Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deforestation
Uploaded by
Rjvm Net Ca FeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deforestation
Uploaded by
Rjvm Net Ca FeCopyright:
Available Formats
Deforestation, clearance orclearing is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is
thereafter converted to a non-forest use.[1] Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to
farms, ranches, or urban use.
Forests are cleared all around the world for a number of reasons, including:
o
Harvesting of timber to produce wood and paper products
o
Clearing land for farms, cash-crop plantations, and cattle ranching
o
Clearing land for urban development, including homes and roads.
Seventy percent of the worlds plants and animals live in forests and are losing their habitats to
deforestation. Loss of habitat can lead to species extinction. This is not only a biodiversity tragedy but also
has negative consequences for medicinal research and local populations who rely on the animals and
plants in the forests for hunting and medicine.
Because this is the way where we get our livelihood.
It is very hard to stop deforestation because our world relies on timber to make infrastructures, paper and
other commonly used equipment. We have no other alternatives so we solely rely on the cutting down of
trees for these resources. The worlds economic state is in such dis-repair that most people do not own
laptops or other forms of computers to do their writing on. Even if this was possible, the majority of the
population would want to print their work which would still use up paper. These by-products wouldnt be so
bad if humans replace the trees that they cut down. Even for people who do replant trees, this makes a
minor effect as trees take a long time to grow to full height.
Its is also hard to stop the building of infrastructures on land where trees have been. This is because as our
world's population grows there is less and less room to build infrastructures, so we turn to land where
trees grow. Humans then chop down the trees to accommodate housing in the land we have so we have
no option but to build on land where trees had been. It is also hard to plant and harvest croon the land we
already have for the same reason. We really have no more room. The land that trees grow on is also mad
of rich soil ideal for agriculture. There is also becoming less and less rich soil that is not already in use.
Soil erosion is a naturally occurring process that affects all landforms. In agriculture, soil erosion refers to
the wearing away of a field's topsoil by the natural physical forces of water (Figure 1) and wind (Figure
2) or through forces associated with farming activities such as tillage.
Causes of Soil Erosion
Land use: Humans play a major role in soil erosion through their use and abuse of natural
resources, for example deforestation, grazing, arable land use, faulty farming systems, high
crop intensity, housing construction, mining etc.
Climate: The two most important climatic factors having a direct effect on erosion are
precipitation and wind velocity. Other climatic factors have an indirect effect on soil erosion,
such as water balance, evapotranspiration, temperature and relative humidity. Indirect factors
affect the erosivity of rainfall by altering the soil moisture regime and the proportion of rainfall
that may become surface runoff. For erosion control it is necessary to investigate physical
characteristics of rainfall, including the amount, distribution, intensity, energy load, seasonality
and variability of rainfall and the formation and course of surface runoff.
Soil: The susceptibility of a soil to erosion is influenced by its physical, hydrological, chemical
and mineralogical properties as well as its soil profile characteristics. Important soil physical
and hydrological properties that affect the resistance of a soil to erosion include texture,
structure, water retention and transmission properties.
Hydrology: Infiltration, surface detention, overland flow velocity, and subsurface water flow
are important soil erosion components of the hydrological cycle. The different types of flow and
their velocities may be turbulent or laminar, steady or unsteady, uniform or non-uniform and
influence the extent of erosion
Landforms: Slope gradient, slope length and shape of slope are the important variables of
landform that affect erosion processes for all types of soil erosion, e.g., splash, sheet, rill, and
gully erosion.
Soil Erosion effects humans by adding additional toxic organic chemicals and heavy metals to
the soil as well as eroding land so that there is less land to farm on.
Soil erosion is second only to population growth as the biggest environmental problem the world faces.
The starting point for longitude is the
Prime Meridian. The Prime Meridian is
at longitude 0.
The starting point for latitude is the equator.
The equator is at latitude
0 (0 degree). At the North Pole, the latitude is
90N (90 degrees north).
At the South Pole, the latitude is 90S (90
degrees south).
The lines of latitude are also known as parallels
of
latitude. That is because the lines of latitude
are parallel to the equator and to
each other.
Longitude ()
Lines of longitude appear vertical with
varying curvature in this projection, but
are actually halves of great ellipses, with
identical radii at a given latitude.
Latitude ()
Lines of latitude appear horizontal with
varying curvature in this projection; but
are actually circular with different radii. All
locations with a given latitude are
collectively referred to as acircle of
latitude.
The equator divides the planet into
a Northern Hemisphere and a Southern
Hemisphere, and has a latitude of 0.
TROPIC OF CAPRICORN
: the parallel of latitude that is approximately
2312 degrees south of the equator and that is
the southernmost latitude reached by the
overhead sun
TROPIC OF CANCER
: the parallel of latitude that is approximately
2312 degrees north of the equator and that is
the northernmost latitude reached by the
overhead sun
The Arctic Circle is one of the five
major circles of latitude that mark maps of the
Earth.
Arctic Circle
The parallel of latitude approximately 6634 no
rth, the southern boundary of the North Frigid Z
one, markingthe approximate limit north of whi
ch the sun remains above the horizon all day o
n the summer solstice.
an imaginary line drawn parallel to the equator,
at 2328prime; S ofthe North Pole: between the
North Frigid Zone and the NorthTemperate Zon
e.
The Antarctic Circle is one of the five major
circles (or parallels) of latitude that mark maps
of the Earth.
Antarctic Circle
The parallel of latitude approximately 6634 so
uth, the northern boundary of the South Frigid
Zone,marking the approximate limit south of w
hich the sun remains above the horizon all day
on the summersolstice.
an imaginary line drawn parallel to the equator,
at 23 28prime; N ofthe South Pole: between th
e South Frigid Zone and the SouthTemperate Zo
ne.
Solving linear inequalities is almost exactly like solving
linear equations.
Solve x
+ 3 < 0.
If they'd given me "x + 3 = 0", I'd have known how
to solve: I would have subtracted 3 from both sides.
I can do the same thing here:
Then the solution is:
x < 3
To solve a multi-step inequality you do as you
did when solving multi-step equations. Take one
thing at the time preferably beginning by
isolating the variable from the constants. When
solving multi-step inequalities it is important to
not forget to reverse the inequality sign when
multiplying or dividing with negative numbers.
Example:
Solve the inequality
You might also like
- Mga Kagawaran at Kalihim NG Pamahalaang PilipinasDocument6 pagesMga Kagawaran at Kalihim NG Pamahalaang PilipinasRjvm Net Ca Fe100% (1)
- Grade 8 Music StudentDocument58 pagesGrade 8 Music StudentRjvm Net Ca Fe0% (1)
- Andres Bonifacio BiographyDocument1 pageAndres Bonifacio BiographyRjvm Net Ca Fe50% (4)
- Centrifugal Pump TheoryDocument5 pagesCentrifugal Pump TheoryFungsam LimNo ratings yet
- Desert BiomeDocument5 pagesDesert BiomeDeo N. SarolNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Impact Value TestDocument6 pagesAggregate Impact Value Testnadz_fynazNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate Change: Causes and EffectsDocument22 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate Change: Causes and EffectsRonix Ong100% (1)
- THE HIGH PRESSURE ROLLER PRESSDocument27 pagesTHE HIGH PRESSURE ROLLER PRESSThaigroup Cement100% (10)
- Mga Lungsod NG NCRDocument5 pagesMga Lungsod NG NCRRjvm Net Ca Fe73% (37)
- Symbiotic Relationships Are A Special Type of Interaction Between SpeciesDocument2 pagesSymbiotic Relationships Are A Special Type of Interaction Between SpeciesRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- The Official Seal of Makati City Depicts A Silhouette of The Territory of MakatiDocument2 pagesThe Official Seal of Makati City Depicts A Silhouette of The Territory of MakatiRjvm Net Ca Fe92% (13)
- Geology of the Desert Southwest: Investigate How the Earth Was Formed with 15 ProjectsFrom EverandGeology of the Desert Southwest: Investigate How the Earth Was Formed with 15 ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 EXERGYDocument37 pagesChapter 8 EXERGYzabidullahNo ratings yet
- Ajit Vadakayil - BEEJ MANTRA - FrequencyDocument94 pagesAjit Vadakayil - BEEJ MANTRA - Frequencyjk.dasguptaNo ratings yet
- Mga Lungsod NG NCR1Document2 pagesMga Lungsod NG NCR1Rjvm Net Ca Fe100% (11)
- Mga Lungsod NG NCRDocument6 pagesMga Lungsod NG NCRRjvm Net Ca Fe71% (38)
- How To Determine Soil Erodibility Factor ''K''Document28 pagesHow To Determine Soil Erodibility Factor ''K''Iftikar Rahman100% (1)
- How Do Humans Affect The Geosphere - (Little Know Facts!) 2Document1 pageHow Do Humans Affect The Geosphere - (Little Know Facts!) 2leo KingNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geography Earth Size and ShapeDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Geography Earth Size and ShapehrdepartmentemailsNo ratings yet
- What Are The Factors Controlling Landform DevelopmentDocument30 pagesWhat Are The Factors Controlling Landform Developmentcss aspirant100% (7)
- Introduction To Soil and Water Conservation EngineeringDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Soil and Water Conservation EngineeringYashraj Singh BhadoriyaNo ratings yet
- CoursewithMaterialDocument106 pagesCoursewithMaterialFikadu AssemagnNo ratings yet
- Allied Schools Home Task Class: 5 Subject:S.st: Unit #1 AnswersDocument1 pageAllied Schools Home Task Class: 5 Subject:S.st: Unit #1 AnswersAman AnsariNo ratings yet
- 1 Soil ConservationDocument23 pages1 Soil ConservationShivangi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument6 pagesNatural Vegetation and WildlifeMax ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Effects ExplainedDocument5 pagesClimate Change Effects ExplainedOmar SharifNo ratings yet
- Causes of Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesCauses of Climate ChangeJoseph McCollinNo ratings yet
- Natural Disasters in India: Causes and ImpactsDocument163 pagesNatural Disasters in India: Causes and ImpactsSachin kumar MaileNo ratings yet
- Øfðjð 7 ÇÐJFÐ: Vþvu: Vi (Þvvþi Li (ÞFJ Øfv L (Þ (FVF SSJÞLL: Uþlfjðv Fuþß (Ua: VFLL (Þaffvf Øfvff Þøiij VifþjføDocument26 pagesØfðjð 7 ÇÐJFÐ: Vþvu: Vi (Þvvþi Li (ÞFJ Øfv L (Þ (FVF SSJÞLL: Uþlfjðv Fuþß (Ua: VFLL (Þaffvf Øfvff Þøiij VifþjføTay Poh LengNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science AssignmentDocument7 pagesEnvironmental Science AssignmentShaista RabailNo ratings yet
- Q1. What Is Deforestation? Ans.1: Loss of Species: Seventy Percent of The World's Plants and Animals Live in Forests andDocument3 pagesQ1. What Is Deforestation? Ans.1: Loss of Species: Seventy Percent of The World's Plants and Animals Live in Forests andSakshamNo ratings yet
- EVS Unit 3 PDFDocument40 pagesEVS Unit 3 PDFAnup UmeshNo ratings yet
- Landscape Design and Site Planning: Assignment VIDocument11 pagesLandscape Design and Site Planning: Assignment VISaleha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Space SciencesDocument4 pagesEarth and Space Sciencesapi-315431582No ratings yet
- UNIT 1 IstDocument5 pagesUNIT 1 IstSachin BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Causes of Climate ChangeDocument3 pagesCauses of Climate ChangeGhraxia ﭢ⎝⎲⎵⎲⎠◀▬▬▬▬▬▬▬◊No ratings yet
- Submitted To: - Pankaj JainDocument37 pagesSubmitted To: - Pankaj JainsandyNo ratings yet
- L1Document76 pagesL1Ching LeoNo ratings yet
- Natural Hazards: Mitigation and Adaptation: Property of STIDocument10 pagesNatural Hazards: Mitigation and Adaptation: Property of STIKyle MorreNo ratings yet
- Causes of LandslidesDocument6 pagesCauses of LandslidesAizat ArifNo ratings yet
- Test 2Document14 pagesTest 2Pulkit MisraNo ratings yet
- Weather & ClimateDocument7 pagesWeather & ClimateSachitNo ratings yet
- Geography ProjectDocument12 pagesGeography ProjectVaibhav BharwardNo ratings yet
- Cause of Soil ErosionDocument9 pagesCause of Soil ErosionManamagna OjuluNo ratings yet
- Endangered Ecosystem: Biology Form 4Document30 pagesEndangered Ecosystem: Biology Form 4Lucas TeoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 34Document9 pagesChapter 34dannyf09No ratings yet
- Environmental Awareness ReviewerDocument15 pagesEnvironmental Awareness Reviewerуважать другихNo ratings yet
- CSS Agriculture and ForestryDocument14 pagesCSS Agriculture and ForestryM Faadi MalikNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument9 pagesClimate ChangeOmar SharifNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument8 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSavera SinghNo ratings yet
- Es CH 09Document5 pagesEs CH 09MaliCk TaimoorNo ratings yet
- Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument6 pagesLand, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlifevikas kumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Climate Change? Explain Its Causes and Affects With The Help of ExamplesDocument6 pagesWhat Is Climate Change? Explain Its Causes and Affects With The Help of ExamplesDivya PardalNo ratings yet
- Destination Geography - GEOTERMSDocument8 pagesDestination Geography - GEOTERMSJodel Bautista DoriaNo ratings yet
- Active Recall Practice 1Document9 pagesActive Recall Practice 1DcsantosNo ratings yet
- What is a Landslide? - Understanding Causes, Types and EffectsDocument9 pagesWhat is a Landslide? - Understanding Causes, Types and EffectsDaljeet SidhuNo ratings yet
- Problems of Land Degradation and Soil ErosionDocument11 pagesProblems of Land Degradation and Soil ErosionImmatureBastard100% (1)
- Kumpletong SagotDocument9 pagesKumpletong SagotChan Mark AyapanaNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion PDFDocument20 pagesSoil Erosion PDFAja FightingNo ratings yet
- Geography Yearly RevisionDocument11 pagesGeography Yearly RevisionPercy JackNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effects Become Serious ProblemDocument2 pagesGreenhouse Effects Become Serious ProblemFabian MoralesNo ratings yet
- Activity3 EarthSciDocument2 pagesActivity3 EarthSciYEEHSHIN JILL GAYONo ratings yet
- Nstp-Cwts Module 6Document8 pagesNstp-Cwts Module 6Harvey BareteNo ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument14 pagesNatural ResourcesCLASH OF DARKNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Landscape Architecture Cont. - Understanding Landforms Site Studies - 19.10.22Document10 pagesIntroduction To Landscape Architecture Cont. - Understanding Landforms Site Studies - 19.10.22Delnard OnchwatiNo ratings yet
- Environment Encompasses All Living andDocument12 pagesEnvironment Encompasses All Living andRanjeet RajputNo ratings yet
- Land - WikipediaDocument35 pagesLand - WikipediaMGR001No ratings yet
- Environmental Studies (SSC202) Lesson 1Document11 pagesEnvironmental Studies (SSC202) Lesson 1Falak Shad MemonNo ratings yet
- Environmental AwarenessDocument38 pagesEnvironmental Awarenessroselyn ayensaNo ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife ResourcesDocument18 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlife ResourcesAlisha ChopraNo ratings yet
- Here are the answers:1) B. Hilly areas2) C. Erosion of surface soil 3) A. Soil erosion4) C. Heavy rains5) D. All of theseDocument15 pagesHere are the answers:1) B. Hilly areas2) C. Erosion of surface soil 3) A. Soil erosion4) C. Heavy rains5) D. All of theseFaisal jamanNo ratings yet
- Dry Lands, Fading Hopes: Aridification and Our Future: Global Collapse, #10From EverandDry Lands, Fading Hopes: Aridification and Our Future: Global Collapse, #10No ratings yet
- AchecheDocument3 pagesAchecheRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- I Am But A Small VoiceDocument2 pagesI Am But A Small VoiceRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Grade8aralingpanlipunanmodyul4 130818182334 Phpapp02Document3,372 pagesGrade8aralingpanlipunanmodyul4 130818182334 Phpapp02Rjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Lectures in Filipino For G10 Students - Ang Mitolohiya NG Mga Taga-Rome - WattpadDocument7 pagesLectures in Filipino For G10 Students - Ang Mitolohiya NG Mga Taga-Rome - WattpadRjvm Net Ca Fe50% (2)
- The Rice MythDocument4 pagesThe Rice MythRjvm Net Ca Fe89% (9)
- Print ResourcesDocument1 pagePrint ResourcesRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- KnapsacksDocument1 pageKnapsacksRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Leonaldo Da Vinci Monalisa by Leaonardo Da VinciDocument2 pagesLeonaldo Da Vinci Monalisa by Leaonardo Da VinciRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Philippine Coins: 5 Centavos 1 PesoDocument1 pagePhilippine Coins: 5 Centavos 1 PesoRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Japan InstrumentDocument2 pagesJapan InstrumentRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Common Micronutrient DifficiencyDocument2 pagesCommon Micronutrient DifficiencyRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Trese IsyuDocument12 pagesTrese IsyuJudielyn Domingo Sespeñe50% (6)
- Sources of Radiant EnergyDocument1 pageSources of Radiant EnergyRjvm Net Ca Fe100% (1)
- How My Brother Leon Brought Home A WifeDocument6 pagesHow My Brother Leon Brought Home A WifeCamille LopezNo ratings yet
- Nuclear EnergyDocument1 pageNuclear EnergyRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- The CentipedeDocument4 pagesThe CentipedeDakila Maloy0% (1)
- Trese IsyuDocument12 pagesTrese IsyuJudielyn Domingo Sespeñe50% (6)
- The MatsDocument5 pagesThe MatsElysee CalasagNo ratings yet
- Parts of The PlantDocument1 pageParts of The PlantRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- BadmintonDocument1 pageBadmintonRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
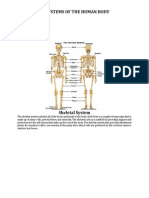
- 11 Systems of Human BodyDocument11 pages11 Systems of Human BodyRjvm Net Ca FeNo ratings yet
- Rules and Refulation For The Classification of Special Service Craft July 2015 - Piping Systems and Presure Plant - ConstructionDocument4 pagesRules and Refulation For The Classification of Special Service Craft July 2015 - Piping Systems and Presure Plant - ConstructionmarboledtNo ratings yet
- Genchem 1 DLPDocument7 pagesGenchem 1 DLPDhevin VergaraNo ratings yet
- TPAO-KTHDB PremiumThread TubingTechSpecSheet PH6Document1 pageTPAO-KTHDB PremiumThread TubingTechSpecSheet PH6ilkerkozturkNo ratings yet
- Deep Bed Filters and High Rate Service OptimizationDocument75 pagesDeep Bed Filters and High Rate Service OptimizationYadav ShwetaNo ratings yet
- Full download book Quantum Dots Fundamentals Synthesis And Applications Pdf pdfDocument41 pagesFull download book Quantum Dots Fundamentals Synthesis And Applications Pdf pdfhilda.pellowski343100% (19)
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 2 Solutions PDFDocument15 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 2 Solutions PDFUmesh S Rathore100% (2)
- Copper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsDocument5 pagesCopper (II) Sulfate - Reagent - Anhydrous 98 - Acros OrganicsGaryoNo ratings yet
- A Snapshot of The Drilling and Completio N Practices in High Temperature Geothermal Wells - SarmientoDocument13 pagesA Snapshot of The Drilling and Completio N Practices in High Temperature Geothermal Wells - SarmientoAdil AytekinNo ratings yet
- VWR® Symphony® Analysis PackagesDocument3 pagesVWR® Symphony® Analysis Packageslusoegyi 1919No ratings yet
- Operating Instructions for Clinical AutoclavesDocument11 pagesOperating Instructions for Clinical AutoclavesEduardo0% (1)
- Benzene Structure and Delocalised Model ExplainedDocument8 pagesBenzene Structure and Delocalised Model ExplainedHisham Jafar AliNo ratings yet
- Astm C990-03Document4 pagesAstm C990-03Joanne WaiNo ratings yet
- Design For Environment PDFDocument20 pagesDesign For Environment PDFAnonymous 7bsvkAEloNo ratings yet
- Dissolution Improvement of Telmisartan by Surface Solid Dispersion MethodDocument5 pagesDissolution Improvement of Telmisartan by Surface Solid Dispersion MethodHafidz PrasetyaNo ratings yet
- ABRASIVE JET MACHINING ModellingDocument3 pagesABRASIVE JET MACHINING ModellingAnkit OlaNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument68 pagesManualMohammadIsmailNo ratings yet
- SPE 37084 Horizontal Well Length: Drill Short or Long Wells?Document9 pagesSPE 37084 Horizontal Well Length: Drill Short or Long Wells?Waleed Barakat MariaNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Presentation - Anish Kumar DakshDocument23 pagesMid Term Presentation - Anish Kumar DakshShubhadeep MajumdarNo ratings yet
- MZ2000W PDS EnglishDocument3 pagesMZ2000W PDS EnglishLeandroNo ratings yet
- Ap T68 06 PDFDocument98 pagesAp T68 06 PDFTauseef HassanNo ratings yet
- Flash Point and Fire Point - FinalDocument33 pagesFlash Point and Fire Point - FinalAnonymous QM0NLqZONo ratings yet
- PCCDocument12 pagesPCCAjit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen MSDS Safety GuideDocument4 pagesOxygen MSDS Safety Guidelutfi_thalib3175No ratings yet
- Development of Ghat River in Jaunpur City: 1-Anil BhartiDocument9 pagesDevelopment of Ghat River in Jaunpur City: 1-Anil BhartiA8304008005No ratings yet