Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medial Geniculate Body: Synapse
Uploaded by
OvguOzenli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesaudıtory info for med students
Original Title
auditory.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentaudıtory info for med students
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
23 views3 pagesMedial Geniculate Body: Synapse
Uploaded by
OvguOzenliaudıtory info for med students
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
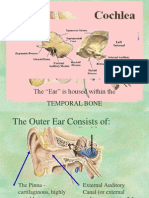
Organ of corti (cochlear hair cells)
(bipolar nerves) spiral (or cochlear) ganglion
cochlear nerve
synapse ->
Neurons in
these nuclei
send both
crossed and
uncrossed
axons ->
trapezoid
body and
some of
them
synapse in
the superior
olivary
nuclei
(distance) ->
The ascending fibers course in the lateral
Latera
lemnisci ->
l
lemnis
Inferior
colluculi
Brachiu
m
medial geniculate body
primary auditory cortex
* inferior colliculi and medial geniculate bodies each receive
impulses derived from both ears
Reflex connections pass to eye muscle nuclei and other
motor nuclei of the cranial and spinal nerves via the tectobulbar
and tectospinal tracts.
These connections are activated by
strong, sudden sounds; the result is reflex turning of the eyes
and head toward the site of the sound.
In the lower pons, the superior olivary nuclei receive input from both ascending
pathways. Efferent fibers from these nuclei course along the
cochlear nerve back to the organ of Corti. The function of this
olivocochlear bundle is to modulate the sensitivity of the
cochlear organ.
Cochlear nerve damage: hearing loss on ipsilateral ear
Hearing cortex damage on right: bilateral hearing loss but on contralateral site
its more
Equilibrium and muscle tonus
Semicircular ducts -> rotational movements of head
Utricle -> vertical and lateral acceleration
Sacule -> linear acceleration
Ampulla in semicircular canals: crista hair cells embedded in
cupula
Utricle + sacule: macula hair cells embedded in otholiths
Ampulla of anterior and lateral semicircular canals + macula of
utricle -> superior vestibular ganglia
Ampulla of posterior semicircular canal + macula of sacule ->
inferior vestibular ganglia
These ganglia are found in fundus deep part of internal acustic
meatus.
Fundus 4 parts: 1) posteriosuperior - > superior vest. ganglion
2) posterioinferior -> inferior vest. ganglion
*fibers coming from 2 different canals: posterior
semicircular duct fibers through
singular canal and sacule
vestibular area.
fibers through saccular
The central branches run within the vestibular
component of cranial nerve VIII to enter the brain stem
and end in the vestibular nuclei
sup + lat vest nuclei -> cerebellum where they end in
the cerebellar cortex within the flocculonodular component
lateral vestibular nuclei -> lateral vestibulospinal tracts to
spinal cord postural adjustments
superior and medial vestibular nuclei ->
1)MLF -> nuclei of the eye muscles
2)medial vesitbulospinal tract - > cervical spinal cord for head
movements
3)Some vestibular nuclei send fibers to the reticular formation.
Some ascending fibers from the vestibular nuclei travel by way
of the thalamus VPL to the parietal cortex (area 40). to be
conscious about balance.
You might also like
- Auditory PathwayDocument21 pagesAuditory PathwayAsad OsmanNo ratings yet
- Brain Template 16x9Document10 pagesBrain Template 16x9AishaNo ratings yet
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (5) The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal ReflexesDocument4 pages511-525chapter 6-8 (5) The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexestomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Auditory pathway: From cochlea to auditory cortexDocument16 pagesAuditory pathway: From cochlea to auditory cortexDrsreeram ValluriNo ratings yet
- 6 CerebellumDocument61 pages6 CerebellumNishanth LakshmanNo ratings yet
- 8 Brainstem 2Document20 pages8 Brainstem 2sjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Brainstem (Yuni)Document34 pagesBrainstem (Yuni)Ayi Abdul Basith100% (2)
- EarDocument4 pagesEarﻧﻮﺭﻭﻝ ﻋﻠﻴﻨﺎ ﺣﺎﺝ يهيNo ratings yet
- Sensory PathwayDocument31 pagesSensory PathwayAlma BaterinaNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Nadz FinalDocument58 pagesCranial Nerve Nadz Finalnadzirah ruslanNo ratings yet
- CNS 4 GoodDocument16 pagesCNS 4 GoodJeff ParkNo ratings yet
- The Ear and Hearing NotesDocument8 pagesThe Ear and Hearing NoteslacyNo ratings yet
- Npte - Neuroanatomy Lec 2Document31 pagesNpte - Neuroanatomy Lec 2Densen Raphael C. Antonio100% (2)
- Tracts of The Spinal CordDocument21 pagesTracts of The Spinal Corddr.a.k.gupta6924100% (10)
- Central Nervous System 3rd Year Medicine Cerebellum & Basal GangliaDocument17 pagesCentral Nervous System 3rd Year Medicine Cerebellum & Basal GangliaGroup 14100% (1)
- LECTURE On Spinal CordDocument11 pagesLECTURE On Spinal CordElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- Trigeminal NerveDocument126 pagesTrigeminal NerveAsha Praveena100% (4)
- Uho - Organ Sluha I RavnoteDocument6 pagesUho - Organ Sluha I RavnoteaiuzuNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum: Principally Because Electrical Excitation of The CerebellumDocument42 pagesCerebellum: Principally Because Electrical Excitation of The Cerebellumdr_mksinhaNo ratings yet
- Midbrain - 2-18-07-2020Document26 pagesMidbrain - 2-18-07-2020Vinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NSDocument8 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NSIsha BhusalNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From SUPERCOPDocument6 pagesMaterial Downloaded From SUPERCOPfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy: Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Medulla SpinalisDocument36 pagesBrain Anatomy: Diencephalon, Brain Stem and Medulla SpinalisAngela FovinaNo ratings yet
- Pyramidal SystemDocument52 pagesPyramidal SystemKowsalya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- PBL 3 MDSC 2002 Upper or LowerDocument15 pagesPBL 3 MDSC 2002 Upper or LoweradaumedNo ratings yet
- Vestibulo Cochlear AppDocument35 pagesVestibulo Cochlear AppApi Rosela AlfiNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum LesionsofbrainstemDocument50 pagesCerebellum LesionsofbrainstemAira LorenzoNo ratings yet
- The Spinal Cord: DR - SatyaDocument61 pagesThe Spinal Cord: DR - SatyacheckmateNo ratings yet
- Auditory System: How We HearDocument6 pagesAuditory System: How We HearNew NeilNo ratings yet
- Eidit CerebelemDocument23 pagesEidit CerebelemTem GemechuNo ratings yet
- Medulla Oblongata Nucleus (Final)Document7 pagesMedulla Oblongata Nucleus (Final)Hassan.shehri100% (3)
- d8c Cranial NervesDocument29 pagesd8c Cranial NervesYhemmy Lhawal JummyNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum Structure and Connections GuideDocument97 pagesCerebellum Structure and Connections GuideAnonymous -No ratings yet
- Physiologyofequilibriumbalance 111029153537 Phpapp01Document43 pagesPhysiologyofequilibriumbalance 111029153537 Phpapp01Dorin PathakNo ratings yet
- Pyramidal TractDocument48 pagesPyramidal TractdenekeNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve ReviewDocument7 pagesCranial Nerve Reviewdwnld5No ratings yet
- Vestibular FunctionsDocument3 pagesVestibular FunctionsMalek ElgmatiNo ratings yet
- CEREBELLUM (Physiotherapy)Document44 pagesCEREBELLUM (Physiotherapy)Richmond tohNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of The Cranial Nerves Vii-XiiDocument38 pagesThe Anatomy of The Cranial Nerves Vii-Xiiabdul azizNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem: Nervous SystemDocument58 pagesBrain Stem: Nervous Systemgabriela4592No ratings yet
- The Anatomy and Physiology of the EarDocument25 pagesThe Anatomy and Physiology of the EarDrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- Pupillary Dilatation ReflexDocument7 pagesPupillary Dilatation ReflexEden Canonizado ChengNo ratings yet
- The Cerebellum-8 PDFDocument83 pagesThe Cerebellum-8 PDFlovelots1234No ratings yet
- Lo 1 Week 5 NeuroDocument36 pagesLo 1 Week 5 NeuroInna DamaNo ratings yet
- MS NeurologyDocument30 pagesMS NeurologyAu CassieNo ratings yet
- Ear 3Document10 pagesEar 3yasinoNo ratings yet
- THE INNER EAR-Structure and Physiology: Presented By: Aksheen Malhotra 1DS17ML002Document22 pagesTHE INNER EAR-Structure and Physiology: Presented By: Aksheen Malhotra 1DS17ML002riya100% (1)
- The Physiology of HearingDocument25 pagesThe Physiology of HearingAyi Abdul BasithNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Somatosensory Axis of the Nervous SystemDocument94 pagesIntroduction to the Somatosensory Axis of the Nervous SystemGks100% (1)
- 2 NeuroanatomyDocument60 pages2 NeuroanatomyMeirina KhairatNo ratings yet
- 7 Brainstem 1Document28 pages7 Brainstem 1sjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves: Anatomy and FunctionsDocument7 pagesCranial Nerves: Anatomy and FunctionsCristina A RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Microscopic Anatomy InterDocument29 pagesAtlas of Microscopic Anatomy InterIndraPerdanaNo ratings yet
- NervesDocument16 pagesNervesDerahNo ratings yet
- Motor Functions of Spinal CordDocument43 pagesMotor Functions of Spinal CordEugeniu CoretchiNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EquilibriumDocument64 pagesPhysiology of EquilibriumSaiNo ratings yet
- 12 Spinal Cord TractsDocument39 pages12 Spinal Cord Tractssjs6r8wwv9No ratings yet
- 2 M 21. I II III IV VI VIII Pairs of Cranial NervesDocument10 pages2 M 21. I II III IV VI VIII Pairs of Cranial NervesVivek ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- A Seminar Presentation On Special Senses Ana 803 (Neuroanatomy)Document24 pagesA Seminar Presentation On Special Senses Ana 803 (Neuroanatomy)Kolawole Adesina KehindeNo ratings yet
- SEX Differentiation by.R.BundakDocument33 pagesSEX Differentiation by.R.BundakOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- Instant Anatomy - EarDocument13 pagesInstant Anatomy - EarOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- LarynxDocument7 pagesLarynxOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- Non Neoplastic WBC DisordersDocument13 pagesNon Neoplastic WBC DisordersSheikh UzairNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis Viruses2Document5 pagesGastroenteritis Viruses2OvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- Endocrinological Diseases (Medical Faculty)Document9 pagesEndocrinological Diseases (Medical Faculty)OvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- Nuclear OncologyDocument33 pagesNuclear OncologyOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- AMEOBADocument20 pagesAMEOBAOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- MammographyDocument22 pagesMammographyOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- Medscape DermatologyDocument38 pagesMedscape DermatologyAli KhalidNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology ReviewDocument151 pagesOphthalmology ReviewOvguOzenliNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System, Part 1 Crash Course AP 8.mp3Document5 pagesThe Nervous System, Part 1 Crash Course AP 8.mp3Carmen Florentina VlaseNo ratings yet
- The Physiology Excitable TissuesDocument71 pagesThe Physiology Excitable TissuesSalih ÇayırNo ratings yet
- Serial Sections of a 10 mm Pig EmbryoDocument16 pagesSerial Sections of a 10 mm Pig EmbryoMichaela Faye100% (1)
- Bruce Frantzis - Learning Bagua (2010)Document23 pagesBruce Frantzis - Learning Bagua (2010)Scoala SolomonaraNo ratings yet
- Ascended Master Kuthumi Entity DetachmentDocument10 pagesAscended Master Kuthumi Entity DetachmentImmalight100% (2)
- Chapter 12 Coordination and Response GuideDocument18 pagesChapter 12 Coordination and Response GuideyokekeannNo ratings yet
- BIO 201 Module 5Document4 pagesBIO 201 Module 5Hii Paul VBNo ratings yet
- Biology M9 Life Support SystemsDocument30 pagesBiology M9 Life Support SystemsRichele FloresNo ratings yet
- 4.block D KGMC Pre-Proff 21 PDFDocument29 pages4.block D KGMC Pre-Proff 21 PDFFida Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemKristiene Kyle AquinoNo ratings yet
- ERA Nursing MSN Spinal Cord InjuryDocument7 pagesERA Nursing MSN Spinal Cord InjuryAru Verma100% (1)
- CAPITIN - AnSci1.1 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument6 pagesCAPITIN - AnSci1.1 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsJuan CapitinNo ratings yet
- PCP - Week 2 - QsDocument4 pagesPCP - Week 2 - Qsapi-502171898100% (1)
- Odontoid Fractures: Update On Management: Review ArticleDocument12 pagesOdontoid Fractures: Update On Management: Review ArticleItha KiloonaNo ratings yet
- ElectrocitoDocument17 pagesElectrocitobachiusach2008No ratings yet
- Neuro SurgeryDocument14 pagesNeuro Surgeryapi-3840195100% (4)
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument25 pagesSpinal Cord InjurySolsona Natl HS Maananteng100% (2)
- Approach To A Patient With Hemiplegia and Monoplegia: Sudhir Kumar, Subhash KaulDocument6 pagesApproach To A Patient With Hemiplegia and Monoplegia: Sudhir Kumar, Subhash KaulTania PetronelaNo ratings yet
- MS NeurosurgeryDocument60 pagesMS NeurosurgeryAdeel RaufNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Close Reduction of Cervical Fracture DislocationsDocument8 pagesPreoperative Close Reduction of Cervical Fracture DislocationsIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Common Spinal Disorders Explained PDFDocument2 pagesCommon Spinal Disorders Explained PDFTamekaNo ratings yet
- Chennai Sahodaya Science Set2 Answer Key 2022-23 PDFDocument17 pagesChennai Sahodaya Science Set2 Answer Key 2022-23 PDFsethu ks50% (2)
- Internal Medicine II GRDocument86 pagesInternal Medicine II GRAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- NCP of Client With Cancer Servix With Multiple Bone MetastasisDocument17 pagesNCP of Client With Cancer Servix With Multiple Bone MetastasisHarismaPratamaNo ratings yet
- Traumatology Orthopaedic EXAMDocument219 pagesTraumatology Orthopaedic EXAMElo GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Vestibular SystemDocument25 pagesDisorders of The Vestibular SystemEnzo VicencioNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Athletic Training Prevention Assessment and Management 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesFoundations of Athletic Training Prevention Assessment and Management 6th Edition Ebook PDFjoshua.lewis822100% (42)
- Med Surg NervesDocument3 pagesMed Surg NervesZachary T HallNo ratings yet
- 001-111 mmv76 Gomon Choerodon 7 WebDocument111 pages001-111 mmv76 Gomon Choerodon 7 WebM DayatNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Functions of the Human Nervous SystemDocument85 pagesThe Structure and Functions of the Human Nervous SystemjoelNo ratings yet