Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OLAP Cube: 2 Hierarchy
Uploaded by
davidarugueteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OLAP Cube: 2 Hierarchy
Uploaded by
davidarugueteCopyright:
Available Formats
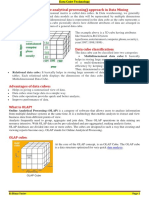
OLAP cube
are derived from the dimension tables.
m
Ti
Products
2 Hierarchy
Cities
The elements of a dimension can be organized as a
hierarchy,[4] a set of parent-child relationships, typically
where a parent member summarizes its children. Parent
elements can further be aggregated as the children of another parent.[5]
For example May 2005s parent is Second Quarter 2005
which is in turn the child of Year 2005. Similarly cities
are the children of regions; products roll into product
groups and individual expense items into types of expenditure.
An example of an OLAP cube
An OLAP cube is an array of data understood in terms 3 Operations
of its 0 or more dimensions. OLAP is an acronym
for online analytical processing.[1] OLAP is a computer- Conceiving data as a cube with hierarchical dimensions
based technique for analyzing business data in the search leads to conceptually straightforward operations to facilifor business intelligence.[2]
tate analysis. Aligning the data content with a familiar visualization enhances analyst learning and productivity.[5]
The user-initiated process of navigating by calling for
1 Terminology
page displays interactively, through the specication of
slices via rotations and drill down/up is sometimes called
A cube can be considered a multi-dimensional general- slice and dice. Common operations include slice and
ization of a two- or three-dimensional spreadsheet. For dice, drill down, roll up, and pivot.
example, a company might wish to summarize nancial
data by product, by time-period, and by city to compare
actual and budget expenses. Product, time, city and scenario (actual and budget) are the datas dimensions.[3]
Cube is a shortcut for multidimensional dataset, given that
data can have an arbitrary number of dimensions. The
term hypercube is sometimes used, especially for data
with more than three dimensions.
OLAP slicing
Slicer is a term for a dimension which is held constant for all cells so that multidimensional information Slice is the act of picking a rectangular subset of a cube by
can be shown in a two dimensional physical space of a choosing a single value for one of its dimensions, creatspreadsheet or pivot table.
ing a new cube with one fewer dimension.[5] The picture
Each cell of the cube holds a number that represents some shows a slicing operation: The sales gures of all sales
measure of the business, such as sales, prots, expenses, regions and all product categories of the company in the
budget and forecast.
year 2004 are sliced out of the data cube.
OLAP data is typically stored in a star schema or
snowake schema in a relational data warehouse or in a
special-purpose data management system. Measures are
derived from the records in the fact table and dimensions
Dice: The dice operation produces a subcube by allowing the analyst to pick specic values of multiple
dimensions.[6] The picture shows a dicing operation: The
new cube shows the sales gures of a limited number of
1
5 SEE ALSO
4 Mathematical denition
In database theory, an OLAP cube is[8] an abstract representation of a projection of an RDBMS relation. Given
a relation of order N, consider a projection that subtends
X, Y, and Z as the key and W as the residual attribute.
Characterizing this as a function,
f : (X,Y,Z) W,
OLAP dicing
the attributes X, Y, and Z correspond to the axes of the
cube, while the W value into which each ( X, Y, Z ) triple
product categories, the time and region dimensions cover maps corresponds to the data element that populates each
the same range as before.
cell of the cube.
Insofar as two-dimensional output devices cannot readily characterize three dimensions, it is more practical to
project slices of the data cube (we say project in the classic vector analytic sense of dimensional reduction, not in
the SQL sense, although the two are conceptually similar),
g : (X,Y) W
OLAP Drill-up and drill-down
Drill Down/Up allows the user to navigate among levels
of data ranging from the most summarized (up) to the
most detailed (down).[5] The picture shows a drill-down
operation: The analyst moves from the summary category
Outdoor-Schutzausrstung to see the sales gures for
the individual products.
which may suppress a primary key, but still have some
semantic signicance, perhaps a slice of the triadic functional representation for a given Z value of interest.
The motivation[8] behind OLAP displays harks back to
the cross-tabbed report paradigm of 1980s DBMS. The
resulting spreadsheet-style display, where values of X
populate row $1; values of Y populate column $A; and
Roll-up: A roll-up involves summarizing the data along a values of g : ( X, Y ) W populate the individual cells
dimension. The summarization rule might be computing southeast of $B2, so to speak, $B2 itself included.
totals along a hierarchy or applying a set of formulas such
as prot = sales - expenses.[5]
5 See also
Comparison of OLAP Servers
Business intelligence
Data mining
Data Mining Extensions
OLAP pivoting
Data warehouse
Data mart
Pivot allows an analyst to rotate the cube in space to see
its various faces. For example, cities could be arranged
vertically and products horizontally while viewing data
for a particular quarter. Pivoting could replace products with time periods to see data across time for a single
product.[5][7]
Fast Analysis of Shared Multidimensional Information
The picture shows a pivoting operation: The whole cube
is rotated, giving another perspective on the data.
Online analytical processing (OLAP)
Pivot Table
Multidimensional Expressions (MDX)
XML for Analysis
References
[1] Just What Are Cubes Anyway? (A Painless Introduction
to OLAP Technology)". Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved
2012-07-25.
[2] Deepak Pareek (2007). Business Intelligence for Telecommunications. CRC Press. pp. 294 pp. ISBN 0-84938792-2. Retrieved 2008-03-18.
[3] Cybertec releases OLAP cubes for PostgreSQL. PostgreSQL. 2006-10-02. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
[4] Oracle9i Data Warehousing Guide hierarchy. Lorentz
Center. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
[5] OLAP and OLAP Server Denitions.
Council. 1995. Retrieved 2008-03-18.
The OLAP
[6] Glossary of Data Mining Terms. University of Alberta.
1999. Retrieved 2008-03-17.
[7] Computer Encyclopedia: multidimensional views. Answers.com. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
[8] Gray, Jim; Bosworth, Adam; Layman, Andrew; Priahesh,
Hamid (1995-11-18). Data Cube: A Relational Aggregation Operator Generalizing Group-By, Cross-Tab, and
Sub-Totals. Proc. 12th International Conference on Data
Engineering. IEEE. pp. 152159. Retrieved 2008-11-09.
External links
Daniel Lemire (December 2007). Data Warehousing and OLAP - A Research-Oriented Bibliography. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
The RDF Data Cube Vocabulary
8 TEXT AND IMAGE SOURCES, CONTRIBUTORS, AND LICENSES
Text and image sources, contributors, and licenses
8.1
Text
OLAP cube Source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OLAP%20cube?oldid=623296069 Contributors: Michael Hardy, Charles Matthews,
Urantian, SEWilco, Rohan Jayasekera, Jmabel, Goethean, Lysy, Sepreece, Vasile, Asqueella, S.K., Fenice, Aranel, John Vandenberg,
.:Ajvol:., Hooperbloob, Cma, Brycen, Kgrr, Gyrae, FluyPanda, MauriceKA, DePiep, Lockley, Jmcc150, Yorrose, EngineerScotty, Cvanhasselt, Crasshopper, Wizzard, Flagboy, Modify, SmackBot, Eskimbot, Ohnoitsjamie, Thumperward, Emurphy42, Sspecter, T-borg,
Wikiolap, Soumyasch, Robosh, Dll99, David Tristram, Quaeler, Bertport, OS2Warp, SqlPac, CmdrObot, Cydebot, Labreuer, LeoHeska, Astazi, Thijs!bot, Hazmat2, CharlesHoman, Lfstevens, Paulrho, Magioladitis, AndyReid, Animum, EagleFan, J.delanoy, McSly, Plasticup, Jrolston, Qseep, VolkovBot, Technopat, Mihirgokani007, Andy Dingley, SieBot, SouthLake, Hiddenfromview, ClueBot,
Niceguyedc, PasabaPorAqui, Yx7557, Addbot, Yobot, Ningauble, AnomieBOT, Materialscientist, Julianhyde, Osiris.toth138, NinjaCross,
Crysb, RjwilmsiBot, Igor Yalovecky, Carmichael, 28bot, ClueBot NG, Helpful Pixie Bot, Infopedian, Anubhab91, Krystof1000, BattyBot,
Monkbot and Anonymous: 103
8.2
Images
File:Edit-clear.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/f/f2/Edit-clear.svg License: ? Contributors: The Tango! Desktop
Project. Original artist:
The people from the Tango! project. And according to the meta-data in the le, specically: Andreas Nilsson, and Jakub Steiner (although
minimally).
File:Internet_map_1024.jpg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/d2/Internet_map_1024.jpg License: CC-BY2.5 Contributors: Originally from the English Wikipedia; description page is/was here. Original artist: The Opte Project
File:Merge-arrow.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/a/aa/Merge-arrow.svg License: Public domain Contributors: ? Original artist: ?
File:OLAP_Cube.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/5/52/OLAP_Cube.svg License: CC-BY-SA-3.0
OLAP_Cube.png <a href='//commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:OLAP_Cube.png' class='image'><img alt='OLAP
Contributors:
Cube.png'
src='//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/OLAP_Cube.png/50px-OLAP_Cube.png'
width='50'
height='43'
srcset='//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/OLAP_Cube.png/75px-OLAP_Cube.png
1.5x,
//upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/7/7d/OLAP_Cube.png/100px-OLAP_Cube.png 2x' data-le-width='280' datale-height='242' /></a>
Original artist: OLAP_Cube.png: Konrad Roeder
File:OLAP_dicing.png Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/d/d0/OLAP_dicing.png License: CC-BY-SA-3.0 Contributors: Own work Original artist: Infopedian
File:OLAP_drill_up&down.png Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/46/OLAP_drill_up%26down.png License:
GFDL Contributors: own illustration Original artist: Infopedian
File:OLAP_pivoting.png Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/cb/OLAP_pivoting.png License: CC-BY-SA-3.0
Contributors: Own work Original artist: Infopedian
File:OLAP_slicing.png Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/ff/OLAP_slicing.png License: CC-BY-SA-3.0 Contributors: Own work Original artist: Infopedian
File:Question_book-new.svg Source: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/9/99/Question_book-new.svg License: ? Contributors:
Created from scratch in Adobe Illustrator. Based on Image:Question book.png created by User:Equazcion Original artist:
Tkgd2007
8.3
Content license
Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0
You might also like
- Pro Microsoft Power BI Administration: Creating a Consistent, Compliant, and Secure Corporate Platform for Business IntelligenceFrom EverandPro Microsoft Power BI Administration: Creating a Consistent, Compliant, and Secure Corporate Platform for Business IntelligenceNo ratings yet
- Model Management and Analytics for Large Scale SystemsFrom EverandModel Management and Analytics for Large Scale SystemsBedir TekinerdoganNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Bug Busting: From Testing through CI/CD to Deliver Business ResultsFrom EverandEnterprise Bug Busting: From Testing through CI/CD to Deliver Business ResultsNo ratings yet
- Data Warehouses and OLAPDocument361 pagesData Warehouses and OLAPNy Laza Alexias Randrianoelina100% (1)
- NLP in Stock Price AnalysisDocument12 pagesNLP in Stock Price AnalysisJyothi BurlaNo ratings yet
- Business Intelligence/ Data Warehousing: Lakshmi Prashad PMGDocument101 pagesBusiness Intelligence/ Data Warehousing: Lakshmi Prashad PMGChiranjeevi SutrayeNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation and AnalysisDocument71 pagesData Presentation and AnalysissweetyNo ratings yet
- Using Data Flow Diagrams: Kendall & Kendall Systems Analysis and DesignDocument49 pagesUsing Data Flow Diagrams: Kendall & Kendall Systems Analysis and DesignPang Pang PangNo ratings yet
- 35 Best New Big Data Ebooks To Read in 2020 - BookAuthority PDFDocument35 pages35 Best New Big Data Ebooks To Read in 2020 - BookAuthority PDFPradyumna GRNo ratings yet
- Presentation SkillsDocument18 pagesPresentation SkillsОксана СеникNo ratings yet
- The Intelligent Investor in An Era of Autonomous LearningDocument15 pagesThe Intelligent Investor in An Era of Autonomous LearningsmysonaNo ratings yet
- Gossip Protocol Introduction - HTMLDocument4 pagesGossip Protocol Introduction - HTMLnewbieputrab13No ratings yet
- w1 - Introduction To MLDocument41 pagesw1 - Introduction To MLSwastik SindhaniNo ratings yet
- Topic Modeling With BERT. - Towards Data ScienceDocument9 pagesTopic Modeling With BERT. - Towards Data ScienceRubi ZimmermanNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocument30 pagesStatistics For Data ScienceArminSayadiNo ratings yet
- OLAP CubeDocument4 pagesOLAP CubeKhalid SalehNo ratings yet
- Functionality: Star Schema Snowflake Schema Relational Database Fact Table Dimension TablesDocument4 pagesFunctionality: Star Schema Snowflake Schema Relational Database Fact Table Dimension TablessakkudocNo ratings yet
- Data Mining New Notes Unit 2 PDFDocument15 pagesData Mining New Notes Unit 2 PDFnaman gujarathiNo ratings yet
- DM Mod2Document42 pagesDM Mod2Srushti PSNo ratings yet
- DM104 - Evaluation of Business PerformanceDocument15 pagesDM104 - Evaluation of Business PerformanceJaysan Ray Ngujo CheeNo ratings yet
- DMDW 2nd ModuleDocument29 pagesDMDW 2nd ModuleKavya GowdaNo ratings yet
- S-OLAP: An OLAP System For Analyzing Sequence DataDocument3 pagesS-OLAP: An OLAP System For Analyzing Sequence Dataaddmaths07No ratings yet
- Typical OLAP Operation DWDMDocument5 pagesTypical OLAP Operation DWDMCHIRAGNo ratings yet
- Manipulating OLAP Cubes: Advanced Techniques For SAS Programmers Rupinder Dhillon, Dhillon Consulting Inc. Harry Droogendyk, Stratia Consulting IncDocument24 pagesManipulating OLAP Cubes: Advanced Techniques For SAS Programmers Rupinder Dhillon, Dhillon Consulting Inc. Harry Droogendyk, Stratia Consulting IncJonathanNo ratings yet
- DM Mod2 PDFDocument41 pagesDM Mod2 PDFnNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Olap in SQL Server 2005 PDFDocument4 pagesAn Introduction To Olap in SQL Server 2005 PDFUmberto AlcarazNo ratings yet
- DWH OlapDocument6 pagesDWH OlapJanmejay PantNo ratings yet
- DWM Unit-III NotesDocument10 pagesDWM Unit-III NotesAnkita PawarNo ratings yet
- Olap (Online Analytical Processing)Document8 pagesOlap (Online Analytical Processing)Ak creations akNo ratings yet
- Building OLAP Cubes5Document20 pagesBuilding OLAP Cubes5Hemanta Kumar DashNo ratings yet
- 2.5 - OLAP - Charac - OPerations - Advantages - Hybper CubesDocument10 pages2.5 - OLAP - Charac - OPerations - Advantages - Hybper CubesSakshi UjjlayanNo ratings yet
- Crearea Unui Cub de Date Cu SQL Server2005Document8 pagesCrearea Unui Cub de Date Cu SQL Server2005Talida TalidaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document34 pagesUnit 2MananNo ratings yet
- CH 4 DWDMDocument15 pagesCH 4 DWDMuttamraoNo ratings yet
- DM and DW Notes-Module2Document18 pagesDM and DW Notes-Module2SonuNo ratings yet
- Online Analytical ProcessingDocument17 pagesOnline Analytical ProcessingShudodhaniNo ratings yet
- DM DW Module2Document148 pagesDM DW Module22BL20IS038 Pooja SulakheNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Data Cube TechnologyDocument6 pagesUnit - 3 Data Cube TechnologyBinay YadavNo ratings yet
- DWM Mod 1Document17 pagesDWM Mod 1Janvi WaghmodeNo ratings yet
- Rajkiya Engineering College Kannauj: Datawarehousing & Data Mining Lab (RCS-654)Document28 pagesRajkiya Engineering College Kannauj: Datawarehousing & Data Mining Lab (RCS-654)sumitNo ratings yet
- OLAPDocument6 pagesOLAPanashussainNo ratings yet
- Online Analytical ProcessingDocument12 pagesOnline Analytical Processingbimam brefNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Warehouse?: Data Mining by IK Unit 2Document21 pagesWhat Is Data Warehouse?: Data Mining by IK Unit 2Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Exp5 2866Document2 pagesExp5 2866officialaniket1108No ratings yet
- Online Analytical ProcessingDocument24 pagesOnline Analytical ProcessingPrachi PatelNo ratings yet
- Snowflake Schema: The Snowflake Schema Is An Extension of Star Schema. in A SnowflakeDocument4 pagesSnowflake Schema: The Snowflake Schema Is An Extension of Star Schema. in A SnowflakeDeepu GoraiNo ratings yet
- Online Analytical Processing (OLAP)Document34 pagesOnline Analytical Processing (OLAP)Suresh KaliyaperumalNo ratings yet
- Data WareHouse Previous Year Question PaperDocument10 pagesData WareHouse Previous Year Question PaperMadhusudan Das100% (1)
- Unit 2 - Data Mining - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument14 pagesUnit 2 - Data Mining - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inBhagwan BharoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DatawarehouseDocument47 pagesChapter 1 Datawarehouselogeswarisaravanan100% (1)
- Batch B DWM ExperimentsDocument90 pagesBatch B DWM ExperimentsAtharva NalawadeNo ratings yet
- Questions On OLAP ServicesDocument11 pagesQuestions On OLAP ServicesppavandsNo ratings yet
- DWDM 1-2Document17 pagesDWDM 1-2kamleshNo ratings yet
- 2.data Warehouse and OLAPDocument14 pages2.data Warehouse and OLAPBibek NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Data CubeDocument5 pagesData Cubekaka_huzefaNo ratings yet
- On-Line Analytical Processing For Business Intelligence Using 3-D ArchitectureDocument3 pagesOn-Line Analytical Processing For Business Intelligence Using 3-D ArchitectureIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNo ratings yet
- It Audit Report For It CompaniesDocument6 pagesIt Audit Report For It CompaniesDaniel BarbourNo ratings yet
- Changing Role of Librarians in Digital Library EraDocument7 pagesChanging Role of Librarians in Digital Library EraShivakumar TcNo ratings yet
- Google Ads Fundamentals Assessment Answers 2019Document38 pagesGoogle Ads Fundamentals Assessment Answers 2019Lukacs Mark-ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Dilger Lustre HPCS May WorkshopDocument45 pagesDilger Lustre HPCS May WorkshopSebastian GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Administre Seu Dinheiro de Forma ConscienteDocument17 pagesAdministre Seu Dinheiro de Forma ConscienteMaxiwendelNo ratings yet
- The Abcs of ErpDocument17 pagesThe Abcs of ErppohilabandhuNo ratings yet
- Subnetting GuruDocument1 pageSubnetting GuruSimran ThapaNo ratings yet
- Sarscape For EnviDocument44 pagesSarscape For EnviMaria DiamantopoulouNo ratings yet
- Sfswmso13 Part 03Document156 pagesSfswmso13 Part 03Gustavo Tromper Trimpis100% (1)
- Hardy Cross Method CompleteDocument25 pagesHardy Cross Method CompleteIlu SinghNo ratings yet
- Excel Macro TrainingDocument21 pagesExcel Macro Trainingapi-373800783% (6)
- Taxonomy of BugsDocument11 pagesTaxonomy of BugsrmvigneshmuraliNo ratings yet
- Data:: Using Predefined TypesDocument2 pagesData:: Using Predefined TypesvikasbumcaNo ratings yet
- SMM Project Report - Group 3Document33 pagesSMM Project Report - Group 3Akarsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - HCI IntroDocument32 pagesLecture 1 - HCI IntroSulaman AhmadNo ratings yet
- C++ ProgrammingDocument241 pagesC++ ProgrammingsoundarpandiyanNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Workforce Timekeeper A Guide For ManagersDocument56 pagesGetting Started With Workforce Timekeeper A Guide For ManagerscswigerNo ratings yet
- HARVARD Referencing Made EasyDocument1 pageHARVARD Referencing Made EasyMediaMassageNo ratings yet
- Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI API) - enDocument76 pagesJava Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI API) - enAugustin LucaNo ratings yet
- UCCNC UsersmanualDocument80 pagesUCCNC UsersmanualcristinaNo ratings yet
- Maple LabsDocument19 pagesMaple LabsvignanarajNo ratings yet
- List of ForumsDocument99 pagesList of Forumseuro198100% (2)
- Smartphone Addiction TestDocument2 pagesSmartphone Addiction TestRizky novita100% (3)
- MSX Computing - Dec 1986-Jan 1987Document68 pagesMSX Computing - Dec 1986-Jan 1987Buleste100% (1)
- KUKA Datenblatt FlexFELLOW enDocument2 pagesKUKA Datenblatt FlexFELLOW enMarincean MihaiNo ratings yet
- SAP SD Down Payment RequestDocument4 pagesSAP SD Down Payment RequestSukanta BrahmaNo ratings yet
- Magic Quadrant For Project and Portfolio Management: Strategic Planning AssumptionsDocument37 pagesMagic Quadrant For Project and Portfolio Management: Strategic Planning AssumptionsHashim SmithNo ratings yet
- Courier Delivery ExectiveDocument3 pagesCourier Delivery ExectiveKarthikeyan TNo ratings yet
- Selenium AutomationDocument58 pagesSelenium AutomationJiji Abhilash100% (1)