Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Consumer Behavior?: Definition
Uploaded by
Mohsen KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Consumer Behavior?: Definition
Uploaded by
Mohsen KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Marketing Quality Circle 1
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
What is Consumer Behavior?
Definition:
Consumer behavior is defined, as a behavior that consumers
display in searching for, purchasing, using, evaluating and disposing of
products and services that they expect will satisfy their needs.
Or
Consumer behavior is the study of when, why, how, and where
people do or do not buy products
The study of consumers helps firms and organizations improve their
marketing strategies by understanding issues such as how
The psychology of how consumers think, feel, reason, and select
between different alternatives (e.g., brands, products);
The psychology of how the consumer is influenced by his or her
environment (e.g., culture, family, signs, media);
The behavior of consumers while shopping or making other
marketing decisions;
Limitations in consumer knowledge or information processing
abilities influence decisions and marketing outcome;
How consumer motivation and decision strategies differ between
products that differ in their level of importance or interest that
they entail for the consumer; and
How marketers can adapt and improve their marketing
campaigns and marketing strategies to more effectively reach the
consumer.
One "official" definition of consumer behavior is "The study of
individuals, groups, or organizations and the processes they use to
select, secure, use, and dispose of products, services, experiences, or
ideas to satisfy needs and the impacts that these processes have on
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 2
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
the consumer and society." Although it is not necessary to memorize
this definition, it brings up some useful points:
Behavior occurs either for the individual, or in the context of a
group (e.g., friends influence what kinds of clothes a person
wears) or an organization (people on the job make decisions as to
which products the firm should use).
Consumer behavior involves the use and disposal of products as
well as the study of how they are purchased. Product use is often
of great interest to the marketer, because this may influence how
a product is best positioned or how we can encourage increased
consumption. Since many environmental problems result from
product disposal (e.g., motor oil being sent into sewage systems
to save the recycling fee, or garbage piling up at landfills) this is
also an area of interest.
Consumer behavior involves services and ideas as well as
tangible products.
The impact of consumer behavior on society is also of relevance.
For example, aggressive marketing of high fat foods, or
aggressive marketing of easy credit, may have serious
repercussions for the national health and economy.
Why Study Consumer Behavior?
Foundations of marketing management
To stay in business by attracting and retaining customers
To benefit from understanding consumer problems.
To establish competitive advantage
Basic objective of the studying consumer behavior is that the firm
needs to know who buys their product. How they buy? When and
where they buy? Why they buy? How they respond to marketing
stimuli. Because they study consumer behavior what is Consumer
Behavior about? How, why, where and when consumers make
purchase decisions? Considers who influences the decisions? What is
Consumer Behavior about? All these are important questions, which
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 3
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
are to be known to the companies so that they can design, and
implement
marketing
strategies
to
satisfy
the
customers.
Consumers determine the sales and profits of a firm by their purchase
decisions, thus the economic viability of the firm. What is Disposable
income and what is Discretionary income what is the stage of family
life cycle stage because these all these factors influence the consumer
behaviors which are very important to the marketers.
Consumer behavior is the procedure throughout the final purchaser
makes buy assessments. This can be defined as Consumer Behavior
Defined as of the processes involved when individuals or groups select,
purchase, use, or dispose of products, services, ideas, or experiences
to satisfy needs and desires (Solomon, 1996). Those actions directly
involved in obtaining, consuming and disposing of products and
services, including the decision processes that precede and follow
those actions. Consumer behavior examines mental and emotional
processes in addition to the physical activities.
3- Research Perspectives of CB?
1. The Decision-Making Perspective:
a. . . . proposes that buying results from consumers perceiving
that they have a problem and then they move through a
series of rational steps to solve the problem
b. Generic Decision Model is:
i. Problem Recognition
ii. Search
iii. Alternative Evaluation
iv. Choice
v. Post acquisition Evaluation
2. The Experiential Perspective:
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 4
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
a. . . . Proposes that in some instances buying results from the
consumers need for fun, to create fantasies, obtain
emotions, and feelings.
b.
Frequently uses interpretative research methods.
3. The Behavioral Influence Perspective:
a. . . . Assumes that strong environmental forces propel
consumers to make purchases without necessarily first
developing strong feelings or beliefs about the product.
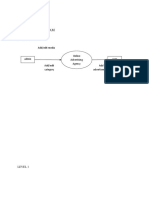
Consumer Behavior Wheel: (The Plan of the Book)
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 5
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
Issues in Consumer Behavior:
1. Relationship marketing:
a. Pioneers are oracle , Siebel & broad vision
b. It is all about building trust between firm & its customers
c. Consumers should feel that they have received something
for being a participant in relationship
d. It results in strong & lasting relationships with a core group
of cusomers [less expensive]
2. Celebrity advertising:
a. Using emotional power of identification
b. Usage of celebrity advertising when customer is unaware
about what the brand stands for.
3. Cultural practices:
a. Core element of Indian philosophy is its belief in doctrine of
karma
b. Indians relies on their elders, superiors & teachers
c. Example;
d. Colgate , surf , lifebuoy
e. Global leaders but failure in India
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 6
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
f. Nike , ray-ban , Kellogg
4. Managing brand associations:
a. Are high visibility campaigns required in all product
categories for building brands?
b. What should be the objective of an advertising campaign &
how should that objective be dovetailed with brand building
efforts?
c. What should be the approach for a marketer who decides to
build brands with limited advertising?
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 7
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
1.1 Why Study Customers?
Before actually studying Consumer behavior, let us answer the question of
why to study this discipline at all? In other words, we will explore and
scope and importance of Consumer behavior.
Effective marketing must begin with a thorough understanding of how
and why customers behave as they do (Merenski, 1998). Specifi- cally, in
order to tailor solutions to customers particular needs and desires, the
marketer requires a grounded knowledge of buyer motivations and
decision-making processes, together with all those environmental factors
which may exert influence upon them. Put another way, the marketer is
seeking to address three basic questions:
Why does the customer want to buy a particular product or service?
How will he or she decide which option to purchase? What factors may
influence this decision?
What is Consumer Behavior?
Let us try to define Consumer behavior
Mental and physical activities undertaken by household and
business customers that result in decisions and actions to pay for,
purchase and use products and services
An important part of the marketing process is to understand why a
customer or buyer makes a purchase. Without such an understanding,
businesses find it hard to respond to the customers needs and wants.
For a marketing manager, the challenge is to understand how customers
might respond to the different elements of the marketing mix that are
presented to them. If management can understand these customer
responses better than the competition, then it is a potentially significant
source of competitive advantage.
Consumer Buying Behavior refers to the buying behavior of the ultimate
consumer. A firm needs to analyze buying behavior for:
Buyers reactions to a firms marketing strategy has a great impact on
the firms success.
The marketing concept stresses that a firm should create a marketing
mix (MM) that satisfies (gives utility to) customers, therefore need to
analyze the what, where, when and how consumers buy.
All this time we have been carrying out our discussion about consumer
behavior without properly defining what or who is a consumer. So who is
a consumer? Let us now define a consumer.
A customer is a person in either a household or an organizational unit
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 8
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
who plays a role in the completion of a transaction with a marketer or
an entity
Who then is a Consumer?
For example, you as a customer purchasing a burger at a restaurant
versus the restaurant purchasing the burger meat, bun and condiments
to prepare the hamburger for sale
Can you bring out the difference between the terms consumer, buyer, and
customer?
Customer Roles
A customer plays different roles
User the person who actually consumes or uses the product and
receives the benefits
E.g. in the example of burger, the person who actually eats the
burger
Payer the person who finances the purchase
E.g. the person who provides the money to pay for the burger
Buyer - the person who participates in acquiring the product
E.g. the person who orders and/or actually hands over the money for
the hamburger
In certain cases one and the same person could play all these three roles
or it could be other way around also; i.e., different people could play
different roles.
Concepts
Role
specialization
User
Users focus on
performance
value
evaluation
Payer
Payer focus on
budget
allocations.
Formalized
process
Users submit a
formal
requisition and
technical
specifications.
Payer use
sound
budgeting
practices.
Accountability
Users
accountable for
correct
Specifications.
Buyer
Buyers often
separate from
users and
payers,
specialize in
Buyers follow
well-laid -out
policies and
processes.
Buyers
Accountable
for
professional
buying.
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
Marketing Quality Circle 9
A Circle of Continuous Improvements
User
capabilities
may lead
to in-house
production
.
Need
identification
on may be an
extended
process.
Users may
automate
The requisition
for rebuys.
Strong
financial
position can
gain favorable
terms for
suppliers.
Buying center
Buying centre
brings all roles
together.
Payers often
are the
Deciders in the
buying centre.
Decision
process
Users most
active at
The
specification
and vendor
screening
stage.
Payers
most active
at the
Decision
stage.
Internal
capabilities
Complexity
Buy class
For new
task buys,
Payers may
have to juggle
money.
Buyers with
low skills may
draw on
external
advice.
Buyers may
need to
coordinate
with multiple
suppliers.
Rebuys may be
reutilized and
Automated.
New task buys
would require
professional
talents of
Buyers bring
vendors and
users together
Buyers active
throughout the
decision
Process.
Superior University, Lahore
www.superior.edu.pk
You might also like
- Consumer Behavior Report 1Document35 pagesConsumer Behavior Report 1adeelngNo ratings yet
- Define Consumer BehaviourDocument8 pagesDefine Consumer Behaviouranon_159165915No ratings yet
- Modules-1 Notes CBDocument22 pagesModules-1 Notes CBMuskan hamdevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, Introduction To Consumer BehaviorDocument5 pagesChapter 1, Introduction To Consumer BehaviorMuthusamy Senthilkumaar100% (2)
- Assignment of Advertising and Sales PromotionDocument7 pagesAssignment of Advertising and Sales PromotionShafaqat Ramzan0% (1)
- IntroductionDocument7 pagesIntroductionTASKIN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Mod Iii-MmDocument10 pagesMod Iii-MmskbsantoshNo ratings yet
- Importance of Studying Consumer BehaviourDocument5 pagesImportance of Studying Consumer BehaviourPrasanjeet Bhattacharjee100% (2)
- Consumer Behavior and Technology Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesConsumer Behavior and Technology Learning Objectivesjobin jacobNo ratings yet
- MBA Study Material on Consumer BehaviourDocument35 pagesMBA Study Material on Consumer Behaviouraruna krishnaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topics On Consumer BehaviourDocument8 pagesThesis Topics On Consumer Behaviouraflohdtogglebv100% (2)
- Consumer Behavior Full NotesDocument42 pagesConsumer Behavior Full NotesDipti PandeyNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument14 pagesConsumer BehaviorshikhilNo ratings yet
- Consumer Beh Final PDFDocument8 pagesConsumer Beh Final PDFsomya bagariaNo ratings yet
- Defining Consumer BehaviorDocument25 pagesDefining Consumer BehaviorZeeshan ch 'Hadi'No ratings yet
- Learn Consumer Behaviour FundamentalsDocument78 pagesLearn Consumer Behaviour FundamentalsNiyonzimaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Consumer BehaviorDocument5 pagesLecture 2 Consumer BehaviorrabiaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards Readymade Garments With Reference To ITCDocument96 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards Readymade Garments With Reference To ITCchunnu12345678980% (5)
- Consumer behaviour: SignificanceDocument68 pagesConsumer behaviour: Significancevishu131No ratings yet
- Understanding Consumer Behavior and Factors Influencing Buying DecisionsDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Consumer Behavior and Factors Influencing Buying DecisionsAditi GuptaNo ratings yet
- CB & MC Unit-IDocument52 pagesCB & MC Unit-Idevendrasaradhana5No ratings yet
- Marketin Buyer BehaviorDocument19 pagesMarketin Buyer BehaviorJake Austria50% (2)
- 3&4 - Importance of Consumer BehavoirDocument7 pages3&4 - Importance of Consumer BehavoirAbdullah YousufNo ratings yet
- Project Report on Marketing Plan for a BusinessDocument31 pagesProject Report on Marketing Plan for a BusinessAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour - Uniti NotesDocument3 pagesConsumer Behaviour - Uniti NotesRathina BalajiNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument17 pagesConsumer BehaviourShabana ShabzzNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior: Its Origins and Strategic ApplicationsDocument38 pagesConsumer Behavior: Its Origins and Strategic Applicationsnisar24No ratings yet
- CUSTOMER LOYALTY TO SONY CENTER CHENNAIDocument79 pagesCUSTOMER LOYALTY TO SONY CENTER CHENNAIMeena SivasubramanianNo ratings yet
- SM 2Document12 pagesSM 2Pavitra JainNo ratings yet
- Consumer Preference To Tea BrandDocument105 pagesConsumer Preference To Tea Brandkingsley_psbNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour WorkbookDocument55 pagesConsumer Behaviour WorkbookSourabh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Dr. Shashi Singhal Asst - Prof. Amity Business SchoolDocument22 pagesDr. Shashi Singhal Asst - Prof. Amity Business SchoolLokesh ShewaniNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument10 pagesConsumer BehaviourwaelsharbaNo ratings yet
- For The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement of The Degree of Master of Management Study (MMS)Document30 pagesFor The Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement of The Degree of Master of Management Study (MMS)Sammi ShahuNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument27 pagesConsumer BehaviourRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management 2Document45 pagesMarketing Management 2reshmasankuNo ratings yet
- Understanding Consumer Buying BehaviorDocument51 pagesUnderstanding Consumer Buying Behaviorarjunmba11962486% (7)
- 5 key factors influencing consumer behaviourDocument7 pages5 key factors influencing consumer behavioursamimahmadNo ratings yet
- What Is Consmer?Document18 pagesWhat Is Consmer?kashif shafiqNo ratings yet
- NOTESDocument31 pagesNOTESkartikeyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour IntroDocument66 pagesConsumer Behaviour IntroSweetzTekwani100% (1)
- Consumer Behavior Before MidsDocument36 pagesConsumer Behavior Before MidsMirza Mustafa NoorNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour - Introduction - Chapter 1Document16 pagesConsumer Behaviour - Introduction - Chapter 1Syed Muheeb HussainNo ratings yet
- EverythingDocument23 pagesEverythingMohd GhaziNo ratings yet
- CB 1Document20 pagesCB 1Purav RiatNo ratings yet
- Why we study consumer behaviourDocument24 pagesWhy we study consumer behaviourksachchuNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior: Understanding the ProcessDocument96 pagesConsumer Behavior: Understanding the Processbhanu prasadNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Consumer Behaviour (For SA1)Document5 pagesUnit 3 - Consumer Behaviour (For SA1)lovellmenezesNo ratings yet
- CB STUDY OF BARISTA AND CAFE COFFEE DAYDocument75 pagesCB STUDY OF BARISTA AND CAFE COFFEE DAYnavdeep2309No ratings yet
- Understanding Customer Satisfaction in Bike IndustryDocument80 pagesUnderstanding Customer Satisfaction in Bike IndustryRAMAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Is DynamicDocument17 pagesConsumer Behaviour Is DynamicShivangi SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour and Satisfaction Level - PriyaDocument4 pagesA Study On Consumer Buying Behaviour and Satisfaction Level - Priyavenkat rahulNo ratings yet
- UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIORDocument77 pagesUNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BUYING BEHAVIORvishakavsNo ratings yet
- Study Notes 5 - Introduction To MarketingDocument6 pagesStudy Notes 5 - Introduction To Marketingmjraikwar26No ratings yet
- About Understanding Consumer Behavior Theories and ConceptsDocument6 pagesAbout Understanding Consumer Behavior Theories and Conceptsnehla1004No ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior InsightsDocument12 pagesConsumer Behavior InsightsVindicatorNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior and Marketing StrategyDocument17 pagesConsumer Behavior and Marketing StrategySuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- Britannia - Project ReportDocument32 pagesBritannia - Project ReportHelpdesk77% (44)
- Understanding Consumer Behavior: Cracking the Code of Consumer PsychologyFrom EverandUnderstanding Consumer Behavior: Cracking the Code of Consumer PsychologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Marketing Strategies Essential Learn How Your Business Can Meet Customer Needs in an Increasingly Competitive MarketFrom EverandMarketing Strategies Essential Learn How Your Business Can Meet Customer Needs in an Increasingly Competitive MarketNo ratings yet
- AddressesDocument8 pagesAddressesMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Audditting Cls Assig On Case StudyDocument2 pagesAudditting Cls Assig On Case StudyMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- AddressesDocument8 pagesAddressesMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- POM Finnal AssingmentDocument7 pagesPOM Finnal AssingmentMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- POM Finnal AssingmentDocument7 pagesPOM Finnal AssingmentMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Rule:: Session 2 What Is Consumer Behavior?Document9 pagesConsumer Rule:: Session 2 What Is Consumer Behavior?Mohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Pom Final ProjectDocument1 pagePom Final ProjectMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Royal Bank of Scotland: Corporate Rap SheetDocument9 pagesRoyal Bank of Scotland: Corporate Rap SheetMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Rabia Ga RibhgugkggDocument3 pagesRabia Ga RibhgugkggMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- FIRM Risk ScorecardDocument2 pagesFIRM Risk ScorecardMohsen Khan71% (7)
- What Is Difference Between Capital Market and Money MarketDocument4 pagesWhat Is Difference Between Capital Market and Money MarketMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Wal Mart:: Second Point ManagementDocument4 pagesWal Mart:: Second Point ManagementMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Shaukat Raza MirzaDocument23 pagesShaukat Raza MirzaMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- FIRM Risk ScorecardDocument2 pagesFIRM Risk ScorecardMohsen Khan71% (7)
- Rabia Ga RibhgugkggDocument3 pagesRabia Ga RibhgugkggMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Telco Grade Server, CRM Software, Network EquipmentDocument10 pagesTelco Grade Server, CRM Software, Network EquipmentMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Rabia Ga RibhgugkggDocument3 pagesRabia Ga RibhgugkggMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Mohsen, KhanDocument3 pagesMohsen, KhanMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Lasani FeedDocument4 pagesLasani FeedMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Mohsen, KhanDocument3 pagesMohsen, KhanMohsen KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 FEEDDocument14 pagesLesson1 FEEDkevNo ratings yet
- Director Corporate Sponsorship in Austin TX Resume Bill HerringDocument2 pagesDirector Corporate Sponsorship in Austin TX Resume Bill Herringbill-atxNo ratings yet
- Case Problems..MG1 ProjDocument17 pagesCase Problems..MG1 ProjIrish Barcelon77% (30)
- Pay Per Click (PPC) : A) Flat-Rate PPCDocument6 pagesPay Per Click (PPC) : A) Flat-Rate PPCTrifan_DumitruNo ratings yet
- Resume Tap Vot 30 Nov 2013Document6 pagesResume Tap Vot 30 Nov 2013api-252614723No ratings yet
- Iloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2017-037Document4 pagesIloilo City Regulation Ordinance 2017-037Iloilo City Council100% (1)
- Feasibilty Chapters 1 - 5Document90 pagesFeasibilty Chapters 1 - 5Jessica Magat Del Rosario100% (5)
- Data Flow Diagram Level 0: Add/edit MediaDocument4 pagesData Flow Diagram Level 0: Add/edit MediaManoj Kumar MohanNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter AssignmentDocument2 pagesCover Letter AssignmentAndreea ZenoviaNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Strategy ChinaDocument14 pagesCoca Cola Strategy ChinaAkram EmNo ratings yet
- Check List For Data AnalystDocument2 pagesCheck List For Data AnalystRajkumar DurairajNo ratings yet
- Speaker Presentation Form Template V2Document8 pagesSpeaker Presentation Form Template V2jaNo ratings yet
- Contoh SoalDocument4 pagesContoh SoalSyaifuddin NoctisNo ratings yet
- Introducing Gain Detergent in ChinaDocument44 pagesIntroducing Gain Detergent in ChinawlonghiniNo ratings yet
- IMB443-Volkswagen in IndiaDocument33 pagesIMB443-Volkswagen in IndiaPutri KartikaNo ratings yet
- A Poster Is Any Piece of Printed Paper Designed To Be Attached To A Wall or Vertical SurfaceDocument3 pagesA Poster Is Any Piece of Printed Paper Designed To Be Attached To A Wall or Vertical SurfaceFitiyaNo ratings yet
- Case Study SONY (UTS Manjik)Document8 pagesCase Study SONY (UTS Manjik)sckalovNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument33 pagesExecutive SummaryRajiv Ranjan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle, Evolution and Marketing StrategiesDocument2 pagesProduct Life Cycle, Evolution and Marketing Strategiesharshan_agNo ratings yet
- Nellen Taxation 2014 PDFDocument95 pagesNellen Taxation 2014 PDFEntot SuhartonoNo ratings yet
- ChenOne lifestyle storeDocument38 pagesChenOne lifestyle storeSyed Muhammad Tayyab50% (6)
- A Summer Training Project Report OnDocument128 pagesA Summer Training Project Report OnHoney SinghNo ratings yet
- Peter Lindbergh Photographic PracticeDocument5 pagesPeter Lindbergh Photographic PracticeJoyce Sarah SunNo ratings yet
- Logical FallaciesDocument2 pagesLogical FallaciesRupasari_MuraiNo ratings yet
- Product ManagementDocument8 pagesProduct Managementsmita_keluskar92No ratings yet
- A Study On Marketing Department of Fidus Quartz Watch Company With Special Reference To Customer Satisfaction (Original)Document62 pagesA Study On Marketing Department of Fidus Quartz Watch Company With Special Reference To Customer Satisfaction (Original)Jomal Mathew PuthenveettilNo ratings yet
- Y3 Module 6 Develop A Business PlanDocument31 pagesY3 Module 6 Develop A Business PlanLucky Mariane Asuncion75% (4)
- Marketing Plan of Pizza HutDocument11 pagesMarketing Plan of Pizza HutCindy LakhramNo ratings yet
- Volume 45, Issue 42, October 17, 2014Document52 pagesVolume 45, Issue 42, October 17, 2014BladeNo ratings yet
- Vels Vidhyalaya Senior Secondary School - Kovilpatti The Triumph of Surgery Grade 9 English HWDocument3 pagesVels Vidhyalaya Senior Secondary School - Kovilpatti The Triumph of Surgery Grade 9 English HWjeya moorthyNo ratings yet