Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Documents Posters Encryption Plotter
Uploaded by
James HeathCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Documents Posters Encryption Plotter
Uploaded by
James HeathCopyright:
Available Formats
Wi-Fi
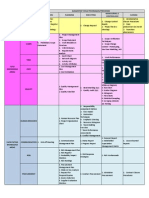
REFERENCE
Update DEMYSTIFIED
Wi-Fi ENCRYPTION
TM
SERIES
STANDARDS
ENCRYPTION PROTOCOLS
Wireless LAN security standards are defined by the IEEE within the 802.11 family. The commercial implementations are specified and
certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Wi-Fi Alliance
Encryption
Protocol
Encryption
Algorithm
Key
Management
Master
Key
Initialization
Vector
Encryption
Key
Data
Integrity Key
Data
Integrity
Relative Security
Strength (1-10 scale)
CCMP
AES
Yes
256 bits
(PMK)
48 bits
128 bits
(TK)
128 bits
(TK)
CBC-MAC,
including header
10
TKIP
RC4
Yes
256 bits
(PMK)
48 bits
128 bits
(TK)
64 bits
(TMK)
Michael,
including header
WEP
RC4
No
40 bits
(WEP-40)
24 bits
64 bits
None
CRC32,
no header
RC4
No
104 bits
(WEP-104)
24 bits
128 bits
None
CRC32,
no header
Certification
Encryption
Protocol
WPA2 Enterprise
2004
CCMP or TKIP 802.1X w/ EAP
WPA2 Personal
2004
CCMP or TKIP Pre-shared Key
Authentication
WPA Enterprise
2003
TKIP or CCMP 802.1X w/ EAP
WPA Personal
2003
TKIP or CCMP Pre-shared Key
802.11a/b/g
with WEP
2000
WEP
Standard
Ratified
Clause
Encryption
Protocol
802.11i
2004
8.3.3
CCMP
8.3.2
TKIP
802.1X w/ EAP
Pre-shared Key
Shared Key
802.11
1997
8.2
WEP
Shared Key
Open System
Round
Key 1
AES Round 1
Key
Schedule
IV
Plain Text
Add
Round
Key
Cipher Text
Data is encrypted in large blocks at once
Output Data
Encryption keystream varies one byte to the next
Multiple rounds operate on 44 byte arrays of data. Each round consists of:
Sub Bytes each byte is replaced with another per a lookup table
Shift Rows each row is shifted cyclically a certain number of steps
Mix Columns combines each column using a transformation
Add Round Key each byte is XORed with a subkey
Key is used to create a 256-bit state table
RC4 algorithm generates pseudo-random
keystream
KeyId
TK
2 bits
128 bits
Key
Confirmation
Key (KCK)
Key
Encryption
Key (KEK)
Temporal
Key
(TK)
128 bits
128 bits
128 bits
AAD Data
IV (TSC)
TK
48 bits
128 bits
64 bits
64 bits
IV
WEP Key
24 bits
64 bits
MIC
Michael = MIC
computation algorithm
Keystream
PN1 Rsvd
IV
Ext IV
MIC
Cipher Text
ICV
FCS
TSC1 WEP TSC0
Seed
Rsvd
Ext Key
IV ID
PN2
PN3
PN4
PN5
bits
PN = Packet Number, the Initialization Vector
(IV) for CCMP. The PN is monotonically
incremented per packet. PN5 is the most
significant octet.
Rsvd = reserved bits, set to 0
Ext IV (1 bit) = indicates 8 byte
CCMP header, always set to 1
Key ID (2 bits) = index that
identifies specific key value used
MIC = Message Integrity Code
P8.v5 2011 Xirrus. All Rights Reserved. Wi-Fi is a trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Rsvd
Ext Key
IV ID
MAC
Header
30 bytes
IV
Cipher Text
ICV
Pad
Ext IV (1 bit) = 1 indicates 4 byte
Extended IV follows, 0 not
Key ID (2 bits) = index that
identifies specific key value used
MIC = Message Integrity Code
ICV = Integrity Check Value
FCS
bytes
TSC2 TSC3 TSC4 TSC5
bits
TSC = TKIP Sequence Counter, the Initialization
Vector (IV) for TKIP. The TSC is monotonically
incremented per packet. TSC5 is the most
significant octet.
WEP Seed = (TSC1 | 0x20) & 0x7f
Rsvd (5 bits) = reserved bits, set to 0
CRC-32 = 32-bit Cyclic
Redundancy Check
|| = Concatenation
function
FCS
bytes
MIC
bytes
PN0
||
XOR
MAC
Header
128 bits
TKIP Only
Station (Supplicant)
IEEE 802.1X Controlled
Port Unblocked
Authenticator
PTK is Known,
Generate GTK
Message 1: GTK, MIC
Install PTK
4-way handshakea key management protocol
defined by 802.11i and based on 802.1X. It
operates between an AP (authenticator) and
station (supplicant) to generate, exchange, and
refresh encryption and data integrity keys.
802.1XIEEE standard for authentication that
uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol
(EAP).
802.11iIEEE standard ratified in 2004 that
defines a security architecture for wireless LANs.
It incorporates both authentication and
encryption methods.
ICV
RC4 Algorithm
WEP Encapsulation
30 bytes
Cipher Text
|| CRC-32
Seed
TK = Temporal Key
MIC
CCMP
Header
Plain Text
40 or 104 bits
||
CBC-MAC
CCM Encryption
Install PTK & GTK
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is the wireless LAN security
protocol defined by the IEEE with the original 802.11 standard
in 1997. It has since been proven insecure and replaced with
802.11i (WPA2/WPA).
Michael
RC4 Key
CCM = Counter Mode
with CBC-MAC
Group Integrity Key (GIK)
128 bits
Message 4: ACK, MIC
DA, SA,
Priority
Data
Key Mixing
CBC-MAC = Cipher Block
Chaining with Message
Authentication Code
Group Encryption Key (GEK)
Install GTK
Message 2: MIC
KEK used to encrypt GTK
KCK used to authenticate message to compute MIC
GLOSSARY
IV
MIC Key
Plain Text MSDU
SA
Nonce = Non-reusable
value across all time
Construct
Nonce
Temporal Rx
MIC Key (TMK2)
WEP
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) is an encryption protocol defined by 802.11i
and certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance as part of WPA. It was designed to allow existing
hardware systems supporting WEP to be upgraded to improve security with larger
keys, dynamic keys, and different encryption and integrity keys.
AAD = Additional
Authentication Data
Increment
Temporal Tx
MIC Key (TMK1)
Key stream XORed into data stream to
encrypt the data
Plain Text MPDU
Group Temporal Key (GTK) 128 bits CCMP, 256 bits TKIP
PTK is Known
KEK used to encrypt GTK
KCK used to authenticate messages to compute MIC
TKIP (WPA)
SA,
Priority
Message 3: GTK, MIC
TKIP Only
A xed, unvarying transformation is used for encryption
48 bits
Derive PTK.
If needed,
Generate GTK
Pairwise Transient Key (PTK)
384 bits CCMP, 512 bits TKIP
Bytes are encrypted sequentially, one at a time
IV (PN)
Group Key Hierarchy describes the temporal keys derived from a randomly generated
master (GMK) for use in multicast communications with CCMP and TKIP as defined by 802.11i.
This key set is unique per group of users in a multicast group per BSSID.
Group Handshake is a two-way handshake as defined by 802.11i used to refresh the
GTK when a device leaves the network or a preset time expires.
Message 2: SNonce, MIC
Cipher Text
CCMP (CTR with CBC-MAC) is the preferred standard encryption protocol defined
by 802.11i and certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance as part of WPA2.
PMK is Known
Generate ANonce
Derive PTK
256 bits
XOR
CCMP (WPA2)
RADIUS Key Distribution
Data Confidentiality and Integrity
Authenticator
PMK is Known
Generate SNonce
256 bits
IV = Initialization Vector
XOR = Exclusive OR Function
Key Management
Message 1: ANonce
Construct CCMP
Header
or
Station (Supplicant)
Pairwise Master Key (PMK)
AES Round 10
Phase 3
Group Master Key (GMK) 256 bits
Dynamic
802.1X/EAP Key
from RADIUS Server
256 bits
XOR
Mix Columns
802.1X Authentication
Phase 2
4-Way Handshake is used to generate, exchange, and refresh keys for
encryption and integrity as defined by 802.11i.
Keystream
Shift Rows
Security Discovery/Negotiation
Master Key (MK)
Key
RC4 Algorithm
........
Round
Key 10
Pairwise Key Hierarchy describes the temporal keys derived from a master by the
4-Way Handshake protocol. These keys are used in unicast communications by CCMP
and TKIP as defined by 802.11i. This key set is unique per station.
Static
Pre-Shared
Key (PSK)
Sub Bytes
AES Round 2
Phase 1
KEY MANAGEMENT
RC4 (Rivest Cipher 4) is a stream cipher developed
by RSA Security. The encryption process is shown
belowthe decryption process is largely symmetric.
General Round
Input Data
Authentication
Server
Authenticator
Phase 4
RC4 ENCRYPTION
Plain Text
Text
Plain
Station
Open System
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is a block cipher encryption standard
defined by Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) PUB 197. The
encryption process is shown belowthe decryption process is largely symmetric.
Key
Authentication
802.1X w/ EAP
Pre-shared Key
AES ENCRYPTION
30 bytes
802.11i is the official security standard for 802.11 wireless LANs as ratified by the IEEE in 2004. Its operation consists
of 4 primary phases to establish secure communications. Phase 4 and a portion of Phase 3 are addressed in this poster;
Phase 2 and portion of Phase 3 are addressed in the companion Wi-Fi Authentication poster.
IEEE
First
Certified
MAC
Header
802.11i
Key
ID
bits
IV = Initialization Vector, random generated
Pad = 6 bits, all zeros
Key ID = 2 bits, identifies 1 of 4 secret key values
ICV = Integrity Check Value
FCS = Frame Check Sequence
+805.262.1600 800.947.7871 posters@xirrus.com www.xirrus.com
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)a
block cipher encryption standard defined by
Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS)
PUB 197.
CBC-MAC (Cipher Block Chaining with
Message Authentication Code)algorithm
used by CCMP to calculate the MIC for data
origin authenticity.
CCM (CTR with CBC-MAC)encryption
mechanism defined by RFC 3610 and used by
802.11i for data confidentiality using CTR and
data integrity using CBC-MAC.
CCMP (CCM Protocol)encryption protocol
defined by IEEE 802.11i and certified by the
Wi-Fi Alliance in WPA2.
CTR (Counter Mode)the block cipher mode
used in conjunction with AES in 802.11i to
provide data confidentiality.
PSK (Pre-shared Key)a static encryption key
shared between and common to both the AP
and client.
Group Handshakea key management
protocol defined by 802.11i and using the
802.1X protocol to refresh group (multicast)
keys.
RC4 (Rivest Cipher 4)a stream cipher
developed by RSA Security.
IV (Initialization Vector)data combined with
an encryption key to produce a unique
keystream.
RSN (Robust Security Network)the
architecture for secure wireless networks
defined by 802.11i, including TKIP and CCMP
but not WEP.
MIC (Message Integrity Code)a value
generated by cryptographic means and used to
protect data from undetected alteration.
Michaelthe algorithm used by TKIP to
generate the MIC.
MPDU (MAC Protocol Data Unit)single
packet of data after fragmentation.
MSDU (MAC Service Data Unit)single packet
of data before fragmentation.
passphrasea sequence of 8-63 characters
shared between the AP and client to control
access to a Wi-Fi network. It is used to derive
the pre-shared key (PSK) in WPA/WPA2.
Rijndael Algorithmthe encryption algorithm
used by AES encryption.
TKIP (Temporal Key Exchange Protocol)an
encryption protocol defined by IEEE 802.11i as
an enhancement to WEP with larger keys,
dynamic keys, and different encryption and
integrity keys.
WEP (Wired Equivalency Protocol)the
original encryption protocol defined by IEEE
802.11 for wireless LANs.
WPA (Wireless Protected Access)the Wi-Fi
Alliance certification of 802.11i that uses TKIP
encryption.
WPA2 (Wireless Protected Access 2)the
Wi-Fi Alliance certification of 802.11i that uses
CCMP/AES encryption.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- S03 P3 Vikas KumarDocument6 pagesS03 P3 Vikas KumarJames HeathNo ratings yet
- WPA2Document6 pagesWPA2James HeathNo ratings yet
- PRMGT-Assignment Requirements Sheet1Document1 pagePRMGT-Assignment Requirements Sheet1James HeathNo ratings yet
- Guide To Computer Forensics and Investigations, Second EditionDocument16 pagesGuide To Computer Forensics and Investigations, Second Editionsilly_rabbitzNo ratings yet
- WLAN Security Today-Siemens Whitepaper - ENDocument18 pagesWLAN Security Today-Siemens Whitepaper - ENJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Key Elements of Total Quality ManagementDocument12 pagesDiscuss The Key Elements of Total Quality Managementdogar153100% (1)
- 71663Document89 pages71663keruksNo ratings yet
- SMS Analysis On GSMDocument5 pagesSMS Analysis On GSMdsidhu100% (5)
- LTA Paper PDFDocument8 pagesLTA Paper PDFWatchrara BoonyodNo ratings yet
- LTE Future of WirelessDocument12 pagesLTE Future of Wirelessjbond07No ratings yet
- Security Measures For VoIP Application A State of The Art PreviewDocument10 pagesSecurity Measures For VoIP Application A State of The Art PreviewJames HeathNo ratings yet
- II - CountingDocument4 pagesII - CountingJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Wireless Communication NetworksDocument5 pagesEvolution of Mobile Wireless Communication NetworksFarhan Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile Wireless CommunicationDocument7 pagesEvolution of Mobile Wireless CommunicationJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Mobile BankingDocument10 pagesMobile BankingNikunj PatelNo ratings yet
- Effective Implementation of Vlan and Acl inDocument7 pagesEffective Implementation of Vlan and Acl inJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Les Dernières Tendances en Matière de PiratageDocument52 pagesLes Dernières Tendances en Matière de PiratagenouvelobsNo ratings yet
- HSSN Tutorials & AnswersDocument22 pagesHSSN Tutorials & AnswersJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Comparison 2 Linux SCHDocument89 pagesComparison 2 Linux SCHJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Mobile Banking Technology Options (2007)Document53 pagesMobile Banking Technology Options (2007)Syed Farrukh HussainNo ratings yet
- X-Lite 4 Windows User Guide R5Document66 pagesX-Lite 4 Windows User Guide R5James HeathNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementDocument40 pagesChapter 12 Project Procurement ManagementMohamed El ArabiNo ratings yet
- V2I8201320Document7 pagesV2I8201320James HeathNo ratings yet
- X-Lite 4 Windows User Guide R5Document66 pagesX-Lite 4 Windows User Guide R5James HeathNo ratings yet
- WWAN SecurityDocument9 pagesWWAN SecurityAndaru FareraNo ratings yet
- X-Lite 4 Windows User Guide R5Document66 pagesX-Lite 4 Windows User Guide R5James HeathNo ratings yet
- Wi MAXDocument4 pagesWi MAXJames HeathNo ratings yet
- WLAN Enterprise Security WP 00Document8 pagesWLAN Enterprise Security WP 00Prudhvi KumarNo ratings yet
- Virtual LAN: Applications and TechnologyDocument7 pagesVirtual LAN: Applications and TechnologyJames HeathNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Job Search & Interview Skills: or Some Real-World Advice That May Prove Useful To YouDocument97 pagesJob Search & Interview Skills: or Some Real-World Advice That May Prove Useful To YouShah NawazNo ratings yet
- Maxiim Vehicle Diagnostic ReportDocument3 pagesMaxiim Vehicle Diagnostic ReportCarlos Cobaleda GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Euroleague Basketball: Change Pays Off ForDocument36 pagesEuroleague Basketball: Change Pays Off ForNikos TagalnikNo ratings yet
- PiraeusDocument9 pagesPiraeusBen JamesNo ratings yet
- Gaps, Pro Versus NoviceDocument2 pagesGaps, Pro Versus Novicertkiyous2947No ratings yet
- Unit 5 PythonDocument10 pagesUnit 5 PythonVikas PareekNo ratings yet
- Ngo OrganizationsDocument2 pagesNgo Organizationsapi-295384272100% (1)
- Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications of Regula Falsi MethodDocument12 pagesAdvantages, Disadvantages and Applications of Regula Falsi MethodMd Nahid HasanNo ratings yet
- JSSG-2010-7 - Crash Systems Handbook PDFDocument155 pagesJSSG-2010-7 - Crash Systems Handbook PDFdaymonNo ratings yet
- ACLU Letter of ConcernDocument5 pagesACLU Letter of ConcernRyan FinnertyNo ratings yet
- Create New Project CodeVision AVR (LED)Document5 pagesCreate New Project CodeVision AVR (LED)calvinNo ratings yet
- in Re Irava Bottle ShopDocument10 pagesin Re Irava Bottle ShopCYMON KAYLE LubangcoNo ratings yet
- Krishna Yadav Cell#+91-9540308010: BjectiveDocument6 pagesKrishna Yadav Cell#+91-9540308010: BjectiveIssac JohnNo ratings yet
- File 1379580604 PDFDocument9 pagesFile 1379580604 PDFMuhammad Salik TaimuriNo ratings yet
- 17 0000362296Document1 page17 0000362296Ekansh BarsiwalNo ratings yet
- Secondary Laboratory Proposal OnlyDocument5 pagesSecondary Laboratory Proposal Onlylaboratory.databaseNo ratings yet
- Assessment Task 1: Written Questions 1. Identify and Describe Five Common Components of A Business PlanDocument6 pagesAssessment Task 1: Written Questions 1. Identify and Describe Five Common Components of A Business PlanJoanne Navarro AlmeriaNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Flash CardsDocument48 pagesCivil Procedure Flash CardsNick Ashjian100% (1)
- Elite 08Document96 pagesElite 08Razza WilliNo ratings yet
- ION 900 Series Owners ManualDocument24 pagesION 900 Series Owners ManualParosanu IonelNo ratings yet
- Reading #11Document2 pagesReading #11Yojana Vanessa Romero67% (3)
- 4-Sided Planer & Moulder Operation Manual: For Spares and Service ContactDocument48 pages4-Sided Planer & Moulder Operation Manual: For Spares and Service ContactAlfred TsuiNo ratings yet
- NDT Technician TrainingDocument6 pagesNDT Technician TraininglarsonndeservicesNo ratings yet
- Dahua Network Speed Dome & PTZ Camera Web3.0 Operation ManualDocument164 pagesDahua Network Speed Dome & PTZ Camera Web3.0 Operation ManualNiksayNo ratings yet
- 2022 Significant FEHB Plan ChangesDocument12 pages2022 Significant FEHB Plan ChangesFedSmith Inc.No ratings yet
- ZIOIEXCELDocument4 pagesZIOIEXCELSunil GNo ratings yet
- Aquamimicry: A Revolutionary Concept For Shrimp FarmingDocument5 pagesAquamimicry: A Revolutionary Concept For Shrimp FarmingMarhaendra UtamaNo ratings yet
- Modern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesDocument10 pagesModern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesCristina AronNo ratings yet
- STB9NK60Z, STP9NK60Z, STP9NK60ZFPDocument19 pagesSTB9NK60Z, STP9NK60Z, STP9NK60ZFPyokonakagimaNo ratings yet
- Topic: Matrix Addition and SubtractionDocument6 pagesTopic: Matrix Addition and SubtractionAnonyNo ratings yet