Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Generic Name: L-Carnitine Brand Name: Carnicor 330 MG Tablet Category: Metabolic Energizer Production Information:l-Carnitine Is A
Uploaded by
Emilyne Joy Mendoza Cabaya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesThis document discusses the metabolic energizer L-carnitine. It is a natural substance present in cells that transports fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production. While the body produces some L-carnitine, diet is important for meeting requirements. It is found in high amounts in heart and skeletal muscles, which rely heavily on fatty acid oxidation for energy. L-carnitine plays a key role in fatty acid metabolism and energy production by facilitating the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria and preventing toxic acyl CoA buildup. It is especially important for cardiac muscle, which uses fatty acids as its preferred energy source.
Original Description:
drug study
Original Title
Generic Name
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the metabolic energizer L-carnitine. It is a natural substance present in cells that transports fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production. While the body produces some L-carnitine, diet is important for meeting requirements. It is found in high amounts in heart and skeletal muscles, which rely heavily on fatty acid oxidation for energy. L-carnitine plays a key role in fatty acid metabolism and energy production by facilitating the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria and preventing toxic acyl CoA buildup. It is especially important for cardiac muscle, which uses fatty acids as its preferred energy source.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views4 pagesGeneric Name: L-Carnitine Brand Name: Carnicor 330 MG Tablet Category: Metabolic Energizer Production Information:l-Carnitine Is A
Uploaded by
Emilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaThis document discusses the metabolic energizer L-carnitine. It is a natural substance present in cells that transports fatty acids into mitochondria for energy production. While the body produces some L-carnitine, diet is important for meeting requirements. It is found in high amounts in heart and skeletal muscles, which rely heavily on fatty acid oxidation for energy. L-carnitine plays a key role in fatty acid metabolism and energy production by facilitating the transport of fatty acids into mitochondria and preventing toxic acyl CoA buildup. It is especially important for cardiac muscle, which uses fatty acids as its preferred energy source.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Generic name: L-carnitine
Brand name: Carnicor 330 mg tablet
Category: metabolic energizer
Production information:L-carnitine is a
natural substance present in all cells of the
body. It is a transport protein. Chemically, LCarnitine is beta-OH-(Y-N-trimethyl ammonio)
butyrate.
L-Carnitine is synthesized by both animals
and humans in the liver, kidney and brain
from amino acids-lysine and methionine,
methionine being the methyl donor for
transmethylation of lysine, to butyrobetaine
and finally L-Carnitine. However, not enough
is synthesized to meet body requirements
which is fulfilled by red meat and dairy
products in the diet.
L-Carnitine is concentrated in the heart and
skeletal muscle where 95% of total body
G: Moxifloxacin
B:
C: Fluoroquinolone Anti Biotic
MOA: The bactericidal action of moxifloxacin
results from inhibition of the enzymes
topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and
topoisomerase IV. DNA gyrase is an essential
enzyme that is involved in the replication,
transcription and repair of bacterial DNA.
Topoisomerase IV is an enzyme known to play a
key role in the partitioning of the chromosomal
DNA during bacterial cell division.
I:
To treat uncomplicated skin and softtissue infections caused by
S. aureus or
Streptococcus pyogenes
%
%
%
SE: abdominal pain dizziness headache indigestion
mild diarrhea nausea Vomiting
carnitine is found. This high content reflects
the considerable ability of these muscles to
obtain energy from oxidation of free fatty
acids, which process requires L-Carnitine.
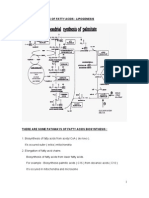
Major Functions of L-Carnitine:L-Carnitine
acts as a co-factor in fatty acid metabolism
specially its transport into the
mitochondorion for beta-oxidation and
ultimately, energy production.
L-Carnitine indirectly regulates glucose (G)
utilization thru control of acetyl CoA/CoA
ration, an important regulator pyruvate
dehydrogenase (PDH) activity and
consequent actyl CoA formation which enters
the TCA cycle and release energy.
The above continuing reactions prevent lactic
acid (LA) formation and accumulation.
L-Carnitine by preventing acyl CoA
accumulation preserves mitonchondrial
adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) activity
thus allowing ATP/ADP exchange (ATP for
extramitochondrial utilization, ADP for
mitonchondrial ATP synthesis).
Role of L-Carnitine in Cardiac
Metabolism:Of three (3) major substrates
available to it, cardiac muscle utilizes free
fatty acid (FFA) as preferential substrate over
glucose and lactate. In fact, it is most
important energy yielding substrate for
oxidative metabolism in cardiomyocytes. 6080% of ATP generated derives from FA
oxidation, the remainder from Glucose and
Lactase metabolism. Important to note is that
there is no anaerobic reserve for residual
energy production from FA metabolism. Lipids
require more oxygen than glucose or lactate
for a given amount of energy to be released.
L-Carnitines role is vital in the mitochondrial
membrane transfer of FFA and energy
generation of oxidative metabolism.
You might also like
- Malaguarnera 2012Document11 pagesMalaguarnera 2012Fernando Stuar Campos MendozaNo ratings yet
- Carnitine - WikipediaDocument57 pagesCarnitine - WikipediaMuhammad KashifNo ratings yet
- Carnitine DeficiencyDocument58 pagesCarnitine DeficiencyRafael Francisco Garcia Munoz100% (1)
- Role of Carnitine in Disease: Open Access ReviewDocument14 pagesRole of Carnitine in Disease: Open Access ReviewКулик МихаилNo ratings yet
- Metabolism OF Amino Acids: Yulia SuciatiDocument37 pagesMetabolism OF Amino Acids: Yulia SuciatiAfnan AlkaffNo ratings yet
- Item-9,10, Lipid MetabolismDocument38 pagesItem-9,10, Lipid MetabolismSheikh FahadNo ratings yet
- Mountain Dog Diet - Injectable Carnitine For Fat LossDocument10 pagesMountain Dog Diet - Injectable Carnitine For Fat LossZacharyJones100% (2)
- L CarnitineDocument2 pagesL CarnitineKim MyNo ratings yet
- 05 01 Lipid Metabolism I 2012Document125 pages05 01 Lipid Metabolism I 2012anthony.johNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Usefulness of Carnitine Supplementation For The Complications of Liver CirrhosisDocument10 pagesNutrients: Usefulness of Carnitine Supplementation For The Complications of Liver CirrhosisDenny BunNo ratings yet
- B Vitamins 1Document1 pageB Vitamins 1api-245692797No ratings yet
- Energy Metabolism of The Heart Under Different PathophysiologicalDocument27 pagesEnergy Metabolism of The Heart Under Different PathophysiologicalAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- CH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Document4 pagesCH1131 Biomolecular Engrg Lipid Metabolism To Coordination Summary 2013Nhân TrầnNo ratings yet
- PhenylalanineDocument4 pagesPhenylalaninemaithili hedaooNo ratings yet
- METABOLISMDocument11 pagesMETABOLISMking untalanNo ratings yet
- Medical Biochemistry (Week-16)Document7 pagesMedical Biochemistry (Week-16)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- Biotin Augments Acetyl CoA Carboxylase 2 Gene Expression in The Hypothalamus, Leading To The Suppression of Food Intake in MiceDocument6 pagesBiotin Augments Acetyl CoA Carboxylase 2 Gene Expression in The Hypothalamus, Leading To The Suppression of Food Intake in MiceElina VereshchakNo ratings yet
- Medical Biochemistry (Week-15)Document5 pagesMedical Biochemistry (Week-15)wasimsafdarNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Lipid MetabolismDocument19 pagesAn Overview of Lipid Metabolismshanto.tn98No ratings yet
- TriheptanoinDocument46 pagesTriheptanoinMustafa IdaisNo ratings yet
- Inborn Errors of Lipid MetbolismDocument13 pagesInborn Errors of Lipid MetbolismMUTHONI IRERINo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism: Metabolism of Fatty Acids - IDocument24 pagesLipid Metabolism: Metabolism of Fatty Acids - Icheckmate100% (1)
- Surgicla Metabolism SabistonDocument66 pagesSurgicla Metabolism SabistonashanialaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism All LecturesDocument18 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism All Lecturesmizare29gNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemDocument27 pagesBiochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemRenaldy PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument46 pagesOxidation of Fatty AcidsRamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of CVSDocument311 pagesBiochemistry of CVSAsne ManNo ratings yet
- 18 - Lipid MetabolismDocument26 pages18 - Lipid Metabolismcheckmate100% (1)
- Lipid Metobolism B Pharm-1Document67 pagesLipid Metobolism B Pharm-1Dhaval TelangNo ratings yet
- MI - 11 - Ciclo de Cori, Creatina Fosfato y Ciclos Energéticos Del MúsculoDocument39 pagesMI - 11 - Ciclo de Cori, Creatina Fosfato y Ciclos Energéticos Del MúsculoANDRÉS FELIPE VALDERRAMA BAEZNo ratings yet
- PBPN Tutorial 7Document3 pagesPBPN Tutorial 7RaysonChooNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry KVDocument4 pagesBiochemistry KVMuhammad Rifqi FakhriNo ratings yet
- Lipid MetabolismDocument94 pagesLipid MetabolismMiki MausNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metabolism Session 2Document36 pagesLipid Metabolism Session 2Kankomba MuleyaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of LipidsDocument46 pagesMetabolism of LipidsDpkNandalNo ratings yet
- BIOSINTESISDocument34 pagesBIOSINTESISAyodia RanggiNo ratings yet
- Chemistrry AllDocument7 pagesChemistrry AllTHARSHANA JERUSALEMNo ratings yet
- VitaminsDocument3 pagesVitaminsWolverineInZenNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemDocument113 pagesBiochemistry of Cardiovascular SystemNindy75% (4)
- FA OxidationDocument15 pagesFA OxidationRith Hengmeng (Study Smart)No ratings yet
- Fatty Acids SynthesisDocument30 pagesFatty Acids SynthesisGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION & Principle of Energy MetabolismDocument84 pagesBIOLOGICAL OXIDATION & Principle of Energy MetabolismOdi YuventiusNo ratings yet
- M.D - Oxidation of FAs & Ketone BodiesDocument48 pagesM.D - Oxidation of FAs & Ketone BodiesAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Carnitine - Tartrate Promotes Human Hair Growth in Vitro: Original ArticleDocument10 pagesCarnitine - Tartrate Promotes Human Hair Growth in Vitro: Original ArticleZhewen TangNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acids and Glycerol - IIDocument25 pagesFatty Acids and Glycerol - IIwax walba haye mediaNo ratings yet
- Lipolysis LipogenesisDocument11 pagesLipolysis LipogenesisImam HartonoNo ratings yet
- Biosynthetic Pathways - GPDocument46 pagesBiosynthetic Pathways - GPGhanshyam R ParmarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: A Short Course: Fatty Acid DegradationDocument22 pagesBiochemistry: A Short Course: Fatty Acid DegradationEli JohnsonNo ratings yet
- The Human Bodys Energy MetabolismDocument39 pagesThe Human Bodys Energy MetabolismMasturina MarsyaNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Biochemistry: Vitamins Dr. Bidhan Chandra KonerDocument50 pagesNutritional Biochemistry: Vitamins Dr. Bidhan Chandra KonerElenanana100% (1)
- Role of Carnitine Esters in Brain Neuropathology: Ashraf Virmani, Zbigniew BiniendaDocument17 pagesRole of Carnitine Esters in Brain Neuropathology: Ashraf Virmani, Zbigniew BiniendacumbredinNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Beta OxidationDocument59 pagesFatty Acid Beta OxidationEve YapNo ratings yet
- Mevalonate PathwayDocument13 pagesMevalonate Pathwayfitriani fajriNo ratings yet
- Lipids MetabolismDocument19 pagesLipids MetabolismOsama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of Lipids (2) NewDocument64 pagesMetabolism of Lipids (2) NewLyra Get100% (1)
- Biochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismDocument6 pagesBiochem CH 27 Integration of MetabolismSchat ZiNo ratings yet
- Carniti NeDocument17 pagesCarniti NeMayuNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Amino Acids To Specialized ProductsDocument15 pagesConversion of Amino Acids To Specialized ProductsmrbrendonNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Lipid MetabolismDocument28 pagesUnit 9 Lipid MetabolismAthina100% (1)
- Drug Therapy Protocols:: PropofolDocument3 pagesDrug Therapy Protocols:: PropofolEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Biperiden: Anticholinergic DrugDocument6 pagesGeneric Name: Biperiden: Anticholinergic DrugEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- DateDocument1 pageDateEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- I. Objectives Within 2 Weeks of Having Nurse-Patient Relationship, The Client Will Be Able ToDocument1 pageI. Objectives Within 2 Weeks of Having Nurse-Patient Relationship, The Client Will Be Able ToEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument12 pagesRRLEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- "Preach The Word, Be Prepared in Season and Out of Season Correct, Rebuke and Encourage With Great Patience and Careful Instruction."-2tim 4:2Document1 page"Preach The Word, Be Prepared in Season and Out of Season Correct, Rebuke and Encourage With Great Patience and Careful Instruction."-2tim 4:2Emilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument46 pagesSchizophreniaEmilyne Joy Mendoza CabayaNo ratings yet
- Metabolisme Sel Prof TriDocument29 pagesMetabolisme Sel Prof Trimanusia bergerakNo ratings yet
- Muscular System: MusclesDocument19 pagesMuscular System: MusclesChristelle Marie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Atp EssayDocument3 pagesAtp EssayValeria PunzoNo ratings yet
- ATP Student PogilDocument5 pagesATP Student Pogiltvuongpham0% (1)
- Worksheet FermentationDocument5 pagesWorksheet FermentationRyan De AlloNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: Blood Haemoglobin and Respiration: - Archit SaraogiDocument6 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: Blood Haemoglobin and Respiration: - Archit SaraogiChictoran RukmaniNo ratings yet
- Bio PermentiationDocument35 pagesBio PermentiationthushalNo ratings yet
- ML Biology Chapter 10Document28 pagesML Biology Chapter 10Evans Junior T. MuvutiNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Peroxide TherapyDocument17 pagesHydrogen Peroxide TherapyAmy MarlerNo ratings yet
- Respiration QuestionsDocument12 pagesRespiration Questionsoghieghie jattoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 8th Edition Lauralee Sherwood Solutions Manualgambolrapinous.ggqcdr100% (39)
- Chemistry: Optional Module - 3 & Laboratory Manual - 4Document348 pagesChemistry: Optional Module - 3 & Laboratory Manual - 4Lakshmi pakala70No ratings yet
- Hy-Lite 2 System: Operating Instructions ManualDocument33 pagesHy-Lite 2 System: Operating Instructions ManualIrfan NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Lactic Acid Energy SystemDocument15 pagesLactic Acid Energy SystemroemriqwewqeNo ratings yet
- ATP SynthaseDocument3 pagesATP Synthaseh_mallowNo ratings yet
- Sports Adaptology: V. N. SeluyanovDocument9 pagesSports Adaptology: V. N. Seluyanovdan_partelly4103No ratings yet
- Short Reading Texts Comprehension 1Document11 pagesShort Reading Texts Comprehension 1Yanela NicosianoNo ratings yet
- Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 892 - Yeast Membrane TransportDocument381 pagesAdvances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 892 - Yeast Membrane TransportRosselle Noyoal0% (1)
- Test 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Document14 pagesTest 1 - APQ Model Answers-1Matsiri ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Antituberculosis DrugsDocument30 pagesAntituberculosis DrugsI Kadek Adi Putra Suandana 2005No ratings yet
- Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections,: Lecture by Edward J. ZaliskoDocument90 pagesCampbell Biology: Concepts & Connections,: Lecture by Edward J. ZaliskoAnnNo ratings yet
- Major Metabolic PathwaysDocument11 pagesMajor Metabolic PathwaysDidem KaraNo ratings yet
- Subject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Document11 pagesSubject: Biochemistry Topic:Lipid Metabolism 2 Lecturer: Dr. Laygo DATE: NOV. 2010Std DlshsiNo ratings yet
- BreathworkDocument20 pagesBreathworkhemera.life.healthNo ratings yet
- Energy Production in Human BodyDocument30 pagesEnergy Production in Human Bodymohitime100% (2)
- Biology 1308 NotesDocument21 pagesBiology 1308 NotesAshley CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Performance-Pdhpe in FocusDocument25 pagesFactors Affecting Performance-Pdhpe in Focusadam100% (1)
- Electron Transport ChainDocument14 pagesElectron Transport ChainMuhammad HamzaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism McKee Chapter8Document44 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism McKee Chapter8David SeidelNo ratings yet
- BIOL 0052 Biology Ii: LECTURER: Dr. Kherie Rowe FACULTY: Biological and Chemical SciencesDocument24 pagesBIOL 0052 Biology Ii: LECTURER: Dr. Kherie Rowe FACULTY: Biological and Chemical SciencesShandarr BladesNo ratings yet