Professional Documents
Culture Documents
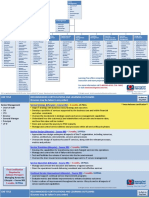
Mountainview ITILV3-2011 HiDef Process Function Poster
Uploaded by
Kaue Oliveira MarquesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mountainview ITILV3-2011 HiDef Process Function Poster
Uploaded by
Kaue Oliveira MarquesCopyright:
Available Formats
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.
co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
mountainview
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
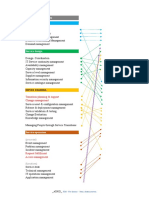
Service Strategy
Service Design
Service Transition
Service Operation
Continual Service Improvement
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
Service
Service
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
Strategy
Design
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
The ITIL Service Lifecycle is
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.co
The an
ITILintegrated
service lifecycle
perspective
closed-loop
system
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
An integrated closed-loop system
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
Functions
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
ITIL a register trademark of AXELOS
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
Copyright Mountainview
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
Version 3.11.4
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
Mountainview ITSM
Accredited Training & Courseware
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com
www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.com www.mountainview-itsm.co
.
Goal
Output
Service Portfolio, Service Pipeline, Service Catalogue, SLP, SDP, LOS, Service Acceptance Criteria, RFC, CMDB, CMS, SKMS, AMIS, CMIS
Measurement of agreed outputs, process metrics, metrics, Mean Time Between Failures of specified equipment, Measurement of maintenance activity,
Training and skills development
Goal
Activity
Input
Goal
Activity
Input
Goal
Goal
Activity
Goal
To provide the rights for users to be able to use a service or group of services.
The execution of policies and actions defined in information security
management.
Request access
Verification
Provide rights
Check and monitor identity status
Log and track access
Remove or restrict rights
Information security policies (from service design), Operational and service
level requirements , performing access management administrative activities
and responding to access management related events, Authorized RFCs to
access rights, Authorized requests
Provision of access to IT services in accordance with information security
policies; Access management records and history of access granted to services;
Access management records and history where access has been denied
To develop a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the internal strengths,
weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats involved in a project,
business venture or any other situation requiring a decision. To provide a
quick overview of a firms strategic situation.
Strengths
Internal attributes of the organization that are helpful to the achievement
of the objective.
Weaknesses
Internal attributes of the organization that are harmful to the achievement
of the objective.
Opportunities
External conditions that are helpful to the achievement of the objective.
Threats
External conditions that are harmful to the achievement of the objective.
Core competencies, Financial resources, competition, technology, cost,
facilities, distribution network, new market or segments, substitutes,
regulations
SWOT Report, CSI Register
Goal
Application Management
Activity
Goal
Service Improvement Program, SLAM Reports, CSI Register
Activity
Goal
Access Management
To provide detailed technical skills and resources needed to support the ongoing operation of the IT Infrastructure. Technical Management also plays an
important role in the design, testing, release and improvement of IT services.
Mainframe, Server, Network, Storage, Database, Directory Services, Desktop, Middleware, Web
Custodian of technical knowledge and expertise related to managing the IT Infrastructure.
Ensures that the knowledge required to design, test, manage and improve IT services is identified, developed and refined.
Provides the actual resources to support the ITSM Lifecycle
Ensure that resources are effectively trained and deployed to design, build, transition, operate and improve the technology required to deliver and
support IT services
Identifying the knowledge and expertise required to manage and operate the IT Infrastructure and to deliver IT services
Documentation of the skills that exist in the organization
Design and delivery of training for users, the Service Desk and other groups
SLA Targets, SLRs, OLAs, Contracts
SWOT Analysis
Authorized RFC, Service package, SLP, SDP, including service model and SAC,
IT service continuity plan and related business continuity plan, Service
Management and operations plans and standards, Technology and procurement
standards and catalogues
Release and deployment plan, Completed RFCs for the release and
deployment activities, Service notification, Updated service catalogue with
the relevant information about the new or changed service, New or changed
Service Management documentation
Resolved problems and actions taken to achieve their resolution, Updated
problem management records, RFCs to remove infrastructure errors,
Workarounds for incidents, Known error records, Problem management
reports, improvement recommendations
Input
Incident Records via recurring incidents, Request Fulfillment feedback and
metrics. All proactive Service Lifecycle processes such as Capacity,
Availability Management
Service Measurement
Objective (Availability, Reliability, Performance of the Service)
Developing a Service Measurement Framework
Different levels of measurement and reporting
Defining what to measure
Setting targets
Service management process measurement
Creating a measurement framework grid
Interpreting and using metrics
Interpreting metrics
Using measurement and metrics
Creating scorecards and reports
CSI policies
Service Reporting
Reporting policy and rules
Output
Goal
Problem detection
Problem logging
Problem categorization
Problem prioritization
Problem investigation and diagnosis
Workarounds
Raising a known error record
Problem resolution
Problem closure
Major problem review
To monitor services and report on improvement opportunities
To manage applications throughout their lifecycle. The Application Management function supports and maintains operational applications and Application
Development plays an important role in the design, testing and improvement of applications of IT service.
Determine whether to buy an application or build it
Maintain and develop applications
It is the custodian of technical knowledge and expertise related to managing applications. In this role Application Management, working together with
Technical Management, ensures that the knowledge required to design, test, manage and improve IT services is identified
It provides the actual resources to support the ITSM Lifecycle. In this role, Application Management ensures that resources are effectively trained and deployed
to design, build, transition, operate and improve the technology required to deliver and support IT services
Application Management Lifecycle: Requirements, Design, Build, Deploy, Operate, Optimize
Identifying the knowledge and expertise
Recruiting or contracting resources
Input
Standard Operation Procedures (SOP), Operations Logs, Shift Schedules and Reports, Operations Schedule, IT Operations Management metrics
Activity
Activity
Backup and Restore, Monitoring tools and agents, Remote desktop tools
HVAC, Surveillance cameras, access card readers
Release and deployment planning
Plans for creating and deploying the release are created
Release build and test
The release package is built, tested and checked into the DML
Deployment
The release package in the DML is deployed to the live environment
Review and close
Experience and feedback are captured, performance targets and
achievements are reviewed and lessons are learned
Service catalogue, SLRs, The service review meeting, Vision and mission
statements, Corporate, divisional and departmental goals and objectives,
Legislative requirements, Governance requirements, Budget cycle, Customer
satisfaction surveys, CSI Register
Input
To plan, schedule and control the build, test and deployment of releases, and
to deliver new functionality required by the business while protecting the
integrity of existing services.
Knowledge gained from presenting and using the information
Agreed implementation plans (from Step 6)
A CSI register for those initiatives that have been initiated from other sources.
Output
knowledge required to make decisions and to manage the IT services,
maintained within an SKMS.Service Knowledge Management Base, Service
Operation and Operations Staff, Problem Management Staff and Transition
Staff
Step 1 Identify the strategy for improvement
Step 2 Define what you will measure
Step 3 Gather the data
Step 4 Process the data
Step 5 Analyse the information and data
Step 6 Present and use the information
Step 7 Implement improvement
To minimize the adverse impact of incidents and problems on the business
that are caused by underlying errors within the IT Infrastructure, and to
proactively prevent recurrence of incidents related to these errors. Determine
the root cause of incidents and initiate actions to improve.
Activity
All knowledge, information and data used by the service provider, as well as
relevant business data.
To collect, analyze, process relevant metrics from a process in order to
determine its weakness and establish an action plan to improve the process.
Software Development tools, Installation and Distribution tools, Testing tools
Output
Customer/User Satisfaction Surveys, Service Desk Metrics, Super-user updates, training, communication with users,
IT Operations Management
function responsible for the daily operational activities needed to manage the IT Infrastructure. This is done according to the Performance Standards defined
during Service Design. There are two sub functions:
IT Operations Control
Generally staffed by shifts of operators and which ensures that routine operational tasks are carried out. IT Operations Control will also provide centralized
monitoring and control activities, usually using an Operations Bridge or Network Operations Centre.
Facilities Management
The management of the physical IT environment, Data Centers or computer rooms. Often Technical and Application Management are co-located with IT
Operations in large Data Centers.
Business vision, mission, goals and objectives, Baseline assessments,
Measurable targets Service & process improvement, Measurements & metrics,
CSI Register
Service Measurement and Reporting
Technical Management
Input
To provide daily operational activities needed to manage the IT Infrastructure. It has two sub-functions: IT Operations Control and Facilities Management
Goal
To act as the primary point of contact for users when there is a service disruption, for service requests or for some categories of Request for Change. The
Service Desk provides a point of communication to the users and a point of coordination for several IT groups and processes.
Business vision, mission, goals and objectives, Baseline assessments,
Measurable targets, Service & process improvement, Measurements & metrics
Activity
Authorized/rejected service requests, Request fulfilment status reports,
Fulfilled service requests, Incidents (rerouted), RFCs/standard changes,
Asset/CI updates, Updated request records, Closed service requests, Cancelled
service requests.
Activity
Designs, plans and configurations from service design packages, Requests for
change and work orders from change management, Actual configuration
information collected by tools and audits, Information in the organizations
fixed asset register.
New and updated configuration records, Updated asset information for use in
updating the fixed asset register, Information about attributes and
relationships of configuration items, for use by all other service management
processes
Plan: Establishes goals for improvement including gap analysis, definition of
action steps to close the gap and establishing and implementing measures to
assure that the gap has been closed and benefits achieved
Do: Development and implementation of a project to close the gap.
Implementation or improvement of processes and establishing the smooth
operation of the process
Check: Comparison of the implemented environment to the measures of
success established in Plan phase. The comparison determines if a gap still
exists between the improvement objectives of the process and the
operational process state
Act ;The decision process to determine if further work is required to close
remaining gaps, allocation of resources necessary to support another round
of improvement.
Input
Work requests, Authorization forms, Service requests, RFCs, Requests from
various sources such as phone calls, web interfaces or email, Request for
information.
Input
Management and planning
Configuration identification
Configuration control
Status accounting and reporting
Verification and audit
Output
Output
Business information: from the organizations business strategy, plans and
financial plans, and information on their current and future requirements,
Supplier and contracts strategy, Supplier plans and strategies, Supplier
contracts, agreements and targets, budgets
SCMIS, Supplier and contract performance information and reports, Supplier
and contract review meeting minutes, Supplier SIPs, Supplier survey reports
Receive request
Request logging and validation
Request categorization
Request prioritization
Request authorization
Request review
Request model execution
Request closure
Rules for reopening requests
Input
Establish the Knowledge management strategy
Establish Knowledge transfer
Manage data, information and knowledge
Enable the service knowledge management system
Responsible for managing the lifecycle of all service requests from the users.
Maintain user and customer satisfaction through efficient and professional
handling of all service requests
Output
To share perspectives, ideas, experience and information; to ensure that
these are available in the right place at the right time to enable informed
decisions; and to improve efficiency by reducing the need to rediscover
knowledge.
Release and Deployment Management
To ensure that the assets required to deliver services are properly controlled,
and that accurate and reliable information about those assets is available
when and where it is needed. I.e. details of how the assets have been
configured and the relationships between assets.
Input
Definition of new supplier and contract requirements
Evaluation of new suppliers and contracts
Supplier categorization and maintenance of the supplier and contract
management information system
Establishment of new suppliers and contracts
Supplier, contract and performance management
Contract renewal or termination
RFC for Incident resolution; Incident record (including resolution and/or
Work-arounds), Resolved and closed Incidents, Communication to Customers,
Management information (reports)
Output
Ensure that suppliers and the services they provide are managed to support IT
service targets and business expectations. To raise awareness of the business
context of working with partners and suppliers. Realise business benefit for
the organization.
Incident record with details sourced from (for example) Service Desk,
networks or computer operations, Configuration details from the
Configuration Management Database (CMDB), Response from Incident matching
against Problems and Known Errors, Resolution details
The goal in using the Deming Cycle is steady, ongoing improvement. It is a
fundamental tenet of Continual Service Improvement.
Output
Activity
Interim evaluation report(s) for change management, Evaluation report for
change management
Output
The documentation and agreement of a definition of the service, Updates to
the Service Portfolio: should contain the current status of all services and
requirements for services, The Service Catalogue
Incident identification
Incident logging
Incident categorization
Incident prioritization
Initial diagnosis
Incident escalation
Investigation and diagnosis
Resolution and recovery
Incident closure
Rules for reopening incidents
Request Fulfillment
Goal
SDP, including service charter and SAC, Change proposal, RFC, change record
and detailed change documentation, Discussions with stakeholders, Test
results and report
Service Asset & Configuration Management
Business information from the organizations business and IT strategy, plans
and financial plans, Business Impact Analysis, changes to service requirements,
Business requirements, Service Portfolio, CMS, Feedback from all other
processes
IT Operations Management
Incident Record, Problem Record, Known Error Data, Change Schedule, Sources of internal knowledge (especially technical or application experts), SKMS, CMS,
Alerts from monitoring tools, SL Targets in SLAs, OLAs, UCs.
Business vision, mission, goals and objectives, Baseline assessments,
Measurable targets Service & process improvement, Measurements & metrics,
CSI Register
Output
Activity
Output
Evaluation plan
Understanding the intended effect of a change
Understanding the unintended effect of a change
Factors for considering the effect of a service change
Evaluation of predicted performance
Evaluation of actual performance
Risk management
Evaluation report
Input
To provide a consistent and standardized means of determining the
performance of a service change in the context of likely impacts on business
outcomes, and on existing and proposed services and IT infrastructure. Assess
against its predicted performance. Identify risks.
Input
Input
Rejected RFCs, Approved RFCs, Change to the services, service or
infrastructure resulting from approved RFCs, CI, Change schedule, Revised
PSO, Authorized change plans, Change decisions and actions, Change
documents and records, Change Management reports.
Service Desk
Logging all relevant incident/service request details, allocating category and priority codes
Providing first-line investigation and diagnosis
Resolving those incidents/service requests they are able
Escalating incidents/service requests that they cannot resolve within agreed timescales
Keeping users informed of progress
Closing all resolved incidents, requests and other calls
Conducting customer/user satisfaction callbacks/ surveys as agreed
Communication with users
Updating the CMS under the direction and approval of Configuration Management
To restore normal service operation as quickly as possible and minimize the
adverse impact on business operations.
Problem Management
Activity
Goal
Business information. Corporate governance and business security policies and
guidelines, security plans, Risk Analysis and responses, IT information, Service
information, Risk Analysis processes and reports, Details of all security events
and breaches, Change information, CMS
Security Management Policy, Security Management Information System (SMIS),
Revised security risk assessment reports, Security controls, Audits and audit
reports, Security test schedules and plans, Security breaches and major
Incidents reports, Supplier security policies
Business vision, mission, goals and objectives, Baseline assessments,
Measurable targets, Service & process improvement, Measurements & metrics
Output
Goal
Activity
Input
Goal
Input
Output
Goal
Activity
Input
Output
Activity
Goal
Activity
Policy and strategies for change and release; Request for Change; Change
proposal, Plans change, transition, release, deployment, test, evaluation
and remediation, Current change schedule and PSO, CMDB, release package,
baseline, Test results, test report
Determine the vision
To understand what the ultimate and long term aims are
Determine where we are now
Creates a baseline of data for services currently being delivered
Determine where we want to be
This is often expressed as business requirements
Determine how to get there
What improvement initiatives are required in the short, medium and long
term? These initiatives should be logged in the CSI register
Determine if we got there
This is documented through monitoring, reporting and reviewing of service
level achievements and actual performance against targets identified by the
business requirements
Deming Cycle Plan Do Check Act
Knowledge Management
Supplier Management
Activity
Production and maintenance of an overall information security policy and a
set of supporting specific policies
Communication, implementation and enforcement of the security policies
Assessment and classification of all information assets and documentation
Implementation, review, revision and improvement of a set of security
controls and risk assessment and responses
Monitoring and management of all security breaches and major security
incidents
Analysis, reporting and reduction of the volumes and impact of security
breaches and incidents
Schedule and completion of security reviews, audits and penetration tests
Communication and escalation to those responsible for further action, Event
log updates, Incident notification, Events that indicate the potential breach
of an SLA or OLA objective, Alerts that indicate completion status, Populated
SKMS with event information and history
To align IT with the business. To assist with decision-making on what
improvement initiatives make sense and add the greatest value back to the
business.
Seven Step Improvement Process
Output
Agreeing and documenting a service definition and description for each
service
Interfacing with service portfolio management to agree the contents of the
service portfolio and service catalogue
Producing & maintaining an accurate service catalogue & contents
Interfacing with the business and ITSCM on the dependencies of business
units
Interfacing with support teams, suppliers and service asset and configuration
management
Interfacing with BRM and SLM to ensure that the information is aligned to
the business and business process
Input
To provide and maintain a single source of consistent information on all
operational services and those being prepared to be run operationally, and to
ensure that it is widely available to those who are authorized to access it.
Goal
Output
To align IT security with business security and ensure that the confidentiality,
integrity and availability of the organizations assets, information, data and IT
services always matches the agreed needs of the business.
Input
Policies, standards and practices defined by legislation, regulators and
enterprise financial managers, Generally Accepted Accounting Practices
(GAAP) and local variations, Supplier data, CMS, service portfolio, customer
agreement portfolio, application and project portfolio
Service valuation, Service investment analysis, Compliance, Cost
optimization, Business impact analysis (BIA), Planning confidence
Typical activities in managing individual changes:
Create and record the RFC
Review the RFC
Filter changes (e.g. incomplete or wrongly routed changes)
Assess and evaluate the change
Establish the appropriate level of change authority
Establish relevant areas of interest (i.e. who is involved in the CAB)
Evaluate the business justification, impact, cost, benefits, risks,
Submit a request for evaluation to initiate change evaluation
Authorize the change
Obtain authorization/rejection
Communicate the decision with all stakeholders and initiator
Plan updates
Coordinate change implementation
Review and close change
Collate the change documentation, e.g. baselines and evaluation reports
Review the change(s) and change documentation
Update service knowledge management system with lessons learned
Close the change document when all actions are completed
Input
Input
Output
Goal
ISO9000
Activity
Improvement
ISO38500
Input
M_o_R
ISO27002
S
T r er v
a n ic e
s
i
t
io
n
COBIT
e
vic ion
r
Se rat
e
Op
SOA
ISO20000
Service
Strategy
Output
Six Sigma
Overall change management activities:
Planning and controlling changes
Change and release scheduling (working with release and deployment
management when appropriate)
Communications
Change authorization
Ensuring that remediation plans are in place
Measurement and control
Management reporting
Understanding the impact of change
Continual improvement
Goal
Service continuity and recovery plans, ITSCM policy strategies , ITSCM plans ,
Emergency Response Plan, Damage Assessment Plan , Salvage Plan , Vital
Records Plan, Crisis Management and Public Relations Plan, Accommodation
and Services Plan , Security Plan
Accounting: chart of accounts, analysis and reporting, action plans
Budgeting: analysis of previous budget, assessment of plans, specification of
changes to funding and spending, cost and income estimation, budget(s)
Charging: charging policies, decide chargeable items, pricing. billing
Input
PRINCE2
Output
TOGAF
To control the lifecycle of all changes, enabling beneficial changes to be
made with minimum disruption to IT services. To respond to the customers
changing business requirements while maximizing value and reducing
incidents, disruption and re-work.
Output
Goal
PMBoK
Activity
CMMI
Activity
Financial Management for IT Services
To secure the appropriate funding to design, develop and deliver services that
meet the strategy of the organization. Identify services that the provider is
not able to provide. Identify the balance between the cost and quality of
service. Balance of supply and demand.
Service reports, Service improvement opportunities for inclusion in the CSI
register, SIP, Service quality plan, SLAs, SLRs, OLAs, Reports on OLAs and
underpinning contracts, Service review meeting minutes and actions, Revised
requirements for underpinning contracts
Output
Business strategy, plans and financial plans, and information on their current
and future requirements, IT information: from the IT strategy and plans and
current budgets, A Business Continuity Strategy and a set of Business
Continuity Plans: SLAs and SLRs
Input
Up-to-date service portfolio, Service charters that authorize the work for
designing and building new services or changes to existing services, Reports
on the status of new or changed services, Reports on the investment made in
services in the service portfolio & ROI
Continual Service
Service
Design
Business strategy, plans and financial plans, and information on its current and
future requirements, BIA, Business requirements, policies and constraints from
service strategy, The service portfolio and service catalogue, RFCs, CMS,
Customer and user feedback
Information Security Management
Goal
Input
Output
Strategy plans, Service improvement opportunities, Financial reports,
Requests, suggestions or complaints from the business, Project updates for
services
Operational and service level requirements associated with events and their
actions, Alarms, alerts and thresholds for recognizing events, Event
correlation tables, rules, event codes and automated response solutions that
will support event management activities
Service Catalogue Management
Activity
Input
Output
Goal
Activity
Define: Inventory services, ensure business cases and validate portfolio data
Analyze: Maximize portfolio value, align, prioritize & balance supply and
demand
Approve: Finalize proposed portfolio, authorize services and resources
Charter: Communicate decisions, allocate resources and charter services
Input
Goal
Stage 1: Initiation
Stage 2: Requirements and Strategy
Requirements Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
Requirements - Risk Analysis M_o_R
IT Service Continuity Strategy
Risk Response Measures , Off-site Storage, ITSCM Recovery Options
Stage 3: Implementation
Organizational Planning
Testing
Walk-through, Full, Partial, Scenario
Stage 4: On-going Operation
Education, awareness, training, review, testing, Change Management
Stage 5: Invocation
Configuration baseline of the testing environment, Testing carried out
(including options chosen and constraints encountered), Results from those
tests, Analysis of the results, e.g. comparison of actual results with expected
results, risks identified during testing activities.
Event occurs
Event notification
Event detection
Event logged
First-level event correlation and filtering
Significance of events
Second-level event correlation
Further action required?
Response selection
Review actions
Close event
Output
Output
To support the overall business continuity management (BCM) process by
ensuring that, by managing the risks that could seriously affect IT services, the
IT service provider can always provide minimum agreed business continuityrelated service levels.
Service Portfolio Management
To ensure that the service provider has the right mix of services to balance
the investment in IT with the ability to meet business outcomes. Track the
investment in services throughout their lifecycle. Ensure that services are
clearly defined and align with business outcomes.
Designing SLA frameworks
Determining, documenting and agreeing requirements for new services and
producing SLRs
Negotiating, documenting and agreeing SLAs for operational services
Monitoring service performance against SLA
Producing service reports
Conducting service reviews and instigating improvements within an overall
service improvement plan
Collating, measuring and improving customer satisfaction
Reviewing and revising SLAs, service scope and underpinning agreements
Reviewing and revising OLAs, underpinning agreements and service scope
Developing contacts and relationships
Handling complaints and compliments
Activity
Stakeholder definitions, Defined business outcomes, Agreement to fund
(internal) or pay for (external) services, customer portfolio, Service
requirements for strategy, design and transition, Customer satisfaction surveys,
Schedule of training and awareness events
Goal
Input
Customer requirements, Customer requests, complaints, escalations or
compliments, The service strategy, the customers strategy, service portfolio,
project portfolio, Service level agreements, Requests for change, Patterns of
business activity and user profiles
To ensure that an agreed level of IT service is provided for all current IT
services, and that future services are delivered to agreed achievable targets.
CMIS, Capacity Plan, Service performance information and reports, Workload
analysis and reports, Ad hoc capacity and performance reports, Forecasts and
predictive reports, Thresholds, alerts and events
IT Service Continuity Management
Goal
Understand the business relationship with the Customer
Establish the Business Relationship Management process
Establish the initiation by customers
Establish the Initiation by the service provider
Establish the BRM process through the lifecycle
The Service Package, SLP, Service Provider Interface Definition, Service
Design Package, Release and Deployment Plans , Acceptance Criteria , RFC
To manage events throughout their lifecycle. To detect events, make sense of
them and determine the appropriate control action that is required by the
event management process.
Incident Management
Service Level Management
Activity
Goal
Activity
Input
Business information: from the organizations business strategy, plans and
financial plans, and information on their current and future requirements,
Service and IT information: from Service Strategy, the IT strategy and plans
and current budgets, covering all areas of technology
Validation and test management
Plan and design tests
Verify test plans and test design
Prepare test environment
Perform tests
Evaluate exit criteria and report
Test clean up and closure
Change proposal, Authorized change, Service design package: Release package
definition and design specification, Test plans, Deployment plans, Service
acceptance criteria (SAC).
Change Management
Input
Output
Service
Transition
Service
Operation
Design-related activities
Exploitation of new technology, Designing resilience,
Ongoing iterative activities
Monitoring, Analysis, Tuning, Implementation
Demand management in capacity management
Modelling and trending
Baselining, Trend analysis, Analytical modelling, Simulation modelling,
Application sizing
Types of Capacity Management
Business, Service, Component
The availability MIS (AMIS), Availability plan, Availability and recovery design
criteria and proposed service targets for new or changed services, Service
availability, reliability and maintainability reports of achievements against
targets, PSO, SIP
Output
Input
Activity
Goal
Business Relationship Management
Business impact information, Reports and registers, Service information,
Service information, Financial information, Change and release information,
Service asset and configuration management Service targets, Component
information, Technology information, performance
To provide objective evidence that the new/changed service supports the
business requirements, including the agreed SLAs.
Change Evaluation
To ensure that the capacity of IT services and the IT infrastructure meets the
agreed capacity- and performance-related requirements in a cost-effective
and timely manner. Meet both the current and future capacity and
performance needs of the business.
To establish and maintain a business relationship between the service provider
and the customer based on understanding the customer and its business needs.
To identify customer needs and ensure that the service provider is able to
meet these business needs.
Establish the Transition strategy
Establish the Service transition lifecycle stages
Prepare for service transition
Planning and coordinating service transition
Provide transition process support
Transition strategy and budget, Integrated set of service transition plans.
Goal
Continual
Service
Improvement
Output
User profiles, Patterns of business activity will be formally documented and
included in the service and customer portfolios, Policies for management of
demand when resources are over-utilized, Policies for utilization
Activity
Goal
Input
Initiative to create a new service, or to change an existing service, Service
models, Customer portfolio, Service portfolio and Customer agreement
portfolio, Charging models, Chargeable items, Service improvement
opportunities and plans
Output
Activity
Identify sources of demand forecasting
Identify patterns of business activity (PBA)
Determine User profiles (UP)
Establish Activity-based demand management
Develop differentiated offerings
Manage or influence operational demand
To provide overall planning for service transitions and to coordinate the
resources that they require. Plan and coordinate the resources to ensure that
the requirements of service strategy encoded in service design are effectively
realized in service operation.
Output
Goal
Input
Service designs and SDPs, revised enterprise architecture, revised
management systems, Revised measurement and metrics methods, Revised
processes, Service portfolio updates, Updates to change records.
Capacity Management
Understand, anticipate and influence customer demand for services and to
work with capacity management to ensure the service provider has capacity to
meet this demand. Ensure services are designed, tested and delivered to
achieve of business outcomes.
Reactive activities
Monitoring, measuring, analysing, reporting and reviewing service and
component availability
Investigating all service and component unavailability and instigating
remedial action
Proactive activities
Planning and designing new or changed services
Determining the VBFs, in conjunction with the business & ITSCM
Risk assessment and management
Implementing cost-justifiable counter-measures, including risk reduction
and recovery mechanisms
Reviewing all new and changed services and test all availability and
resilience mechanisms
Continual reviewing and improvement
Service charters, Change requests, Business & IT strategy, plans and financial
plans, Business impact analysis, service portfolio, constraints and resource
limitations, Governance, Corporate, legal and regulatory policies and
requirements, project schedule, CMS, EA, Metrics
Strategic plans, Tactical plans, Strategy review schedules and documentation,
Mission and vision statements, Policies, Strategic requirements for new
services, and input into which existing services need to be changed
Demand Management
To ensure that an agreed level of IT service is provided for all current IT
services, and that future services are delivered to agreed achievable targets.
Continual Service Improvement Approach
Event Management
Service Validation and Testing
Service Transition Planning & Support
Activity
Activity
Overall lifecycle stage activities include:
Define and maintain policies and methods
Plan design resources and capabilities
Coordinate design activities
Manage design risks and issues
Improve service design.
Individual design activities include:
Plan individual designs
Coordinate individual designs
Monitor individual designs
Review designs and ensure handover of SDPs.
Output
Existing plans, Research on aspects of the environment, Vendor strategies and
product roadmaps, Customer interviews and strategic plans, Service portfolio,
Service reporting, Audit reports that indicate compliance with (or deviation
from) the orgs strategy.
Ensure the goals and objectives of the service design stage are met by
providing and maintaining a single point of coordination and control for all
activities and processes within this stage of the service lifecycle.
Goal
Goal
Input
Activity
Strategic assessment
Analyze the internal environment
Analyze the external environment
Define market spaces
Identify strategic industry factors
Establish objectives
Strategy generation, evaluation and selection
Determine the perspective
Form a position
Develop a plan
Adopt patterns of action
Strategy execution
Other service management processes
Align assets with customer outcomes
Optimize critical success factors
Prioritize investments
Measurement and evaluation
Continual service improvement
Expansion and growth
Output
Goal
Activity
Input
Output
Defining and maintaining an organizations perspective, position, plans and
patterns with regard to its services and the management of those services.
Ensure that the strategy is defined, maintained and achieves its purpose.
Service strategy articulates how a service provider will enable an organization
to achieve its business outcomes and establish the criteria for success.
Availability Management
Activity
Design Coordination
Strategy Management for IT Services
library
infrastructure
technology
information
ITIL Edition 2011 Processes & Functions
Measurement of agreed outputs, Process metrics, Application performance, Measurement of maintenance activity, Application Portfolio, Application
Requirements
You might also like
- Cold ShadowsDocument130 pagesCold ShadowsDrraagh100% (4)
- 2022 AUSL Purples Notes Criminal Law and Practical ExercisesDocument305 pages2022 AUSL Purples Notes Criminal Law and Practical ExercisesNathalie Joy Calleja100% (6)
- ITIL Job Function MappingDocument13 pagesITIL Job Function Mappingvikrms1978No ratings yet
- (PALE) PP vs. DE LUNA PDFDocument3 pages(PALE) PP vs. DE LUNA PDF8111 aaa 1118No ratings yet
- ITIL v.3 Processes & FunctionsDocument5 pagesITIL v.3 Processes & FunctionsAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Stakeholder involvement classDocument6 pagesStakeholder involvement classmorcamtecNo ratings yet
- Best Practices of IT Organization Design enDocument35 pagesBest Practices of IT Organization Design enMosheh LangatNo ratings yet
- Free Help Desk Evaluation ChecklistDocument18 pagesFree Help Desk Evaluation ChecklistNguyen Huu TrungNo ratings yet
- ITIL Change ManagementDocument4 pagesITIL Change ManagementShanKumarNo ratings yet
- ITIL Guide to Access ManagementDocument3 pagesITIL Guide to Access ManagementBabul BhattNo ratings yet
- Itil KpiDocument5 pagesItil Kpikatz3011100% (1)
- IT Governance FrameworkDocument41 pagesIT Governance Frameworkmusaab elameenNo ratings yet
- ISO 50001 Audit Planning MatrixDocument4 pagesISO 50001 Audit Planning MatrixHerik RenaldoNo ratings yet
- Example Copy of ETS Service Catalog TemplateDocument13 pagesExample Copy of ETS Service Catalog TemplateSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Ohio OAKS comparison of organization functions with ITIL servicesDocument3 pagesOhio OAKS comparison of organization functions with ITIL servicesroddickersonNo ratings yet
- ITIL Planning To Implement Service ManagementDocument12 pagesITIL Planning To Implement Service ManagementyellowsteelNo ratings yet
- ITIL Cobit MappingDocument16 pagesITIL Cobit Mappingapi-383689667% (3)
- Best Practices For IT Strategic Planning en PDFDocument32 pagesBest Practices For IT Strategic Planning en PDFAnonymous iMq2HDvVqNo ratings yet
- Ray Kroc's Visionary Leadership at McDonald'sDocument4 pagesRay Kroc's Visionary Leadership at McDonald'sViknesh Kumanan100% (1)
- Service CatalogDocument10 pagesService Catalogmarcelorgs100% (2)
- ITSM Assessment Artifacts-1Document1 pageITSM Assessment Artifacts-1Murali PvNo ratings yet
- Service Level Management Leveraging Your Network InvestmentsDocument16 pagesService Level Management Leveraging Your Network InvestmentsΟλυμπίδης ΙωάννηςNo ratings yet
- 03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue JourneyDocument28 pages03 Derek Gillard - Service Catalogue Journeyarsman1100% (1)
- Change Management Policies FinalDocument24 pagesChange Management Policies FinalBPG ServiceNo ratings yet
- ABC's IT Services CatalogDocument14 pagesABC's IT Services CatalogManav Patel100% (1)
- ISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsDocument1 pageISO 20000 Master List of DocumentsAditya YerunkarNo ratings yet
- ITIL - IM KPIs and Reports PDFDocument3 pagesITIL - IM KPIs and Reports PDFkaraspideyNo ratings yet
- Quicho - Civil Procedure DoctrinesDocument73 pagesQuicho - Civil Procedure DoctrinesDeanne ViNo ratings yet
- The Failure To Prevent Genocide in Rwanda The Role of BystandersDocument329 pagesThe Failure To Prevent Genocide in Rwanda The Role of BystandersAlexandra CiarnauNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapAllanNo ratings yet
- ITIL4FO POSTER 2021 NewDocument5 pagesITIL4FO POSTER 2021 Newexternalhdd239No ratings yet
- Change ManagmentDocument78 pagesChange ManagmentAnkit GuptaNo ratings yet
- ITIL Process Maturity FrameworkDocument2 pagesITIL Process Maturity FrameworkpdsramaraoNo ratings yet
- Release and Deployment Management: A CA Service Management Process MapDocument15 pagesRelease and Deployment Management: A CA Service Management Process MappjoseptNo ratings yet
- Glenfis COBIT5 Eng Questionnaire BAI07 r2 v2.0Document38 pagesGlenfis COBIT5 Eng Questionnaire BAI07 r2 v2.0Hawkdollar HawkdollarNo ratings yet
- ITIL v3 Service Request ManagementDocument3 pagesITIL v3 Service Request ManagementAbhirup SarkarNo ratings yet
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingDocument17 pagesITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloNo ratings yet
- Screenshots Itil Process Map VisioDocument16 pagesScreenshots Itil Process Map Visionico0j100% (1)
- Problem Management Overview: PM Process, KPIs, BenefitsDocument26 pagesProblem Management Overview: PM Process, KPIs, Benefits1buckeyeNo ratings yet
- HL - ITSM Assessment v0.2Document23 pagesHL - ITSM Assessment v0.2Vamsi aravetiNo ratings yet
- Human Resources Service DeliveryDocument21 pagesHuman Resources Service DeliveryNamoos e RisalatNo ratings yet
- Itsm Academy Project Charter 04-25-07v3Document12 pagesItsm Academy Project Charter 04-25-07v3kkuppachiNo ratings yet
- Language Hub Student S Book Elementary Unit 1 1Document9 pagesLanguage Hub Student S Book Elementary Unit 1 1Paulo MalheiroNo ratings yet
- Olimpiada Engleza 2010 Etapa Locala IXDocument4 pagesOlimpiada Engleza 2010 Etapa Locala IXAdrian TufanNo ratings yet
- BMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperDocument10 pagesBMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperRoss ManningNo ratings yet
- JAR23 Amendment 3Document6 pagesJAR23 Amendment 3SwiftTGSolutionsNo ratings yet
- Service Catalogue TemplateDocument3 pagesService Catalogue TemplateJerod King100% (1)
- It Services and ManagementDocument18 pagesIt Services and ManagementAshish SinghNo ratings yet
- ITSM Process Maturity AssessmentDocument31 pagesITSM Process Maturity Assessmentalain_charpentierNo ratings yet
- Itil V3 Cobit V4.1 Mapping OverviewDocument8 pagesItil V3 Cobit V4.1 Mapping OverviewDwdroo DiwokNo ratings yet
- IT Service Management Improvement PlanDocument31 pagesIT Service Management Improvement Planrajesh.j162763No ratings yet
- Process Improvement Calculations ToolsDocument65 pagesProcess Improvement Calculations ToolsNevets Nonnac100% (1)
- Process Vs PraticesDocument1 pageProcess Vs PraticesAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Process To PraticesDocument3 pagesProcess To PraticesAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Itil and The CMDBDocument5 pagesItil and The CMDBPaul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Itam PPT 1Document35 pagesItam PPT 1Karunesh MathurNo ratings yet
- License Table - Competency - 10sept19Document20 pagesLicense Table - Competency - 10sept19mabarcauNo ratings yet
- Director IT Service Delivery in Metro Atlanta GA Resume Burke MeanusDocument2 pagesDirector IT Service Delivery in Metro Atlanta GA Resume Burke MeanusBurke MeanusNo ratings yet
- Iso20000 2Document4 pagesIso20000 2Karloz PsyNo ratings yet
- IT Service Management: OwnershipDocument22 pagesIT Service Management: OwnershipchandrukanthNo ratings yet
- Introduction To It Service Management: Slide 1Document10 pagesIntroduction To It Service Management: Slide 1Chandra RaoNo ratings yet
- Continual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Definition of CSI InitiativesDocument1 pageContinual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Definition of CSI InitiativesAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- ITSM Consultant, ITIL SME, Project ManagerDocument4 pagesITSM Consultant, ITIL SME, Project Managerapi-121359016No ratings yet
- ITIL Service Availability Report TemplateDocument3 pagesITIL Service Availability Report Templatepasc colcheteNo ratings yet
- CA Service Catalog Advanced ConceptsDocument23 pagesCA Service Catalog Advanced Conceptsumairakhlaque78No ratings yet
- Software Price ListDocument100 pagesSoftware Price Listapi-26152534No ratings yet
- List of Countries in The Eurovision Song ContestDocument26 pagesList of Countries in The Eurovision Song ContestNajda DurmoNo ratings yet
- Penyebaran Fahaman Bertentangan Akidah Islam Di Media Sosial Dari Perspektif Undang-Undang Dan Syariah Di MalaysiaDocument12 pagesPenyebaran Fahaman Bertentangan Akidah Islam Di Media Sosial Dari Perspektif Undang-Undang Dan Syariah Di Malaysia2023225596No ratings yet
- In Bengal, Erosion Leads To Land Loss: Shiv Sahay SinghDocument1 pageIn Bengal, Erosion Leads To Land Loss: Shiv Sahay SinghRohith KumarNo ratings yet
- APWU Contract Effective DatesDocument5 pagesAPWU Contract Effective DatesPostalReporter.comNo ratings yet
- 1) Anuj Garg Vs Hotel Association of India: Article 15Document26 pages1) Anuj Garg Vs Hotel Association of India: Article 15UriahNo ratings yet
- Day 16. The 10th ScoringDocument8 pagesDay 16. The 10th ScoringWahyu SaputraNo ratings yet
- Intrepid Group Annual Report 2018Document53 pagesIntrepid Group Annual Report 2018Andre Febrima100% (1)
- PEST Analysis of the Indian Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument8 pagesPEST Analysis of the Indian Pharmaceutical IndustryAnkush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Pooling Harness Sets: For Blood and Blood ComponentsDocument1 pagePooling Harness Sets: For Blood and Blood ComponentsCampaign MediaNo ratings yet
- F1 English PT3 Formatted Exam PaperDocument10 pagesF1 English PT3 Formatted Exam PaperCmot Qkf Sia-zNo ratings yet
- Taylor Swift Tagalig MemesDocument34 pagesTaylor Swift Tagalig MemesAsa Zetterstrom McFly SwiftNo ratings yet
- DEALCO FARMS vs. NLRCDocument14 pagesDEALCO FARMS vs. NLRCGave ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Annamalai University: B.A. SociologyDocument84 pagesAnnamalai University: B.A. SociologyJoseph John100% (1)
- 5 8 Pe Ola) CSL, E Quranic WondersDocument280 pages5 8 Pe Ola) CSL, E Quranic WondersMuhammad Faizan Raza Attari QadriNo ratings yet
- Second Letter To DOJ Re Victims 9.8.23 FinalDocument3 pagesSecond Letter To DOJ Re Victims 9.8.23 FinalBreitbart NewsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Human Resource Planning, Recruitment, and SelectionDocument9 pagesChapter 3: Human Resource Planning, Recruitment, and SelectionramilgarciaNo ratings yet
- Sana Engineering CollegeDocument2 pagesSana Engineering CollegeandhracollegesNo ratings yet
- Chap1 HRM581 Oct Feb 2023Document20 pagesChap1 HRM581 Oct Feb 2023liana bahaNo ratings yet
- Charity Extends Help To Seniors: Donating Is Made EasierDocument16 pagesCharity Extends Help To Seniors: Donating Is Made EasierelauwitNo ratings yet
- Courts Jamaica Accounting and Financing ResearchDocument11 pagesCourts Jamaica Accounting and Financing ResearchShae Conner100% (1)