Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atpl - Meteorology Set
Uploaded by
HamidK.FarhatCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Atpl - Meteorology Set
Uploaded by
HamidK.FarhatCopyright:
Available Formats
ATPL - METEOROLOGY Set - B
Study online at quizlet.com/_npymr
1.
1. What is the relationship
between QFE and QNH at an
airport 50ft below MSL?
c. QFE > QNH
2. Which cloud type may indicate
the presence of severe
turbulence?
8.
c. Altocumulus
lenticularis
3. What causes wind?
a. Difference in
pressure
a. Difference in pressure
b. Rotation of the earth
c. Frontal systems
d. Difference in temperature
4.
4. In what cloud is icing and
turbulence most severe?
9.
a. Cb
5. Which cloud would you
encounter the most intensive
rain?
b. Ns
10.
a. Ci
b. Ns
c. St
d. Sc
6.
6. How do you calculate the
lowest usable flight level?
a. Lowest QNH and lowest
negative temperature below ISA
b. Lowest QNH and highest
negative temperature below ISA
c. Highest QNH and highest
temperature above ISA
d. Highest QNH and lowest
temperature
8. Generally, as altitude
increases:
b. Temperature, pressure
and density decreases
9. Where is wind shear the
greatest?
a. Near a strong low level
inversion and in the region
of a thunderstorm
a. Near a strong low level
inversion and in the region
of a thunderstorm
b. Near a valley with wind
speeds greater than 35kts
c. On the windward side of a
mountain
d. When the wind is greater
than 35kts
a. Cb
b. Ns
c. Sc
d. Ci
5.
a. Clear ice
a. Temperature decreases
and density increases
b. Temperature, pressure
and density decreases
c. Temperature and
pressure increase and
density decreases
d. Temperature decreases
and pressure and density
increase
a. Cirrocumulus
b. Nimbostratus
c. Altocumulus lenticularis
d. Stratocumulus
3.
7. The most dangerous form
of airframe icing is:
a. Clear ice
b. Hoar frost
c. Dry ice
d. Rime ice
a. QFE = QNH
b. QFE < QNH
c. QFE > QNH
d. There is no clear relationship
2.
7.
10. Where do you find the
majority of the air within the
atmosphere?
a. Troposphere
a. Troposphere
b. Stratosphere
c. Tropopause
d. Mesosphere
a. Lowest QNH and
lowest negative
temperature below ISA
11.
11. Where is the 300mb level
approximately in ISA?
a. 30,000ft
b. 39,000ft
c. 18,000ft
d. 10,000ft
a. 30,000ft
12.
12. What type of precipitation would
you expect at an active unstable cold
front?
d. Showers
associated
with
thunderstorms
a. Freezing rain
b. Light to moderate continuous rain
c. Drizzle
d. Showers associated with
thunderstorms
13.
13. Where are icing conditions on route
specified?
14. You are flying at FL170. The
pressure level which is closest to you is
the:
20.
c. SWC (sig.
weather chart)
and SIGMET
15. In which weather report would you
expect to find information about icing
conditions on the runway?
16. TAFs are usually valid for:
a. For the period indicated in the TAF
itself
b. For 18 hours
c. For 24 hours
d. For 8 hours
17.
17. When a TREND is included at the
end of a METAR, the trend is a forecast
valid for:
21.
18. VOLMETs are updated
a. Every hour
b. 4 times a day
c. 2 times a day
d. Every half hour
21. An inversion is:
a. A decrease of pressure with
height
b. A decrease of temperature with
height
c. An increase of temperature with
height
d. An increase of pressure with
height
c. METAR
22.
a. For the
period
indicated in
the TAF itself
b. 2 hours after
the time of
observation
a. 1 hour after the time of observation
b. 2 hours after the time of observation
c. 2 hours after it was issued
d. 1 hour after it was issued
18.
20. What is normally the most
effective measure to reduce or avoid
CAT effects?
c. 500mb
a. GAFOR
b. TAF
c. METAR
d. SIGMET
16.
b. 1025 hPa
a. Change of flight
level
a. Change of flight level
b. Change of course
c. Increase of speed
d. Decrease of speed
a. 300mb
b. 700mb
c. 500mb
d. 850mb
15.
19. QFE is 1000 hPa with an airfield
elevation of 200m AMSL. What is
QNH? (use 8m per hPa)
a. 975 hPa
b. 1025 hPa
c. 1008 hPa
d. 992 hPa
a. TAF and METAR
b. METAR and SIGMET
c. SWC (sig. weather chart) and
SIGMET
d. SPECI and TREND
14.
19.
d. Every half
hour
22. The isobars drawn on a surface
weather chart represent lines of
equal pressure:
c. An increase of
temperature with
height
d. Reduced to sea
level
a. At flight level
b. At height of observatory
c. At a determined density altitude
d. Reduced to sea level
23.
23. How does a pilot react to heavy
freezing rain at 2,000ft/AGL, when
he is unable to deice nor land?
a. He ascends to the cold air layer
above
b. He continues to fly at the same
altitude
c. He turns back before the aircraft
loses maneuverability
d. He descends to the warm air layer
below
c. He turns back
before the aircraft
loses
maneuverability
24.
24. Two aircrafts, one with a sharp wing
profile (S) and the other with a thick
profile (T), are flying through the same
cloud with the same true airspeed. The
cloud consists of small supercooled
droplets. Which of the following
statements is most correct concerning ice
accretion?
d. Aircraft
S
experiences
more icing
than T
25. ATC will only report wind as gusting if:
a. Gust speed exceeds mean speed by
>15kts
b. Gusts to over 25kts
c. Gusts exceed mean speed by 10kts
d. Gusts to under 25kts
26.
26. A flight is to depart from an airport
with runway 09 and 27. Surface wind is
270/05; an inversion is reported at 300
feet with turbulence and wind shear. The
wind just above the inversion is 090/30.
What is the safest departure procedure?
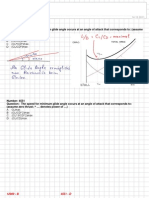
27. You are cruising at FL 200, OAT is 40C, sea level pressure is 1033 hPa.
Calculate the true altitude.
c. Gusts
exceed
mean speed
by 10kts
b. Depart
on runway
09 with a
tailwind
28. In what frequency band is the ATIS
normally broadcasted?
a. LF
b. HF
c. ADF
d. VHF
31.
d. 19, 340 ft
d. VHF
d. 300 hPa
31. The station pressure used in
surface weather charts is:
a. Met vis is
usually less than
RVR
a. QNE
a. QNE
b. QFF
c. QFE
d. QNH
32.
32. What is the coldest time of the
day?
d. 1/2 hour after
sunrise
a. 1hr before sunrise
b. 1/2 hr before sunrise
c. At exact moment of sunrise
d. 1/2 hour after sunrise
33.
a. 20,660 ft
b. 21,740 ft
c. 18,260 ft
d. 19, 340 ft
28.
30. With regard to RVR and Met vis:
a. Met vis is usually less than RVR
b. Met vis is usually greater than RVR
c. RVR is usually less than met vis
d. Met vis and RVR are usually the
same
a. Take-off is not possible under these
conditions
b. Depart on runway 09 with a tailwind
c. Depart runway 27 with maximum
throttle during the passage through the
inversion
d. Depart runway 27 with as steep an
ascent as possible
27.
29. Which constant pressure altitude
chart is standard for a 30,065 ft
pressure level (FL 300)?
a. 200 hPa
b. 700 hPa
c. 500 hPa
d. 300 hPa
30.
a. Aircraft T experiences more icing than S
b. Aircraft S and T experience the same
amount of icing
c. Neither of the aircrafts accumulate ice
due to the small size of droplets
d. Aircraft S experiences more icing than T
25.
29.
33. The code "BECMG FM 1100 RASH" in a METAR means:
a. From 1100UTC, the cessation of
rain showers
b. Becoming from 1100UTC slight rain
showers
c. Becoming from 1100UTC rain
showers
d. Becoming from 1100UTC till
0000UTC slight rain showers
b. Becoming from
1100UTC slight
rain showers
34.
34. Which of the following
statements is an interpretation
of the METAR?
00000KT 0200 R14/0800U
R16/P1500U FZFG VV001
m03/m03 Q1022 BECMG 0800
=
d. RVR for runway 14
800m, vertical visibility
100ft, calm,
meteorological visibility
improving to 800m in
the next 2 hours
36.
LSAW SWITZERLAND 0307
SIGMET 2 VALID
030700/031100 LSSW mod to
sev cat fcst north of alps btn fl
260 and fl 380 / stnr / intsf =
a. Meteorological visibility
200m, RVR for runway 16
1500m, temperature -3C,
vertical visibility 100m
b. Meteorological visibility
200ft, RVR for runway 16 more
than 1500m, vertical visibility
100ft, fog with hoar frost
c. Meteorological visibility for
runway 14 800m, fog with hoar
frost, RVR for runway 16 more
than 1500m
d. RVR for runway 14 800m,
vertical visibility 100ft, calm,
meteorological visibility
improving to 800m in the next
2 hours
35.
35. Refer to the following TAF
for Zurich
LSZH 261019 20018G30KT
9999 -RA SCT050 BKN080
TEMPO 23012KT 6000 -DZ
BKN015 BKN030 BECMG 1518
23020G35KT 4000 RA
OVC010=
The lowest visibility forecast at
ETA Zurich 1430 UTC is:
a. 6km
b. 6nm
c. 4km
d. 10km
36. Which of the following
statement is an interpretation
of the SIGMET?
c. Moderate to severe
clear air turbulence to be
expected north of the
Alps. Intensity
increasing. Danger zone
between FL260 and
FL380
a. Severe turbulence observed
below FL 260 north of the Alps.
Pilots advised to cross this
area above FL 380
b. Moderate to strong clear air
turbulence of constant
intensity to be expected north
of the Alps
c. Moderate to severe clear air
turbulence to be expected north
of the Alps. Intensity
increasing. Danger zone
between FL260 and FL380
d. Zone of moderate to severe
turbulence moving towards the
area north of the Alps.
Intensity increasing. Pilots
advised to cross this area
above FL260
a. 6km
37.
37. From a pre-flight briefing
you know a jet stream is at
31,000ft whilst you are at
FL270. You experience
moderate CAT. What would be
the best course of action?
b. Descend
a. Stay level
b. Descend
c. Climb
d. Reduce speed
38.
38. In which zone of a
jetstream is the strongest CAT
to be expected?
a. The warm air side of the core
b. Exactly in the center of the
core
c. About 12,000ft above the core
d. The cold air side of the core
d. The cold air side of the
core
39.
39. In an area of converging air
b. Clouds can be formed
a. Clouds cannot be formed
b. Clouds can be formed
c. Convective clouds can be dissolved
d. Stratified clouds can be dissolved
40.
40. The greater the pressure gradient the:
a. Closer the isobars and the lower the temperatures
b. Further the isobars will be apart and the higher the temperature
c. Closer the isobars and the stronger the wind
d. Further the isobars will be apart and the weaker the wind
c. Closer the isobars and the stronger the wind
You might also like
- Meteorology Guide: Key Concepts for ATPL ExamDocument185 pagesMeteorology Guide: Key Concepts for ATPL Examtahirh1985No ratings yet
- MET Question BankDocument136 pagesMET Question BankIvan100% (1)
- Meteorology (CAAB)Document84 pagesMeteorology (CAAB)MoshiurRahmanNo ratings yet
- Meteorology 001Document193 pagesMeteorology 001Andrin JohnsonNo ratings yet
- MeteorologyDocument99 pagesMeteorologymkzgroundNo ratings yet
- Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate Meteorology TestDocument26 pagesDry Adiabatic Lapse Rate Meteorology TestNam Anh LêNo ratings yet
- Meteorology Guide: Composition, Winds, Thermodynamics & MoreDocument193 pagesMeteorology Guide: Composition, Winds, Thermodynamics & MoreBharat HarmilapiNo ratings yet
- Meteorology PDFDocument71 pagesMeteorology PDFOmkar jituriNo ratings yet
- Airnav CPLDocument4 pagesAirnav CPLshombisNo ratings yet
- Technical Instructor ResultsDocument98 pagesTechnical Instructor Resultscapt_hiralNo ratings yet
- General Navigation Practice TestDocument17 pagesGeneral Navigation Practice TestDharmendraNo ratings yet
- 1108.1201 FT Final (Retest)Document36 pages1108.1201 FT Final (Retest)Akshay MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Meteorology Question BankDocument10 pagesMeteorology Question BankSaheb SinghNo ratings yet
- Met SurendraDocument56 pagesMet SurendraVivek ChandraNo ratings yet
- Atmosphere Questions and AnswersDocument35 pagesAtmosphere Questions and AnswerssajjadNo ratings yet
- Radio Nav Sample Q's (1-2-3) 2008Document45 pagesRadio Nav Sample Q's (1-2-3) 2008momanbh100% (3)
- Question Bank Met2Document32 pagesQuestion Bank Met2sajjadNo ratings yet
- ATPL Radio Aids ReviewDocument5 pagesATPL Radio Aids ReviewAbhinaya Sekar100% (2)
- JET QueDocument5 pagesJET QueDharavGosaliaNo ratings yet
- Gen Nav WeOneDocument272 pagesGen Nav WeOneAnkitBhuta67% (3)
- Explainations of General Navigation QuestionsDocument11 pagesExplainations of General Navigation QuestionsZarrar Khan100% (1)
- IC Joshi Aviation Met Total QDocument89 pagesIC Joshi Aviation Met Total Qsakshee gojreNo ratings yet
- ICAO Annexes & Conventions ExplainedDocument99 pagesICAO Annexes & Conventions ExplainedAyse sahin100% (1)
- 11 - CPL Questions Rad NavigationDocument73 pages11 - CPL Questions Rad NavigationMoshiurRahman100% (2)
- Systems Atpl PDFDocument111 pagesSystems Atpl PDFMay Be100% (1)
- Average Height of the Tropopause by LatitudeDocument482 pagesAverage Height of the Tropopause by LatitudeNeha Xavier100% (1)
- Atpl OralDocument4 pagesAtpl OralAjay KoikalNo ratings yet
- Meteorology multiple choice questionsDocument68 pagesMeteorology multiple choice questionsAnandhanNo ratings yet
- Aviation Meteorology Test 3Document10 pagesAviation Meteorology Test 3ayushNo ratings yet
- Atpl - Aerodinamics PDFDocument6 pagesAtpl - Aerodinamics PDFarief wicaksono rachmatNo ratings yet
- DGCA Meteorology QuestionDocument2 pagesDGCA Meteorology QuestionShibin Johney100% (1)
- Air Regs HandbookDocument90 pagesAir Regs Handbookjitansh singhNo ratings yet
- Fragen - Principles of FlightDocument313 pagesFragen - Principles of FlightTomasz Kurdziel50% (2)
- Air Navigation Questionnaire CPL PatternDocument18 pagesAir Navigation Questionnaire CPL Patternnodynaren100% (1)
- Sahil Khurana Answer KeyDocument5 pagesSahil Khurana Answer KeyDibyajivan MohantyNo ratings yet
- Red Bird Technical Question BankDocument48 pagesRed Bird Technical Question BankMeme DankNo ratings yet
- Q Bank MetDocument94 pagesQ Bank MetsajjadNo ratings yet
- Radio Bearings QuestionsDocument5 pagesRadio Bearings QuestionsJai Sachdev50% (2)
- Sahil Khurana Answer KeyDocument9 pagesSahil Khurana Answer KeyAmit KhannaNo ratings yet
- Metrology PDFDocument17 pagesMetrology PDFrahulNo ratings yet
- Flight Planning & Flight MonitoringDocument2 pagesFlight Planning & Flight MonitoringNat ChuenjumlongNo ratings yet
- 040 Human Performance & Limitations - V2+v3 - 31OUT09Document166 pages040 Human Performance & Limitations - V2+v3 - 31OUT09kest32No ratings yet
- R.k.Bali 20 Q.P PDFDocument124 pagesR.k.Bali 20 Q.P PDFPrerak Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation 172Document172 pagesInstrumentation 172adarsh snija100% (1)
- ATC Clearances Quiz With AnswersDocument11 pagesATC Clearances Quiz With AnswersAaron GuerreroNo ratings yet
- PPL NavigationDocument5 pagesPPL NavigationAubrey AndresonNo ratings yet
- CP, PNR Num.Document4 pagesCP, PNR Num.Lohrasp Suraliwala75% (4)
- Air Navigation Test No.3Document15 pagesAir Navigation Test No.3Vivek ChandraNo ratings yet
- Air Navigation in IndiaDocument14 pagesAir Navigation in IndiaRamBabuMeena100% (1)
- FP PNR, Pet, CTDocument31 pagesFP PNR, Pet, CTadityaNo ratings yet
- AvMet ATPLDocument4 pagesAvMet ATPLRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- AIR REGS 4: Safety Regulations for Aircraft Refueling and Restricted AirspaceDocument34 pagesAIR REGS 4: Safety Regulations for Aircraft Refueling and Restricted Airspacetopgun320100% (1)
- CPL RNav5 NDB - ADFDocument5 pagesCPL RNav5 NDB - ADFvivekNo ratings yet
- September 21 (Test 3)Document11 pagesSeptember 21 (Test 3)Karun SharmaNo ratings yet
- Review 3 MeteorologyDocument6 pagesReview 3 MeteorologyAvocado BananaNo ratings yet
- Questions MetDocument8 pagesQuestions MetAsim AnandNo ratings yet
- Sahil Khurana Met QuestionDocument75 pagesSahil Khurana Met Questionchainkart projectNo ratings yet
- Question 2Document213 pagesQuestion 2Aakash Shokeen100% (3)
- Circulating Heat Pump Water Heater Versati (Air To Water Heat Pump)Document10 pagesCirculating Heat Pump Water Heater Versati (Air To Water Heat Pump)blmasinaNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Water BalanceDocument25 pagesAtmospheric Water BalanceKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Clint Over Prodotti ENG-GREEK 2018 WDocument2 pagesClint Over Prodotti ENG-GREEK 2018 WlibegradNo ratings yet
- The StratosphereDocument3 pagesThe StratosphereSuman JyotiNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric ChartDocument1 pagePsychrometric ChartAbhi Ram M100% (1)
- Psychrometric Chart: Twet As A Function of Tdry and HRDocument34 pagesPsychrometric Chart: Twet As A Function of Tdry and HRsamNo ratings yet
- McQuiston HVAC Analysis Design 6th Solutions PDFDocument313 pagesMcQuiston HVAC Analysis Design 6th Solutions PDFIgor LomesNo ratings yet
- Air MassDocument3 pagesAir MassTotztutz Togodunz TonztunzNo ratings yet
- 14thermal Expansion of Materials - 227-249Document11 pages14thermal Expansion of Materials - 227-249KAMAL KANT KUSHWAHANo ratings yet
- Module Meteorology For MarinersDocument3 pagesModule Meteorology For MarinerssbdmanNo ratings yet
- Marine MeteorologyDocument49 pagesMarine MeteorologyMahdi Bordbar100% (12)
- Humidity Control Unit: Hcuc SeriesDocument2 pagesHumidity Control Unit: Hcuc SeriesRafael RuizNo ratings yet
- Met For AircrewDocument17 pagesMet For AircrewtiklimastiNo ratings yet
- Ami 310Document6 pagesAmi 310MumkoNo ratings yet
- Improve cooling tower energy efficiencyDocument36 pagesImprove cooling tower energy efficiencyDimpu SihombingNo ratings yet
- 10 Pressure RedDocument32 pages10 Pressure Redkawa21No ratings yet
- Comfort and HumidityDocument7 pagesComfort and HumidityaNo ratings yet
- Ari 210.240-94Document46 pagesAri 210.240-94Suthi TunkNo ratings yet
- Tugas 9 Peralatan Fluida Termal: Oleh: ASLAM KAMAL AFDHAL (1410912034)Document12 pagesTugas 9 Peralatan Fluida Termal: Oleh: ASLAM KAMAL AFDHAL (1410912034)Aslam Kamal AfdhalNo ratings yet
- Weather and Climate FactorsDocument24 pagesWeather and Climate Factorsdefinite ChibvongodzeNo ratings yet
- 050 MeteorologyDocument894 pages050 MeteorologykgyjuhiNo ratings yet
- 16 Climate Analysis PDFDocument38 pages16 Climate Analysis PDFmadhura1khaireNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficiency of Light Weight Steel StructuresDocument12 pagesEnergy Efficiency of Light Weight Steel StructuresAravind NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Meteo ROLOGIADocument46 pagesMeteo ROLOGIAAne Miren Navarro AparicioNo ratings yet
- Hospital Maintenance Log Provides Insight Into Daily OperationsDocument180 pagesHospital Maintenance Log Provides Insight Into Daily OperationsRaja AliNo ratings yet
- TRACE 700: Load CalculationDocument7 pagesTRACE 700: Load CalculationSajib Chandra RoyNo ratings yet
- TDP-632 Rooftop Units Level 2 Constant Volume (Preview)Document8 pagesTDP-632 Rooftop Units Level 2 Constant Volume (Preview)willis000050% (2)
- Racqb 2Document7 pagesRacqb 2ratchagaraja0% (1)
- Dew Point and RH TableDocument2 pagesDew Point and RH Tablejunidomar86% (7)