F
or Z10CF17
Stainless 18/10
AISI 304L
Z2CN 18-10
Mo Other
2 N:
0,11 380 HV*
2,5 max
7,93
2 N:
0,11
2,5 max
7,98
135
2 N:
0,11 380 HV*
2,5 max
7,97
Austenitic stainless
steel; very good
corrosion and
chemical resistance
Better corrosion
resistance than above
stainless due to
molybdenum
* Indicative values
OTHER METALS AND GLASS
Material
Tungsten carbide
Glass
Titanium
Brass
Bronze
Hastelloy C
Chemical
composition
Hardness
Kg/dm3
Density
94 % Wc + 6 % Co
1550 HV
14,90
70 80 % SiO2
45 HRC
2,5
Properties
Extremely hard and abrasion resistant
Good corrosion resistance used in valves, but also in special
bearings
Pure titanium
130 - 180 HB
4,5
Good corrosion resistance, bio-compatible, low density
63 % Cu
180 - 200 HB
8,4
Good electrical conductivity
68.5 % 71,5 % Cu
200 - 220 HB
8,5
Good electrical conductivity
Ni 57 % Mo 17 % Cr 16 %
80-220 HB
8,94
Very good corrosion and high temperature resistant
- Tl : 33 (0)1 44 29 00 00 - Fax : 33 (0)1 46 22 26 10 - www.cimap.fr
MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS
CERAMICS
CHARACTERISTICS
Crystalline structure.........................................
Chemical formula.............................................
Purity ........................................................... %
Density................................................. Kg/dm3
Hardness .................................................... HV
Compression strength............................... MPa
Elastic strength ......................................... MPa
Flexural strength ...................................... MPa
Rsilience KIC.................................... MPa.m1/2
Elasticity ................................................... GPa
Thermal expansion coef. .................... 10-6. K-1
Thermal conductivity........................... W/mK
Thermal capacity ................................... J/kgK
Usable maximum temprature.................... C
Acid resistance ................................................
Base resistance .................................................
Sapphire
Ruby
Alumina
Silicon
Nitride
HP
Zirconia
Y-TZP
Tungsten Stainless Chrome
Carbide
Steel
Steel
100 Cr6
*
*
*
mono
Poly
Poly
Poly
Poly
99 %
AI2O3
Si3N4
ZrO2
Wc (6T10)
AI2O3
99,80
90
90 95
Wc94+Co6
99,99 % 1 % Cr2O3
3,99
3,90
3,10 3,20
6,00
15
2 300
1 650
1 600
1 100 1 500
1 550
~ 4 000
2 100
2 400
3 000
5 300
280
400
390
470
1 000
700 1 100
1 900
1
4
6
10
430
380
320
200
610
5,30
4,50
5,50
3,20
10
5,50
36
29
40
2
80
755
900
750
500
201
1 800 2 000
1 500 1 800 1 200 1 500
1 000
very good
very good
very good
good
limited
good
good
good
good
limited
Poly
Poly
8
7,85
500 800
762 865
2 240
500 1 500
30-80
200
205
10 12
300 600
450
limited
non resistant
limited
non resistant
* For comparison.
APPLICATIONS
- High precision and high speed bearings.
- Hip joints.
- Valves.
- Measuring devices.
- Reference balls for 3D measuring machines.
- Ball gauges and triggers for 3D measuring machines and balls
for gauges and triggers.
07/02
ADVANTAGES
- High hardness (>1 300 Vickers).
- Low density (3 6 kg/dm3).
- Wear resistance due to low friction coefficient.
- High elasticity module (200 400 GPa).
- Chemical and thermal resistance. Electrical insulation
- High mechanical resistance (bending resistance :
400 to 1 000 MPa, up to approx. 1 000 C).
- Low porosity (<0,5 %), very high quality surface polish.
- Machining and polishing precision e.g : for a 14 mm Al2 O3
ball, variation on diameter is less than 0,1 m and surface
roughness (Ra) is less than 0,005 m.
- Tl : 33 (0)1 44 29 00 00 - Fax : 33 (0)1 46 22 26 10 - www.cimap.fr
You might also like
- A-Health Advance - Application Form With InstructionsDocument14 pagesA-Health Advance - Application Form With InstructionsExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- TUBE INSPECTION SOLUTIONS: SELECTION GUIDEDocument28 pagesTUBE INSPECTION SOLUTIONS: SELECTION GUIDEAkhileshNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS Employee Medical Top-Up PlanDocument2 pagesPETRONAS Employee Medical Top-Up PlanExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- April 2015. Any New Application Form Must Reach Us Before The Stipulated DateDocument1 pageApril 2015. Any New Application Form Must Reach Us Before The Stipulated DateExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Farris Valve ManualDocument11 pagesFarris Valve ManualsumsolcaggNo ratings yet
- Engineering Your Future PDFDocument605 pagesEngineering Your Future PDFExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- RFET Technique Detects Local and Gradual DefectsDocument4 pagesRFET Technique Detects Local and Gradual DefectsExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- SSI Guideline V3 PDFDocument34 pagesSSI Guideline V3 PDFSyed Mohd FirdausNo ratings yet
- Farris Series 2600Document96 pagesFarris Series 2600johngoff100% (1)
- Astm C 692 PDFDocument7 pagesAstm C 692 PDFExsan Othman100% (1)
- Senarai Nama Arkitek BerdaftarDocument150 pagesSenarai Nama Arkitek BerdaftarCgu Bola Tampar83% (6)
- P91 T91 Engl PDFDocument3 pagesP91 T91 Engl PDFparmodrtkNo ratings yet
- Astm C 871Document5 pagesAstm C 871Exsan Othman100% (2)
- Asmt C 795Document4 pagesAsmt C 795Exsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- MetrodeHandbook - ZavarivanjeDocument416 pagesMetrodeHandbook - ZavarivanjetonicmiraNo ratings yet
- EPA RMP OSHA PSM State Law SummaryDocument1 pageEPA RMP OSHA PSM State Law SummaryExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
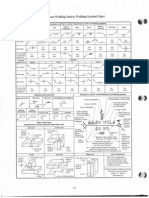
- AWS Weld Symbol ChartDocument1 pageAWS Weld Symbol ChartExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- AWS Specifications For Filler MaterialDocument9 pagesAWS Specifications For Filler MaterialExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Calculation Minimum Required Thickness For Straight Pipe 8inch Leak May10Document6 pagesCalculation Minimum Required Thickness For Straight Pipe 8inch Leak May10Exsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Calculation Minimum Required Thickness For Bending Pipe r2Document11 pagesCalculation Minimum Required Thickness For Bending Pipe r2Exsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Piping CalDocument13 pagesPiping CalglazetmNo ratings yet
- Pipeline DataDocument4 pagesPipeline DataExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- MaterialsDocument181 pagesMaterialsExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Design SpreadsheetDocument1 pageMechanical Design SpreadsheetHoney TiwariNo ratings yet
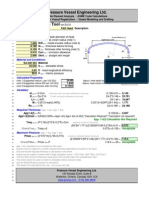
- Hemispherical Head Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDDocument1 pageHemispherical Head Design Tool: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDExsan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Design Tool AnalysisDocument2 pagesNozzle Design Tool AnalysisArt G. EnziNo ratings yet
- 300 - F&D Head Design Tool Ver E4.01Document1 page300 - F&D Head Design Tool Ver E4.01Honey TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- List of Timoshenko BooksDocument6 pagesList of Timoshenko BooksUdhamNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Polietileno Chemium Hdpe 2285 (7000f)Document1 pageFicha Tecnica Polietileno Chemium Hdpe 2285 (7000f)Carlos SiuNo ratings yet
- Using CES EduPack For Tackling Problems Beyond The TextbookDocument27 pagesUsing CES EduPack For Tackling Problems Beyond The TextbookLula LeleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electron Microscopy and MicroanalysisDocument56 pagesIntroduction To Electron Microscopy and MicroanalysisPerlita2013100% (1)
- Worksheet-22 Reflection & Refraction of LightDocument2 pagesWorksheet-22 Reflection & Refraction of Lightanjalitashu01No ratings yet
- SA LAB - Singly Reinforced BeamDocument8 pagesSA LAB - Singly Reinforced BeamAjayNo ratings yet
- CE6402-Strength of MaterialssDocument23 pagesCE6402-Strength of MaterialssSedhu CivilNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument37 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsmanoNo ratings yet
- BS 970 SteelsDocument8 pagesBS 970 SteelsTamal Guha100% (2)
- Government Polytechnic Ambad: (Electric Power Transmission)Document21 pagesGovernment Polytechnic Ambad: (Electric Power Transmission)Sachin PatharkarNo ratings yet
- Macro-Microporous Carbon With A Three-Dimensional Channel From Waste Sun Flower Seed ShellDocument9 pagesMacro-Microporous Carbon With A Three-Dimensional Channel From Waste Sun Flower Seed ShellMuhamad SuharNo ratings yet
- Erickson Josephson J Project ProposalDocument4 pagesErickson Josephson J Project ProposalAdam Graham EricksonNo ratings yet
- Stress and StrainDocument56 pagesStress and StrainAl Faisal SiregarNo ratings yet
- 2020-Machinability of Inconel 718 A Critical Review On The Impact of Cutting TemperaturesDocument40 pages2020-Machinability of Inconel 718 A Critical Review On The Impact of Cutting TemperaturesVikash SrivastvaNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Mos CapacitorDocument33 pagesThe Ideal Mos Capacitortennisbat91No ratings yet
- Risk Analysis of Mercury-Contaminated Aluminum Heat ExchangersDocument16 pagesRisk Analysis of Mercury-Contaminated Aluminum Heat Exchangersmostafa_1000No ratings yet
- 11ADocument2 pages11ALorenzo Daniel Antonio67% (3)
- Cyprus National Annex en 1993-1-1Document11 pagesCyprus National Annex en 1993-1-1ruovNo ratings yet
- Connections in Precast Concrete Structures - Effects of Restrained Creep and ShrinkageDocument20 pagesConnections in Precast Concrete Structures - Effects of Restrained Creep and Shrinkageunix0123No ratings yet
- CE 21 CorrectionDocument4 pagesCE 21 CorrectionGintokiNo ratings yet
- Flexitallic CGI Torque Chart Spiral Wound GasketsDocument1 pageFlexitallic CGI Torque Chart Spiral Wound GasketstinzarmoeNo ratings yet
- Titanium Ti-6Al-4V Alloy DataDocument2 pagesTitanium Ti-6Al-4V Alloy DataAdriano100% (1)
- BS ABUTMENT DESIGNDocument17 pagesBS ABUTMENT DESIGNEng Venance Masanja100% (1)
- PT Slab DesignDocument18 pagesPT Slab DesignwelwelNo ratings yet
- Structural AnalysisDocument35 pagesStructural AnalysisNagaraj RamachandrappaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Materials For Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), MoldedDocument3 pagesOverview of Materials For Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), MoldedarmandoNo ratings yet
- Modeling Cracked Section Properties For Shear Wall and Slab - ETABS - CSIDocument3 pagesModeling Cracked Section Properties For Shear Wall and Slab - ETABS - CSItrungceNo ratings yet
- Tempered Martensite: H. K. D. H. BhadeshiaDocument20 pagesTempered Martensite: H. K. D. H. BhadeshiaBahaa Eldin Sayed BahaaNo ratings yet
- DLP Electric ChargeDocument13 pagesDLP Electric Chargeapi-668571149No ratings yet