Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DOM (10 ME 53) Model Paper1
Uploaded by
SumitKumarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DOM (10 ME 53) Model Paper1
Uploaded by
SumitKumarCopyright:
Available Formats
R V College of Engineering, Bangalore 560059
Fourth Semester B.E. Mechanical Engg
Dynamics of Machines (10 ME 53)
Model Question Paper I
Time: 3 Hours
Max. Marks: 100
Not
e
1
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
1.6
1.7
1.8
1.9
1.10
1.11
1.12
1.13
1.14
1.15
1.16
1.17
1.18
1.19
1.20
(a)
(b)
1.
Part-A is Compulsory
2.
Answer any 5 full questions from choosing one question from each
unit in Part-B
PART- A
The type of analysis in which the inertia forces are ignored in comparison with external loads is
called ----------------The principle used for analyzing linkages with two or more forces taking effect of one at a time and
adding them algebraically is known as -----------------A device used to minimize the fluctuations of torque in engines & machines performing intermittent
operations is --------------------.
With usual notations, the hoop stress developed in a flywheel is given by ------------------.
The unit of mass moment of inertia of a flywheel is --------------------.
If an engine speed is maintained 10 rpm above and 10 rpm below a mean speed of 2000 rpm, the
coefficient of fluctuation of speed is --------------.
The effect of centrifugal tension on the power transmitted by a belt drive is -------------------.
The relative motion between the pulley and the belt due to lack of frictional grip between them is
called ----------------The angle of contact when a belt surrounds (5/12) th of the circumference of the pulley is----------.
If the controlling force on a spring controlled governor is given by F=ar+b, the governor is said to
be ------------------.
The phenomenon of continuous fluctuation of speed above and below the mean speed is known
as---------------------.
If for all the radii of rotation within the working range, the equilibrium speed remains constant, the
governor is said to be -------------------.
Secondary unbalance force in reciprocating engines has a frequency -------------- times the primary
unbalance force.
If the rotating unbalance in a grinder is 0.1 kg-cm, and the speed of the grinder is 1000 rpm, the
unbalance force is ------------------ Newton.
If 50% of reciprocating masses are balanced in an engine of piston mass m and crank radius r and
angular velocity of crank the resultant unbalanced primary force is ----------------.
Direct and reverse crank method is used for checking balance of --------------------- type of engines
The gyroscopic effect is analyzed by using ------------------------- rule.
The front end of the ship is also known as -------------------.
If a vehicle is speeding with a velocity V around a curve of radius R, the angular velocity of
precession of the road wheels is ----------------------.
With usual notations, the expression for gyroscopic couple is ----------------.
PART-B
Unit-I
Determine the required input torque on the crank of a slider crank mechanism for the static
equilibrium when the applied piston load is 1500 N. The lengths of the crank and the connecting rod
are 400 mm and 1000 mm respectively and the crank has turned through 45 0 from the inner dead
center.
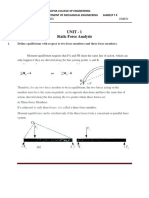
For the static equilibrium of the quaternary link ABCD shown in fig, determine the magnitude of
forces F2 and F3 and the direction of F3.
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
01
10
06
30
F3
60 mm
50 mm
40 mm
F1 =200 N
50 mm
30
90
30
F4 =300 N
Fig 2 (b)
(a)
Define kinetically equivalent system and obtain the condition for equivalence of two masses.
(b)
Explain the inertia force analysis of a slider crank mechanism which is subjected to force P at the
piston.
Unit II
What is a flywheel? Mention the types of flywheel & its applications.
(a)
(b)
06
10
04
The torque output diagram for a single cylinder engine is as shown in fig. The average speed of the
engine is 3000 rpm. Determine the coefficient of fluctuation of energy and the mass moment of
inertia of the flywheel required to limit the crank speed at 10 rpm above and 10 rpm below the
average speed.
Torque N-m
80
60
40
20
12
0
-20
-40
Fig 4 (b)
(a)
(b)
(a)
(b)
The equation of TMD for an engine is given by T= (2500-750 sin3 Nm, where is the angle
turned through by the crank from IDC. Mass moment of inertia of the flywheel is 40 kg-m 2 and the
mean speed is 300 rpm. Calculate the power developed by the engine. Also determine the total
percentage fluctuation of speed if;
(i)
The resisting torque is constant
(ii)
The resisting torque is (2500+360 sin
Unit III
With usual notations, derive an expression for the ratio of tensions in a flat belt drive.
A belt embracing 1650 of a pulley of effective diameter 1000 mm is transmitting 10 KW. The pulley
is rotating at 250 rpm. The coefficient of friction is 0.3. Density of the belt material is 1.2 gm/cc and
thickness of the belt is 10 mm. Considering centrifugal tension, find the width of the belt and initial
tension in the belt. Take the safe working stress in the belt as 1.5 MPa.
Define the following terms w.r.t governors;
(i)
Sensitiveness (ii) Stability (iii) Isochronism (iv) Power
In a porter governor, all the arms are 150 mm long. Upper & lower arms are pivoted to links 20 mm
& 30 mm respectively from the axis of rotation. Central sleeve mass is 40 kg. Mass of each ball is 4
kg. Force of friction is 30 N and the extreme radii are 80 mm & 100 mm. Determine the range of
speed of the governor.
Unit IV
16
06
10
04
12
(a)
(b)
10 (a)
(b)
11
Explain the terms static & dynamic balancing with necessary equations.
A shaft carries four masses A, B, C & D placed in parallel planes. The masses B & C are 40 kg & 28
kg and both are at 16 mm radius, while the masses in planes A & D are at 20 mm radius. Angle
between B & C is 1000, B & A is 1900 both measured in the same sense. Planes A & B are 250 mm
apart; B & C are 500 mm apart. If the shaft is to be in complete balance, determine
(i)
Masses in planes A & D
(ii)
Distance between planes C & D
The cranks and connecting rod of a 4 cylinder in line engine running at 1800 rpm are 50 mm and 250
mm respectively. The cylinders are numbered 1 to 4 in sequence from left end and are placed 150
mm apart. The cranks appear at intervals 0f 90 0 in an end view in the order 1-4-2-3. The reciprocating
mass corresponding to each cylinder is 1.5 kg. Determine;
(i)
Unbalanced primary & secondary forces
(ii)
Unbalanced primary & secondary couples w.r.t the central plane of the engine.
Unit V
With usual notations, obtain an expression for the gyroscopic couple.
A ship is propelled by a turbine rotor which has a mass of 5000 kg and has a speed of 2100 rpm. The
rotor has a radius of gyration of 0.5 m and rotates in clockwise when viewed from the stern.
Determine the gyroscopic couple and its effect under the following conditions;
(i)
The ship runs at a speed of 16 knots (1 knot=1860 m/hr)
(ii) The ship pitches 60 above and 60 below the horizontal position with SHM of period 20 secs
with the bow descending with its maximum velocity.
(iii)
The ship rolls at a certain instant with an angular velocity 0.03 rad/sec.
The following particulars refer to a symmetrical tangent cam having a roller follower. Maximum
radius of the cam = 40 mm, lift= 20 mm, speed = 360 rpm, roller diameter = 44 mm, angle of ascent
=600. Calculate the acceleration of the follower at the beginning of the lift. Also find its values when
the roller just touches the nose and is at the apex of the circular nose. Sketch the variation of
displacement, velocity and acceleration during ascent.
************
04
12
16
10
04
12
16
You might also like
- Aadhaar Bill Issues For Consideration 08.03.16Document3 pagesAadhaar Bill Issues For Consideration 08.03.16SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- 7 Injection TimingDocument13 pages7 Injection TimingSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- 2 LHRDocument17 pages2 LHRSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- RBI Governor Raghuram Rajan On Aadhaar, Payments Banks, Over-Invoicing, Spectrum Auctions & More - MediaNamaDocument8 pagesRBI Governor Raghuram Rajan On Aadhaar, Payments Banks, Over-Invoicing, Spectrum Auctions & More - MediaNamaSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Dynasty in Democracy - FrontlineDocument3 pagesDynasty in Democracy - FrontlineSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- First Steps To Investing A Beginners Guide Prithvi Haldea PDFDocument21 pagesFirst Steps To Investing A Beginners Guide Prithvi Haldea PDFnagaravikrishnadiviNo ratings yet
- UPSC ESE Mechanical Engineering SyllabusDocument4 pagesUPSC ESE Mechanical Engineering SyllabusSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Rashtreeya Sikshana Samithi TrustDocument2 pagesRashtreeya Sikshana Samithi TrustSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Dramatic Example of Law Vs Religion' - FrontlineDocument9 pagesDramatic Example of Law Vs Religion' - FrontlineSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Energies: An Intelligent Regenerative Braking Strategy For Electric VehiclesDocument17 pagesEnergies: An Intelligent Regenerative Braking Strategy For Electric VehiclesSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Calendar of Events - R V College of EngineeringDocument7 pagesCalendar of Events - R V College of EngineeringSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- DOM (10 ME 53) Model Paper 2Document3 pagesDOM (10 ME 53) Model Paper 2SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 5 PDFSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document10 pagesUnit 2SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- A Car Air-Conditioning System Based On An Absorption Refrigeration CycleDocument6 pagesA Car Air-Conditioning System Based On An Absorption Refrigeration Cycleme641sivaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document7 pagesUnit 4SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 57 PDFDocument9 pagesUnit 5 57 PDFSurendra SainiNo ratings yet
- GateDocument6 pagesGateParveen SwamiNo ratings yet
- LP GDC 2015Document9 pagesLP GDC 2015SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- ME 5-6 Sem Final Syllabus 09-08-2012Document49 pagesME 5-6 Sem Final Syllabus 09-08-2012SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document30 pagesLecture 3SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- Scoring PDFDocument1 pageScoring PDFKarthik TejaNo ratings yet
- Gate 2015 Blue PrintDocument3 pagesGate 2015 Blue PrintDurai RajNo ratings yet
- 12me52 MQP-1Document3 pages12me52 MQP-1SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- CAT EligibilityDocument4 pagesCAT Eligibilityv2299No ratings yet
- 2 Ies Me 2013 Obj Paper IIDocument17 pages2 Ies Me 2013 Obj Paper IISumitKumarNo ratings yet
- RVCE Golden Jubilee Celebrations Chief Guest Vice President of IndiaDocument1 pageRVCE Golden Jubilee Celebrations Chief Guest Vice President of IndiaSumitKumarNo ratings yet
- 180714061432calender of Events44 2014 15Document4 pages180714061432calender of Events44 2014 15SumitKumarNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- College Physics EOC Questions Chapter 8Document9 pagesCollege Physics EOC Questions Chapter 8Sri RNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy StorageDocument22 pagesFlywheel Energy StorageNavaid MohammadNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery Question BankDocument8 pagesDynamics of Machinery Question BankArun ShawnNo ratings yet
- Governor Characteristics Class NoteDocument10 pagesGovernor Characteristics Class NoteNirupam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Douglas C Giancoli DownloadDocument38 pagesTest Bank For Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Douglas C Giancoli Downloadmarissaarmstrongpbfzemcsji100% (17)
- ME Mechanical Engineering Dynamics of Machines Sem-VI NotesDocument4 pagesME Mechanical Engineering Dynamics of Machines Sem-VI NotesNabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Handouts MD Day 3Document8 pagesHandouts MD Day 3Obane Ordnael P.No ratings yet
- Hsslive-xi-physics-Ayyappan-chapter 7 - Systems of Particles - Rotational Motion (Repaired)Document10 pagesHsslive-xi-physics-Ayyappan-chapter 7 - Systems of Particles - Rotational Motion (Repaired)Harish SridharNo ratings yet
- Flywheels Store Kinetic Energy for Smoothing Speed FluctuationsDocument4 pagesFlywheels Store Kinetic Energy for Smoothing Speed Fluctuationscobalt boronNo ratings yet
- MEC 291 Dynamics Lab Experiments GuideDocument22 pagesMEC 291 Dynamics Lab Experiments GuideHaFiy HaZimNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking Systems (RBS) (Future of Braking Systems)Document4 pagesRegenerative Braking Systems (RBS) (Future of Braking Systems)Sushant VanveNo ratings yet
- Fly Wheel: B.I.T., Mesra Engg - Mechanics LabDocument6 pagesFly Wheel: B.I.T., Mesra Engg - Mechanics LabSanatan MurmuNo ratings yet
- Project Report - Self Balancing - Aditya RaoDocument27 pagesProject Report - Self Balancing - Aditya RaoAditya RaoNo ratings yet
- Machine Design 2Document43 pagesMachine Design 2kenneth roblesNo ratings yet
- Starting Torque of FanDocument3 pagesStarting Torque of Fanlaxmi55No ratings yet
- GOVERNORSDocument9 pagesGOVERNORSraghurockramNo ratings yet
- ME8594-Dynamics of MachinesDocument29 pagesME8594-Dynamics of MachinesVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Mech307 - 2015-16 Spring - Project - Larger FiguresDocument4 pagesMech307 - 2015-16 Spring - Project - Larger FiguresYazan HarbNo ratings yet
- Previous Questions DomDocument5 pagesPrevious Questions DomSafeer MNo ratings yet
- Flywheel Energy Storage System: Bachelor of TechnologyDocument13 pagesFlywheel Energy Storage System: Bachelor of Technologymadhu kotlaNo ratings yet
- General Design Principles For Assembly Techniques - Welding, Adhesive Bonding PDFDocument54 pagesGeneral Design Principles For Assembly Techniques - Welding, Adhesive Bonding PDFkfaravNo ratings yet
- Ic Engine Terminolgy PDFDocument20 pagesIc Engine Terminolgy PDFDinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Rationality and the Taming of ComplexityDocument22 pagesRationality and the Taming of ComplexityEdwin OlooNo ratings yet
- Concept2 Setting The Drag FactorDocument3 pagesConcept2 Setting The Drag FactorpisofNo ratings yet
- 10me54 Notes PDFDocument100 pages10me54 Notes PDFKyanuNo ratings yet
- Embrague 15.5Document2 pagesEmbrague 15.5Jesus Alberto Guzman BeltranNo ratings yet
- N Une: INSTRUCTIONS: Solve The Following ProblemsDocument7 pagesN Une: INSTRUCTIONS: Solve The Following ProblemsAaron Elijah RabayaNo ratings yet
- Voltage Sag Mitigation August 2012 Technical Note 11Document16 pagesVoltage Sag Mitigation August 2012 Technical Note 11Hitarth BuchNo ratings yet
- Storage PresentationDocument43 pagesStorage PresentationHafeez Khan TareenNo ratings yet
- General Electric Water Wheel Driven Generators OCRDocument19 pagesGeneral Electric Water Wheel Driven Generators OCRPablo Thomasset Trakalo100% (1)