Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Framework For Implementation of Risk Management System in Third Party Managed Cloud
Uploaded by
DannyPrastOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Framework For Implementation of Risk Management System in Third Party Managed Cloud
Uploaded by
DannyPrastCopyright:
Available Formats
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 19
A Framework for Implementation of Risk Management System in third Party managed
Cloud
Adeniran Solomon Abiodun
Tshwane University of Technology, South Africa
biodundudu02@yahoo.com
Abstract
A lot of research has been carried out in the field of risk management, as well as IT auditing,
however risks and operation of information and data still threaten organizations processes and
activities. Also, these two disciplines have been discretely managed and researched in the industry
and academic, respectively. It therefore will be of importance to investigate the interface between
the two disciplines. The purpose of this research is to investigate and understand audit and risk
management system in the information technology environment. To lay a foundation for a
discussion of the role of information systems in risk management, we must first define and
understand the needs that drive organizations to implement risk management functions (Gibson,
1997). Information System (IS) was introduced to the business as a means of improving
operational efficiency. It was initially used as a tool only for performing organisations operations,
now it is a very important aspect of an organisations existence and survival, no operation can be
carried out in an organisation without IS. Therefore we have to place an emphasis on IS risk
management. The disruption of operations can also become more Important than the replacement
of IS assets. Due to the costly cost of delays brought about by breakdown of IS which sometimes
is caused by negligence and malicious intent the need for Risk management of IS facilities, process
and staff came about and since the advent of this there has been a great improvement in business
process because disruptions are less (Kamesam, 2001). In ideal risk management, a prioritization
process is followed whereby the risks with the greatest loss and the greatest probability of
occurring are handled first, and risks with lower probability of occurrence and lower loss are
handled in descending order of occurrence and can often be mishandled (ISO/IEC, 2009). Risk
management also faces difficulties allocating resources. This is the idea of opportunity cost.
Resources spent on managing risks could have been spent on more profitable activities. Again,
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 20
ideal risk management minimizes spending while maximizing the reduction of the negative effects
of risks.
Keywords: Information System, Risk Management, Risk, Business. Operations
Introduction
Introduction to the field of study
The advent of new technological inventions and innovations causes continual change in modern
day way of life; Information Technology is the most influential one of these technologies being
applied in almost every aspect of human life. The turn of the twenty-first century has been largely
dubbed the information age due to the immense influence of the field of information
technologies and systems on daily life. The speed of information and data transfer enabled by
computing and communication technologies in todays world is a huge difference compared to the
1970s communication atmosphere. The face of the business world experienced a global change
with exposure to a growing range of information systems capabilities over the past three decades.
The numerous security issues involved in the use of computing technology may seem subdued as
a result of effort into mitigation techniques that are implemented by security experts to counter
known and perceived threats. However, organizations and individuals suffer one form of loss or
other due to security related issues with distributed computing. Cloud computing, which is a major
landmark in recent history of computing and is recording a very fast growth in adoption rate, does
not lack its own security issues; they range from loss of control to multi-tenancy. The virtualization
nature of cloud computing brings about intricacies in the monitoring of all resources in the several
(virtual) layers; this is as a result of the utilization of numerous server resources concurrently (Ko
et al 2010).
This research aims to identify these security concerns with a view to recommendations of possible
measures to reduce these security risks and vulnerabilities at enterprise level especially. It is rather
pertinent that organizations develop and adhere to their own security framework to enable the
overall management of data securely which boosts the level of trust in using the information
systems in general. In the application areas in information security risk management, cloud
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 21
computing is commercially feasible alternative for enterprises in seeking a cost-effective storage
and server solution (Waxer 2010).
Addressing issues related to privacy control and security vulnerabilities within the versatile use of
computing technology increases cloud technology adoption as a result of established or perceived
trust. Keeping security risks to a minimal level does not only augur well for vendors and their
clients but also deters nefarious activities that could compromise security and privacy. The number
of enterprises that are taking to cloud computing technology as a technique to minimize cost and
increase profitability are increasing, industry CIOs usually have the burden of reducing capital
assets, staff unit numbers, and other costs, through the use of cloud computing systems (Brendl,
2010).
In conducting these kinds of studies in this area, it gives the (academic) researchers the opportunity
to identify further trends, increase chances of solving problems, developing and unifying of
frameworks, and most importantly contribution to the IS body of knowledge etc.due to the flexible
and scalable attributes of cloud computing, it is possible to remotely develop, deploy, and sell
software and IT services. This exposes the plethora of risks that an organization faces at every
phase of the project process. Knowing the risks that the organization is prone to allows for
coordinated mitigation actions, like formulating and implementing a security and risk framework,
which will detail risks, triggers, response actions etc. The role that this study also plays is to
increase interest in advancing security infrastructure that keeps the cloud safer to cruise (Buyya
2009).
Due to gained trust, the return on investment for cloud computing technologies becomes more
stable and viable; these virtual servers host various data centers which are then used to create cloud
services culminates a significant investment in capital expenditure and ongoing operational costs.
The entities that adopt the technology are now exposed to a wider range of capabilities due to the
encouraged research and development in the area of computing technology and innovation. A few
risks of the Cloud clients are taken over by the vendor or third party managed processes such as
the seamless integration of applications, systems or platforms, updates and upgrades, etc. Cloud
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 22
adoption has been argued to be on the rise as result of lower costs on overall services but Greenberg
et al (2009) still asks the question of where the costs actually go.
Background of study
The adoption of virtualization technologies had become prevalent in corporate organizations since
the 1990s. As a result of the complex capabilities that are offered by virtual networking, managed
cloud implementations and/or adoptions around the world are on the increase. The actual nature
of virtualization in the case of cloud technology basically describes a computer network that is
permanently
connected to the internet and provides a platform of delivering an array of capabilities and services.
Implementing security and threat aversion protocols is a part and parcel of the computing culture
Cloud capabilities have been largely adopted in corporate circles as the new norm for networking
and shared resources. Even free cloud services like Google drive and Dropbox just to mention a
few are available, which makes it viable for widespread corporate adoption, due to a general public
that had already in some way profited from cloud technology offerings, various online services
especially data storage capability and hosted services.
In comparison to grid computing, cloud accommodates clients that are part of enterprise that
processes data in the cloud environment while subject to an inherent level of vulnerabilities. When
data stored on the cloud, it is imperative to ensure data integrity; making sure the data is correctly
stored and can be retrieved later. The size of data stored by the cloud for a specific client could be
massive, it is impractical (and might also bevery costly) to retrieve all the data, if ones purpose is
just to make sure that it is stored correctly. Hence there is a need to provide such guarantees to a
client..
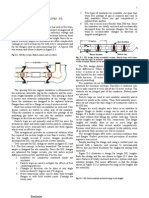
Below is a model that depicts the nature and options of cloud computing technology environment.
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 23
Overview of cloud systems (Source: Schubert et al., 2010)
Research problem statement
With the inception of the internet came security and privacy concerns that influences trust with
this form of technology. Although these issues had existed within various forms of distributed
computing, the recent emergence of cloud computing places these concerns on a high alert, given
the nature of how cloud is actually a host of virtual servers. A key issue area with clients is security
and privacy, which can be managed appropriately to reduce related threats, this helps to form a
level of trust between service provider and client.
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 24
Hence there is a need to further build on the gap in the body of knowledge by developing a model
that can serve as a guide for enterprise in safer cloud adoption methods and also a more secure
service offering from a vendor point of view in third party managed cloud.
Research objectives
Goal
The goal of this study is to evaluate inherent and emerging security risks in CipherClouds third
party managed cloud model.
Objectives
(i) To identify security risks (prevalent or emerging) in managed cloud
(ii) To determine factors that can reduce security risks and vulnerabilities
(iii) To identify major trust issues (if any) that is associated with cloud security threats
(iv) To formulate a model to help minimize security risks in cloud computing to improve trust
Research Questions
Primary Research Question
How to evaluate security risks and vulnerabilities that exist in cloud computing?
Secondary research questions
(i) What are the main security risk factors for clients using managed cloud computing?
(ii) What are the mitigating factors that can reduce security risks in cloud environment?
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 25
(iii) How is possible trust concerns linked with security risks in managed cloud?
Justification of the study
Owing to the evolution of cloud, which is rapidly changing the face of computing, it is pertinent
that enterprise in service provider-client relationship deliver their cloud offering with a high level
security and privacy in mind to create a trust relationship. It is relevant to promoting security in
cloud and importantly establishing further knowledge of the clients perceptions. Vouk (2008)
identified that security in the cloud computing environment is a research and engineering challenge
that is worth attention.
This kind of study allows vendors providing cloud services access to sets of methods to combat
security and privacy issues because when clients hire outsourced services from cloud provider,
there is a loss of control on a physical and logical level. Kumar et. al. (2012) states that Network
security measures are implemented to get protection from various threats and prevent these threats
from entering or spreading on a given network.
Expected research contribution
This study is expected to contribute to the information technology body of knowledge on managed
cloud model security frameworks in the South African and African cloud environment. The model
that is proposed to be developed will be applicable practically by cloud services providers,
enterprise and researchers in the area of computing security. It may also have theoretical
implications due to the evolution stages of cloud.
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 26
Literature Review
Roaming in the Clouds
Overview
Resources and services, which are managed and/or delivered on various computing technology
platforms, are expected to be secure in order to achieve its set objectives (protecting the integrity,
availability, and confidentiality of information system resources) (NIST 2006). Since the
inception of high-speed digital networks which has been widely used by consumers. The reports
of new attack techniques on various distributed digital networks have become prevalent in the 21century.While policy makers are to highly prioritize legislation on breaching of computer security.
Computer software/hardware dedicated to security has shown increasing vulnerabilities that makes
it susceptible to attack. Some attacks are due to the strategic design flaws that hinder optimal
performance when compromised by breach in the security standards(Stallings 2011). Security
attacks may be classified in two parts namely, passive and active.
The 21st century environment of IT infrastructures is largely characterized by changes in handling
of resources, resource usage and the general economic and financial methods used in service
provision and subscription-consumption. In the particular case the virtualization of a series
computing resources on a cloud technology, which is the most recent form of distributed
computing and shared resources, the privacy and security issues that are inherent are also a serious
challenge to be addressed (Zissis and Lekkas 2012). Using appropriate measures to mitigate these
security threats boosts confidence in the use of cloud technology. Cloud models essentially enable
ubiquitous and convenient computing, allowing a real-time on-demand network access to shared
set of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and
services). The services and resources provided thus are done at a rapid rate with minimal effort
from service provider, using a software distribution model where applications and other resources
are hosted by a service provider and is made available to clients on a distributed virtual network
for remote access (Kumar et. al. 2012). In order to successfully implement cloud computing at
enterprise level, requires a thorough plan and to understand the inherent and emerging risks,
threats, vulnerabilities, and possible countermeasures to reduce them.
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 27
Strengths and Benefits of Cloud
The strong point of cloud computing in information security risk mitigation is the ability to manage
security risk more efficiently from a central control point.
Bendandi (2009) highlights the top security benefits of cloud computing:
o Large scale implementation are cost-effective even security threats countermeasures, fast
response to incidents and a centralized security risk management.
o Improved security practices encourage many cloud clients to buy on the basis of the
reputation of confidentiality and integrity.
o Rapid and smart scaling of resources where cloud provider dynamically reallocates
resources for various processes.
o Auditing; where dedicated pay-per-session detailed images of virtual machines are
accessible without taking infrastructure offline.
o Environmental (green) benefits
o Array of shared configurable resources - provide access for SMEs more advanced ICT
allowing faster movement into new markets with less financial risk
o Creating open market technology opportunity for IT providing industry their services
gain commercial benefits consequently.
Challenges and trends
Formulating and implementing cloud-specific security protocols is a high profile challenge for the
service provider. However, the idea of having a singular digitized market scenario that incorporates
various geographical locations faces the obstacles of legal regulations and the lack of boundaries
on the internet. Use of intelligent strategies to usurp known challenges in cloud security is being
exploited.
Currently being applied in cloud computing is the use of trust protocols for distributed
systems/wireless networks. This is an attempt to securing the cloud and a sign of the dedicated
effort from security professionals to minimize threats. Gartner Inc. predicted that by 2012, 80
percent of Fortune 1000enterprises will commit financially to some cloud-computing service,
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 28
while 30 percent acquire cloud-computing infrastructure (Waxer 2010). Just like in most other
areas of computers, security is considered to be a key impediment for cloud computing, researchers
and experts have varying views on the issue of security in cloud computing which ranges from the
pros to cons (Kumar et. al. 2012).
Costs/Weaknesses of Cloud computing
The cost of cloud computing in information security risk management comprises of the costs of:
designing, migrating, implementing, integrating, and training staff. Also it includes the cost of
training supporting people in the new processes. The newly adopted architecture could pose new
security vulnerabilities thereby driving cost up. While the technology has its fair share of negatives
(such as privacy and security concerns), an undisputable potential benefit is turning a lot cloud
cynics into fans (Waxer, 2010).
Related Work
Current Cloud technology practices make it difficult for transparency that allows the user to
understand the level of security they have on their resources and data. This inability of the customer
to actually verify the implemented security protocols of a cloud computing service provider
because the customer generally has no access to the providers facility which can be comprised of
multiple facilities around the world (Anantwar et al 2012). Anantwar et al (2012) suggests further
study in implementing some security strategies with technology and management ways.
Bannerman (2011) indicates limitations in the study: the state of practice data was drawn from
industry commentary rather than academic experience reports and sampling was not random; the
field is developing so rapidly that it is very difficult for one researcher to span all
available/emerging information, and; the scope was limited to adoption, at the expense of
provision. However, these limitations provide opportunities for future research.
Theoretical foundations: IS theory
Theoretical framework: this guides the study, by influencing what things to measure, and what
statistical relationships are important.
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 29
PARADIGM RESEARCH
METHODOLOGY METHODS
APPROACH
Positivist
Quantitative
Survey Research
Close-ended
Questionnaire,
Statistical
Analysis, Documentation
Deductive process
review, Discussions.
Conceptual framework: this translates theory into meaningful practice. This concept for this
study is derived from the activity theory.
References
Anantwar, R.G., Chature, P.N., and Anantwar, S.G. 2012. Cloud Computing and Security Models:
A Survey. International Journal of Engineering Science and Innovative Technology
(IJESIT) Vol.1, No.2.
Bisong, A., and Rahman, S.M. (2011). An overview of the security concerns in enterprise cloud
computing. International Journal of Network Security & Its Applications (IJNSA), Vol.3,
No.1
Brandl D., (2010). Don't cloud your compliance data. Control Engineering, Vol.57 No. 23.
Buyya, R. et al., 2009. Cloud computing and emerging IT platforms: Vision, hype, and reality for
delivering computing as the 5th utility. Future Generation Computer Systems, Issue 25
Greenberg, A., Hamilton, J., Maltz, D. and Patel, P. (2009). The Cost of a Cloud: Research
Problems in Data Center Networks. In ACM SIGCOMM CCR, January 2009
Journal of IT and Economic Development 4(2), 19-30, October 2013 30
Kamesam, V. (2001). The Information Systems Audit Manual, prepared by the Working Group
on the Introduction of Information Systems Audit in Reserve Bank of India.
Ko, R.K.L, Lee, B.S. and Pearson, S. (2010). Towards Achieving Accountability, Auditability and
Trust in Cloud Computing. Paper delivered at: IEEE Second International Conference on
Cloud Computing Technology and Science (CloudCom), 30/11/2010
Kumar. D.K., Rao. G.V., and Rao. S.R. (2012). Cloud Computing: An Analysis of Its Challenges
& Security Issues. International Journal of Computer Science and Network (IJCSN).
Vol.1, No.5
Waxer, C. (2010). The benefits of cloud computing. Webhostingunleashed.com. Retrieved on
November 5, 2013from http://www.webhostingunleashed.com/features/cloud-computingbenefits
Copyright of Journal of Information Technology & Economic Development is the property of
Global Strategic Management, Inc. and its content may not be copied or emailed to multiple
sites or posted to a listserv without the copyright holder's express written permission.
However, users may print, download, or email articles for individual use.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Asset Management Council 1205 TheAsset0602 PDFDocument48 pagesAsset Management Council 1205 TheAsset0602 PDFSushmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Email Gateway DefenceDocument8 pagesEmail Gateway DefenceNiven MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Hose Reel System For Primary School at Alor Setar KedahDocument6 pagesHose Reel System For Primary School at Alor Setar KedahSyafiqah ShahuriNo ratings yet
- I Used To Be A Desgin StudentDocument256 pagesI Used To Be A Desgin StudentMLNo ratings yet
- Sample Business Report FormatDocument1 pageSample Business Report FormatmironkoprevNo ratings yet
- Sample Annual BudgetDocument4 pagesSample Annual BudgetMary Ann B. GabucanNo ratings yet
- MachXO2 Lattice Semiconductor ManualDocument23 pagesMachXO2 Lattice Semiconductor ManualAdrian Hdz VegaNo ratings yet
- TLC Pharmaceutical Standards: Safety Data SheetDocument4 pagesTLC Pharmaceutical Standards: Safety Data SheetFABIOLA FLONo ratings yet
- Formatting TextsDocument3 pagesFormatting TextsCelestineNo ratings yet
- Public Private Partnership in Public Administration Discipline A Literature ReviewDocument25 pagesPublic Private Partnership in Public Administration Discipline A Literature ReviewJuan GalarzaNo ratings yet
- IEA PVPS Trends 2018 in Photovoltaic Applications PDFDocument88 pagesIEA PVPS Trends 2018 in Photovoltaic Applications PDFCarlos Tadeo CapistranNo ratings yet
- Privacy Protection Based Access Control Scheme in Cloud-Based Services - 1crore ProjectsDocument5 pagesPrivacy Protection Based Access Control Scheme in Cloud-Based Services - 1crore ProjectsLalitha PonnamNo ratings yet
- Hussain 2020Document13 pagesHussain 2020Prince RajputNo ratings yet
- IOT Door Buzzer & Home Security DeviceDocument5 pagesIOT Door Buzzer & Home Security Devicekutty vickyNo ratings yet
- Masurare Grosime Vopsea 1 - Fisa-tehnica-Extech-CG204Document1 pageMasurare Grosime Vopsea 1 - Fisa-tehnica-Extech-CG204RizzoRo1No ratings yet
- Fluid IIDocument2 pagesFluid IIJefara 01No ratings yet
- Regional Memorandum: Adjusted Search Timeline Activity Date RemarksDocument2 pagesRegional Memorandum: Adjusted Search Timeline Activity Date RemarksKimttrix WeizsNo ratings yet
- A. Introduction: Module Gil BasicsDocument12 pagesA. Introduction: Module Gil BasicsMayuresh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: An To The Nature of ManagementDocument32 pagesChapter One: An To The Nature of ManagementHaymanot endaleNo ratings yet
- Basic Functions of Healthcare FieldDocument10 pagesBasic Functions of Healthcare FieldShraddha BendkhaleNo ratings yet
- Bou CatddDocument2 pagesBou CatddDJNo ratings yet
- Social Media Critical ThinkingDocument21 pagesSocial Media Critical ThinkingHeidi TieuNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management ImportanceDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Management ImportanceT S Kumar KumarNo ratings yet
- 8 Form Reading The Stronger ManDocument8 pages8 Form Reading The Stronger Manмаксим соловейNo ratings yet
- RapportStage SOCOTUDocument20 pagesRapportStage SOCOTUdorsafhasni69No ratings yet
- Master Formula New UpdateDocument5 pagesMaster Formula New UpdateAdhoNo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision MakingDocument8 pagesConsumer Decision Making9986212378No ratings yet
- Daikin Ducable Unit 5 5tr To 16 7trDocument2 pagesDaikin Ducable Unit 5 5tr To 16 7trరాజా రావు చామర్తిNo ratings yet
- Drill CollarsDocument3 pagesDrill CollarsRambabu ChNo ratings yet
- Big Data Tools-An Overview: ArticleDocument16 pagesBig Data Tools-An Overview: ArticleAdzan YogaNo ratings yet