Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
Vishnu SharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning Objectives
Uploaded by
Vishnu SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
HERELITHOSP
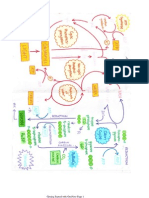
Learning Objectives for Environmental Management IGCSE - Page One RESOURCES and DEVELOPMENT
RESOURCES
DEVELOPMENT
Students should be able to describe the following physical structures and
processes
Students should be able to describe the human management of the
environment as follows;
1.1
1.2
1.3
2.1
The earths internal structure; core, mantle, crust
The types of rock; igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
The distribution type and reserves of metal ore minerals and fossil
fuels
The formation of fossil fuels
Plate tectonics; earth movements (folding, faulting, mountain
building)
The formation, composition and classification of soils
2.2
Variations in plant growth and land use according to soil type
1.4
1.5
3.1 The methods of searching and extracting rocks, minerals and fossil
fuels
3.2 The uses of rocks and minerals in industrial processes
3.3 Types of energy production from fossil and nuclear fuels
3.4 Location of mining and energy supply in relation to settlement and
industry
3.5 Influence of supply and demand on extraction of resources
3.6 Economic aspects and limitations of earthquake and volcanic areas
3.7 The patterns and implications of global trade in minerals and fuels
PHEREHYDROS
3.8 The achievement of social and economic goals through industrial
development
6.1
The water cycle
6.2
Variation in surface water
6.3
The role of the water cycle within ecosystems rainfall,
interception, run-of
7.1
The role of the ocean as an environment for interdependent
ecosystems
7.2
The resource potential of the oceans
7.3
The distribution of ocean currents and their efects on climate and
fisheries
7.4
The reversal of ocean current patterns e.g. El Nino and its efects
3.9 The collection and control of water resources
3.10 Competition, demand and supply of water
3.11 The impacts of flood and drought on development
3.12 The global pattern of fishery productivity
3.13 The methods of ocean bed mineral and fossil fuel extraction
3.14
The factors limiting the exploitation of oceanic resources
HEREATMOSP
14.1
The sun as an energy source, variations in insolation
14.2
The Earths atmospheric heat balance radiation, absorption,
reflection
14.3
The structure and composition of the atmosphere
14.4
The balances which maintain the Earths atmosphere as a mixture
of gases
14.5
Measuring and interpreting weather
14.6
Major climatic types and their graphical representation
14.8
14.9
Power production from wind, solar and water
Air pollution by smoke and exhaust fumes
14.10
The influence of climate on farming and settlement
REBIOSPHE
14.7
Extreme weather events, causes and locations - cyclones, floods
and droughts
20.1 The concept of an ecosystem
20.2 Organisaton within the ecosystem population, community,
habitat, niche
20.3 Physical factors temp. humidity, water, salinity, light, pH, soil,
nutrient, wind
20.4 Relationships of living organisms
20.5 Energy flow through the ecosystem
20.6 Nutrient cycling as exemplified by the carbon and nitrogen cycle
20.7 The resource potential of biodiversity
21.1
The major biome types and their relation to climatic regions
14.11 The transition of humans from components to determinants for the
ecosystem
14.12 The global population explosion
14.13 Factors influencing population growth
14.14 Analysis of population structure
14.15 Migration patterns
14.16 The demographic transition model and its limitations
14.17 The history of clearing natural vegetation
14.18 Types of farming and the environmental, social, technological and
economic factors that influence them
14.19 Recent developments in agriculture to improve yield
14.20
Global patterns in the trade of agricultural commodities
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- What Influences Enzyme ActivityDocument27 pagesWhat Influences Enzyme ActivityVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Exam Practice Answers 1Document1 pageExam Practice Answers 1Vishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Heat CVD Lungs CF QuestionsDocument73 pagesUnit 1-Heat CVD Lungs CF Questionsareyouthere9267% (3)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Essentialbiology09 Plantscienceahl 110207054725 Phpapp02Document18 pagesEssentialbiology09 Plantscienceahl 110207054725 Phpapp02Vishnu Sharma100% (1)
- Isotonic Point of A PotatoDocument12 pagesIsotonic Point of A PotatoVishnu Sharma100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument6 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ess Revision NotesDocument36 pagesEss Revision NotesVishnu Sharma100% (8)
- 3rd Chap QnbankDocument8 pages3rd Chap QnbankVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 NotesDocument8 pagesTopic 7 NotesVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 NotesDocument23 pagesTopic 2 NotesVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- ESS Command PromptsDocument2 pagesESS Command PromptsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper ChromatographyDocument3 pagesPaper ChromatographyumictNo ratings yet
- Ib Biology Syllabus-NewDocument20 pagesIb Biology Syllabus-NewVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Systems & Societies Notes: Topic 1: Systems and ModelsDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Systems & Societies Notes: Topic 1: Systems and ModelsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ex MehekDocument2 pagesEx MehekVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 NotesDocument29 pagesTopic 3 NotesVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes: Seria L No. Questions 1) (w13 Qp11)Document8 pagesEnzymes: Seria L No. Questions 1) (w13 Qp11)Vishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 0620 s05 Ms 1Document4 pages0620 s05 Ms 1Vishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Bank Igcse BiologyDocument24 pagesMCQ Bank Igcse BiologyVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4th Chap QnbankDocument4 pages4th Chap QnbankVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition: Serial No. QuestionsDocument4 pagesPlant Nutrition: Serial No. QuestionsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2nd Chap QnbankDocument21 pages2nd Chap QnbankVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Test BioDocument10 pagesTest BioVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Test Bio2Document5 pagesTest Bio2Vishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisrussell_mahmoodNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: Serial No. Questions 1) (w13 Qp11)Document7 pagesTransport in Plants: Serial No. Questions 1) (w13 Qp11)Vishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Challenging QuestionsDocument55 pagesChallenging QuestionsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Paper Ess MsDocument6 pagesPaper Ess MsVishnu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Igcse - Past PaperDocument6 pagesBiology - Igcse - Past Papersollu786_889163149100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- ClassiCool 12K To 72K - R410A - IOM - tcm478-51424Document88 pagesClassiCool 12K To 72K - R410A - IOM - tcm478-51424Dessouki SamakNo ratings yet
- Final Draft Business ProposalDocument8 pagesFinal Draft Business Proposalapi-384392869No ratings yet
- H2 Kinematics Tutorial 2015Document9 pagesH2 Kinematics Tutorial 2015Ronnie QuekNo ratings yet
- Fp-Boq Ammonia PalntDocument3 pagesFp-Boq Ammonia PalntMark Anthony ValbuenaNo ratings yet
- Calculations For IB ChemistryDocument16 pagesCalculations For IB Chemistryanthor100% (3)
- Wire¤t Rating PDFDocument2 pagesWire¤t Rating PDFVIKRAM DESAINo ratings yet
- Feb. 2005 Printed in Korea P/No.:3828ER3035PDocument36 pagesFeb. 2005 Printed in Korea P/No.:3828ER3035PMihaela CaciumarciucNo ratings yet
- PDF DC Address by BeeDocument1 pagePDF DC Address by BeePranabesh MallickNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Payment of Compensation Towards Damages in Regard To RoWDocument46 pagesGuidelines For Payment of Compensation Towards Damages in Regard To RoWclicknagpal100% (1)
- Manual of - Installation - Operation - Maintenance Light Oil and Biodiesel Burners Progressive and Fully Modulating Versions PG30 PG90 PG510 PG60 PG91 PG515 PG70 PG92 PG520 PG80 PG81Document52 pagesManual of - Installation - Operation - Maintenance Light Oil and Biodiesel Burners Progressive and Fully Modulating Versions PG30 PG90 PG510 PG60 PG91 PG515 PG70 PG92 PG520 PG80 PG81OSAMANo ratings yet
- I 210 DatasheetDocument8 pagesI 210 DatasheetMichael WilkinNo ratings yet
- SpittelauDocument20 pagesSpittelauFranco PiaggioNo ratings yet
- Well Completions ServicesDocument10 pagesWell Completions ServicesEgitie GodswillNo ratings yet
- Newfound Landing NewspaperDocument22 pagesNewfound Landing NewspaperAudra ToopNo ratings yet
- Workshop Manual 320 420 620 634Document116 pagesWorkshop Manual 320 420 620 634Henry Hla Khine0% (1)
- 5000m3 LPG Tank FarmDocument2 pages5000m3 LPG Tank FarmLpgTankFarmNo ratings yet
- Practix - Convenio Philips Mobile X-RayDocument243 pagesPractix - Convenio Philips Mobile X-RayNilufer Medical95% (19)
- From Lec.1 To Lec.26Document114 pagesFrom Lec.1 To Lec.26Youssry Elsayed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Biotech ReportDocument17 pagesBiotech ReportsrushtiNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Palestinian Economic Initiative - AHLC 26-9-2013Document14 pagesSummary of The Palestinian Economic Initiative - AHLC 26-9-2013Max BlumenthalNo ratings yet
- Best Tech KoreanDocument8 pagesBest Tech KoreanUkay Dedi SukardiNo ratings yet
- Thermogravimetric Analysis: W. J. P. RedfernDocument19 pagesThermogravimetric Analysis: W. J. P. RedfernKpam SokpoNo ratings yet
- H&H Compressor OilDocument2 pagesH&H Compressor Oilmister_no34No ratings yet
- Transformer NameplateDocument2 pagesTransformer NameplateHamza AliNo ratings yet
- Robotic Welding Intelligence and AutomationDocument390 pagesRobotic Welding Intelligence and AutomationAleksandar Arsov100% (1)
- 06 FEED Development - Onshore and OffshoreDocument2 pages06 FEED Development - Onshore and Offshorezdq02No ratings yet
- Parts Docs KOMATSU D65 Px16Document966 pagesParts Docs KOMATSU D65 Px16Mayki100% (11)
- 2a - Packed ColumnsDocument55 pages2a - Packed ColumnsDoaa Badarneh100% (1)
- Final Paper Gas Hydrates Around Makassar StraitsDocument6 pagesFinal Paper Gas Hydrates Around Makassar StraitsriowicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Operating Characteristics: Inlet Volumetric Rate of FlowDocument19 pagesOperating Characteristics: Inlet Volumetric Rate of FlowSandi AslanNo ratings yet