Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urban Air Quality
Uploaded by
rustam222Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urban Air Quality
Uploaded by
rustam222Copyright:
Available Formats
Urban Air Quality
Aims
To explain:
Importance of monitoring and managing air quality
Problems with monitoring air quality
Parameters that should be included in monitoring of urban air
Locations to monitor urban air quality
Actions to tackle and improve local air quality
Importance of monitoring and managing air quality
There are various range of air pollutants in the outdoors, which are known to or
suspected of causing adverse effects to the human health and also to the environment.
Since the 1950s research has been undertaken to find out the effects of outdoor
pollutants on health, such as studies by APHEA (air pollution on health: European
Approach). Their studied was based on a database from ten different European
countries with a population of over 25 million in 15 different cities and their data
consisted of daily measurements of SO2, suspended air particles, NO2 and ozone (O3).
They concluded that there was a correlation between deaths and the amount of both
NO2 and O3. Where a 50g/m3 increase in NO2 and O3 was associated with 1.3%
increase in the number of daily deaths due to NO2 and 2.9% increase in the number of
daily deaths due to O3.
Air pollution is not limited to just having adverse effects on human health but also on
various other things such as:
Vegetation As the level of pollutant exposure to vegetation increase the
effects of it become more severe such as biochemical alterations,
physiological response, visible symptoms, and finally death. The major
pollutants that are toxic to plants are ozone, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide,
fluorides, and peroxyacetyl nitrate. And this will also have an economic
affect, which has been estimated to be between $1 - $5 billion in the United
States
This figure shows how increases pollutants effect vegetation in terms of
degree of injury.
Materials fundamental effect of pollutants on metals is corrosion. Which
causes changes in shape of the material due to loss from corrosion and also
changes in the materials properties.
Atmosphere - this can be noticed in very industrialized countries smog
covering the sky such as china, where you have a lot of power plants and
burning of fossil fuels
Parameters that should be included in monitoring of urban air
Sulphur
Nitrogen
Fine
Ozone
Carbon
Dioxide
Dioxide
Particles
monoxide
Effects
on
Human
Health
Narrowing
of airways
and the
feeling of
tightening
in chest
Respirator
y illnesses
and
increase in
the
likelihood
of lung
infection
Linked to
asthma
and
chronic
bronchitis
and long
term
exposure
can be
more fatal
Damage
and
irritation
to lungs
Cause
headache,
dizziness,
nausea and at
high levels
death by
depriving the
blood from
oxygen
Benzene
1,3 Butadiene
Carcinogeni
c substance
that can
cause
cancer of
blood
system
Also a
carcinogenic
which can
cause cancer
of the lymph
and also
blood system
This table shows the effects of various pollutants on human health
Problems with monitoring air quality
Reasons to why it is difficult to properly monitor air quality:
Wind the direction at which the pollutants travel is determined by the wind
direction, in particular air pollutant concentrations which are most sensitive to
it. But it is more complex than just this, such as getting wind direction shear,
which is a result of change in directions of the wind. And you also have
different wind speeds at different altitudes that also needs to be taken into
consideration. Wind speed has an effect to dilute pollutants continuously and
also affects dispersion rate
Turbulence Which is irregular movement of the wind. In which you very
rapid erratic movements that do not flow smoothly. This mixes polluted air
with relatively unpolluted air, which causes the polluted air to be at lower
concentrations
Extreme weather - Frequency or severity of extreme weather events can cause
an increase in the chance of flooding, high winds, leading to the displacement
of any Continuous automated monitoring probes, which can lead to
compromised results
Temperature Usually warmer temperatures increase the concentration of
pollutants.
This figure shows the movement of pollutants.
Locations to monitor urban air quality
The area for monitoring the air pollution is based on, what information it wants to
gather such as the type of pollutant, method used to analyse the air pollutants, and
what data will be used for.
Examples of places of monitoring air quality
In a Urban area residential ,commercial area cites, parks which are away
from trees, big streets, and open areas of a educational purpose, sports, or
recreation facilities
In a Suburban area this includes where there is large population, crops that
are sensitive to pollutants, and ecosystems.
In a Rural area points of sampling area near vegetation, natural ecosystems,
forests, or crops. Which are away from trees, buildings, and does not need to
be near habituated places such as factories.
In traffic stations which mainly located at traffic sites where you have
emissions coming from nearby traffics in roads, motorway, and highways
In Industrial station emissions mainly coming from industrial sources which
include power generations, incinerators, and waste treatment plants. Which
should be downwind to the nearest residential area
Background station This is placed where it is not influenced by nearby
pollution sites. This is so it can take an integrated contribution from all sources
Actions to tackle and improve local air quality
The best way to minimise or reduce pollution and improve air quality is by taking
green initiatives and focusing on sustainability. Such as by looking more into
renewable energy forms.
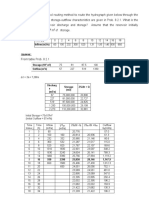
For example This table showing green initiatives:
References
Websites
http://uk-air.defra.gov.uk/air-pollution/effects
Book
Fundamentals of air pollution. Author vallero. Published by Elsevior. 2008
Book
Improving air quality in urban environments guidance for construction industry. By
Vina Kukadia and David Hall
You might also like
- WewewweweDocument1 pageWewewwewerustam222No ratings yet
- Few Things in A ThingDocument1 pageFew Things in A Thingrustam222No ratings yet
- WewefefefDocument1 pageWewefefefrustam222No ratings yet
- AQA Mathematics + Further Mathematics A-LevelDocument1 pageAQA Mathematics + Further Mathematics A-Levelrustam222No ratings yet
- Blast Effects On Buildings - GC Mays & PD SmithDocument68 pagesBlast Effects On Buildings - GC Mays & PD SmithGregory SimmonNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology Concepts and Water Budget EquationsDocument30 pagesEngineering Hydrology Concepts and Water Budget Equationsrustam222No ratings yet
- YeahhahdhDocument1 pageYeahhahdhrustam222No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Importance of Natural Resource Accounting in India: A Case Study On The Mineral and Energy ResourcesDocument9 pagesImportance of Natural Resource Accounting in India: A Case Study On The Mineral and Energy ResourcesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Essay On "Forestry Sector of Pakistan-An Overview"Document21 pagesEssay On "Forestry Sector of Pakistan-An Overview"Zainab QuddoosNo ratings yet
- Savanna Ecosystems Characterized by Open Canopies and Seasonal RainfallDocument24 pagesSavanna Ecosystems Characterized by Open Canopies and Seasonal RainfallAnjum Ansh KhanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development: Published Online: 09 July 2013Document2 pagesSustainable Development: Published Online: 09 July 2013ReynNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScreeningDocument11 pagesEnvironmental ScreeningSreedhar BhuduruNo ratings yet
- Elevating Sustainability Through PT Astra Agro's 2021 ReportDocument192 pagesElevating Sustainability Through PT Astra Agro's 2021 ReportQamar UddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2jezreel salomonNo ratings yet
- Agric ss2Document1 pageAgric ss2Jesse MosesNo ratings yet
- Soil Structure Evidence Synthesis ReportDocument35 pagesSoil Structure Evidence Synthesis ReportrezahosseinpourNo ratings yet
- PEST AnalysisDocument2 pagesPEST Analysism_tahir_saeed57270% (1)
- Philippine Waters - DEMODocument10 pagesPhilippine Waters - DEMORommel CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution and Dal LakeDocument3 pagesEnvironmental Pollution and Dal LakeYaqeen Ul Haq Ahmad SikanderNo ratings yet
- Mitsuru Osaki, Nobuyuki Tsuji (Eds.) - Tropical Peatland Ecosystems-Springer Japan (2016)Document633 pagesMitsuru Osaki, Nobuyuki Tsuji (Eds.) - Tropical Peatland Ecosystems-Springer Japan (2016)Natalia Cáceres100% (1)
- Soil and Water Conservation: Free E-BookDocument12 pagesSoil and Water Conservation: Free E-BookPrasun KumarNo ratings yet
- Applying local knowledge to wetland rehabilitationDocument13 pagesApplying local knowledge to wetland rehabilitationchazunguzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 38. Seabirds Contributors: Ben Lascelles (Convenor), Jake Rice (Lead Member and Editor of PartDocument17 pagesChapter 38. Seabirds Contributors: Ben Lascelles (Convenor), Jake Rice (Lead Member and Editor of PartAbhinavSinghNo ratings yet
- Lucrare de Examen La Disciplina Limba Straina IiDocument6 pagesLucrare de Examen La Disciplina Limba Straina IiTóth CsabiNo ratings yet
- Bustamante - NSTP100 Essay #9Document1 pageBustamante - NSTP100 Essay #9Jimin ParkNo ratings yet
- How biodiversity contributes to ecosystem sustainabilityDocument27 pagesHow biodiversity contributes to ecosystem sustainabilityLey Domingo Villafuerte GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Biomes Teachers PlanDocument29 pagesBiomes Teachers PlanAshita NaikNo ratings yet
- Earth Summit - WikipediaDocument4 pagesEarth Summit - WikipediaEnrique IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Transitioning To A Progressive Green Economy in The PhilippinesDocument40 pagesTransitioning To A Progressive Green Economy in The PhilippinesEmi NaitoNo ratings yet
- Solid Waste Pollution in Ho Chi Minh CityDocument33 pagesSolid Waste Pollution in Ho Chi Minh CityLamTraMy13No ratings yet
- Answer:: Time (H) Inflow (m3/s)Document6 pagesAnswer:: Time (H) Inflow (m3/s)kpop is moodNo ratings yet
- Flyer Sustainable Hydro Power 2011 11 11Document2 pagesFlyer Sustainable Hydro Power 2011 11 11vesselNo ratings yet
- Presented By:-Aniket Khujneri Anshul Sharma Bharti BaghelDocument11 pagesPresented By:-Aniket Khujneri Anshul Sharma Bharti BaghelitislovNo ratings yet
- Apr 05Document33 pagesApr 05Paulo Miguel Alves TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Environmental Quiz 4Document4 pagesEnvironmental Quiz 4Isaiah Peligrino50% (2)
- Instant Download Ebook PDF An Introduction To Conservation Biology 2nd Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF An Introduction To Conservation Biology 2nd Edition PDF Scribdcharles.brookshire691100% (38)
- Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesReading ComprehensionYeraldin MARTINEZ ANCHICONo ratings yet