Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Buffalo 03 PDF
Uploaded by
Ruben Dario50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
309 views4 pagesBritish Purchasing Commission ordered a total of 170 Model 339Es in two separate contracts under the British designation Buffalo Mk. I. The 339E was basically a denavalized variant of the F2A-2, powered by an export-approved Wright R-1820-G105 Cyclone engine of 1100 hp. The first three production models were sent to Great Britain in April of 1941 for trials.
Original Description:
Original Title
Buffalo-03.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBritish Purchasing Commission ordered a total of 170 Model 339Es in two separate contracts under the British designation Buffalo Mk. I. The 339E was basically a denavalized variant of the F2A-2, powered by an export-approved Wright R-1820-G105 Cyclone engine of 1100 hp. The first three production models were sent to Great Britain in April of 1941 for trials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
309 views4 pagesBuffalo 03 PDF
Uploaded by
Ruben DarioBritish Purchasing Commission ordered a total of 170 Model 339Es in two separate contracts under the British designation Buffalo Mk. I. The 339E was basically a denavalized variant of the F2A-2, powered by an export-approved Wright R-1820-G105 Cyclone engine of 1100 hp. The first three production models were sent to Great Britain in April of 1941 for trials.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
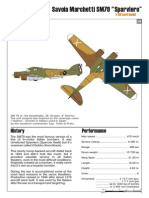
Brewster 339E Buffalo Mk.
I
No V8138
488 Squardon RAF
Singapore, late 1941
03/2004
In early 1940, the British Purchasing Commission
ordered a total of 170 Model 339Es in two separate contracts
under the British designation Buffalo Mk. I. This was a major
turnaround, since as recently as October of 1939 the British Air
Ministry had declared the Brewster fighter as unsuitable for
RAF use. However, they were deemed suitable for use in the
Far East.
The 339E was basically a denavalized variant of the
F2A-2, powered by an export-approved Wright R-1820-G105
Cyclone engine of 1100 hp. A number of changes were made to
bring the aircraft up to current European combat standards: a
British-built Mark III reflector gunsight replaced the ring-andbead arrangement, armor plate was provided for the pilot, and
armored glass was added to the wind screen. The Curtiss
Electric cuffed propeller was replaced with a 10-foot one-inch
Hamilton Standard propeller. The 339E was the only Buffalo
variant to feature an internal gun camera. The small retractable
naval-type tail wheel was replaced by a larger fixed tail wheel.
These changes brought the gross weight to 6500
pounds, almost a thousand pounds heavier than the standard
F2A-2. The maximum speed was lowered to 330 mph and the
rate of climb was lowered to only 2600 feet per minute. In
addition, this increased weight raised the wing loading,
increased the landing speed, and adversely affected the
maneuverability. Another problem was that the Buffalo Mk. I did
not use the same fuel line pressurization system as the F2A-2,
and fuel starvation problems were often experienced above
18,000 feet.
The Wright Cyclone R-1820-G105 engine installed in
the Buffalo Mk. I had been selected in part because there were
sufficient numbers of this engine available at the time to meet
the first British contract. However, when the second contract
was issued, there were not enough new Cyclone engines
available, and Brewster was forced to purchase used Cyclone
engines from commercial airlines which had been using them to
power their Douglas DC-3 airliners. These used engines were
returned to Wright, which remanufactured them to -G105
standards.
The first three production Model 339Es were sent to
Great Britain in April of 1941 for trials. The remaining Buffalos of
the British order were shipped directly to the Far East to serve
with units in Malaya, Singapore and Burma. The first Buffalos
arrived in Singapore in the spring of 1941.
Five Commonwealth squadrons were formed around
the Buffalo -- Nos. 67 and 243 Squadrons, RAF; Nos. 21 and 43
Squadrons of the RAAF; and No. 488 Squadron of the RNZAF.
No. 67 Squadron was based in Burma and the other four were
stationed at bases near Singapore. Each squadron was issued
with 15 aircraft. A shortage of pilots prevented the formation of
additional squadrons, and many Buffalos were placed in
storage. Many of the pilots in the Commonwealth Buffalo
squadrons were relatively new and inexperienced, and some
20 Buffalos were lost in training accidents during the autumn of
1941.
War in the Burma/Malaya theater began on December
8, 1941 with a Japanese landing on the Malayan coast. The
Brewsters did experience some initial successes against
Japanese Army Air Force Ki-27s and Ki-43s, and there were at
least three Commonwealth pilots who became aces during this
period. However, when the Japanese Navy A6M Reisen (Zero
Fighter) appeared, the Buffalo was completely outclassed. The
Zero was faster, more maneuverable and had a heavier
armament. In an attempt to improve the Buffalo's performance,
ground crews removed all unnecessary equipment to lower the
weight, sometimes replacing the 0.50-inch machine guns with
lighter 0.303-inch guns and reducing the ammunition and fuel
load. However, these modifications did not even come close to
closing the performance gap between the Buffalo and the Zero.
The situation in Malaya rapidly deteriorated as the
Japanese advance gained momentum, and Commonwealth
squadrons were forced to withdraw to Singapore Island.
Attrition and combat losses took their toll, and by February of
1942 there were only a few airworthy Buffalos left. These were
withdrawn to the nearby islands of the Netherlands East Indies.
When the British evacuated the aircrews to Australis, at least
four Buffalos were turned over to Dutch squadrons.
In Burma, No. 67 Squadron flew alongside the 3rd
Squadron, American Volunteer Group (the famous 'Flying
Tigers') in the defense of Rangoon. No. 67 Squadron had some
initial successes against attacking Japanese bomber
formations. However, attrition and the lack of spare parts
steadily eroded the squadron's strength, and by the time that
Rangoon fell, only six Buffalos were still airworthy. The
surviving No. 67 Squadron Buffalos were evacuated to India,
along with a few Hawker Hurricanes that had been rushed to
Rangoon's defense. Some of the Buffalos that made it to India
were taken on strength by No. 146 Squadron, RAF. There are
even reports that at least one Buffalo was transferred to the
Indian Air Force.
Many official British historical sources blame the loss of
Malaya and Singapore largely on the Buffalo's poor
performance. However, the picture is not entirely that of an
unmitigated disaster, and many Buffalo-equipped units gave a
good account of themselves before they were overwhelmed by
superior Japanese numbers. Accurate figures on the combat
losses of British Buffalos are difficult to come by. Approximately
60 to 70 Buffalos were lost in air combat, 40 were destroyed on
the ground, twenty were lost in various non-combat related
accidents, four were transferred to the Dutch, and six were
evacuated to India. Commonwealth Buffalo squadrons claimed
at least 80 kills, and some units may have achieved a 2-to-1 kill
ratio.
Specification of Brewster Buffalo Mk. I (Model B 339E):
Powerplant: One Wright R-1820-G105A Cyclone ninecylinder, single-row air-cooled radial, rated at 1100 hp for
takeoff. Performance: Maximum speed of 324 mph at 21,000
feet, 313 mph at 13,000 feet. Cruising speed 256 mph. Initial
climb rate 2600 ft/min. An altitude of 15,000 feet could be
reached in 6.3 minutes. Service ceiling 30,675 feet. Weights:
4479 pounds empty, 6500 pounds gross, 6840 pounds
maximum takeoff. Dimensions: Wingspan 35 feet 0 inches,
length 26 feet 0 inches, height 12 feet 1 inches, wing area 209
square feet. Armament: Two 0.50 inch machine guns in the
wings, two 0.30-inch machine guns in the upper fuselage.
15A
32A
32A
32A
32A
32A
32A
35B
35A
35B
C
E
34
34a
34a
34a
35D
11A
35C
23B
23B
8A
8B
a
35
b
c
23C
23C
23A
33
27+28
28
34
27
II
1 thread 6
14
17
10
11
II
29
21
8A
8B
35
DE
19
20
G
12
34a
22
16 15+15a
2
30
17a
31+32
23C
25
23A
11
23B
12
1
23
23B
23C
24
23A
13
23
13
13c
21
10
17a
22
17
18
7
20c
16
d
15
13
a
19
c
b
b
b 20
2
15a
25
25
23
a
3
14
24
33
12
11
11
32
31
30
29
26
28
27
23
You might also like
- SAMOLOTYDocument28 pagesSAMOLOTYstuleeNo ratings yet
- Happy New Year 2005 Happy New Year 2005: Free IssueDocument5 pagesHappy New Year 2005 Happy New Year 2005: Free Issuemam73100% (1)
- The Grumman WildcatDocument12 pagesThe Grumman Wildcatseafire47100% (4)
- (Aviation) - (Osprey) - (Aircam Aviation N°06) - Curtis Kittyhawk MKI-IV in RAF-SAAF-RAAF-RNZAF-RCAF-NEIAF ServiceDocument52 pages(Aviation) - (Osprey) - (Aircam Aviation N°06) - Curtis Kittyhawk MKI-IV in RAF-SAAF-RAAF-RNZAF-RCAF-NEIAF Servicesid-jon100% (7)
- Modeller's Guide To Early P-51 Mustang VariantsDocument10 pagesModeller's Guide To Early P-51 Mustang Variantsseafire47100% (3)
- All Ahead Full: World War II Memoirs of an Lsm 215 VeteranFrom EverandAll Ahead Full: World War II Memoirs of an Lsm 215 VeteranNo ratings yet
- Night of the Intruders: The Slaughter of Homeward Bound USAAF Mission 311From EverandNight of the Intruders: The Slaughter of Homeward Bound USAAF Mission 311No ratings yet
- Air-Ground Teamwork On The Western Front - The Role Of The XIX Tactical Air Command During August 1944: [Illustrated Edition]From EverandAir-Ground Teamwork On The Western Front - The Role Of The XIX Tactical Air Command During August 1944: [Illustrated Edition]No ratings yet
- Japanese Submarine Losses to Allied Submarines In World War 2From EverandJapanese Submarine Losses to Allied Submarines In World War 2No ratings yet
- US ARMY Boeing P-26A FighterDocument7 pagesUS ARMY Boeing P-26A FighterClaudioAlfredoSpotoNo ratings yet
- One-Man Airforce [Illustrated Edition]From EverandOne-Man Airforce [Illustrated Edition]Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- n1k1 Rex PDFDocument13 pagesn1k1 Rex PDFCe Ácatl Topiltzin Quetzalcóatl100% (1)
- CAC-13 Boomerang ModelDocument8 pagesCAC-13 Boomerang ModelMalyNo ratings yet
- USMC F-4 Phantom II Squadron History Series, No. 02, VMFA-531 “Grey Ghosts,” 1962: 1982From EverandUSMC F-4 Phantom II Squadron History Series, No. 02, VMFA-531 “Grey Ghosts,” 1962: 1982No ratings yet
- FlugRevue - Hawker Tornado - TyphoonDocument4 pagesFlugRevue - Hawker Tornado - TyphoonStargazer100% (1)
- The Petrol Navy: British, American and Other Naval Motor Boats at War 1914 – 1920From EverandThe Petrol Navy: British, American and Other Naval Motor Boats at War 1914 – 1920No ratings yet
- Marek - Grumman F6F 3 Hellcat 2Document4 pagesMarek - Grumman F6F 3 Hellcat 2Sam AE100% (1)
- North American P-51B Mustang's extra fuel tank and increased rangeDocument4 pagesNorth American P-51B Mustang's extra fuel tank and increased rangecastropereira100% (1)
- MANIPUR MohawksDocument8 pagesMANIPUR Mohawkspachro100% (1)
- Seversky P-35 in DetailDocument10 pagesSeversky P-35 in Detailseafire47100% (1)
- Luftwaffe Transport Junkers Ju 52 in ActionDocument52 pagesLuftwaffe Transport Junkers Ju 52 in ActionHerman Pentz Moore100% (3)
- MareK - P 47M 1Document4 pagesMareK - P 47M 1Reimar HortenNo ratings yet
- Modelart 1 32 Messerschmitt BF 109Document13 pagesModelart 1 32 Messerschmitt BF 109mommyNo ratings yet
- Bunrindo - Famous Airplanes of The World 23 - Kawasaki-Ki100 'Goshikisen' Army Type 5 FighterDocument83 pagesBunrindo - Famous Airplanes of The World 23 - Kawasaki-Ki100 'Goshikisen' Army Type 5 FighterJohannes100% (12)
- Bismarck3den PDFDocument19 pagesBismarck3den PDFi_kostadinovic100% (1)
- Regia Aeronautica Camouflage 1940Document8 pagesRegia Aeronautica Camouflage 1940seafire47100% (2)
- MMPBooks LeafletDocument4 pagesMMPBooks LeafletCasemate PublishersNo ratings yet
- Me 109 PT 1Document87 pagesMe 109 PT 1David Gayton100% (5)
- (Aircraft Profile 006) - Bristol BulldogDocument12 pages(Aircraft Profile 006) - Bristol BulldogPeter de Clerck100% (3)
- Coastal Dawn: Blenheims in Action from the Phoney War through the Battle of BritainFrom EverandCoastal Dawn: Blenheims in Action from the Phoney War through the Battle of BritainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- RAF Duxford: A History in Photographs from 1917 to the Present DayFrom EverandRAF Duxford: A History in Photographs from 1917 to the Present DayNo ratings yet
- (AeroArchív) AVIA B-534Document40 pages(AeroArchív) AVIA B-534DolomaNo ratings yet
- Bunrindo - Famous Airplanes of The World 90 - Nakajima G5N 'Shinzan' & G8N 'Renzan'Document68 pagesBunrindo - Famous Airplanes of The World 90 - Nakajima G5N 'Shinzan' & G8N 'Renzan'Johannes92% (13)
- Fiat CR 42Document20 pagesFiat CR 42seafire47No ratings yet
- Africa To The Alps: The Army Air Forces In The Mediterranean Theater [Illustrated Edition]From EverandAfrica To The Alps: The Army Air Forces In The Mediterranean Theater [Illustrated Edition]No ratings yet
- Sharkmouth Typhoon: Special EditionDocument4 pagesSharkmouth Typhoon: Special EditionsharkmouthNo ratings yet
- Messerschmitt BF 109Document9 pagesMesserschmitt BF 10918912170100% (2)
- Mustang!: Air ForceDocument7 pagesMustang!: Air ForceJan Gądek100% (1)
- Scale Military Vehicle Conversions PDFDocument89 pagesScale Military Vehicle Conversions PDFRuben DarioNo ratings yet
- (Papermodels@Emule) (GPM 029) - UH-1D IroquoisDocument9 pages(Papermodels@Emule) (GPM 029) - UH-1D IroquoisGustavo Perez100% (3)
- Sparviero MODELO PARA ARMAR - Savoia - Marchetti - SM79 - Sparviero - 1x48 - K PDFDocument8 pagesSparviero MODELO PARA ARMAR - Savoia - Marchetti - SM79 - Sparviero - 1x48 - K PDFRuben Dario100% (1)
- Zis 3 PDFDocument18 pagesZis 3 PDFRuben Dario100% (3)
- PDF Created With Pdffactory Trial VersionDocument12 pagesPDF Created With Pdffactory Trial VersionRuben DarioNo ratings yet
- Jeep SAS Desert Rat's 1942 PDFDocument11 pagesJeep SAS Desert Rat's 1942 PDFRuben DarioNo ratings yet
- Panhard AML90 PDFDocument81 pagesPanhard AML90 PDFRuben Dario100% (10)
- Csaba Instr PDFDocument9 pagesCsaba Instr PDFRuben Dario100% (3)
- Tailplanes PDFDocument1 pageTailplanes PDFRuben DarioNo ratings yet
- Afterburnersformers PDFDocument1 pageAfterburnersformers PDFRuben DarioNo ratings yet
- Jagdpanzer Jagdpanzer IVDocument13 pagesJagdpanzer Jagdpanzer IVRuben Dario100% (2)
- 8-2C500 Woodworking Plans - Projects 1-200Document752 pages8-2C500 Woodworking Plans - Projects 1-200Angel ArchilaNo ratings yet
- National Transportation Safety Board: Spool Bearing Failures in Rolls-Royce 250-Series EnginesDocument3 pagesNational Transportation Safety Board: Spool Bearing Failures in Rolls-Royce 250-Series EnginesBahadorNo ratings yet
- 1407 Sport Aviation 201407Document140 pages1407 Sport Aviation 201407JoseNo ratings yet
- Hitler's BombDocument4 pagesHitler's BombNikolaTesla7No ratings yet
- Gmail - EASA approved training program (Airbus A 320 and B 737Document1 pageGmail - EASA approved training program (Airbus A 320 and B 737SatishReddyNo ratings yet
- Epsc ChartsDocument3 pagesEpsc ChartsjazzmanPLNo ratings yet
- Basic Flight Instrument o Six PackDocument51 pagesBasic Flight Instrument o Six PackMarlene S. BethNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning System OverviewDocument364 pagesAir Conditioning System OverviewradheyNo ratings yet
- Jet Engines EngineDocument516 pagesJet Engines Enginemurari90% (20)
- Dgca Module 07 Part 07Document29 pagesDgca Module 07 Part 07Gaurav SinghNo ratings yet
- NTSB Investigative Update On Helicopter Crash That Killed Kobe BryantDocument11 pagesNTSB Investigative Update On Helicopter Crash That Killed Kobe BryantMelissa Hanson100% (1)
- Lecture 8-Aviation History-Speeds of FlightDocument25 pagesLecture 8-Aviation History-Speeds of Flightペブリヤナ サンディ100% (1)
- Commercial Engines: Special ReportDocument26 pagesCommercial Engines: Special ReportajsanherNo ratings yet
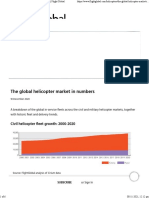
- Global helicopter market analysis by numbersDocument6 pagesGlobal helicopter market analysis by numbersVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Helicopter Safety Foundation - Crashworthiness - 1989 PDFDocument6 pagesHelicopter Safety Foundation - Crashworthiness - 1989 PDFSharol Vera BravoNo ratings yet
- Ops CircularDocument41 pagesOps CircularSwastika MishraNo ratings yet
- 1999 Q2-Advanced Maintenance Techniques For The 757-300Document8 pages1999 Q2-Advanced Maintenance Techniques For The 757-300tlnrsNo ratings yet
- C-130 General FamiliarizationDocument99 pagesC-130 General FamiliarizationChatchai PrasertsukNo ratings yet
- List of Philippine Aviation Schools, Colleges and UniversitiesDocument12 pagesList of Philippine Aviation Schools, Colleges and UniversitiesJojo Banzon100% (2)
- Get Started with NEOFLYDocument9 pagesGet Started with NEOFLYSebastian LlambiNo ratings yet
- Boeing 717Document7 pagesBoeing 717s3m3staNo ratings yet
- M. Tech. Bulletin 2020-2021 Aerospace DeptDocument8 pagesM. Tech. Bulletin 2020-2021 Aerospace DeptRajan RahulNo ratings yet
- Avro VulcanDocument9 pagesAvro Vulcanjb2ookworm100% (1)
- TacairDocument11 pagesTacaircatseekit 캣시킷No ratings yet
- Aircft Circulars Ltioi:L Advisofy Col:.Ii Ttle For Azroeijt 106Document12 pagesAircft Circulars Ltioi:L Advisofy Col:.Ii Ttle For Azroeijt 106rritter78No ratings yet
- 5 ClimbDocument21 pages5 Climbchhetribharat08No ratings yet
- Plane ConnectDocument4 pagesPlane ConnectDarren G. SarvisNo ratings yet
- CYFIDocument10 pagesCYFIGFNo ratings yet
- Air International - June 2020 UK PDFDocument92 pagesAir International - June 2020 UK PDFwilliam bayona100% (1)
- Ata Chapter 100Document1 pageAta Chapter 100Reza H GuswanNo ratings yet














![Air-Ground Teamwork On The Western Front - The Role Of The XIX Tactical Air Command During August 1944: [Illustrated Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/259895642/149x198/ac23a1ff63/1617227775?v=1)








![One-Man Airforce [Illustrated Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/299706563/149x198/1d62184812/1627141697?v=1)






























![Africa To The Alps: The Army Air Forces In The Mediterranean Theater [Illustrated Edition]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/259900264/149x198/9976cba35f/1617227775?v=1)