Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MM361 Lec10
Uploaded by
Mustansar CheemaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MM361 Lec10
Uploaded by
Mustansar CheemaCopyright:
Available Formats
15/09/2014
Lec 10: Carbanion, Carbcation and
Free Radical
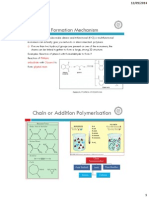
Ionic Addition Polymerisation
Many ionic polymerisation proceed at much higher rates than free-radical
polymerisation, because the concentration of actively propagating chains is
very much higher.
A propagating ionic active centre is accompanied by a counter-ion
Termination cant occur (anionic polymerization) by reaction between two
ionic active sites because they are of similar charge
15/09/2014
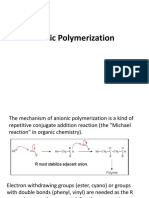
Anionic Polymerisation
Monomers can be polymerised anionically if there is an excess of one electron
at the active site i.e. a negative charge.
The active site may be a carbanion or an oxanion (formed during an anionic
ring-opening polymerization).
Initiators:
Grignard reagent (R-X-Mg), organometallic
compounds, alkali metals, metal amides.
Termination does not occur in anionic
polymerisation (except protic solvents), as alkali
counterions do not combine with carbanionic
active sites.
Such polymers which permanently retain their active centres and continue to
grow until the monomer is available are called living polymers.
Anionic Polymerisation
The initiator in anionic polymerization may be any compound providing a
strong nucleophile (Grignard reagents and other organometallic
compounds). Initiation involves the addition of the initiator to the double
bond of the monomer.
If a solvent that is able to release a proton is used, it can react with the
active site. Ammonia is an
example of such a protic
solvent and the reaction results in
the formation of a negatively
charged NH2 ion, which can
initiate the polymerization of a
new chain. In other words, we
have chain transfer to the solvent.
15/09/2014
Anionic Polymerisation:
Applications
Can you make polystyrene chain by anionic
polymerisation using K-NH2 initiator ?
Initiation involves the dissociation of K-NH2 followed by addition of amide
ions to styrene.
KNH 2 K NH 2
CH CHPh
NH 2 CH 2 CHPh H 2 NCH 2 CH K Ph 2
Anionic Polymerisation:
Styrene in liquid ammonia
K-NH2 K+ + NH2-
No living polymer of polystyrene in this case as the chain is
transferred to ammonia.
15/09/2014
Anionic Polymerisation:
Triblock copolymer
Anionic Monomers
15/09/2014
Cationic Polymerisation
Cationic polymerizations involve an active site/centre where there is a
positive charge (deficit of one electron, hence electrophile).
Initiators
Protonic acids (H2SO4, HClO4), or Lewis acids (BF3, SnCl4, AlCl3) with
cocatalyst, such as water or organic chloride (R-Cl)
BF3 H 2O H ( BF3OH )
AlCl3 RCl R ( AlCl 4 )
HCl cant be used, why?
Termination can occur either by unimolecular rearrangement of the ion pair,
(anion-cation recombination) or through chain transfer to the monomer.
Many side reactions can also occur; with trace amounts of water.
Cationic Polymerisation:
Lewis Acid initiator
15/09/2014
Cationic Polymerisation:
Applications
Butyl Rubber by copolymerization of isobutylene with small quantities of
isoprene at low temperatures (-90C) using AlCl3 initiator and
Chlomomethane.
Coordination Polymerisation
Some polymerisation reactions involve complexes formed between a
transition metal and the -electrons of the monomer.
Reaction/addition of monomer is similar to anionic polymerizations
These types of polymerizations usually lead to linear and stereoregular
chains (isotactic) and use catalysts, also called Ziegler-Natta catalysts
Ziegler-Natta catalysts generally consist of a metallo-organic nature
involving a metal (from groups I-Ill) such as triethyl aluminium, and a
transition metal compound (from groups IV-VIII), such as titanium
tetrachloride.
The degree of stereo-regularity depends on the nature of the catalyst, the
nature of the monomer, temperature, the nature of the solvent.
15/09/2014
Coordination Polymerisation:
Ziegler-Natta catalyst
The metal organic compound acts as a weak anionic initiator, first forming a
complex. The transition metal ion (Ti) is connected to the end of the growing
chain and simultaneously coordinates the incoming monomer at a vacant
orbital site.
Coordination Polymerisation:
Ziegler-Natta catalyst
Ethylene, in the presence of a combination of an organo-aluminum and a
zirconium compound, at relatively low pressure, produced polyethylene.
The gas ethylene could be polymerized at 100, 20, or 5 atmospheres and
finally even at atmospheric pressure very rapidly in the presence of certain,
easily prepared, catalysts to give a high molecular weight plastic.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- PSE - Polymer SynthesisDocument54 pagesPSE - Polymer SynthesisRishi VyasNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Optimization of Polymerization ReactorsDocument103 pagesModeling and Optimization of Polymerization ReactorsAdeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Socio Syllabus For MidDocument1 pageSocio Syllabus For MidMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Labelling Theory PresDocument39 pagesLabelling Theory PresMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- CultureDocument37 pagesCultureSufyan JawedNo ratings yet
- Liaison Package MediaFest 2015Document11 pagesLiaison Package MediaFest 2015Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Socio Lecture # 1Document6 pagesSocio Lecture # 1Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy & Characterization of Polymers: Chain MicrostructureDocument10 pagesSpectroscopy & Characterization of Polymers: Chain MicrostructureMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- POlymer EngineeringDocument9 pagesPOlymer EngineeringSyed Hashim Shah HashmiNo ratings yet
- NMR for sequence and structural isomerism analysisDocument19 pagesNMR for sequence and structural isomerism analysisSyed Hashim Shah HashmiNo ratings yet
- MM361 Lec8-9Document5 pagesMM361 Lec8-9Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Socio Lecture # 2,3Document41 pagesSocio Lecture # 2,3Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- MM361 Lec6Document5 pagesMM361 Lec6Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- MM361 Lec22-24Document18 pagesMM361 Lec22-24Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Polymer TacticityDocument6 pagesPolymer TacticitySyed Hashim Shah HashmiNo ratings yet
- CH 321 Quiz 1Document2 pagesCH 321 Quiz 1Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Thermo II Lacture 31-33Document14 pagesThermo II Lacture 31-33Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- MM361 - Lec 1-4Document19 pagesMM361 - Lec 1-4Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Heat engines, refrigerators and heat pumps explainedDocument4 pagesHeat engines, refrigerators and heat pumps explainedMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Chapter 14 PDFDocument21 pagesFormula Sheet Chapter 14 PDFMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- CPT Review & Lab Assignments for May 1-2Document1 pageCPT Review & Lab Assignments for May 1-2Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Size ReductionDocument30 pagesSize ReductionMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet Chapter 13Document8 pagesFormula Sheet Chapter 13Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- MM211 Lec10Document4 pagesMM211 Lec10Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Carbon DioxideDocument2 pagesCarbon Dioxidekurisuchiness100% (1)
- CPT Review & Lab Assignments for May 1-2Document1 pageCPT Review & Lab Assignments for May 1-2Mustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- EE211 C & D - EE211 C & D - Assignment 01 PDFDocument3 pagesEE211 C & D - EE211 C & D - Assignment 01 PDFMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- Taekwondo's Class For GikianDocument4 pagesTaekwondo's Class For GikianMustansar CheemaNo ratings yet
- PMMA - SynthesisDocument8 pagesPMMA - Synthesiscuongtran_siegenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Polymer ScienceDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Polymer ScienceAnshul GautampurkarNo ratings yet
- SiliconesDocument77 pagesSiliconesRobert HicksNo ratings yet
- Anionic Chain PolymerizationDocument32 pagesAnionic Chain PolymerizationBùi Bảo NgânNo ratings yet
- 3 PolymersDocument36 pages3 PolymersMuhammad TanweerNo ratings yet
- Anionic PolymerisationDocument3 pagesAnionic PolymerisationChayanAnandNo ratings yet
- VuHaiNam - Assignment 7Document4 pagesVuHaiNam - Assignment 7Nam VuNo ratings yet
- SBS-A4-lug09 Polimero EuropeoDocument10 pagesSBS-A4-lug09 Polimero Europeoosvaldo gutierrezNo ratings yet
- Ed 083 P 443Document4 pagesEd 083 P 443ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Chap 7 Ionic and Living PolymerizationsDocument57 pagesChap 7 Ionic and Living PolymerizationsSyuan CNo ratings yet
- Polystyrene PreparationDocument15 pagesPolystyrene PreparationZeinab A. ElBhnsawiNo ratings yet
- Anionic PolymerizationDocument20 pagesAnionic PolymerizationMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument35 pagesUnit 4 - Chemistry - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inAyush Kr. SharmaNo ratings yet
- SynthesisOfHydroxyl TerminatedDocument7 pagesSynthesisOfHydroxyl TerminatedFridausNo ratings yet
- JornalDocument3 pagesJornalIshu SethiNo ratings yet
- 1 CHE315 (Polymerization Mechanisms Note)Document31 pages1 CHE315 (Polymerization Mechanisms Note)Praise BamwaNo ratings yet
- Reveiw Materials For Mid-Term ExamDocument6 pagesReveiw Materials For Mid-Term Exam章晴昱No ratings yet
- This Difference Between Living and NonDocument1 pageThis Difference Between Living and Noncuongtran_siegenNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument120 pagesPolymerJustine GuardarioNo ratings yet
- Che 523-Polymer-Science-&-TechDocument56 pagesChe 523-Polymer-Science-&-TechTahiru SakaNo ratings yet
- Polymers 2Document17 pagesPolymers 2VIJAYKUMAR CHORAPALLINo ratings yet
- Acs Chemrev 5b00441Document74 pagesAcs Chemrev 5b00441MEGAN ASBROCKNo ratings yet
- 2014 ML Pa6Document6 pages2014 ML Pa6Yash VoraNo ratings yet
- Degradable Aliphatic PolyestersDocument162 pagesDegradable Aliphatic PolyestersCarlotta C.No ratings yet
- Polymers: Lecture 3 Unit-2b: The Mechanism of Addition PolymerizationDocument3 pagesPolymers: Lecture 3 Unit-2b: The Mechanism of Addition PolymerizationUtkarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Solution-polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber with end-group functionalization for improved silica-filled compositesDocument13 pagesSolution-polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber with end-group functionalization for improved silica-filled compositesthinkpad x1No ratings yet
- A Study and Analysis of Manifacturing Process of Thiokol Rubber Swapna V, K. MounikaDocument8 pagesA Study and Analysis of Manifacturing Process of Thiokol Rubber Swapna V, K. Mounikamuhammad sameer ansariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Ionic Polymerization-2Document22 pagesLecture 4 - Ionic Polymerization-2Lester John VeraNo ratings yet