Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)
Uploaded by
Fakhar AbbasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)
Uploaded by
Fakhar AbbasCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 3.
1 (Solutions)
mathcity.org
Calculus and Analytic Geometry, MATHEMATICS 12
Merging man and maths
Available online @ http://www.mathcity.org, Version: 1.0.0
Question # 1(i)
y = x 2 1 (i)
x = 3 & x = 3.02 3 = 0.02
2
y + y = ( x + x ) 1
y = ( x + x ) 1 x2 + 1
2
= ( x + x ) x2
Put x = 3 & x = 0.02
2
Question # 2(ii)
Do yourself as above
Question # 2(iii)
x 4 + y 2 = xy 2
Taking differential
d x 4 + d y 2 = d xy 2
( ) ( )
y = ( 3 + 0.02 ) (3) 2
4 x 3 dx + 2 ydy = x 2 ydy + y 2 dx
2 ydy 2 xydy = y 2 dx 4 x3 dx
y = 0.1204
2 y (1 x ) dy = y 2 4 x 3 dx
Taking differential of (i)
dy = d x 2 1
dy = 2 x dx
Put x = 3 & dx = x = 0.02
dy = 2 ( 3)( 0.02 )
&
dy = 0.12
Question # 1(ii)
Do yourself as above.
Question # 1(iii)
1
y = x = x 2 . (i)
x = 4 & x = 4.41 4 = 0.41
1
y + y = ( x + x)2
1
y = ( x + x)2 x2
Put x = 4 & x = 0.41
1
y = ( 4 + 0.41) 2 ( 4 ) 2
= 2.1 2
Taking differential of (i)
d 12
dy =
x dx
dx
1 1
= x 2 dx =
2
y = 0.1
1
1
2x 2
dx
Put x = 4 & dx = x = 0.41
1
0.41
dy =
1 ( 0.41) =
4
2 4 2
( )
dy = 0.1025
Question # 2(i)
xy + x = 4
Taking differential on both sides
d ( xy ) + dx = d ( 4 )
xdy + ydx + dx = 0
xdy + ( y + 1) dx = 0
xdy = ( y + 1) dx
( )
dy
y +1
=
dx
x
dx
x
&
=
dy
y +1
dy
y 4x
=
dx
2 y (1 x )
2
2 y (1 x )
dx
=
dy
y 2 4 x3
Question # 2(iv)
xy ln x = c
Taking differential
d ( xy ) d ( ln x ) = d ( c )
1
xdy + ydx dx = 0
x
1
xdy = dx ydx
x
1
= y dx
x
1 xy
xdy =
dx
x
dy
1 xy
=
dx
x2
dx
x2
&
=
dy
1 xy
Question # 3(i)
Let
y = f ( x) = 4 x
where x = 16 and x = dx = 1
Taking differential of above
dy = d 4 x
( )
1
= d ( x)4
1 14 1
x dx
4
1 34
=
x dx
4
1
=
dx
3
4x 4
Put x = 16 and dx = 1
1
dy =
3 (1)
4 (16 ) 4
=
( )
4 2
3
4 4
1
= 0.03125
4 (8)
FSc-II / Ex- 3.1 - 2
Now f ( x + dx ) y + dy
= f ( x) + dy
4
4
16 + 1
17
(2 )
1
4 4
Q y = f ( x)
16 + 0.03125
+ 0.03125
Now dy = d ( sin x )
= cos x dx
Put x = 60o and dx = x = 0.01745
dy = cos 60o ( 0.01745 )
Now
Question # 3(ii)
Let y = f ( x) = ( x )
Where x = 8 & x = dx = 0.2
Taking differential of above
sin 61o = 0.866 + 0.008725
= 0.8747
dy = d ( x )3
1
( )
2
3 3
dx
( 0.2 )
3 2
1
( 0.2 )
3( 4)
= 0.01667
Now f ( x + x ) y + dy
= f ( x) + dy
1
3
(8 + 0.2 )
(8.02 )3 =
Question # 4
Let x be the length of side of cube where
x = 5 & x = 5.02 5 = 0.02
Assume V denotes the volume of the cube.
Then
V = x x x
3x 3
Put x = 8 and dx = 0.2
1
dy =
0.2 )
2 (
3 (8)3
(8)
1
3
Q y = f ( x)
+ 0.01667
2 + 0.01667
= 2.01667
Question # 3(iii)
1
Let y = f ( x) = x 5
Where x = 32 & x = dx = 1
Try yourself as above.
Question # 3(iv)
Let y = f ( x ) = cos x
rad
180
= 0.01745 rad
Where x = 30o & x = 1o =
Now dy = d ( cos x )
= sin x dx
Put x = 30o and dx = x = 0.01745
dy = sin 30o ( 0.01745 )
= ( 0.5 )( 0.01745) = 0.008725
Now f ( x + x ) y + dy
= f ( x) + dy
cos ( 30 1) = cos 30o + 0.008725
cos 29o = 0.866 + 0.008725
= 0.8747
Question # 3(v)
Let y = f ( x) = sin x
rad
180
= 0.01745 rad
Where x = 60o & x = 1o =
0.008725
= f ( x) + dy
sin ( 60 + 1) = sin 60o + 0.008725
1
3
1 2
= ( x ) 3 dx =
3
( 0.5 )( 0.01745 ) =
f ( x + x ) y + dy
=
= 2 + 0.03125 = 2.03125
= x3
Taking differential
dV = 3 x 2 dx
Put x = 5 & dx = x = 0.02
2
dV = 3 ( 5) ( 0.02 )
= 1.5
Hence increase in volume is 1.5 cubic unit.
Question # 5
Let x denotes diameter of a disc
Where x = 44 cm & x = 44.4 44 = 0.4
x
Then radius =
2
Let A denotes the area of the disc
2
Then A = ( radius )
x
2
= =
x
4
2
Taking differential
dA = d x 2
4
=
2 x dx =
x dx
4
2
Put x = 44 and dx = x = 0.4
dA =
( 44 )( 0.4 )
2
= ( 3.14 )( 22 )( 0.4 )
= 27.65
Hence change in area is 27.65 cm2
2
---- The End ---
Tuesday, 20 September 2005
By mathcity.org, mathcity@gmail.com
NOTE
If you find any mistake in these notes or you
think you have easiest method of any
question in these notes. Please submit it to
the above email or post it or hand over at
House # 143, St #6, Mehar Colony, 49Tail, Sargodha. ( : (048)3750143
You might also like
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument35 pagesDifferentiationMariAm NabiLah NaSrudinNo ratings yet
- Exercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)Document2 pagesExercise 3.1 (Solutions) : Question # 1 (I) Question # 2 (Ii) Question # 2 (Iii)sohail2798No ratings yet
- Exercise 2.4 (Solutions) : X y X X U X U y U Du D X DX DX X D D X X X X DX DX X y X X U X X X X y U U U X Du D X X DX DXDocument7 pagesExercise 2.4 (Solutions) : X y X X U X U y U Du D X DX DX X D D X X X X DX DX X y X X U X X X X y U U U X Du D X X DX DXOsamaNo ratings yet
- 14 - FDWK C4 Ism 07Document33 pages14 - FDWK C4 Ism 07Andy GaoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.7 (Solutions) : y X X X XDocument9 pagesExercise 2.7 (Solutions) : y X X X XFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Calculus: Differentiation RulesDocument17 pagesCalculus: Differentiation RulesAoSd' TikmanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XDocument6 pagesExercise 2.3 (Solutions) : y X X XFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- 09 04 Second Order Derivatives PDFDocument19 pages09 04 Second Order Derivatives PDFSri DNo ratings yet
- 30 Diffrentiation Part 1 of 1dddddddddddddDocument18 pages30 Diffrentiation Part 1 of 1dddddddddddddVishal VjNo ratings yet
- Revision Sheet Math 2Document8 pagesRevision Sheet Math 2Ahmed Abo nNo ratings yet
- Fe Tutorials Sem2Document8 pagesFe Tutorials Sem2narendasreNo ratings yet
- Algebra - Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide NCERTGUESSDocument155 pagesAlgebra - Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide NCERTGUESSAsma HussainNo ratings yet
- 11900-0130670227 Ismsec2 PDFDocument7 pages11900-0130670227 Ismsec2 PDFJosh JacobsonNo ratings yet
- Ans 2Document5 pagesAns 2teju1996coolNo ratings yet
- Ex 3 2 FSC Part2 Ver214Document5 pagesEx 3 2 FSC Part2 Ver214adnanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Hussien HassanNo ratings yet
- Knf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeDocument37 pagesKnf1013 Week9 Differentiation Compatibility ModeSyura PisyuNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1000A, Section 007Document30 pagesCalculus 1000A, Section 007arrowroot1No ratings yet
- Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesDifferential EquationsHarris LeeNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument4 pagesMathsVirusMusic & Co.No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document1 pageTutorial 2Vishwansh KumarNo ratings yet
- HW3 Exact Equations and Solutions by SubstitutionDocument1 pageHW3 Exact Equations and Solutions by SubstitutionAna RangelNo ratings yet
- Diferenciales Alvaro Mamamni Lanchipa 2011041679Document7 pagesDiferenciales Alvaro Mamamni Lanchipa 2011041679Adrian SalazarNo ratings yet
- © Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper CDocument3 pages© Science Exam Papers: Worked Solutions Edexcel C4 Paper CPa GesNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sheet 1 MA2020 Differential Equations (July - November 2016)Document1 pageAssignment Sheet 1 MA2020 Differential Equations (July - November 2016)Siddharth NathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Miscellaneous ProblemsDocument20 pagesChapter 3 Miscellaneous ProblemsAngel HilasacaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document1 pageTutorial 2parrybamra22No ratings yet
- Soal IntegralDocument29 pagesSoal IntegralMuhammad BurhannzNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1Document20 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials Ex 2.1anilNo ratings yet
- Advanced DifferentiationDocument5 pagesAdvanced DifferentiationcataiceNo ratings yet
- Jawaban KalkulusDocument30 pagesJawaban KalkulusanitaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1Document11 pagesExercise 5A: Dy DX 2 1kamaldinho11No ratings yet
- D3NN1S 4Document52 pagesD3NN1S 4Molina Armas Hugo RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Differential EquationDocument28 pagesDifferential Equationronhuman14No ratings yet
- Course 1 May 2001 Answer KeyDocument25 pagesCourse 1 May 2001 Answer KeyAnisah NiesNo ratings yet
- Quiz 02dif Background SolutionDocument6 pagesQuiz 02dif Background SolutionBunty SangralNo ratings yet
- Tut ODEDocument3 pagesTut ODEAbsyarie SyafiqNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument3 pagesIntegralLatifahUfairohZahidahZulfaNo ratings yet
- BASIC CALCULUS Week 2Document16 pagesBASIC CALCULUS Week 2EliNo ratings yet
- Worksol2 16Document7 pagesWorksol2 16Joko IsnantoNo ratings yet
- IntegralDocument8 pagesIntegralthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Faeez ZainNo ratings yet
- Assignment 6Document1 pageAssignment 6Dishant PandyaNo ratings yet
- MA1102RSoln8 (Partial)Document3 pagesMA1102RSoln8 (Partial)yuanz29No ratings yet
- Sem II MCQ Questions 2016Document5 pagesSem II MCQ Questions 2016Jayesh JainNo ratings yet
- Avaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoDocument13 pagesAvaliações 2009-1 - GabaritoEduardobelloNo ratings yet
- Semester III BCA3010 Computer Oriented Numerical MethodsDocument12 pagesSemester III BCA3010 Computer Oriented Numerical MethodsRaman VenmarathoorNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Module Tests AnswersDocument28 pagesUnit 2 Module Tests AnswersashtigosineNo ratings yet
- bbmp1103 Sem 2Document13 pagesbbmp1103 Sem 2irisardellaNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesUnit 03 Differential EquationsAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Exercises Problem No. 3Document4 pagesLesson 2 Exercises Problem No. 3Vahn RaymundoNo ratings yet
- DE Problem SetDocument1 pageDE Problem SetYagami LightsNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2.1 (Solutions)Document6 pagesExercise 2.1 (Solutions)Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ODEDocument1 pageTutorial ODENISCHAY VERMANo ratings yet
- Numerical and Engineering AnalysisDocument8 pagesNumerical and Engineering Analysisfatma abdullahNo ratings yet
- Solution of Assignment 01 (MTH401) (Differential Equation) : InstructionsDocument5 pagesSolution of Assignment 01 (MTH401) (Differential Equation) : InstructionsAhsanNo ratings yet
- MA2020 Differential Equations (July - November 2014) Assignment Sheet-1 (Covering Quiz-I Syllabus)Document2 pagesMA2020 Differential Equations (July - November 2014) Assignment Sheet-1 (Covering Quiz-I Syllabus)RK MEHTANo ratings yet
- Fismat SigitDocument3 pagesFismat SigitAnonymous Y2osIzqW9No ratings yet
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Time and Work Problems: A. B. C. DDocument2 pagesTime and Work Problems: A. B. C. DFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationDocument2 pagesA. B. C. D.: Answer: ExplanationFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Group Decoders For Correlated Massive MIMO Systems: The Use of Random Matrix TheoryDocument5 pagesGroup Decoders For Correlated Massive MIMO Systems: The Use of Random Matrix TheoryFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Multi-Pair Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Relaying With Very Large Antenna ArraysDocument6 pagesMulti-Pair Full-Duplex Amplify-and-Forward Relaying With Very Large Antenna ArraysFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis and Location Optimization For Massive MIMO Systems With Circularly Distributed AntennasDocument13 pagesPerformance Analysis and Location Optimization For Massive MIMO Systems With Circularly Distributed AntennasFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- A Wavelet Compression Based Channel Feedback Protocol For Spatially Correlated Massive MIMO SystemsDocument5 pagesA Wavelet Compression Based Channel Feedback Protocol For Spatially Correlated Massive MIMO SystemsFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Massive MIMO For Cell-Boundary UsersDocument15 pagesPerformance Analysis of Massive MIMO For Cell-Boundary UsersFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- On The Mutual Orthogonality of Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO ChannelsDocument5 pagesOn The Mutual Orthogonality of Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO ChannelsFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Antenna Grouping Based Feedback Compression For FDD-based Massive MIMO SystemsDocument14 pagesAntenna Grouping Based Feedback Compression For FDD-based Massive MIMO SystemsFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Using Raised Cosine Filter To Reduce Inter Symbol Interference in OFDM With BPSK TechniqueDocument5 pagesUsing Raised Cosine Filter To Reduce Inter Symbol Interference in OFDM With BPSK TechniqueFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Duality of Antennas and Subcarriers in Massive MIMO-OFDM Downlink SystemDocument2 pagesDuality of Antennas and Subcarriers in Massive MIMO-OFDM Downlink SystemFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Massive MIMO With Non-Ideal Arbitrary Arrays: Hardware Scaling Laws and Circuit-Aware DesignDocument16 pagesMassive MIMO With Non-Ideal Arbitrary Arrays: Hardware Scaling Laws and Circuit-Aware DesignFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Engineering Workshop Laboratory Manual: (LAB # 01) Introduction and Usage of Basic ToolsDocument8 pagesEngineering Workshop Laboratory Manual: (LAB # 01) Introduction and Usage of Basic ToolsFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Challan FormDocument1 pageChallan FormFakhar Abbas100% (1)
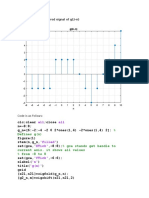
- Heaviside Function: X y On 'X Axis' 'Y Axis' On OffDocument2 pagesHeaviside Function: X y On 'X Axis' 'Y Axis' On OffFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Shifted and Flipped Signal of Mid IDocument2 pagesShifted and Flipped Signal of Mid IFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Level 2 Analytical ReasonigDocument30 pagesLevel 2 Analytical ReasonigFakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- SNS Weekly Meeting Form Lab6Document1 pageSNS Weekly Meeting Form Lab6Fakhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Aucet 2017 BrochureDocument18 pagesAucet 2017 BrochureNEELIMANo ratings yet
- Ordinary Differential EquationDocument16 pagesOrdinary Differential EquationCarlos ImperialNo ratings yet
- The University of Edinburgh Probability NotesDocument16 pagesThe University of Edinburgh Probability NotesHaaziquah TahirNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document232 pagesLecture 1Lujain nassirNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Grade 11Document4 pagesSyllabus Grade 11Mohammed AbdallahNo ratings yet
- First Order ODE Forced OscillationsDocument2 pagesFirst Order ODE Forced OscillationsDerek WangNo ratings yet
- MAT3005 Applied-Numerical-Methods TH 1 AC40Document2 pagesMAT3005 Applied-Numerical-Methods TH 1 AC40ashutosh rayNo ratings yet
- Medp U2 A1 RommDocument3 pagesMedp U2 A1 RommchabeNo ratings yet
- Problem Set & Solutions: Differential Equation: Ibnu RafiDocument73 pagesProblem Set & Solutions: Differential Equation: Ibnu RafiAllan Mugisha100% (1)
- 27 Introduction To Laplace TransformsDocument21 pages27 Introduction To Laplace TransformsSadek AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document61 pagesChapter 13Alice BotNo ratings yet
- OdeDocument36 pagesOdeSyed M AdnanNo ratings yet
- Poisson Equation: by Li ChenDocument18 pagesPoisson Equation: by Li ChenCristofer TejedaNo ratings yet
- Continuity & DifferentiabilityDocument48 pagesContinuity & DifferentiabilityPratham MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Calculus 1 Assignment 1Document1 pageCalculus 1 Assignment 1Md Rubaiyat BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- C3 Differentiation Topic AssessmentDocument6 pagesC3 Differentiation Topic AssessmentFaddy OrahaNo ratings yet
- Partial Differential Solution With MatlabDocument10 pagesPartial Differential Solution With MatlabDaniel Casas-OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics - 4 - 10MAT41Document86 pagesEngineering Mathematics - 4 - 10MAT41Shawn BeziNo ratings yet
- Math 212-1 - Exam 2Document2 pagesMath 212-1 - Exam 2Taleb AbboudNo ratings yet
- B.E. - Chemical - 2011 2012Document65 pagesB.E. - Chemical - 2011 2012Rajat MittalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - IDocument3 pagesMathematics - Isinguru shankarNo ratings yet
- The Product & Quotient RulesDocument4 pagesThe Product & Quotient RuleswolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Gauss'S Hypergeometric Equation, Leguerre'S Equation by Differential Transform MethodDocument7 pagesSolutions of Gauss'S Hypergeometric Equation, Leguerre'S Equation by Differential Transform MethodUmer Sayyab KhalidNo ratings yet
- Assignment 7Document2 pagesAssignment 7vpn userNo ratings yet
- Differential and Difference Equations A Comparison of Methods of Solution by Leonard C. MaximonDocument166 pagesDifferential and Difference Equations A Comparison of Methods of Solution by Leonard C. MaximonLeonardo DanielliNo ratings yet
- MST129 TMA Spring 2022-2023Document8 pagesMST129 TMA Spring 2022-2023rawan elhadidiNo ratings yet
- The Derivative of A FunctionDocument10 pagesThe Derivative of A FunctionSebastiánEspinozaNo ratings yet
- Implicit Differentiation Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesImplicit Differentiation Practice ProblemsabrilalywosnNo ratings yet
- ΚΕΧΑΓΙΑΣ DIAFORIKES EXISOSEISDocument272 pagesΚΕΧΑΓΙΑΣ DIAFORIKES EXISOSEISdimitirs boufasNo ratings yet
- Module 1-Rules For DifferentiationDocument3 pagesModule 1-Rules For DifferentiationEmmanuelle M. Hermosilla100% (1)