Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module Questions
Uploaded by
zulkarnainCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module Questions
Uploaded by
zulkarnainCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
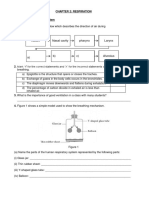
1.
Diagram below shows a cross section of the spinal cord. Name the parts of the
spinal cord labelled as P, Q, R and S.
2.
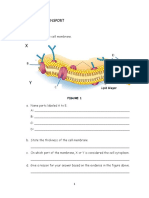
Diagram below shows two types of neurones.
(a) Identify P and Q.
P :____________________________ Q :___________________________
(b) Label P with the following terms :
Receptor cell
cell body
axon
(c) Label Q with the following terms :
Dendrite
synaptic terminals
myelin sheath
(d) Show the direction of flow of an impulse in P and Q during the transmission of an
impulse from a receptor.
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
3.
Diagram below shows a synapse.
(a)
(i)
What is the role of mitochondria in a synapse?
____________________________________________________
(ii)
State two neurodegenerative diseases that are associated with
the decrease in secretion of neurotransmitters.
____________________________________________________
(b)
Describe the transmission of information across a synapse.
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
4.
Match the following hormones to their functions.
Hormone
Antidiuretic
hormone (ADH)
Insulin
Androgens
Function
Stimulate development of male secondary sexual
characteristics and spermatogenesis.
Stimulates development of the uterine lining and
formation of the placenta.
Decreases blood glucose levels and promotes
conversion of glucose to glycogen.
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
Prolactin
Growth hormone
Progesterone
Stimulates water reabsorption by kidneys.
Stimulates milk production and secretion from
mammary glands.
Stimulates growth, protein synthesis and fat
metabolism.
5.
Diagram above shows the position of the major endocrine organs in the human
body. Label the main glands of the endocrine system.
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
Islet cells in
pancreas stimulated
to secrete insulin
Blood glucose
rises
Normal blood
glucose level
Normal blood
glucose level
Blood glucose
drops
Islet cells in
pancreas stimulated
to secrete glucagon
6. The schematic diagram above shows the regulation of blood glucose level.
Choose the correct answers for the empty boxes labelled as A, B, C, D and E.
Insulin also stimulates the conversion of glucose to glycogen in liver and muscle cells,
for storage.
Glucagon stimulates the liver to break down glycogen to glucose.
Glucagon also promotes lipid breakdown, which releases fatty acids that can be
metabolized for energy.
The adipose cells use the breakdown of glucose to form fats.
Insulin stimulates the uptake of glucose by liver, muscle and adipose cells, for
respiration.
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
7.
Diagram above shows a part of nephron. Name the processes that occur in
parts P, Q and R
P :________________________________________
Q :________________________________________
R :________________________________________
8.
The diagram below shows the structure of a synapse.
(a)
Name the parts labelled P-U.
P : ____________________________________
Q : ____________________________________
R : ____________________________________
S : ____________________________________
T : ____________________________________
U : ____________________________________
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
(b) Name the chemical substances found in Q
__________________________________________________________________
(c) State the importance of organelle R existing in large number in structure P.
__________________________________________________________________
(d) Describe briefly how a nerve impulse crosses a synaptic cleft.
__________________________________________________________________
(e) Explain why a nerve impulse is transmitted in only one direction from one
neurone to the next neurone.
__________________________________________________________________
9.
Diagram below shows the position of some endocrine glands in a human body.
(a)
Name the endocrine glands labelled L, M, N and O.
L : _______________________________________
M : _______________________________________
N : _______________________________________
O : _______________________________________
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
(b)
Name an endocrine gland in the human male that controls his sexual
characteristics.
__________________________________________________________________
(c) (i) Name the main gland in the body that controls the activities of many other
endocrine glands.
__________________________________________________________
(ii) Name a hormone that is produced by the main gland that controls the secretion
of gland M.
__________________________________________________________
(d) (i) Name a hormone that is secreted by gland M.
__________________________________________________________
(ii) State two functions of hormone in (d)(i).
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
(e) Explain what would happen if a diet for a young child is deficient in iodine.
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
10.
Diagram below shows the structure of a kidney nephron.
(a)
Formation of urine involves three main processes. Name these processes.
(i) ___________________________________________
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
(ii) ___________________________________________
(iii) ___________________________________________
(b)
(i)
Name the process that occurs between the glomerulus and the Bowmans
capsule.
__________________________________________________________
(ii)
Describe briefly how process in (b)(i) occurs.
__________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________
(c) (i)
Name two blood components found in the glomerulus but not in the
filtrate.
__________________________________________________________
(ii)
Suggest a reason for the component difference in (c) (i).
__________________________________________________________
(d)
Why is there a difference in the chemical composition of the filtrate in the
Bowmans capsule and the filtrate in the loop of Henle? Explain your answer.
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
(e)
Name the organ in the human body where urea is produced.
__________________________________________________________________
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
ESSAY QUESTIONS
1.
Diagram 1(a) shows a reflex arc and Diagram 1(b) shows the regulation of glucose
in the blood. Both figures illustrate coordination systems in the human body.
Diagram 1(a)
Diagram 1(b)
(i)
Describe the reflex action in Diagram 1(a)
(ii)
Compare the coordination system shown in Diagram1(a) and 1(b).
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
10
2. Diagram 2 shows a ball and socket joint with tissues P, Q , R and S which are
responsible for locomotion in a human.
DIAGRAM 12
S
Diagram 2
Based on Diagram 2 discuss how the structure and organization of P,Q,R and
S produced movement at the joints.
3.
A doctor is going to do a test to examine a patients nervous system.
CHAPTER 11: COORDINATION AND
RESPONSE
11
Diagram 3
Based on Diagram 3, describe the pathway transmission of nerve impulses to
show whether the patients nervous system is normal or not.
4. Diagram 4 shows the organs and glands involved in regulating the human
temperature.
Diagram 4
A student skates on an ice skating.
Based on Diagram 4, explain how regulation of the students body temperature
occurs.
You might also like
- Biology Workbook Mid & Final TermDocument81 pagesBiology Workbook Mid & Final TermSayma AkterNo ratings yet
- UJIAN SELARAS MAC TINGKATAN 3 2018 BAHAGIAN 2Document23 pagesUJIAN SELARAS MAC TINGKATAN 3 2018 BAHAGIAN 2hazyengNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExerciseDocument8 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Textbook ExerciseLeena HingNo ratings yet
- S8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestDocument2 pagesS8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestWilliam Anthony50% (8)
- S8 - End of Unit 1 TestDocument2 pagesS8 - End of Unit 1 Testchicken.nougat123No ratings yet
- Science f3 UB1Document7 pagesScience f3 UB1LEENA HingNo ratings yet
- Science Form3 Chap 1Document7 pagesScience Form3 Chap 1wansuu100% (1)
- SR 1 Ch3 Movement Across Membrane - WatermarkDocument25 pagesSR 1 Ch3 Movement Across Membrane - WatermarkBryan LeeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Cross SectionDocument5 pagesRespiratory System Cross SectionHU LEE LEE MoeNo ratings yet
- Apakah Hidoasaf Tankasa FizeDocument6 pagesApakah Hidoasaf Tankasa FizeMining DarshanNo ratings yet
- Kertas 2 Pep. Set 2 SPM 2016 - SoalanDocument16 pagesKertas 2 Pep. Set 2 SPM 2016 - SoalanAzrel YusoffNo ratings yet
- Human Respiratory System ExplainedDocument8 pagesHuman Respiratory System ExplainednoorNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: QuestionsDocument18 pagesRespiratory: QuestionskonstanpatNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 QuestionsDocument54 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Respiration & Gas Exchange Theory QPDocument44 pagesRespiration & Gas Exchange Theory QPVivehaNo ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit One Cells TutorialDocument10 pagesCape Biology Unit One Cells Tutorialakeisha kingNo ratings yet
- Exercises On Cell and TissuesDocument14 pagesExercises On Cell and TissueskamilNo ratings yet
- B Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesB Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- .Archivetempt1 MOLECULES OF LIFE - Q Modul II (1-7)Document7 pages.Archivetempt1 MOLECULES OF LIFE - Q Modul II (1-7)Fatin HananiNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Biology Questions ExplainedDocument9 pagesMultiple-Choice Biology Questions ExplainedAaron LiuNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - QuestionsDocument37 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Soalan Biologi Kertas 2 Tingkatan 4Document14 pagesSoalan Biologi Kertas 2 Tingkatan 4azszah100% (17)
- TOPIC 3 - Cell TransportDocument7 pagesTOPIC 3 - Cell TransportSiti Nurqistina Balqis Syahrul EffendyNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Multiple Choice and Structured QuestionsDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis Multiple Choice and Structured QuestionsLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- ATP A Level: NameDocument38 pagesATP A Level: Namedfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION - classwork on anaerobic and aerobic (2)Document2 pagesRESPIRATION - classwork on anaerobic and aerobic (2)Mariah CampbellNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Form 1 - Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeDocument2 pagesTopical Test Form 1 - Chapter 2 Cell As The Basic Unit of LifeMei Yun LiewNo ratings yet
- Pat (Modul) F4 K2Document16 pagesPat (Modul) F4 K2NOOR HAFEZAH BT MOHD MOKHTIAR MoeNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Assessment BookletDocument36 pagesTopic 1 Assessment BookletLinNo ratings yet
- Pt3 Science Seminar ModuleDocument28 pagesPt3 Science Seminar ModuleSuntharan Muniandy100% (5)
- Chapter 7 Gaseous Exchange and Its ControlDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Gaseous Exchange and Its ControlLisa AllisyaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term f4 2008-Paper 2Document7 pagesMid Term f4 2008-Paper 2hamzah79No ratings yet
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- Test 1 SC F3Document9 pagesTest 1 SC F3tengkusuhaidaNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System ChapterDocument2 pagesHuman Digestive System ChapterNirmala RasamuthuNo ratings yet
- A Level Homework 4Document6 pagesA Level Homework 4szyzypNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Molecules of LifeDocument17 pagesTopic 1 - Molecules of LifeSyakirah MunirNo ratings yet
- STPM BIOLOGY Lower Six FinalDocument6 pagesSTPM BIOLOGY Lower Six FinalVentus TanNo ratings yet
- MGS M07 2011 Na CHT A 02Document4 pagesMGS M07 2011 Na CHT A 02rofi modiNo ratings yet
- KBU Biology Exam Questions on Molecules and TransportDocument16 pagesKBU Biology Exam Questions on Molecules and Transportsamantha_ong_22No ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Carbohydrates EQDocument24 pages3.1.2 Carbohydrates EQteeb1826No ratings yet
- Mammalian Physiology: T.A. Blakelock High SchoolDocument25 pagesMammalian Physiology: T.A. Blakelock High SchoolAbhishek SainiNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane of Host CellDocument8 pagesCell Membrane of Host CellAshique FarhadNo ratings yet
- SMJK Pei Yuan Kampar Monthly Test March 2011 Science Form 4 1 HourDocument10 pagesSMJK Pei Yuan Kampar Monthly Test March 2011 Science Form 4 1 HourAlan WongNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical RX WSHDocument1 pageTypes of Chemical RX WSHLeonardo SierraNo ratings yet
- Junior Lyceum annual biology exam questionsDocument4 pagesJunior Lyceum annual biology exam questionsPui Pui LamNo ratings yet
- NewDocument1 1Document18 pagesNewDocument1 1Paweł KorczakNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions ExplainedDocument7 pagesCell Structure and Functions ExplainedNuraina NabihahNo ratings yet
- Biology Form IV Exam Guide and QuestionsDocument11 pagesBiology Form IV Exam Guide and Questionsmark smithNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sainsf1Document13 pagesSoalan Sainsf1Husna IzaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Bio AnnualDocument25 pagesClass 7 Bio Annualdebarati.cambridgeNo ratings yet
- WaterDocument16 pagesWaterdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Ireland - GoodDocument25 pagesExam Questions Ireland - GoodMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- PAT Bio f4 P2 2015Document14 pagesPAT Bio f4 P2 2015unieezzNo ratings yet
- Mon Omers and Polymers a LevelDocument57 pagesMon Omers and Polymers a Leveldfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering Challenges: A Chemical Engineering InsightFrom EverandBiomedical Engineering Challenges: A Chemical Engineering InsightNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Pillared Metal-Organic Frameworks: Properties and ApplicationsFrom EverandPillared Metal-Organic Frameworks: Properties and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsFrom EverandPhysical Chemistry of Polyelectrolyte SolutionsMitsuru NagasawaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of SPM Bio Qs 2016Document3 pagesAnalysis of SPM Bio Qs 2016zulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Rumus BiologiDocument1 pageRumus Biologizulkarnain100% (3)
- Seminar Bio P2 SMART 2018Document179 pagesSeminar Bio P2 SMART 2018zulkarnain100% (1)
- Paper 1, SPMRSM 2016Document48 pagesPaper 1, SPMRSM 2016zulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Paper 3, SPMRSM 2016Document14 pagesPaper 3, SPMRSM 2016zulkarnainNo ratings yet
- XAPlus 2016 MiauDocument24 pagesXAPlus 2016 Miauzulkarnain100% (1)
- XAPlus 2016 Answer MiauDocument24 pagesXAPlus 2016 Answer MiauzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Paper 2, SPMRSM 2016Document32 pagesPaper 2, SPMRSM 2016zulkarnain100% (1)
- 4.4 LipidsDocument10 pages4.4 Lipidszulkarnain100% (1)
- 5.1 MitosisDocument18 pages5.1 MitosiszulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 SoalanDocument22 pagesTrial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k2 SoalanzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- 4.5 EnzymesDocument21 pages4.5 Enzymeszulkarnain100% (1)
- 4.3 - ProteinsDocument13 pages4.3 - ProteinszulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k3 SoalanDocument11 pagesTrial Kedah Biologi SPM 2015 k3 SoalanYk TayNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Types of NutritionDocument15 pages6.1 Types of Nutritionzulkarnain0% (1)
- 4.2 CarbohydratesDocument6 pages4.2 CarbohydrateszulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Biologi Ting 4 ModulDocument20 pagesBiologi Ting 4 ModulNoine AiniNo ratings yet
- VariationDocument21 pagesVariationzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Trial SPM 2015 Biology Paper 1 Answer Scheme NO Answer NO AnswerDocument1 pageTrial SPM 2015 Biology Paper 1 Answer Scheme NO Answer NO AnswerzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- 4551-Skema BIO Trial SPM 2015Document22 pages4551-Skema BIO Trial SPM 2015zulkarnain100% (1)
- Module QuestionDocument19 pagesModule Questionzulkarnain100% (1)
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul5Document17 pages07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul5jyen92No ratings yet
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul4Document15 pages07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul4Komalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionDocument13 pages2.1 Cell Structure and FunctionpjolNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Biology Fe Pahang 2008Document11 pagesPaper 3 Biology Fe Pahang 2008zulkarnainNo ratings yet
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul3Document15 pages07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul3zulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Module QuestionsDocument14 pagesModule QuestionszulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Biology Module Inheritance3Document23 pagesBiology Module Inheritance3widad.osmanNo ratings yet
- 07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul1Document19 pages07 JPNT Bio f4 Modul1Hazimah YusofNo ratings yet
- Werner & Ingbar’s The Thyroid 8th EditionDocument10 pagesWerner & Ingbar’s The Thyroid 8th Editionbyrock66No ratings yet
- Alphabet Soup SheetDocument1 pageAlphabet Soup Sheetapi-306398192No ratings yet
- Lecture 10 PlasticityDocument36 pagesLecture 10 PlasticityDrGasnasNo ratings yet
- Frog Dissection GuideDocument16 pagesFrog Dissection GuideGabrielle PortillasNo ratings yet
- The Endocrine System Evy SulistyoningrumDocument100 pagesThe Endocrine System Evy SulistyoningrumPiko CandyNo ratings yet
- G9 Biology Extension Manual 01 Digestion 2021 AnsDocument4 pagesG9 Biology Extension Manual 01 Digestion 2021 AnsBen WongNo ratings yet
- Acute adrenal insufficiency emergencyDocument6 pagesAcute adrenal insufficiency emergencySteven SetioNo ratings yet
- SP1ES EGRA Class Reading Profile Grade 2Document2 pagesSP1ES EGRA Class Reading Profile Grade 2Camille Langit DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Lady GagaDocument4 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Lady GagaGerishelaWimandaNo ratings yet
- DX 2Document3 pagesDX 2Krizia R. PingkeNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Surgical Recall Chapter 17Document2 pagesFlashcards Surgical Recall Chapter 17Wade Bullock0% (1)
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument32 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisEzekiel moraraNo ratings yet
- ICU Patient ChartDocument2 pagesICU Patient ChartbouncedNo ratings yet
- 1651048027class 7 (Science Notes CH 2 Nutrition in Animals)Document4 pages1651048027class 7 (Science Notes CH 2 Nutrition in Animals)VijayaLakshmi KuchimanchiNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancyDocument10 pagesMaternal and Perinatal Outcome in Jaundice Complicating PregnancymanognaaaaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of HormonDocument16 pagesBiochemistry of HormonMuhamad SdeqNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular EmbryologyDocument10 pagesCardiovascular EmbryologyChristianus LeonardNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle: DR Rida Ajmal KhanDocument29 pagesCardiac Cycle: DR Rida Ajmal KhanMooma fatimaNo ratings yet
- Plabable Gems Endocrine PDF P7aDocument44 pagesPlabable Gems Endocrine PDF P7aayşenur sevinçNo ratings yet
- Introduction EmgDocument3 pagesIntroduction EmgVaneet KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte and Acid Base DisordersDocument46 pagesElectrolyte and Acid Base DisordersMia ValdesNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Flow ChartDocument2 pagesDigestive System Flow ChartMelodee Peters79% (24)
- Association of Empty Sella and Neuroendocrine Disorders in Childhood 1995Document5 pagesAssociation of Empty Sella and Neuroendocrine Disorders in Childhood 1995Paúl Otañez MolinaNo ratings yet
- GENITO URINARY SYSTEM 2nd Year BSC NursingDocument8 pagesGENITO URINARY SYSTEM 2nd Year BSC NursingShreyas WalvekarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Water Metabolism and Diabetes InsipidusDocument36 pagesChapter 1 - Water Metabolism and Diabetes InsipidusSteffi AraujoNo ratings yet
- BaZi YHZP Accidents and InjuriesDocument3 pagesBaZi YHZP Accidents and InjuriesSALIM100% (1)
- Visual Mnemonics Immunology 40 Medical MnemonicDocument110 pagesVisual Mnemonics Immunology 40 Medical MnemonicRad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Benign Diseases of ThyroidDocument70 pagesBenign Diseases of ThyroidMounica MekalaNo ratings yet
- Acute Liver Dysfunction Criteria in Critically Ill Children - The PODIUM Consensus ConferenceDocument7 pagesAcute Liver Dysfunction Criteria in Critically Ill Children - The PODIUM Consensus ConferenceZakirin WeinNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System Bio FactsheetDocument4 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Bio FactsheetEleanor WilliamsNo ratings yet