Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Think Link Ecg Notes: Normal Sinus Rhythm at 70 Beats/min
Uploaded by
Willington CuaresmaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Think Link Ecg Notes: Normal Sinus Rhythm at 70 Beats/min
Uploaded by
Willington CuaresmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Think Link
ECG NOTES
What is your Nursing Management?
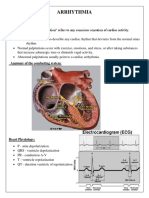
Electrical System of the Heart
Pulmonary Embolism
Atrial Fibrillation
Assess the patient.
What is the Drug of choice?
Atropine Sulfate
Sinus Tachycardia at 129 beats/min
Causes:
Basic ECG Interpretation and
NursingManagement
Normal Sinus Rhythm at 70 beats/min
Atrial Rate of 400 600 beats per minute
No identifiable P Wave
Underlying heart disease
Alcoholism
Infection
Stress
Causes:
Exercise, pain, fever, hypotension
Myocardial Ischemia, CHF, Anemia Hyperthyroidism,
Theophylline , Epinephrine, Caffeine
What is its significance?
Embolus formation
High risk for?
Pulmonary Embolism
What is your Nursing Management?
What are the Treatments?
Find First the cause
What is the Drug of Choice?
Beta Blockers
Atrial Flutter
All the measurement are within the normal range
Understanding your Normal Rhythm is very Important.
Doing a quick Count, The rhythm of the Patient is 70 beats/ min
Cardioversion- synchronizes electric cardioversion
IV ibutilide (corvert)- chemical cardioverion
Catheter ablation
What are the drugs to be given?
Verapamil,( vasodilation, prolonged AV node
conduction time)
Diltiazem,( slows AV node, Decrease contractility)
Digoxin, (Slows AV node conduction)
Heparin, (warfarin) blood thinner
Sinus Bradycardia at 55 beats/ min
What if the PRI is prolonged?
What are the causes of atrial flutter?
Causes:
Parasympathomimetic drug
Increase Intracranial pressure
Myocardial Infarction (inferior)
Normal with trained athletes
P-R Interval 0.12- 0.20 sec.
QRS
- Less than 0.10 sec.
Q-T interval Under 38 sec.
Think Link: My Self Review Guide For Nurses
Saw-tooth flutter waves
Atrial rate of 240 400 beats per minute
No identifiable P wave
Significance:
Decrease Cardiac Output
Decrease Blood Pressure
Angina
Change Level of consciousness
Answer. Coronary artery disease,
Hypertension,
Mitral valve disorder
Cardiomyopathy
Cor Pulmonale
Pulmonary heart disease
What is its significance?
Embolus formation
High risk for?
www.thinklink.weebly.com
Heart Block. A- V Block
Can occur as a results of structural changes in the
conduction system.
Prolonged PR interval
Normal PR interval ( 0.12 - 0.20 Sec. )
Causes:
Tumors
Myocardial Infarction
Coronary Artery Disease,
Infections of the heart
Toxic effect of Digitalis
Think Link
ECG NOTES
Digitalis Toxicity
o
o
Irregular heart beat
Asymptomatic
2nd degree block (2:1) Wenckebach
Associated with heart blocks
Check Pulse Rate (Toxicity Rate)
< 60 bpm for adult
< 80 bpm for child
< 100 bpm for neonatal
Evaluation of Digitalis Level
Therapeutic level
0.9-1.2 ng/mL
Spike is the term use and can be seen at the ECG
For the use of Pacemaker
Treatment of choice for
2nd and 3rd degree AV block
Pacemaker ( Spike )
Atrial pacing
(2:1) 2 Pwave for every 1 set of QRS
2nd degree block (2:1, 3:1)
Toxic level
2.0 ng/mL
100% Ventricular-paced rhythm
Nausea, vomiting and seeing Halos around eyes (yellowGreen), Diplopia, Blurred Vision
Photophobia, Headache Drowsiness
(2:1 , 3:1) more than 2 Pwaves for every 1 set of QRS
Check potassium level (3.5 5.5 meq/L)
Hypokalemia can cause Digitalis toxicity
Give Potassium I.V or orally
Give Isuprel and Atropine Increase Heart Rate
High Fiber Diet ( constipation contributes to digitalis
toxicity )
3rd degree Complete Block
(unidentifiable)
Second degree AV- Block
is a block in which impulse reach
the ventricles but others do not
The results of this heart block
Hypotension
Siezure
Cerebral ischemia
Cardiac arrest
( unidentifiable ) The P wave has no correlation with the QRS )
st
1 degree block (1:1)
An increased irritability of the ventricles
Early ventricular Complexes
Life threatening PVCs
What are the symptoms of digitalis toxicity?
Bullets
Life Threatening Dysrhythmias
Premature Ventricular Contraction
Third Degree Heart Block( Complete Heart Block )
erratic heart rates where SA and AV
are beating independently
If there are more than 6 PVCs in one full minute
Multiform / multifocal PVC
R on T phenomena
Couplet ( Two Consecutive PVC )
Triplet ( Three consecutive PVC )
Chest Pain with increased Frequency of PVC
What is the first thing you need to do?
Pacemakers
P: Patients identification, Medic Alert Card
A: Aware your dentist
C: Check for signs of hiccups
E: Electric Machine are avoided
M: MRI are avoided
A: Avoid driving for the first 6 months
K: Keep a record of Pulse Rate.
E: Educate the patient in taking Pulse Rate 1 full
minute.
R: Report signs of dizziness, faintness fever,
Redness, swelling, soreness, blackouts or
Increase Pulse Rate
S- Stand Clear
Notify the Physician.
What Electrolyte you need to check?
Potassium ( hypokalemia can cause PVC ).
What do you need to prepare for Wide and Chaotic PVC?
Prepare Lidocaine.
What if it is a Narrow PVC (hypoxic PVC)?
Give Oxygen.
Failure to Sense
The rate set by the pacemaker has not reacted.
(1:1) 1 P wave for every 1 set of QRS
First degree AV-Block
SA continues to function but the
transmission of impulse fails
Think Link: My Self Review Guide For Nurses
Failure to Capture
There is no response after a spike
( impulse given by the pacemaker)
Failure to Discharge
Battery Failure, dislodge leads, wire fracture
During the Exam
www.thinklink.weebly.com
Think Link
ECG NOTES
Answer. Epinephrine
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular Fibrillation (Course)
Ventricular Fibrillation (Fine)
It is a repititve Firing of an irritable Ventricular Ectopy.
140 250 beats / minute or greater
Prepare for this question..
( elective procedure )
Awake/ Alert/ oriented
Informed Consent
Synchronized
10- 200 joules
Biphasic50- 100 joules
Monophasic
100- 200
You can use cardioversion with:
Is there a Pulse? Yes
Prepare oxygen, antidysrhythic drugs and prepare for a
synchronized cardioversion
Is there a Pulse? No
Electrical therapy
Cardioversion
no discernible waves or complexes to measure
the heart is fibrillating
no cardiac output
What are your interventions?
Prepare for Defibrillation and CPR
Answer. Assess the patient
Activate the EMS
Perform continues CPR
Defibrillation
Give Adrenalin and Antidysrhythmic Therapy
Torsades de Pointes
What is the drug of choice for ventricular fibrillation?
Answer. Epinephrine
Asystole
Atrial Tachycardia,
A.Flutter,
A.Fibrillation,
Ventricular Tachy. With pulse
PSVT, WPW
Defibrillation
Emergency procedure
Unconscious
Check for DNR
Asynchronized
300j CPR Assess rhythm360j CPR Assess rhythm360j CPR- Assess rhythm-
Common Interpretation that is being ask in
examination:
Prominent U wave:
Flat or inverted T wave:
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia
Peak T Wave:
Widened QRS:
Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia
Prolong ST interval:
Shortened ST segment:
Hypocalcemia
Hypercalcemia
Wide and Chaotic QRS:
Prolong PRI:
Shortened PRI:
PVC
AV Block
Junctional
Inverted T wave:
Hypoxia
Presence of Q wave:
Necrosis
S-T elevation:
Myocardial Injury
You can use defibrillation with:
Another type of ventricular tachycardia
Irregular rhythm with fast heart beat.
What is the main reason of Torsades de Pointes?
Answer. Hypomagnesaemia
What is the expected drug to be given?
Answer. Magnesium Sulfate
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular Tachycardia (pulseless )
Pulses Electrical Activity
Cardiac Arrest
No cardiac movement
No rhythm
Thank You for visiting:
www.thinklink.weebly.com
For Online group review discussion
Log on:
What is your first intervention?
http://xat.com/ThinkLinkRevieweeCommunity
Answer. Assess the patients responsiveness before
checking the machine
Emir Kahn R. Bautista R.N.
(Review Specialist)
Are you allowed to defibrillate the patient?
Answer. No! You cannot shock a shocked heart
What is the drug of choice?
Think Link: My Self Review Guide For Nurses
www.thinklink.weebly.com
You might also like
- Sample Medical Guidelines: ACLS-BradycardiaDocument2 pagesSample Medical Guidelines: ACLS-BradycardiaCheewin KhawprapaNo ratings yet
- ECG Dysrhthmias IIIDocument31 pagesECG Dysrhthmias IIIAmani KayedNo ratings yet
- Life Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementDocument40 pagesLife Threatening Arrhythmia and ManagementRuki HartawanNo ratings yet
- Emergency in Medicine 2012Document202 pagesEmergency in Medicine 2012micheal1960No ratings yet
- Arrhythmia: PalpitationDocument36 pagesArrhythmia: PalpitationHala BahaaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrythmias in The ED Menbeu Edited From AnaDocument106 pagesCardiac Arrythmias in The ED Menbeu Edited From AnaTemesgen Geleta100% (1)
- Supraventricular ArrhythmiasDocument56 pagesSupraventricular ArrhythmiasGading AuroraNo ratings yet
- Management of Cardiac Arrhytmia in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)Document34 pagesManagement of Cardiac Arrhytmia in Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)rhezzaagxxNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (Acls) Part Ii: ACP 202 Module 6Document32 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life Support (Acls) Part Ii: ACP 202 Module 6MoeNo ratings yet
- Departemen Kardiologi FK USU RSUP. H. Adam Malik MedanDocument64 pagesDepartemen Kardiologi FK USU RSUP. H. Adam Malik MedanBonitavanyNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (Acls)Document45 pagesAdvanced Cardiovascular Life Support (Acls)Erinne DefrianiNo ratings yet
- Basic Arrythmias: Prof. Maximin A. Pomperada, RN, MNDocument70 pagesBasic Arrythmias: Prof. Maximin A. Pomperada, RN, MNRellie CastroNo ratings yet
- Med-Surge Study GuideDocument39 pagesMed-Surge Study Guidefbernis1480_11022046No ratings yet
- 5-Approach To PalpitationsDocument103 pages5-Approach To PalpitationsEverythingNo ratings yet
- Allergy and Immunology: Immunodeficiency 10 Warning Signs of ImmunodeficiencyDocument24 pagesAllergy and Immunology: Immunodeficiency 10 Warning Signs of Immunodeficiencyacque100% (2)
- Arrhythmias Sherry Vickers, RN, MSN, CCRNDocument9 pagesArrhythmias Sherry Vickers, RN, MSN, CCRNSydney DeringNo ratings yet
- Approach To PalpitationsDocument74 pagesApproach To PalpitationsDarawan MirzaNo ratings yet
- Ngaji Arrythmia Cordis 3Document122 pagesNgaji Arrythmia Cordis 3Dhita Dwi NandaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (Acls) Part Iii: ACP 202 Module 6Document39 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life Support (Acls) Part Iii: ACP 202 Module 6MoeNo ratings yet
- Basic Echocardiography, MantapDocument54 pagesBasic Echocardiography, MantapDr Edi Hidayat50% (2)
- CardioDocument9 pagesCardioVirgilio Reyes ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 7 - Arrhythmias: Lecture OutlineDocument6 pagesCardiology 7 - Arrhythmias: Lecture Outlineمحمد احمد محمدNo ratings yet
- Critical Care NursingDocument159 pagesCritical Care NursingJoy Jarin50% (2)
- Cardiac - Potpourri Rev 2015Document80 pagesCardiac - Potpourri Rev 2015Sanaz NikiNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome EditedDocument38 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome EditedSurgicalgownNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument75 pagesShockaulianmediansyahNo ratings yet
- Topic: Cardiac Arrest Megacode: MD Khairulamin AS Nursing Lecturer PAPRSB Institute of Health Sciences UBDDocument38 pagesTopic: Cardiac Arrest Megacode: MD Khairulamin AS Nursing Lecturer PAPRSB Institute of Health Sciences UBDulipah100% (2)
- Interesting ECG Sharing: Ms. Yiu Sau-Chi, GigiDocument49 pagesInteresting ECG Sharing: Ms. Yiu Sau-Chi, GigiCarmen FongNo ratings yet
- Intern Survival Guide (UIC)Document51 pagesIntern Survival Guide (UIC)medstick100% (1)
- Supplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Document14 pagesSupplementary Material 4.3 Cardiac Rhythm Disorders-2Andrea Love PalomoNo ratings yet
- Synthesis: History Report SBAR Complete PA Know Your Patho!!! Don't Get Caught W/drawersDocument30 pagesSynthesis: History Report SBAR Complete PA Know Your Patho!!! Don't Get Caught W/drawersmmcgee002No ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) : By: Diana Blum MSN Metropolitan Community College Nursing 2150Document16 pagesAdvanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) : By: Diana Blum MSN Metropolitan Community College Nursing 2150Vikneswara SoorianarayananNo ratings yet
- Ecg in Emergency: Adi SulistyantoDocument41 pagesEcg in Emergency: Adi Sulistyantomech_pilot2203No ratings yet
- Advance Cardiac SuppDocument32 pagesAdvance Cardiac SuppVijith.V.kumarNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms SlideDocument26 pagesACLS Algorithms SlidehrsoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Case StudyDocument5 pagesModule 1 Case Studyapi-564432337100% (1)
- Cardiac ArrestDocument14 pagesCardiac ArrestCloudySkyNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia, Pericardial and Myocardial Diseases (DR Praveen) 2Document44 pagesArrhythmia, Pericardial and Myocardial Diseases (DR Praveen) 2hashini1997nisansalaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Library Small GroupDocument33 pagesCardiovascular Library Small GroupSarah SabtiNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmia 6 YrDocument72 pagesArrhythmia 6 YrPiyush MalikNo ratings yet
- ECG-Arrhythmias: Tiang Soon WeeDocument63 pagesECG-Arrhythmias: Tiang Soon WeeasdasdasdasNo ratings yet
- Palpitations: DR Polamuri Tabitha PG First YrDocument37 pagesPalpitations: DR Polamuri Tabitha PG First YrNinaNo ratings yet
- Electroconvulsive Therapy: An UpdateDocument39 pagesElectroconvulsive Therapy: An UpdateAnonymous 83o62cNo ratings yet
- Holter Monitoring: Dr. Kazi Alam NowazDocument19 pagesHolter Monitoring: Dr. Kazi Alam NowazRadison sierraNo ratings yet
- ACLS Pitfalls Osce For ExternDocument35 pagesACLS Pitfalls Osce For ExternKrittin NaravejsakulNo ratings yet
- Basic Dysrhythmias: Scott Prewitt, RN, MSN, APRN-BCDocument42 pagesBasic Dysrhythmias: Scott Prewitt, RN, MSN, APRN-BCtuffie85No ratings yet
- Acls Study Guide 2016 For Pulse 2016Document8 pagesAcls Study Guide 2016 For Pulse 2016eng78ineNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 036 Arrhythmias ClassDocument129 pagesChapter - 036 Arrhythmias ClassWisdomIsMiseryNo ratings yet
- Perfusion, Class 11 ReviewedDocument45 pagesPerfusion, Class 11 ReviewedMelissa GPNo ratings yet
- Dysrhythmias NotesDocument23 pagesDysrhythmias NoteskmimmackNo ratings yet
- ACLS-Pediatric Wide Complex Tachycardia: Sample Medical GuidelinesDocument2 pagesACLS-Pediatric Wide Complex Tachycardia: Sample Medical GuidelinesFebrialitaFatoniNo ratings yet
- Ecg 2Document10 pagesEcg 2AANo ratings yet
- Penyakit Kardiovaskular Yang Sering DijumpaiDocument121 pagesPenyakit Kardiovaskular Yang Sering Dijumpaiandikaagus13No ratings yet
- Acute Miocard InfarkDocument32 pagesAcute Miocard InfarkhansNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument50 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsamirNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiaDocument31 pagesArrhythmiaAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms 2011 PDFDocument6 pagesACLS Algorithms 2011 PDFmaya_fitrianaNo ratings yet
- 15 Walters LLSA ArticlesDocument33 pages15 Walters LLSA ArticlesericNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 IntersubjectivityDocument32 pagesChapter 6 IntersubjectivityWillington Cuaresma67% (3)
- Biological Science Major - Part 1Document9 pagesBiological Science Major - Part 1Willington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Manage Chest TubesDocument75 pagesManage Chest TubesWillington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Inpt Nursing Adult AssessmentDocument8 pagesInpt Nursing Adult AssessmentWillington Cuaresma100% (1)
- Paternalism Justice Confidentiality VeracityDocument5 pagesPaternalism Justice Confidentiality VeracityWillington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Euthanasia - and NonmaleficenceDocument7 pagesEuthanasia - and NonmaleficenceWillington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Virtue EthicsDocument2 pagesVirtue EthicsWillington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Pharmacy NotesDocument151 pagesComprehensive Pharmacy NotesWillington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- 1.CD Control Program: RD RDDocument18 pages1.CD Control Program: RD RDKen Mark CatubigNo ratings yet
- Law Rights and JurisprudenceDocument6 pagesLaw Rights and JurisprudenceWillington CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Glucose Tolerance TestDocument4 pagesGlucose Tolerance TestNikhil KanikaNo ratings yet
- جورنال جاهزDocument4 pagesجورنال جاهزasrd ramiNo ratings yet
- Doenges, Et. Al, (2008) - Nurse's Pocket Guide. 11 Edition. F.A. Davis Company. P. 385Document3 pagesDoenges, Et. Al, (2008) - Nurse's Pocket Guide. 11 Edition. F.A. Davis Company. P. 385Theresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- Post Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis PPV MF A Case Report of A Patient Transplanted After An Adverse Reaction To Covid VaccinationDocument5 pagesPost Polycythemia Vera Myelofibrosis PPV MF A Case Report of A Patient Transplanted After An Adverse Reaction To Covid VaccinationLord 11No ratings yet
- Skin Care and Management of Pressure UlcerDocument24 pagesSkin Care and Management of Pressure UlcerchellczyNo ratings yet
- Prognostic Factors in Tuberculosis Related Mortalities in Hospitalized PatientsDocument7 pagesPrognostic Factors in Tuberculosis Related Mortalities in Hospitalized PatientsAshok PanjwaniNo ratings yet
- 7.1. Anemia 2023Document30 pages7.1. Anemia 2023MichellyTjoaNo ratings yet
- Sabreen Ma K19Document396 pagesSabreen Ma K19Medical ReportNo ratings yet
- Guilford Child & Adolescent Psychology Chapter SamplerDocument97 pagesGuilford Child & Adolescent Psychology Chapter SamplerAdelaKočanBahtoNo ratings yet
- Stroke BrochureDocument2 pagesStroke Brochurenananana123No ratings yet
- Elevator Pitch James Baxter s2896471-3Document1 pageElevator Pitch James Baxter s2896471-3api-335944748No ratings yet
- A Short History of OnchocerciasisDocument12 pagesA Short History of OnchocerciasisAldo Sánchez100% (1)
- Primary Secondary SurveyDocument38 pagesPrimary Secondary SurveySyiema ZainalNo ratings yet
- Spitz Nevi Dan Nodular MelanomaDocument5 pagesSpitz Nevi Dan Nodular MelanomaMeta SakinaNo ratings yet
- Pes Cavus ....Document34 pagesPes Cavus ....Rupika Sodhi100% (2)
- 300+ TOP Digestive System MCQs and Answers PDF Quiz ExamDocument11 pages300+ TOP Digestive System MCQs and Answers PDF Quiz ExamMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- The Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaDocument4 pagesThe Colleges of Medicine of South AfricaRichard100% (1)
- PUERPERAL SEPSIS CoverDocument9 pagesPUERPERAL SEPSIS CoverKerpersky LogNo ratings yet
- v19 n4Document178 pagesv19 n4Jaa DeeNo ratings yet
- PE - Module 5Document8 pagesPE - Module 5Hanah Grace GomezNo ratings yet
- Weber, J. and Kelley, J. (2018) Health Assessment in Nursing. Sixth EditionDocument18 pagesWeber, J. and Kelley, J. (2018) Health Assessment in Nursing. Sixth EditionClare Collado100% (1)
- ENT DefinationDocument22 pagesENT Definationيدا واحدةNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities For Oxygen AdministrationDocument3 pagesNursing Responsibilities For Oxygen AdministrationJahseh WolfeNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease - UpToDateDocument23 pagesTreatment of Chronic Graft-Versus-Host Disease - UpToDatemihaela popescuNo ratings yet
- Applied Biology (PERSONALIZED MEDICINE)Document9 pagesApplied Biology (PERSONALIZED MEDICINE)HAZEL LEELA A P RICHARDNo ratings yet
- Wesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesDocument2 pagesWesleyan: College of Nursing and Allied Medical SciencesShane Aileen AngelesNo ratings yet
- Objective Testing of Pelvic Floor FunctionDocument2 pagesObjective Testing of Pelvic Floor FunctionSteven ElvyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Inguinal RegionDocument24 pagesAnatomy of The Inguinal RegionAhmed ShehadaNo ratings yet
- 00 H&N NotesDocument16 pages00 H&N NotesHythem HashimNo ratings yet
- Anu Omr Long CaseDocument29 pagesAnu Omr Long CaseAnurtha AnuNo ratings yet