Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pipeline Design-Operation
Uploaded by
Faridah ZahraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pipeline Design-Operation
Uploaded by
Faridah ZahraCopyright:
Available Formats
SUBSEA PIPELINE DESIGN CRITERIA
OPERATION CONDITION
Calculate by: Faridah Zahra
15510049
1. Description
This file provides detail calculation for designing subsea pipeline that includes:
Wall thickness selection;
On-bottom stability analysis; and
Free-span analysis
Detail calculation here only provides for operation condition, while calculation on other condition has been provided in other file.
2. Design Basis
2.1 Pipeline Design Parameter.
Corrosion coating thickness
tcorr := 4mm
Outer diameter
Ds := 24in = 609.6 mm
2.2 Material Properties
3
Steel density
s := 490pcf = 7.849 10 kg m
Corrosion coating density
corr := 80pcf
Concrete coat density
cc := 190pcf = 3.044 10 kg m
Modulus elasticity
E := 207000MPa = 3.002 10 psi
Coefficient of thermal expansion
:= 11.7 10
Structural damping
:= 0.126
Poisson ratio
:= 0.3
Pipeline material
API5L_Gr_X := 52
6 1
SMYS :=
290MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 42
317MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 46
359MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 52
386MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 56
414MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 60
448MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 65
483MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 70
SMYS = 3.59 10 Pa
SMTS :=
414MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 42
SMTS = 4.55 10 Pa
434MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 46
455MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 52
490MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 56
517MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 60
531MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 65
565MPa if API5L_Gr_X = 70
Manufacturing process
Seamless = 1
UO; TRB; ERW = 2
UOE = 0.85
PF := 1
2.4 Environmental Parameter
PC := 3
Pipeline condition
Installation = 1
Hydrotest = 2
Operation = 3
Highest astronomical tide
HAT := 0.53m
Lowest astronomical tide
LAT := 0.61m
Water depth
dmax := 22.708m + HAT
dmax = 23.238 m
dmin := 14.935m + HAT
dmin = 15.465 m
5 2
Kinematic viscosity of seawater
v := 1.076 10
ft sec
Seawater density
sw := 64pcf = 1.025 10 kg m
( Gravity)
g = 9.807 m s
Current at 90% water depth
Ur :=
0.45m s
0.48m s
Significant wave height
Hs :=
1
1
if PC = 1 PC = 2
Ur = 0.48
Ts :=
if PC = 3
1.8m if PC = 1 PC = 2
Hs = 3.6 m
3.6m if PC = 3
Significant Wave period
6.3s if PC = 1 PC = 2
8.3s if PC = 3
Ts = 8.3 s
2.5 Pipeline Operational Data
3
cont :=
Content density
0kg m
if PC = 1
3
1025kg m
if PC = 2
57.522pcf if PC = 3
P o :=
Design pressure
0psi if PC = 1
1350psi if PC = 3
1.5 1350psi if PC = 2
Design temperature
Td := 140F
Seabed temperature
Tsw := 23 C
Corrosion allowance
Ca := 2.54mm
External pressure
P e.max := sw g dmax
P e.max = 2.336 10 Pa
P e.min := sw g dmin
P e.min = 1.555 10 Pa
Axial pressure
F a := 0N
Bending stress
M := 72% SMYS
M = 258.48 MPa
2.6 Soil Parameter
Soil type
1 = sand
2 = clay
soil := 2
3
Medium density of sand
sand := 1860kg m
Medium density of clay
clay := 326.309kg m
Medium density of soil
soil :=
sand if soil = 1
clay if soil = 2
Undrained shear stress
S u := 2kPa
soil = 326.309
kg
3
2.8 Design Factor
Internal pressure factor design
ASME B31.4
F 1 := 0.72
API RP 1111
fd := 0.72
Weld joint factor
ASME B31.8
Ee := 1
API RP 1111
fe := 1
Temperature derating factor
ASME B31.8
T := 1
API RP 1111
ft := 1
Collapse factor
ASME B31.8
API RP 1111
f0 := 0.7
Ovalitas
DNV OS F101
fo := 0.005
Propagation buckling design factor
ASME B31.8
API RP 1111
fp := 0.8
Local buckling factor
DNV 1981
Longitudinal stress usage factor
xp := 0.72
Hoop stress usage factor
yp := 0.92
Material resistance factor
m := 1.15
Incidental factor
inc := 1.05
3. Wall Thickness Selection
3.1 Internal Pressure Collapse Criteria
3.1.1 Internal Pressure Contaiment ASME B31.8 Design Criteria
tint.ipc.ASME := 11mm
Initial wall thickness
( Po Pe.max)
Hoop stress
y :=
Internal pressure contaiment criteria
IPC_ASME_Criteria :=
2 tint.ipc.ASME
Ds
y = 2.514 10 Pa
"accepted" if y F1 SMYS
"not accepted" otherwise
IPC_ASME_Criteria = "accepted"
Safety factor
SFipc.ASME :=
F1 SMYS
y
SFipc.ASME = 1.028
3.1.2 Internal Pressure Contaiment API RP 1111 Design Criteria
Initial steel wall thickness on hydrotest condition
Initial steel wall thickness
tint.ipc.API := tint.ipc.API.h + Ca
tint.ipc.API.h := 16mm
tint.ipc.API = 18.54 mm
3.2 External Pressure Collapse
External pressure (Pe) on hydrotest condition is smaller than internal pressure (Pi), hence wall thickness selection
calculation on external pressure collapse criteria isn't done in this condition.
3.3 Local Buckling Criteria
External pressure (Pe) on hydrotest condition is smaller than internal pressure (Pi), hence wall thickness selection
calculation on local buckling criteria isn't done in this condition.
3.4 Propagation Buckling Criteria
External pressure (Pe) on hydrotest condition is smaller than internal pressure (Pi), hence wall thickness selection
calculation on API RP 1111 propagation buckling criteria isn't done in this condition.
3.5 Selected Wall Thickness
This following t.int.ins is selected wall thickness from hydrotest condition.
The final selected wall thickness is obtain from comparing this initial wall thickness eith other initial wall thicness
from installation and operation condition.
tint.op := max tint.ipc.ASME , tint.ipc.API
tint.ins := 9mm
(Obtained from installation condition calculation)
tint.hyd := 17mm
(Obtained from hydrotest condition calculation)
tint.op := 18.54mm
Selected wall thickness from calculation
tcalc := max tint.ins , tint.hyd , tint.op
Selected wall thickness
Pipe OD 6.625" WT 0.75"
tcalc = 0.73 in
ts := 0.75in
4. On Bottom Stability Analysis
4.1 Vertical Stability
4.1.1 Pipe Weight Calculation
Initial concrete coating thickness
tint.cc := 0mm
Internal diameter
ID := Ds 2 ts Ca
ID = 576.58 mm
Corrosion coating diameter
Dcorr := Ds + 2 tcorr
Dcorr = 617.6 mm
Total outer diameter
Dtot := Ds + 2 tcorr + 2 tint.cc
Dtot = 617.6 mm
Steel pipe mass / length
2
2
mst := Ds ID s
kg
mst = 241.454
m
Corrosion coating mass / length
2
2
mcorr := Dcorr Ds corr
kg
mcorr = 9.881
m
Concrete coat mass / length
2
2
mcc := Dtot Dcorr cc
kg
mcc = 0
m
Content mass / length
2
mcont := ID cont
4
kg
mcont = 240.582
m
Added mass;
Dicplaced water; Buoyancy / length
B :=
4 tot sw
B = 307.118
Total pipe mass / length
mtot := mst + mcorr + mcc + mcont B
kg
m
kg
mtot = 184.8
m
Total pipe weight / length
3 N
Wtot = 1.812 10
m
Wtot := mtot g
4.1.2 Vertical Stability Calculation
Vertical stability
VS :=
( mtot + B)
VS = 1.602
B
Vertical_Stability :=
"accepted" if VS > 1.1
"not accepted; enlarge concrete coating thickness" if VS 1.1
Vertical_Stability = "accepted"
4.2 Lateral Stability
4.2.1 Hydrodynamics Parameter Calculation
4.2.1.1 Wave-Induced Particle Velocity
Spectral peak period
Tp := 1.05 Ts
Periode
referensi
Tn :=
Peakedness
parameter
:=
Tp = 8.715 s
dmin
Tn = 1.256 s
g
Tp
Hs
:=
= 4.593
0.5
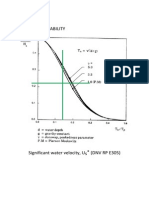
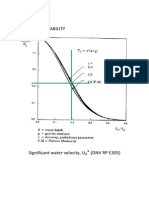
5 if 3.6
sec
= 3.3
m
1 if 5
sec
m
3.3 otherwise
Figure 4.1 Significant water velocity, Us * (DNV RP E305)
Water particle velocity
(Wave induced)
Tn
= 0.144
Tp
Us :=
0.31 H s
Tn
Us = 0.889
m
s
4.2.1.2 Zero-Up Crossing Period
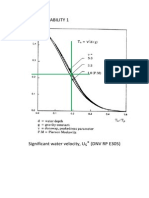
Figure 4.2 Zero-up crossing period, Tu (DNV RP E305)
Zero-up crossing period
Tu := 0.95 Tp
Tu = 8.279 s
4.2.1.3 Average Velocity on Pipeline
Velocity on 90% depth
Ur = 0.48
m
s
The amount of current passing through the pipe is affected by the type of seabed soil in which the pipe is laid.
In terms of the soil is clay soil, the soil roughness is negligible, so in this case U D = Ur
UD := Ur
UD = 0.48
m
s
4.2.1.4 Hydrodynamics coefficient
Reynold's number
( UD + Us)
Re :=
v
Wave - current velocity ratio
M :=
Dtot
Re = 8.456 10
UD
M = 0.54
Us
Drag coefficient
CD :=
1.2 if Re < 5 10
CD = 0.7
1.3 if 5 10 < Re < 1 10
Re 105
1.53
if 1 10 < Re < 2.5 10
0.7 otherwise
Lift coefficient
CL :=
1.5 if Re < 5 10
4
CL = 0.7
5
1 if 5 10 < Re < 1 10
Re 105
1.2
if 1 10 < Re < 2.5 10
0.7 otherwise
Inertia coefficient
CM :=
2 if Re < 2.5 10
Re 105
2.5
1.5 otherwise
CM = 1.5
5
if 2.5 10 < Re < 5 10
4.2.2 Seabed Soil Factor
Figure 4.4 Recommended friction factors for clay (DNV RP E305)
ratio :=
Soil friction
factor
Dtot Su
ratio = 0.682
mtot g
:= 1.3
4.2.3 Hydrodynamics Force
Wave particle acceleration
Us
As := 2
Tu
Lift force
fL.( ) :=
1 sw
2
D tot CL Us cos( ) + UD
2 g
Drag force
fD.( ) :=
1 sw
2
Dtot CD Us cos( ) + UD
2 g
Inertia force
m
As = 0.674
2
s
fI.( ) :=
Dtot
4
sw
g
CM As sin( )
4.2.4 Lateral Stability Calculation
4.2.4.1 Calibration Factor
Figure 4.3 Calibration factor, Fw, as function of K and M (DNV RP E305)
Keulegan-Carpenter number
Calibration factor
K :=
Us Tu
K = 11.913
Dtot
F w := 1.15
4.2.4.2 Lateral Stability Check
phase angle range
i := 0 .. 180
i := i deg
Required submerged weight
ms.( ) :=
( fD.( ) + fI.( ) ) + fL.( )
Fw
mreq.( ) := max ms.( )
mreq.( ) = 89.618
SFw :=
LATERAL STABILITY
LS :=
kg
m
mtot
mreq.( )
SFw = 2.062
"accepted" if SFw 1
"not accepted, enlarge concrete coating thickness" if SFw < 1
LS = "accepted"
5. Free Span Analysis
5.1 Static Analysis
Static span length
Lfr.st := 60m
Total pipe weight / length
3 N
Wtot = 1.812 10
m
Drag force
F D = 415.131
F I = 310.696
F I := max fI.( ) g
Inertia force
Support type
F D := max fD.( ) g
1 = pinned - pinned
2 = fixed - pinned
3 = fixed - fixed
( End condition constant )
N
m
N
m
support := 1
Cfr.st :=
Cfr.st = 8
8 if support = 1
10 if support = 2
12 if support = 3
Distributed pipe weight
Wd :=
Area moment of inertia
I :=
Section modulus
Z :=
Longitudinal stress
Wtot + F D + F I
D 4 ID4
64 s
I = 1.354 10
Z = 4.441 10
Ds
2
l :=
3 N
Wd = 1.885 10
m
Wd Lfr.st
2
8
l = 1.91 10 Pa
Cfr.st Z
y = 2.514 10 Pa
Hoop stress
Equivalent stress
e :=
Allowable stress
allow :=
l + y
e = 3.158 10 Pa
( 0.72 SMYS) if PC = 1
( 0.9 SMYS ) if PC = 2 PC = 3
8
allow = 3.231 10 Pa
Static span criteria
static_span_criteria :=
"Static span length accepted" if e < allow
"Minimize static span length" otherwise
static_span_criteria = "Static span length accepted"
Safety factor
SFfr.st :=
allow
e
( SFfr.st) = 1.023
5.2 Dynamic Analysis
5.2.1 Critical Span Length
5.2.1.1 Stability Parameter
Effective mass
meff := mst + mcorr + mcc + mcont + B
kg
meff = 799.036
m
Stability parameter
Ks :=
2 meff
sw Dtot
Ks = 0.515
5.2.1.2 Reduced Velocity
Figure 5.1 Reduced velocity for cross-flow oscillations based on the reynolds number.
Figure 5.2 Reduced velocity for inline oscillations based on the stability parameter
5
Reynold's number
Re = 8.456 10
Reduced velocity for cross-flow
oscillation
Vr.cf := 5.9
Reduced velocity for inline oscillation
Vr.in := 1.4
5.2.1.3 Critical Span Length
2
Cfr.dy :=
End condition constant
Cfr.dy = 9.87
if support = 1
15.5 if support = 2
22 if support = 3
Critical span length for cross-flow
motion
Lfr.dy.cf :=
Critical span length for inline motion
Lfr.dy.in :=
Critical span selected for dynamic
analysis criteria
Cfr.dy Vr.cf Dtot
2 U s + U r
Cfr.dy V r.in Dtot
2 Us + U r
E I
Lfr.dy.cf = 49.764 m
meff
E I
Lfr.dy.in = 24.241 m
meff
Lfr.dy := min Lfr.dy.cf , Lfr.dy.in
Lfr.dy = 24.241 m
5.2.2 Dynamic Stress
5.2.2.1 Vortex Shedding Frequency
Figure 5.3 Strouhal's number for circular cylinder as function of Reynold's number
5
Re = 8.456 10
Reynold's number
Strouhal's number
Vortex shedding frequency
fv :=
S t Us + Ur
S t := 0.2
fv = 0.443
D tot
1
s
5.2.2.2 Pipeline Natural Frequency
Pipeline natural frequency
Pipe frequency criteria
fn :=
Cfr.dy
2
E I
4
meff Lfr.dy
pipe_frequency_check :=
0.5
fn = 1.583
1
s
"pipeline critical span accepted" if fv 0.7fn
"redesign pipe" otherwise
pipe_frequency_check = "pipeline critical span accepted"
DEFINITION
pcf :=
lb
3
ft
year
C
:= :=
K 31536000sec
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Report of Lifting Beam DesignDocument5 pagesReport of Lifting Beam Designnarutothunderjet216100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Student WorksheetsDocument24 pagesChapter 13 Student WorksheetsGhazi Dally100% (1)
- Risk Register ExampleDocument4 pagesRisk Register ExampleFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Design-InstallationDocument19 pagesPipeline Design-InstallationFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Design-InstallationDocument19 pagesPipeline Design-InstallationFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Load Dermaga BBMDocument31 pagesLoad Dermaga BBMFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Grafik1 On Bottom StabilityDocument7 pagesGrafik1 On Bottom StabilityFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- GRAFIKDocument1 pageGRAFIKFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- PC Spun PilesDocument2 pagesPC Spun PilesFaridah Zahra100% (1)
- Procurement: Kode Pekerjaan Sub Pekerjaan A1Document3 pagesProcurement: Kode Pekerjaan Sub Pekerjaan A1Faridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- GRAFIKDocument1 pageGRAFIKFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- GRAFIKDocument1 pageGRAFIKFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- GRAFIKDocument1 pageGRAFIKFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- OBS InstallationDocument6 pagesOBS InstallationFaridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - Tugas 5Document19 pagesMathcad - Tugas 5Faridah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Lift Load Distribution and Structural Load DistributionDocument3 pagesLift Load Distribution and Structural Load DistributionPrajeesh RajNo ratings yet
- Bilangan Tak BerdimensiDocument12 pagesBilangan Tak Berdimensimuhammad lukmanNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine DesignDocument58 pagesWind Turbine DesignAdeel Anjum50% (2)
- Wax Test MethodsDocument10 pagesWax Test MethodsJrg Trjlo100% (1)
- Midterm Study Guide 08Document2 pagesMidterm Study Guide 08carolynshinNo ratings yet
- 15 - krohne-DK46-800Document24 pages15 - krohne-DK46-800meritnoorNo ratings yet
- Depressuring & BDVDocument9 pagesDepressuring & BDVAmir Ali Haddadi100% (1)
- Basic Oilfield CalculationsDocument17 pagesBasic Oilfield CalculationslaaliautoNo ratings yet
- Energy, Processes and CyclesDocument51 pagesEnergy, Processes and CyclesJodel SerranoNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration System For Food StoragesDocument46 pagesRefrigeration System For Food StoragesFiseha Mengisteab100% (2)
- Fluid Mechanics (He304) : Department of Harbour and Ocean EngineeringDocument21 pagesFluid Mechanics (He304) : Department of Harbour and Ocean EngineeringkhumisoNo ratings yet
- Pumps - Dairy Processing HandbookDocument6 pagesPumps - Dairy Processing HandbookMeera NairNo ratings yet
- File 5f2a7cecb9b64Document32 pagesFile 5f2a7cecb9b64GovindharajNo ratings yet
- Hot Wire Anemometer LengkapDocument97 pagesHot Wire Anemometer LengkapAhmad FaizalNo ratings yet
- 2.properties & Testing MethodsDocument87 pages2.properties & Testing MethodsSamuel EsparteroNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamic Evaluation On Formula SAE VehiclesDocument9 pagesAerodynamic Evaluation On Formula SAE Vehiclesmikael bezerra cotias dos santosNo ratings yet
- 64bestPaper1Uniaxial True Stress-Strain After NeckingDocument12 pages64bestPaper1Uniaxial True Stress-Strain After NeckingBrian ForsmanNo ratings yet
- Tugas Uts Termodinamika - Syarif KurrahmanDocument3 pagesTugas Uts Termodinamika - Syarif KurrahmanSyarif KurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Minimum Weight Design of Sandwich Beams With Honeycomb Core of Arbitrary DensityDocument21 pagesMinimum Weight Design of Sandwich Beams With Honeycomb Core of Arbitrary DensitySri PupNo ratings yet
- 3a Liquid Liquid Phase EquilibriumDocument30 pages3a Liquid Liquid Phase EquilibriumAbdulrahim SegirNo ratings yet
- Isrm SM Triaxial Compressive Strength - Revised - 1983Document6 pagesIsrm SM Triaxial Compressive Strength - Revised - 1983Evandro SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Bending Moment and Shear ForceDocument13 pagesBending Moment and Shear ForceYixiang TanNo ratings yet
- Asme PTC 19.5 With ExplanationDocument4 pagesAsme PTC 19.5 With ExplanationRoi OcoNo ratings yet
- Cooling TowerDocument10 pagesCooling TowerSalmanAslamGondalNo ratings yet
- Design of Riveted JointsDocument12 pagesDesign of Riveted JointsK ULAGANATHAN100% (1)
- Pre Stressing Wire GBDocument6 pagesPre Stressing Wire GBHayder AlsalihNo ratings yet
- Modul 3 Strain Measurement v2 PDFDocument11 pagesModul 3 Strain Measurement v2 PDFFachrudin HanafiNo ratings yet
- Heat and MassDocument13 pagesHeat and MassMohammed AliraqiNo ratings yet