Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Linkages of Four Bar Mechanism
Uploaded by
Naganathan SivabalanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Linkages of Four Bar Mechanism
Uploaded by
Naganathan SivabalanCopyright:
Available Formats
13216-1-2P
AID: 1825 | 26/08/2014
By fixing any one of the links of the kinematic chain of a four bar linkage mechanism,
the type of inversions that results are,
Double crank mechanism
Double rocker mechanism
Crank rocker mechanism
Double crank mechanism
It is also called as drag link mechanism. This inversion is achieved by fixing the shortest
link. The other two links rotates on a full circle. The other link makes a complete
revolution.
It converts rotary motion from a crank to another crank (or link). The other link or crank
can be present in another plane or axis.
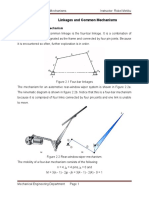
Show the double crank mechanism as in Figure (1).
Double rocker mechanism
Here, no link undergoes a complete revolution. Rather two links will make an oscillatory
motion and other two links form a coupler.
It is also called as rocker-rocker mechanism. Show the double rocker mechanism as in
Figure (2).
Crank-rocker mechanism
In this mechanism, the crank rotates about a fixed centre which makes the other link to
oscillate. It is designed to convert rotary motion to reciprocating motion.
Show the crank-rocker mechanism as in Figure (3).
Check whether all these linkages satisfy Grashofs law.
Express Grashofs law.
sl pq
Here, shortest length is s, longest link is l, and length of other two links is p and q.
1 in.
5 in.
3 in.
Substitute
for s,
for l,
for p, and
1 in. 5 in. 3 in. 5 in.
6 in. 8 in.
Hence, all the linkages satisfy Grashofs law.
5 in.
for q.
You might also like
- What Are Inversions of A Four-Bar Mechanism?Document5 pagesWhat Are Inversions of A Four-Bar Mechanism?darklord338No ratings yet
- Inversions of Four Bar Mechanisms ExplainedDocument6 pagesInversions of Four Bar Mechanisms ExplainedMegh BantawaNo ratings yet
- Table of Contents:-: - o o o o o o Singal Slider Mechanisms o Double Slider MechanismsDocument12 pagesTable of Contents:-: - o o o o o o Singal Slider Mechanisms o Double Slider MechanismsRajesh PowerNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 Objective: Four Bar Mechanism (Fig 5.1)Document6 pagesExperiment No. 5 Objective: Four Bar Mechanism (Fig 5.1)Waqas IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Machines and Mechanisms GuideDocument38 pagesMachines and Mechanisms GuideMudit MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Class Note: 3 Inversions of MechanismDocument8 pagesClass Note: 3 Inversions of MechanismShweta PradhanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Lab Manual GuideDocument18 pagesKinematics Lab Manual Guideshailendra_236No ratings yet
- MECHANICS OF VEHICLES: Simple Mechanisms to Vehicle ControlDocument18 pagesMECHANICS OF VEHICLES: Simple Mechanisms to Vehicle ControlRufi RizwanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 merchDocument66 pagesLecture 3 merchMuhammad Amir TajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Basics of MechanismsDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - Basics of MechanismsNagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- BASICS OF MECHANISMSDocument9 pagesBASICS OF MECHANISMSNagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- TOM Exp.Document9 pagesTOM Exp.Aneesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Inversion of Mechanisms for Changing Motion TypesDocument78 pagesInversion of Mechanisms for Changing Motion TypesQasim AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 HandoutDocument12 pagesChapter 2 HandoutRobel Metiku100% (1)
- Inversion of The MechanismDocument5 pagesInversion of The MechanismRanjit Rajendran100% (1)
- InversionDocument32 pagesInversionRohit NewarNo ratings yet
- Planar Linkages: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Document9 pagesPlanar Linkages: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Akash SoniNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms BasicsDocument64 pagesMechanisms BasicsarulmuruganNo ratings yet
- Pimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismDocument43 pagesPimpri Chinchwad Polytechnic, Nigdi: Chapter 01-Inversions of MechanismNarendra ChavdaNo ratings yet
- Kom Unit 1 Notes: Types of Constrained MotionsDocument7 pagesKom Unit 1 Notes: Types of Constrained MotionsParkunam RandyNo ratings yet
- INVERSIONS of MECHANISMSDocument39 pagesINVERSIONS of MECHANISMSDibakar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Kinematics and Theory of MachinesDocument109 pagesKinematics and Theory of MachinesSachin BahugunaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingDocument40 pagesCHAPTER THREE ACTUATOR InterfacingdanielNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery (AU 402) : Types of Kinematic Chain With Four Lower PairsDocument11 pagesKinematics of Machinery (AU 402) : Types of Kinematic Chain With Four Lower PairsJanardhanaNo ratings yet
- Inversion of MechanismsDocument15 pagesInversion of MechanismsAkunwa GideonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-1 Sub:-Kinematics of MachineDocument11 pagesTutorial-1 Sub:-Kinematics of MachineParth JadavNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Machinery NotesDocument25 pagesKinematics of Machinery Notesnishanth87No ratings yet
- Helicopter Power TransmissionDocument4 pagesHelicopter Power TransmissionTamil AzhahanNo ratings yet
- KOM ProjectDocument15 pagesKOM ProjectArvene Binmer JesaryNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 2 - Inversion of MechanismDocument34 pagesLecture - 2 - Inversion of MechanismGorkha EngineeringNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2-Linkages - 2023 FinalDocument46 pagesCHAPTER 2-Linkages - 2023 Finalaymane dibNo ratings yet
- Box Transport MechanismDocument36 pagesBox Transport MechanismInzi Gardezi81% (16)
- Planar MechanismDocument2 pagesPlanar MechanismNaganathan Sivabalan100% (1)
- IIT Guwahati Mechanical Engineering Lab ManualDocument10 pagesIIT Guwahati Mechanical Engineering Lab Manualdab111No ratings yet
- JSS3 Scheme of WorkDocument5 pagesJSS3 Scheme of WorkAbdullateef Adedoyin0% (1)
- Mechanical Actuation Systems DesignDocument34 pagesMechanical Actuation Systems Designdildar123100% (2)
- Inversion Mechanisms ExplainedDocument16 pagesInversion Mechanisms ExplainedImran TahirNo ratings yet
- Me6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulDocument64 pagesMe6401 Kom Notes RejinpaulkjsdjsdaNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machine - Kme 603 Question BankDocument11 pagesTheory of Machine - Kme 603 Question BankPrabal SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2Document11 pagesExperiment 2rajeevNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Actuation SystemsDocument14 pagesMechanical Actuation SystemsnkchandruNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument25 pagesKinematicsjsph021603No ratings yet
- MMSDocument12 pagesMMSDuke Stan100% (1)
- LAB 09 Oscillating Cylinder MechanismDocument11 pagesLAB 09 Oscillating Cylinder Mechanismmehtab ul hassanNo ratings yet
- Linkage MechanismsDocument15 pagesLinkage MechanismsSahilye GehaNo ratings yet
- Principle of Epicyclic GearingDocument11 pagesPrinciple of Epicyclic GearingAnuj AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Planar Linkages Mechanism GuideDocument8 pagesPlanar Linkages Mechanism GuideAlbert ArominNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Kinematic Chains and InversionsDocument41 pagesIntroduction to Kinematic Chains and InversionsB03Kavya MNo ratings yet
- Bp-Fullguide - Planetary GearsDocument10 pagesBp-Fullguide - Planetary GearsJohn Cadenillas RumayNo ratings yet
- Mechanical ActuatorsDocument39 pagesMechanical ActuatorsKashif UsmanNo ratings yet
- Submitted To:-: Sir FaisalDocument10 pagesSubmitted To:-: Sir FaisalSaad khanNo ratings yet
- Quick Return MechanismsDocument2 pagesQuick Return MechanismsAbhinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Using Crank and Slotted Link MechanismDocument22 pagesAir Compressor Using Crank and Slotted Link MechanismSaravanan Viswakarma75% (4)
- Chapter Two 2. Linkages MechanismsDocument41 pagesChapter Two 2. Linkages Mechanismssamuel mechNo ratings yet
- UNIT-I_TOMDocument37 pagesUNIT-I_TOMBandi KumarreddyNo ratings yet
- Kom Lab Manuals FinalDocument47 pagesKom Lab Manuals Finalappannusa0% (1)
- Kinematics of MachinesDocument40 pagesKinematics of MachinesAravind MuddebihalNo ratings yet
- Theory of Machines Experiments Student ManualDocument28 pagesTheory of Machines Experiments Student ManualHoneyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanisms: 2 Mechanisms and Simple MachinesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Mechanisms: 2 Mechanisms and Simple MachinesRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- 507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesFrom Everand507 Mechanical Movements: Mechanisms and DevicesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- Normal Statistical Table Standard Normal TableDocument1 pageNormal Statistical Table Standard Normal TableNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocument1 pageFlexible Manufacturing SystemNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Growth: Vascular Plant Zygote Fertilisation EmbryoDocument9 pagesGrowth: Vascular Plant Zygote Fertilisation EmbryoNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Control ResolutionDocument1 pageControl ResolutionNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Family, and Specific Code Is Given To Each Family. in This System, Machine Tools Are Arranged in A Cell and Used For Each Part FamilyDocument1 pageFamily, and Specific Code Is Given To Each Family. in This System, Machine Tools Are Arranged in A Cell and Used For Each Part FamilyNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Robotic LawsDocument1 pageRobotic LawsNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Hooke's LawDocument1 pageHooke's LawNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Stretch FormingDocument1 pageStretch FormingNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Types of Cutting Tools - Single & Multi PointDocument1 pageTypes of Cutting Tools - Single & Multi PointNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- PipesDocument1 pagePipesNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Bio MetalsDocument1 pageBio MetalsNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Integrated Manufacturing System Diagram and ComponentsDocument1 pageIntegrated Manufacturing System Diagram and ComponentsNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- GlassDocument1 pageGlassNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument1 pageStoichiometryNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Resisting MaterialsDocument1 pageCorrosion Resisting MaterialsNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- TRS BT: Point Bending or Four Point Bending Test Is UsedDocument1 pageTRS BT: Point Bending or Four Point Bending Test Is UsedNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Thermal ConductivityDocument1 pageThermal ConductivityNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Abrasives ProcessesDocument1 pageAbrasives ProcessesNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Specific HeatDocument1 pageSpecific HeatNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical MachiningDocument1 pageElectrochemical Machininganon_405561610No ratings yet
- Stretch FormingDocument1 pageStretch FormingNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Punch Is Used in Blanking Operation To Apply Pressure, Which Makes The Sheet Metal To GoDocument1 pagePunch Is Used in Blanking Operation To Apply Pressure, Which Makes The Sheet Metal To GoNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Electron MicroscopeDocument1 pageElectron MicroscopeNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Yield StrengthDocument1 pageYield StrengthNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Some of The Additives Combined With Rubber During Compounding Are As FollowsDocument1 pageSome of The Additives Combined With Rubber During Compounding Are As FollowsNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Shaping ProcessesDocument1 pageShaping ProcessesNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- A Tolerance Is Defined As Physical Dimensions, Physical Property and Other Measured Values That May Vary in The Size and Geometry of The PartDocument1 pageA Tolerance Is Defined As Physical Dimensions, Physical Property and Other Measured Values That May Vary in The Size and Geometry of The PartNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Types of IndustriesDocument1 pageTypes of IndustriesNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- Resist I VityDocument1 pageResist I VityNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet
- The Precision of A Measurement System Is Defined As Degree of Exactness of A Measurement or How Measured Values Are Close To Each OtherDocument1 pageThe Precision of A Measurement System Is Defined As Degree of Exactness of A Measurement or How Measured Values Are Close To Each OtherNaganathan SivabalanNo ratings yet