Professional Documents
Culture Documents
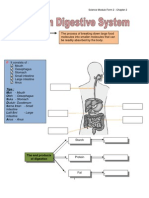
Science Notes Year 6
Uploaded by
esther1phanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
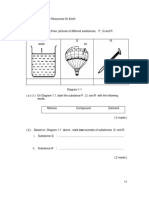
Science Notes Year 6
Uploaded by
esther1phanCopyright:
Available Formats
Animals that Live in Groups & in Solitary
Examples of Group Animals
Animals live in...
groups
a mob/clan of
meerkats
a swarm of
jellyfish
a flock of
crows
a pack of
wolves
a herd of
elephants
a colony of
penguins
a school of fish
a pride of lions
a flamboyance of
flamingos
solitary
live and hunt for
food alone
except when
mating or
rearing the
young
live together
with other
members of
their species in a
habitat
Examples of Solitary Animals
advantages
can
cooperate
to hunt for
food
can help
each other
to defend
themselves
from
enemies
advantages
can help
each other
to build
their nest
can avoid
competition
for food
can avoid
competition
for space
Note: Generally, most solitary animals are predators while their prey usually
live in groups.
lizard
panda
snake
spider
octopus
tiger
leopard
tapir
pangolin
Interaction Among Living Things
produce new generations
of individuals that are
stronger and fitter
Interaction
interdependence
among living
things
control the populations
of living things in a
habitat
Importance of
Competition Among
Living Things
can either be in
the form of
reduce overcrowding
in one habitat
maintain
balance of nature
Note: Competition does not threaten species of plants and animals to the
brink of extinction.
for food, shelter
and protection
cooperation or
competition
Types of Interaction Among Animals
Cooperation
Animals
compete for
Plants
compete for
food
nutrient
water
water
shelter
territory (space)
breeding partner
sunlight
root space
living things cooperate with one another in order to
survive
get benefits from each other
get food, protection or transportation
Competition
when two species are competing for the same limited
amount of resources
only one of the animals gets the benefits
compete for food, water, shelter, territory (space) and
breeding partner (only for same species)
Cooperation among Animals of Same Species
Examples of Cooperation of Same Species
Buffalo in a herd
help protect each
other.
Each member of
a honey bee
colony has a specific
role. All contribute
to the survival of
the colony.
Ants work together
to build their nest.
Musk oxen live in
herds. The herd
forms a defensive
circle with calves
inside as protection
against wolves.
Wolves in a pack
help hunt together.
Dolphins rely on
each other to find
food,
communicating
through clicks and
squeaks.
Cooperation among Animals of Different Species
Examples of Cooperation of Different Species
The ox pecker gets
food without any
threat or
competition and in
turn the buffalo gets
the benefit of
getting rid of the
annoying insects
from its skin.
Clownfish receives
food, shelter, and
protection from Sea
Anemone. In return,
it protects Anemone
by chasing away
Butterfly Fish that
like to bite off the
ends of Anemones
tentacles.
The shark is getting
cleaned and
groomed while the
remora is getting
fed and transported.
Competition among Animals of Same Species
Intraspecies (same species) Competition
Competition among Animals of Different Species
Interspecies (different species) Competition
Food
A few birds competing with a
squirrel for limited food.
Territory (space)
This clown fish lives with a sea anemone. It
will defend its small territory against other
clown fish.
Shelter
Food
Polar bear will defend its den
from being taken over by other
animals such as wolf.
Two roosters fighting
over a worm.
Shelter
Water
Number of swallows
grows, competition
for boxes increases.
Animals in a same habitat have
to compete for limited water
during drought.
Breeding Partner
Water
Deers compete with
each other for the
pick of the females
to mate with.
Zebras have to
compete for the
limited water during
dry season.
Territory (space)
The woodpecker is prepared to
fight with the squirrel for its
territory.
Note: (1) Interspecies did not compete for breeding partner.
(2) To avoid competition, populations in an ecosystem often have different
food requirements.
Competition between Plants
Extinct and Endangered Species
Plants compete because of limited...
Extinct
Species
...sunlight that can reach them.
Plants need sunlight to make
their own food. Plants of the
same height should be planted
together to avoid competition for
sunlight.
are species
that no
longer exist
or entire
species died
due to
change in
climate and
weather on
the earth
as well as
human
activities
such as
excessive
hunting and
destruction
of their
habitats
...water resources.
One of the basic needs for plants
to make their own food. Roots of
some plants grow extensively to
compete for water.
...nutrients.
...space.
Plants need nutrients for healty
growth. Avoid planting too many
plants in a small area which will
result in unhealty growth.
Plants cannot grow well in
limited space. Plants should be
planted further apart to avoid
competition for space.
Note: Competition for sunlight, water, nutrients and space has resulted in
trees of different heights in the forest.
tasmanian
wolf
Examples of Extint
Animals
auk bird
quagga
caspian tiger
dinosaur
dodo bird
mammoth
Endangered Animal Species
hunted for
live-animal
trade
hunted for
its fur
Endangered
Species
hunted for
sports and
its meat
hunted for
its meat and
shell
rafflesia
are species of animals
or plants that are
facing the threat of
becoming extinct
hunted for
its tusk
hunted for
its horn
Endangered
Plant Species
more members of
species lose natural
habitat
venus flytrap
pitcher plant
hard to obtain basic
needs
hunted for
its feather,
meat and
beak
hunted for
its skin and
bones
mangrove tree
caused by:
hunted for
its meat and
teeth
hunted for
its meat and
fats
illegal and excessive logging
illegal and excessive hunting
excessive deforestation for
development
slipper orchid
Preventing Animal and Plants from Extinction
Impact of Human Activities on Environment
through
soil erosion
conservation the intelligent and proper management
and a systematic use of natural resources such as living
things to prevent waste, loss and damage to the
resources
preservation keep natural resources such a living
things and the environment in their original and
balanced state
due to excessive logging
soil exposed when trees are cut down
to
flash flood
protect natural habitat from being destroyed
protect natural resources being depleted
maintain population of endangered species
maintain a balanced ecosystem to minimize destruction
of natural habitat
soil erosion causes soil to flow into rivers and they
become shallow
during heavy rain, the rivers overflow and cause flash
floods
steps
due to logging and mining activities
soil erosion causes soil to be washed into rivers and they
become muddy
excessive use of fertilisers, pesticides and herbicides
also due to improper waster management
preservation setting up forest reserved; setting up
marine parks
conservation selective logging, leaving some matured
plants and many small plants; replanting cut down areas
education create awareness on preservation and
conservation
importance;
campaign
against
excessive/illegal logging; avoid using products made
from endangered species
law enforcement authorities taking action against
lawbreakers
landslides
soil erosion causes soil to become loose and fall downhill
as landslide
water pollution
air pollution
due to improper air pollutants management in factories
also due to heavy use of motor vehicles
You might also like
- 7) Fusion Accounting Hub For Insurance Premium - External SourceDocument18 pages7) Fusion Accounting Hub For Insurance Premium - External Sourcekeerthi_fcmaNo ratings yet
- Modul Penulisan Bahasa Inggeris PT3Document84 pagesModul Penulisan Bahasa Inggeris PT3Damit Jaffar Mohd Thani100% (1)
- Science Year 4 (Short Note) : Theme 1: Investigating Living ThingsDocument8 pagesScience Year 4 (Short Note) : Theme 1: Investigating Living ThingsHasmi HassanNo ratings yet
- c4 InterdependenceDocument52 pagesc4 InterdependenceultrakaweNo ratings yet
- Science Year 4 Exam PaperDocument18 pagesScience Year 4 Exam Paperniwintra100% (2)
- Science Notes Year 6Document1 pageScience Notes Year 6esther1phan100% (2)
- Chapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofDocument17 pagesChapter 3 - Matter 1. Diagram 1 Shows Pictures ofRozaini Othman100% (15)
- Year 3 Unit 3: Types and Functions of TeethDocument6 pagesYear 3 Unit 3: Types and Functions of TeethMasnizan Binti HamdanNo ratings yet
- Community StructureDocument69 pagesCommunity Structureapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Sce Form 2Document22 pagesSce Form 2williamkong123No ratings yet
- How Do Animal Protect ThemselvesDocument8 pagesHow Do Animal Protect ThemselvesSiti Anwar100% (1)
- Performance and Mechanical Running Tests of Centrifugal CompressorsDocument5 pagesPerformance and Mechanical Running Tests of Centrifugal CompressorsVicky KumarNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Year 6Document6 pagesScience Notes Year 6esther1phan100% (1)
- Ting 1 PPT 2019 WritingDocument5 pagesTing 1 PPT 2019 WritingShima HamiriNo ratings yet
- Tips and Techniques of Answering Paper 2 Questions in UPSRDocument50 pagesTips and Techniques of Answering Paper 2 Questions in UPSRkz2uhehe100% (42)
- Science Year 4 Paper 1Document15 pagesScience Year 4 Paper 1NormaNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Year 6Document6 pagesScience Notes Year 6esther1phanNo ratings yet
- Hospital & Clinical Pharmacy Q&ADocument22 pagesHospital & Clinical Pharmacy Q&AKrishan KumarNo ratings yet
- Topical Exercises Year 4: Chapter 1: Investigating Living ThingsDocument6 pagesTopical Exercises Year 4: Chapter 1: Investigating Living ThingsHusna Zakaria80% (5)
- Year 4 UASA ENGLISH MODEL 5 SETS + ANSWERSDocument45 pagesYear 4 UASA ENGLISH MODEL 5 SETS + ANSWERSPHANG YEEN CHENG Moe100% (2)
- FINAL YEAR SCIENCE EXAMDocument18 pagesFINAL YEAR SCIENCE EXAMLin100% (1)
- Powerpoint Science Year 6Document41 pagesPowerpoint Science Year 6FT Geeyah Tahir100% (2)
- Science Notes Year 6Document6 pagesScience Notes Year 6esther1phanNo ratings yet
- Modul F2 Science C2Document14 pagesModul F2 Science C2NorelyanaAli67% (3)
- Form 2 Science Chapter 3Document23 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 3qq23592% (25)
- Modul UPSR Terbaik Cuti Sekolah Pertengahan Tahun 2018 Bahasa InggerisDocument75 pagesModul UPSR Terbaik Cuti Sekolah Pertengahan Tahun 2018 Bahasa InggerisGee Yoke TingNo ratings yet
- Trial Upsr 2009 Tamil SainsDocument24 pagesTrial Upsr 2009 Tamil Sainsse291171550189% (35)
- Science Year 4 Notes On HEAT ENERGYDocument1 pageScience Year 4 Notes On HEAT ENERGYNrhfzhjrzfzNo ratings yet
- English Form 1 Midterm Specimen Test & AnswersDocument12 pagesEnglish Form 1 Midterm Specimen Test & AnswersNor Haziani100% (3)
- News Break by Max FatchenDocument6 pagesNews Break by Max FatchenAnisNo ratings yet
- Science Notes Year 6Document2 pagesScience Notes Year 6esther1phan100% (1)
- Mind Map Year 6 (L.area)Document7 pagesMind Map Year 6 (L.area)radenesNo ratings yet
- Triumph Redong Vol 2 PDFDocument100 pagesTriumph Redong Vol 2 PDFParthiban Muthiah100% (2)
- English F2 Paper1Document15 pagesEnglish F2 Paper1Smk Dato Shahbandar HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Heat 1. Diagram 1 Below Shows TheDocument12 pagesChapter 7 - Heat 1. Diagram 1 Below Shows TheRozaini Othman100% (4)
- English SPM Module 1Document18 pagesEnglish SPM Module 1Mohd Yusoff TahirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Variety Resources On EarthDocument14 pagesChapter 4 - The Variety Resources On EarthRozaini Othman71% (7)
- Soalan Kerja Year 5 ScienceDocument11 pagesSoalan Kerja Year 5 ScienceSangkari SreeNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Exam PT3 FormattedDocument8 pagesForm 1 Exam PT3 FormattedMohd Hazrin Bin HarunNo ratings yet
- Mind Mapping Yaer 6 Modul CemerlangDocument21 pagesMind Mapping Yaer 6 Modul CemerlangHelyza Hayes100% (3)
- Nota Sains Tahun 5Document46 pagesNota Sains Tahun 5mohdfirdaushada100% (2)
- SCTA Pra-UPSR Y6 BI 2015Document8 pagesSCTA Pra-UPSR Y6 BI 2015Kosongz Toh100% (1)
- Jawapan Soalan Latihan Sains Tahun 4, 5, 6Document27 pagesJawapan Soalan Latihan Sains Tahun 4, 5, 6FT Geeyah TahirNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument7 pagesForm 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Form 1 Poem News BreakDocument1 pageForm 1 Poem News BreakMohd Hazrin Bin HarunNo ratings yet
- Mid Year Exam Form1 2018 NewDocument10 pagesMid Year Exam Form1 2018 NewMiera MijiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Moon Phases and Animal RespirationDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Moon Phases and Animal RespirationNana AngkingNo ratings yet
- Essay-My Flood ExperienceDocument2 pagesEssay-My Flood Experiencefarah fauziNo ratings yet
- Form 1 English Sample PaperDocument12 pagesForm 1 English Sample PaperEugene JosephNo ratings yet
- Documents - Tips Exam Form 1 English Pt3 FormatDocument6 pagesDocuments - Tips Exam Form 1 English Pt3 FormatBairah KamilNo ratings yet
- Upsr ScienceDocument30 pagesUpsr ScienceShyweyNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggeris P1 Trial PMR Perak 2009Document12 pagesBahasa Inggeris P1 Trial PMR Perak 2009HaFez Hisham100% (3)
- Spelling Bee Qualifying Test NoticeDocument9 pagesSpelling Bee Qualifying Test NoticeTheebaaRamasamyNo ratings yet
- Year 5 English Plus 1unit 5 WritingDocument16 pagesYear 5 English Plus 1unit 5 WritingWONG SWEE LIN MoeNo ratings yet
- Animals Live in Solitary Animals Live in Group: Unit 1: Interaction Among Living ThingsDocument5 pagesAnimals Live in Solitary Animals Live in Group: Unit 1: Interaction Among Living ThingsSanthanadevi MunusamyNo ratings yet
- Interaction Living Thing Cooperation, Competition Cooperation Fair Situasion EverybodyDocument54 pagesInteraction Living Thing Cooperation, Competition Cooperation Fair Situasion Everybodymohamad nizam bin mahbob0% (1)
- INTERACTION AMONG LIVING THINGSDocument24 pagesINTERACTION AMONG LIVING THINGSMahenthiran PachaiNo ratings yet
- Community EcologyDocument34 pagesCommunity EcologysarwaNo ratings yet
- Presentation3 (1)Document16 pagesPresentation3 (1)roseannbello625No ratings yet
- Living Things Depend on EnvironmentDocument6 pagesLiving Things Depend on Environmentdianie joyNo ratings yet
- Predation & CompetitionDocument21 pagesPredation & Competitionellen joy d. pacienteNo ratings yet
- Environmental ScienceDocument41 pagesEnvironmental ScienceIshwar RajputNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Species InteractionsDocument41 pagesBiodiversity and Species InteractionsImperial Ma LizaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 (Group 1)Document4 pagesExperiment 4 (Group 1)Webster Kevin John Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PTA Resolution for Donation to School WashroomDocument2 pagesPTA Resolution for Donation to School WashroomMara Ciela CajalneNo ratings yet
- Class9. CVD and PVDDocument30 pagesClass9. CVD and PVDiraNo ratings yet
- VERALLIA WHITE-BOOK EN March2022 PDFDocument48 pagesVERALLIA WHITE-BOOK EN March2022 PDFEugenio94No ratings yet
- Byk-A 525 enDocument2 pagesByk-A 525 enさいとはちこNo ratings yet
- Amaryllidaceae Family Guide with Endemic Philippine SpeciesDocument28 pagesAmaryllidaceae Family Guide with Endemic Philippine SpeciesMa-anJaneDiamos100% (1)
- Ielts Band Score 7Document2 pagesIelts Band Score 7Subhan Iain IINo ratings yet
- Regulation of Body FluidsDocument7 pagesRegulation of Body FluidsRuth FamillaranNo ratings yet
- MPQ2908 - 48V Buck Converter Automotive Reference DesignDocument4 pagesMPQ2908 - 48V Buck Converter Automotive Reference DesignShubham KaklijNo ratings yet
- Training and Supervision of Health Care WorkersDocument12 pagesTraining and Supervision of Health Care WorkerspriyankaNo ratings yet
- Overhead Set (OBC)Document19 pagesOverhead Set (OBC)MohamedNo ratings yet
- Understanding Anxiety Disorders and Abnormal PsychologyDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Anxiety Disorders and Abnormal PsychologyLeonardo YsaiahNo ratings yet
- Naskah PublikasiDocument14 pagesNaskah PublikasiNirmala malaNo ratings yet
- Jamec Air FittingsDocument18 pagesJamec Air Fittingsgoeez1No ratings yet
- Chin Cup Therapy An Effective Tool For The Correction of Class III Malocclusion in Mixed and Late Deciduous DentitionsDocument6 pagesChin Cup Therapy An Effective Tool For The Correction of Class III Malocclusion in Mixed and Late Deciduous Dentitionschic organizerNo ratings yet
- H1 Revision Notes DNA and GenomicsDocument6 pagesH1 Revision Notes DNA and GenomicsJiaLi XieNo ratings yet
- English 10 - HVC - ĐềDocument22 pagesEnglish 10 - HVC - ĐềAlin NguyenNo ratings yet
- Edna Adan University ThesisDocument29 pagesEdna Adan University ThesisAbdi KhadarNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Snack Market Grade BDocument3 pagesVietnam Snack Market Grade BHuỳnh Điệp TrầnNo ratings yet
- Yanagiba Sharpening: Everything You Need To KnowDocument16 pagesYanagiba Sharpening: Everything You Need To KnowT ChenNo ratings yet
- Smart Goals ExerciseDocument2 pagesSmart Goals Exerciseapi-594661640No ratings yet
- SmithfieldDocument11 pagesSmithfieldandreea143No ratings yet
- Density of Aggregates: ObjectivesDocument4 pagesDensity of Aggregates: ObjectivesKit Gerald EliasNo ratings yet
- No.10 Procedure For The Selection, Training, Qualification and Authorisation of Marine Management Systems Auditors No.10Document9 pagesNo.10 Procedure For The Selection, Training, Qualification and Authorisation of Marine Management Systems Auditors No.10William DaslerNo ratings yet
- Personal Chiller 6-Can Mini Refrigerator, Pink K4Document1 pagePersonal Chiller 6-Can Mini Refrigerator, Pink K4Keyla SierraNo ratings yet
- Jaimin PatelDocument3 pagesJaimin PatelSanjay SinghNo ratings yet
- Rundingan Perdagangan Antara Malaysia Dan Indonesia Di Wisma Putra, Kuala Lumpur 1967Document15 pagesRundingan Perdagangan Antara Malaysia Dan Indonesia Di Wisma Putra, Kuala Lumpur 1967nixyingboNo ratings yet