Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Security
Uploaded by
Poorna Chandra GaralapatiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Security
Uploaded by
Poorna Chandra GaralapatiCopyright:
Available Formats
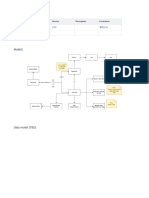
Data Security
Data security for Oracle Web Customers, Oracle Web Employees, and
Oracle Web Suppliers is controlled by:
Secure Socket Layers (SSL) to secure communication between
client and server
HTTP cookies
encryption of password, parameter function, and session
identifier
session expiration
securing and excluding attribute control
Session Management
Attribute Control
Session management features include:
each session is assigned a unique identifier, which is stored in a
table
session identifier returned to client encrypted via cookie
encryption includes IP address to validate physical machine as
well as the user
session expiration based on number of hours or number of hits
By using securing and excluding attributes, you can control users
access to data based on their ID and their responsibility. Attributes are
first defined using the Web Applications Dictionary. They become
securing or excluding attributes when you define responsibilities and
users using the system administration functions of Oracle Application
Object Library. See: Defining Attributes: page 3 25.
Securing Attributes for RowLevel Security
Securing attributes allow rows (records) of data to be visible to specified
users or responsibilities based on the specific data (attribute value)
contained in the row.
For example, to allow a hypothetical user, Sue, in the ADMIN
responsibility to see rows containing a CUSTOMER_ID value of 1000,
assign the securing attribute of CUSTOMER_ID to the ADMIN
Overview of SelfService Web Applications
1 15
responsibility. Then give Sue a security attribute CUSTOMER_ID value
of 1000.
When Sue logs into the Admin responsibility the only customer data she
will have access to will have a CUSTOMER_ID value of 1000.
Note: Users can have multiple values made available to them.
See: Users Window, Oracle Applications Users Guide, Release 11 and
Responsibilities Window, Oracle Applications Users Guide, Release 11.
Excluding Attributes for ColumnLevel Security
Excluding attributes prevent certain columns of data from being visible
to specified responsibilities.
For example, if for security reasons you did not want the hypothetical
user Sue in the ADMIN responsibility to see data in the
CONTACT_NAME column, you would assign her the excluding
attribute CONTACT_NAME to the ADMIN responsibility. No users
with the ADMIN responsibility can see CONTACT_NAME information.
See: Responsibilities Window, Oracle Applications Users Guide, Release 11.
Seeded Securing Attributes
Assign a securing attribute and value to define an attribute that must be
matched by the user to see records. Attributes are defined using the
Web Applications Dictionary. Assign securing attribute values for each
user, and for each securing attribute assigned to all responsibilities for
this user.
You may designate a user as an employee, supplier, and / or customer.
This automatically assigns a contact ID value to this user for appropriate
securing attributes as follows:
Contact
ID
Customer Contact
ICX_CUSTOMER_CONTACT_ID
Internal Contact
ICX_HR_PERSON_ID
Supplier Contact
ICX_SUPPLIER_CONTACT_ID
In addition, the following securing attributes are seeded:
1 16
Oracle SelfService Web Applications Implementation Manual
Contact
ID
Customer
ICX_CUSTOMER_ORG_ID
Organization
ICX_HRG_ORG_ID
Supplier
ICX_SUPPLIER_ORG_ID
Customer Site
ICX_CUSTOMER_SITE_ID
Internal Site (location)
ICX_HR_SITE_ID
Supplier Site
ICX_SUPPLIER_SITE_ID
Predefined Security at Responsibility Level
The following list shows which responsibilities have predefined
securing and excluding attributes:
Responsibility
Securing Attributes
Credit Cards
ICX_HR_PERSON_ID
Excluding Attributes
Customer Registration
Customer Services (Full Access)
Customer Services (by Customer)
Customer Services (by Customer
Contact)
EDI Transmissions (by Customer Site) ICX_CUSTOMER_SITE_ID
EDI Transmissions (Full Access)
Events and Seminars
Executive Overview
Expense Reports
Expense Reporting
Global Assets Information
Partner Information (by Customer)
ICX_CUSTOMER_ORG_ID
Payments and Credits (by Customer)
ICX_CUSTOMER_ORG_ID
Table 1 1 (Page 1 of 2)
Overview of SelfService Web Applications
1 17
Responsibility
Securing Attributes
Excluding Attributes
Payments and Credits (Full Access)
Plan Inquiries
Products and Orders (by Customer
Contact)
Products and Orders (Full Access)
ICX_CUSTOMER_CONTACT_ID
Products and Orders (Guest Access)
Project Control (by Employee)
ICX_HR_PERSON_ID
Project Information (by Customer)
ICX_CUSTOMER_ORG_ID
Purchasing
Registration
Requisitions
Requisitions (by Preparer)
PREPARER_ID
Requisitions (by Requester)
ICX_REQUESTOR_ID
Requisitions (Full Access)
Salesperson Services (by Employee)
ICX_CUSTOMER_ORG_ID
Salesperson Services (Full Access)
Service and Support (Full Access)
Service and Support (by Customer
Contact)
Service and Support (by Customer)
CS_PUBLIC_COMMENT
ICX_CUSTOMER_CONTACT_ID
CS_COMMENT
ICX_CUSTOMER_ORG_ID
CS_COMMENT
Supplier Services
ICX_LEVEL_ALTERED
Supplier Services (by Supplier Site)
ICX_LEVEL_ALTERED,
ICX_SUPPLIER_SITE_ID
ICX_LEVEL_ALTERED,
ICX_SUPPLIER_ORG_ID
ICX_DISTRIBUTION_ID,
ICX_SUPPLIER, ICX_SUPSITE
ICX_DISTRIBUTION_ID,
ICX_SUPPLIER, ICX_SUPSITE
ICX_DISTRIBUTION_ID,
ICX_SUPPLIER, ICX_SUPSITE
ICX_DISTRIBUTION_ID
Supplier Registration
Supplier Services (by Supplier)
Supplier Services (Full Access)
Web Planning Inquiries
Table 1 1 (Page 2 of 2)
1 18
Oracle SelfService Web Applications Implementation Manual
Query Processing
When a user queries for data using Oracle Web Customers, Oracle Web
Employees, and Oracle Web Suppliers, the Web Applications Dictionary
determines if any securing attributes exist in a region, and, if so,
determines whether the securing attributes match those assigned to the
responsibility.
If there are securing attributes assigned at the responsibility level that
exactly match those at the region level, securing attribute values are
checked at the user level.
If there are no securing attributes assigned at the user level that match,
no data is returned. If there are securing attributes assigned at the user
level that match, data is returned to the user, but only if the users
securing attribute values exactly match the values of the returned data.
Excluded attributes assigned at the responsibility level prevent data
being returned for these attributes.
For example, assume that Sue has the following attribute values:
Securing Attribute
Value
CUSTOMER_ID
1000
SITE_ID
123
SITE_ID
345
SITE_ID
567
CONTACT_ID
9876
Table 1 2
Assume that Sue requests data for CUSTOMER_ID, SITE_ID, or
CONTACT_ID, and these attributes are defined in Web Applications
Dictionary and for the Customer responsibility. For any rows of data
with these attributes, Sues securing attribute values are checked for
exact matches.
In this case, any rows with a CUSTOMER_ID of 1000; SITE_ID of 123,
345, or 567; and CONTACT_ID of 9876 are returned.
Overview of SelfService Web Applications
1 19
You might also like
- MICROSOFT AZURE ADMINISTRATOR EXAM PREP(AZ-104) Part-2: AZ 104 EXAM STUDY GUIDEFrom EverandMICROSOFT AZURE ADMINISTRATOR EXAM PREP(AZ-104) Part-2: AZ 104 EXAM STUDY GUIDENo ratings yet
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900From EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900No ratings yet
- Oracle Apps AOLDocument194 pagesOracle Apps AOLAmit R Tiwari100% (4)
- Oracle Apps Technical ConceptDocument14 pagesOracle Apps Technical Conceptamit_xyzNo ratings yet
- Sysadmin Advanced Level SecrurityDocument9 pagesSysadmin Advanced Level Secrurityvedavyas4funNo ratings yet
- Security MechanismDocument18 pagesSecurity MechanismShino IbañezNo ratings yet
- MSDAX2012 Security Roles Licensing WhitepaperDocument12 pagesMSDAX2012 Security Roles Licensing WhitepaperTariq RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Tririga SsoDocument26 pagesTririga Ssojulian100% (1)
- Isupplier TREIKODocument2 pagesIsupplier TREIKOharishNo ratings yet
- Oracle HelpDocument1 pageOracle HelpAshish SaxenaNo ratings yet
- BW SecuritypdfDocument33 pagesBW SecuritypdfKiran JayNo ratings yet
- Data_protection_and_security_in_QlikViewDocument20 pagesData_protection_and_security_in_QlikViewivkesdNo ratings yet
- Configure Azure Active Directory app manifestDocument13 pagesConfigure Azure Active Directory app manifestTamNo ratings yet
- 2021-07-12 - Security Architecture AXDocument2 pages2021-07-12 - Security Architecture AXKangeyan DhanapalanNo ratings yet
- Database Application Security ModelsDocument55 pagesDatabase Application Security ModelsRaj ShahNo ratings yet
- 15 AAA Principles and ConfigurationDocument16 pages15 AAA Principles and ConfigurationOsama DsokyNo ratings yet
- Forms Authentication and AuthorizationDocument9 pagesForms Authentication and AuthorizationshivuhcNo ratings yet
- Fin CustomerProfileServiceAMDocument32 pagesFin CustomerProfileServiceAMMagedNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Certified Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals Skills MeasuredDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Certified Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals Skills MeasuredMayank VishwasNo ratings yet
- Kiến trúc WindowsDocument492 pagesKiến trúc WindowsĐănggNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document20 pagesCH 5nimona2024hirkoNo ratings yet
- Sec User Services 15 1 BookDocument1,291 pagesSec User Services 15 1 BookEnis ByciNo ratings yet
- Integration Doc-2Document11 pagesIntegration Doc-2AsimNo ratings yet
- Obi SsoDocument31 pagesObi Ssokevinchristee21No ratings yet
- Topic-4 VPDDocument48 pagesTopic-4 VPDRaj ShahNo ratings yet
- September 2011Document71 pagesSeptember 2011Zuhair Abdullah FadhelNo ratings yet
- BCB-Access Control (AC) - 051223-044950Document7 pagesBCB-Access Control (AC) - 051223-044950Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Exam SC 900 Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals Skills MeasuredDocument9 pagesExam SC 900 Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals Skills Measuredzawzaw htetNo ratings yet
- Oracle ADF SecurityDocument30 pagesOracle ADF SecurityiamsonalNo ratings yet
- Exam SC 900 Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals Skills MeasuredDocument8 pagesExam SC 900 Microsoft Security Compliance and Identity Fundamentals Skills MeasuredrossivoNo ratings yet
- Roles and Security - AX2012Document11 pagesRoles and Security - AX2012ankitm_240No ratings yet
- Platform-Spec-8 - Chapter 3. SecurityDocument18 pagesPlatform-Spec-8 - Chapter 3. SecurityCiprian Nicu RosuNo ratings yet
- Online Banking Software RequirementsDocument59 pagesOnline Banking Software RequirementsArun KolluriNo ratings yet
- Standards Ac Management ProvisionDocument5 pagesStandards Ac Management ProvisionmukeshNo ratings yet
- E5 Security Implementation GuideDocument30 pagesE5 Security Implementation GuidertkaushikNo ratings yet
- AAA Network Security ServicesDocument20 pagesAAA Network Security ServicesSandeep Kushwaha100% (1)
- SAP Security OverviewDocument40 pagesSAP Security OverviewMiftahur Rahman100% (1)
- Azure Active DirectoryDocument4 pagesAzure Active Directorytrinitycloud001No ratings yet
- Symantec Validation & Id Protection Service (Vip) : Integration Guide For Ca Siteminder®Document14 pagesSymantec Validation & Id Protection Service (Vip) : Integration Guide For Ca Siteminder®deals4kbNo ratings yet
- Xirrus Application Note WPR Final 011810Document15 pagesXirrus Application Note WPR Final 011810Gua SyedNo ratings yet
- SailPoint Technical Integration GuideDocument8 pagesSailPoint Technical Integration Guidesree.miboxNo ratings yet
- Exam SC-900: Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredDocument8 pagesExam SC-900: Microsoft Security, Compliance, and Identity Fundamentals - Skills MeasuredaxleNo ratings yet
- Implementing Data Security For Financials in Fusion SaaS R12Document9 pagesImplementing Data Security For Financials in Fusion SaaS R12NoExpiryNo ratings yet
- Ax2012 Enus Devi 04Document20 pagesAx2012 Enus Devi 04sergio_741No ratings yet
- SAP Net Weaver BI SecurityDocument30 pagesSAP Net Weaver BI SecurityRajeshwar Rao TNo ratings yet
- Data security and access controls in AD360Document9 pagesData security and access controls in AD360PrimeNo ratings yet
- Unidad 3 Seguridad en Redes AAADocument64 pagesUnidad 3 Seguridad en Redes AAAbeleniuxNo ratings yet
- 300-LARAVEL-Intro API RESTful PDFDocument30 pages300-LARAVEL-Intro API RESTful PDFJan Mota JimenezNo ratings yet
- Hotel Management SystemDocument12 pagesHotel Management SystemNikitha JeganathanNo ratings yet
- Access Control Using TrustSecDocument86 pagesAccess Control Using TrustSeczmartina0% (1)
- Secure Acceptance SOPDocument121 pagesSecure Acceptance SOPBharathi AppachiappanNo ratings yet
- Software Architecture Assignment - 2Document18 pagesSoftware Architecture Assignment - 2Maltesh BannihalliNo ratings yet
- Enforcing Microsoft Active Directory Policies Using LDAP Attribute MapsDocument34 pagesEnforcing Microsoft Active Directory Policies Using LDAP Attribute MapsKaddour El HallaouiNo ratings yet
- B-Connected API With Widget IntegrationDocument16 pagesB-Connected API With Widget IntegrationKarthikRamaswamyNo ratings yet
- RBACDocument5 pagesRBACramnath.makelifesmarterNo ratings yet
- Quick Reference Guide - Access Control SAP v5.2 - GRC Applications Integration DocumentationDocument33 pagesQuick Reference Guide - Access Control SAP v5.2 - GRC Applications Integration Documentationadi8066No ratings yet
- 03 Connecting Authentication and CredentialsDocument9 pages03 Connecting Authentication and CredentialsChristopher WilliamsNo ratings yet
- (ISC)2 CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional Official Study GuideFrom Everand(ISC)2 CCSP Certified Cloud Security Professional Official Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Using Oracle Advance Pricing in Oracle PurchasingDocument8 pagesUsing Oracle Advance Pricing in Oracle PurchasingPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- R12 APS OverviewDocument81 pagesR12 APS OverviewPoorna Chandra Garalapati100% (1)
- Buyers Guide To Punchout and Transparent PunchoutDocument266 pagesBuyers Guide To Punchout and Transparent PunchoutabhisterNo ratings yet
- Map Categories in iProcurementDocument6 pagesMap Categories in iProcurementPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- ARDocument3 pagesARPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- OneTime Address Documen1Document10 pagesOneTime Address Documen1Poorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Product Development - Session1Document29 pagesProduct Development - Session1Poorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Cash ManagementDocument3 pagesCash ManagementPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- All QuestionsDocument15 pagesAll QuestionsPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- For OPM Modules 11iDocument49 pagesFor OPM Modules 11iPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Punchout Supplier SiteDocument3 pagesPunchout Supplier SitePoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Setup XML PO through OSNDocument13 pagesSetup XML PO through OSNPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Streamline Quality Management ProcessesDocument15 pagesStreamline Quality Management ProcessesPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- About Page - Banking DetailsDocument7 pagesAbout Page - Banking DetailsPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- RUP Patches For IsupplierDocument9 pagesRUP Patches For IsupplierPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Handy SQL InventorylDocument18 pagesHandy SQL InventorylPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Application Short IDDocument2 pagesOracle Application Short IDPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- SCM Isupplier Collaboration Presentation v4.5Document43 pagesSCM Isupplier Collaboration Presentation v4.5Poorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- I-Supplier Short NoteDocument10 pagesI-Supplier Short NotePoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- GUI Telnet Installation ProcedureDocument1 pageGUI Telnet Installation ProcedurePoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Isupplier Portal - DatasheetDocument5 pagesIsupplier Portal - DatasheetSapan JoshiNo ratings yet
- GUI Telnet Installation ProcedureDocument1 pageGUI Telnet Installation ProcedurePoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Oracle Sourcing r12 Implementation and Administration GuideDocument164 pagesOracle Sourcing r12 Implementation and Administration GuideEduardo Padilla UlloaNo ratings yet
- GUI Telnet Installation ProcedureDocument1 pageGUI Telnet Installation ProcedurePoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Crossword Book PDFDocument44 pagesCrossword Book PDFPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Oracle SCM Course ContentDocument5 pagesOracle SCM Course ContentPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Enhance Drop Ship Using Oracle Internet Supplier PortalDocument26 pagesEnhance Drop Ship Using Oracle Internet Supplier Portalellyacool2319No ratings yet
- Pkirch PpteDocument44 pagesPkirch PptePoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Oracle SCM Course ContentDocument5 pagesOracle SCM Course ContentPoorna Chandra GaralapatiNo ratings yet
- Commissioning Handover Plan FINAL (Amy Phillips)Document6 pagesCommissioning Handover Plan FINAL (Amy Phillips)Christian LlorcaNo ratings yet
- EF FS EnCase Forensic Imager WebreadyDocument1 pageEF FS EnCase Forensic Imager WebreadyMirela BeatrizNo ratings yet
- WLAN Product Interoperation Configuration GuideDocument558 pagesWLAN Product Interoperation Configuration GuidegurungeNo ratings yet
- VertexNA ISPv16 IndividualsDocument17 pagesVertexNA ISPv16 IndividualsSergio ArtinanoNo ratings yet
- DepEd Advisories BOSY 2017-2018 Enrolment FacilitiesDocument3 pagesDepEd Advisories BOSY 2017-2018 Enrolment FacilitiesChelie TrangiaNo ratings yet
- Catalog Important SoftwareDocument77 pagesCatalog Important SoftwareSaurabh KoranglekarNo ratings yet
- 6th YearDocument2 pages6th YearAbin PNo ratings yet
- Brief SummaryDocument2 pagesBrief SummaryBts SellerNo ratings yet
- IT - ISCAP - Mariana Malta: Cloud ComputingDocument18 pagesIT - ISCAP - Mariana Malta: Cloud ComputingMarian IonciuNo ratings yet
- Virtualization SecurityDocument33 pagesVirtualization SecurityStéphane KenthorNo ratings yet
- Sandblast Battle CardDocument3 pagesSandblast Battle CardLeonardo PereiraNo ratings yet
- VI. Bill of Rights (Part F. Freedom of Expression, Right To Assembly, and Academic Freedom)Document131 pagesVI. Bill of Rights (Part F. Freedom of Expression, Right To Assembly, and Academic Freedom)dnel13No ratings yet
- Proposed Mississippi Sports Betting RulesDocument21 pagesProposed Mississippi Sports Betting RulesUploadedbyHaroldGaterNo ratings yet
- JustificationDocument8 pagesJustificationBiniyamNo ratings yet
- DRMDocument54 pagesDRMthe_tigdraNo ratings yet
- (산업연구원) 보고서 - 글로벌 IT 기업의 방위산업 진출 동향과 시사점Document183 pages(산업연구원) 보고서 - 글로벌 IT 기업의 방위산업 진출 동향과 시사점Daewon KimNo ratings yet
- 1756-IF16 WiringDocument24 pages1756-IF16 WiringjfeyesNo ratings yet
- PKI Admin TrainingDocument2 pagesPKI Admin TrainingLe NguyenNo ratings yet
- Fingerprint and Password Based Door Lock System Using Raspberry PiDocument2 pagesFingerprint and Password Based Door Lock System Using Raspberry PiEliyasuddin AliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - How Can I Use The Internet As A Tool For Effective ResearchDocument50 pagesLesson 2 - How Can I Use The Internet As A Tool For Effective Researchsienn100% (2)
- ZMT Admin GuideDocument34 pagesZMT Admin GuideAngel JiménezNo ratings yet
- Applied Cryptography 1Document5 pagesApplied Cryptography 1Sehrish AbbasNo ratings yet
- Supremacy PDFDocument95 pagesSupremacy PDFMark Ballinger50% (2)
- HIPAA Compliance Checklist DownloadDocument1 pageHIPAA Compliance Checklist DownloadHetik GoNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document22 pagesCH 13iamthe11No ratings yet
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: Fingerprint Door LockDocument17 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: Fingerprint Door LockRiahabh jainNo ratings yet
- Password Reset A2+ B1 UT Answer KeyDocument3 pagesPassword Reset A2+ B1 UT Answer KeyPatryk ParlickiNo ratings yet
- Coc3 ServerDocument2 pagesCoc3 ServerBryan BautistaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Symmetric-Key CiphersDocument73 pagesTraditional Symmetric-Key CiphersKevin SarserNo ratings yet
- Honeywell 5809 Install GuideDocument2 pagesHoneywell 5809 Install GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringNo ratings yet