Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Natural State Acceleration Theory
Uploaded by
rach31Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Natural State Acceleration Theory
Uploaded by
rach31Copyright:
Available Formats
10/4/11
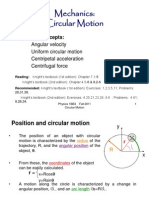
Our natural state in transla'on
Accelera'on
Theory
Lesson
1
part
1
Our natural state in rota'on
transla'onal
iner'a
is
resistance
to
change
in
movement
Change in mo'on is accelera'on
No accelera'on
(Equilibrium)
Rota'onal
iner'a
is
resistance
to
change
in
rota'on
Acceleration
10/4/11
Transla'onal accelera'on caused by net force
Rota'onal accelera'on caused by net moment
No net torque
No net force
Net force = 7 N (right)
Net
torque
=
3
2
=
6
N
m
(clockwise)
4N
3N
3N
3N
10 N
2 cm 1.5 cm
rectangles
3N
3N
3N
3N
Increase in rightward speed
Increase
in
clockwise
Rota'on
4N
NET* = INERTIA ACCELERATION
Transla'onal:
Fnet
=
m
a
Rota'onal:
Mnet
=
I
Chkpt 1a: Transla'onal iner'a
Which one has greater iner'a?
A: 10 Pound bowling ball at rest.
B: 10 Pound bowling ball at high speed.
C: Same
15
10/4/11
Chkpt 1b: Rota'onal iner'a
Chkpt 1c: Iden'fying valid conclusions
1. object experiences transla'on accelera'on
2. object experience rota'on accelera'on
3. a net force acts in direc'on of mo'on
4. a net moment cause object to turn
Which one has greater rota'onal iner'a?
A: Rotating pen at centre.
B: Rotating pen at tip.
C: Same.
16
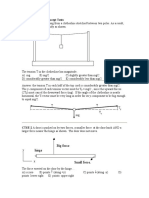
Chkpt 1d: Is the object accelera'ng?
Chkpt 1e: Predict next posi'on if ini'ally at rest
object moves in circle constant speed
C.G.
10/4/11
Chkpt 1f: Predict next posi'on if ini'ally at rest
Chkpt 1g: Iden'fy if object is in equilibrium
F2
C.G.
Fill in the blanks
with YES or NO.
F1
21
Drag force, D is experienced when there is
rela've movement of object and uid it is in
Drag
force,
D
D
Theory
Lesson
1
part
2
Direction of drag oppose motion
(most of the time)
10/4/11
Drag, D increases as
cross sectional area increases
Velocity
of
object
Velocity of object
Shape of object aects magnitude of D
D increases as velocity increases
Velocity of object
Velocity of object
Drag, D of a plane is at an angle
D
Increasing D for the same cross sec'onal
area and velocity
Velocity of objects
N3L:
air pushed to the right
plane pushed to the left
Velocity of object
10/4/11
Chkpt 2a: Rank D in increasing order
A:
spherical object of mass 2 kg, diameter 10 cm, falling at 0.7 m s1
Chkpt 2b: Direc'on of FNET
Object is thrown in air.
At a particular instant it moves at 45
B:
spherical
object
of
mass
5
kg,
diameter
10
cm,
falling
at
0.3
m
s1
C:
spherical
object
of
mass
2
kg,
diameter
5
cm,
falling
at
0.3
m
s1
E
B
Theory Lesson 1 Summary of main ideas
Chkpt 2c: Predict falling mo'on of this object
-
-
-
-
Greater iner'a means harder to change
Accelera'on is change
Transla'onal accelera'on caused by net force
Rota'onal accelera'on caused by net torque
- Drag force occurs if there is rela've mo'on between object
and uid
- Drag force direc'on depends on shape of object, usually has a
dominant component is direc'on opposing mo'on
You might also like
- Physics Chapter 12Document20 pagesPhysics Chapter 12praveen181274No ratings yet
- Physics Circular Motion and Centripetal Acceleration Study Material For Cbse BoardDocument20 pagesPhysics Circular Motion and Centripetal Acceleration Study Material For Cbse BoardscribdvivekbhutaniNo ratings yet
- G9, 1.3 Forces and MovementDocument5 pagesG9, 1.3 Forces and MovementKinmokusei MyoeNo ratings yet
- SPM PhysicsDocument21 pagesSPM PhysicsWoody Cys100% (2)
- Chapter - 5 - Applying Newton's Laws of Motion - R K ParidaDocument12 pagesChapter - 5 - Applying Newton's Laws of Motion - R K Paridaraunakrathor2005No ratings yet
- Circular Motion ExplainedDocument40 pagesCircular Motion ExplainedAli KasimNo ratings yet
- Educator 101Document12 pagesEducator 101Mary ChildNo ratings yet
- General Physics NotesDocument10 pagesGeneral Physics NotesMino1996No ratings yet
- Lecture 9Document32 pagesLecture 9HamzahNo ratings yet
- General Physics: Name: SectionDocument5 pagesGeneral Physics: Name: Sectionanjero hortelanoNo ratings yet
- Centripetal ForceDocument15 pagesCentripetal ForcePrincess SabinoNo ratings yet
- Higher Unit 1Document35 pagesHigher Unit 1alexgibson93No ratings yet
- Physics 1Document6 pagesPhysics 1garduqueerichgabriel.mendelNo ratings yet
- 1.4 BiodynamicsDocument34 pages1.4 BiodynamicsFartLord1No ratings yet
- Mastering Physics - Newton's Second Law LabDocument9 pagesMastering Physics - Newton's Second Law LabpalparasNo ratings yet
- "View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter MenuDocument96 pages"View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter Menugatortd8to10No ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Physics Circular Motion and Gravitational AttractionDocument19 pagesCIE IGCSE Physics Circular Motion and Gravitational Attractionyousaf KhanNo ratings yet
- "View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter MenuDocument96 pages"View" "Slide Show.": Resources Chapter Menuclarice_anneNo ratings yet
- DLS 212Document16 pagesDLS 212WILBERT QUINTUANo ratings yet
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDocument8 pagesGce o Level Physics MatterBakhita Maryam100% (1)
- Concept Summary: Batesville High School PhysicsDocument20 pagesConcept Summary: Batesville High School PhysicssbdmanNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument10 pagesPhysics ReviewerIGNACIO, Nemiel (3B)No ratings yet
- Phy 01 01 PresentDocument33 pagesPhy 01 01 PresentclemesgNo ratings yet
- Physics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes: by Samuel Lees and Adrian GuillotDocument41 pagesPhysics Igcse 2012 Exam Revision Notes: by Samuel Lees and Adrian Guillotnadia sykesNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Newton's Second Law of MotionDocument35 pagesCH 5 Newton's Second Law of MotionMalik Nazim ChannarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document34 pagesChapter 04benjaminblakkNo ratings yet
- 6 Further Mechanics StudentDocument30 pages6 Further Mechanics StudenthuzaNo ratings yet
- Reading Materials Rotational KinematicsDocument5 pagesReading Materials Rotational KinematicsYanda EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum & ImpulseDocument45 pagesLinear Momentum & Impulsetala al husseiniNo ratings yet
- Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityDocument47 pagesRotational Motion and The Law of Gravitymahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument8 pagesCircular MotionGreg Eleftheriou0% (1)
- Quick Revision For o Level PhysicsDocument33 pagesQuick Revision For o Level Physicsqwertymujtaba474No ratings yet
- Forces and Motion ExplainedDocument25 pagesForces and Motion ExplainedEbrahimNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Energy and MomentumDocument63 pagesGrade 10 Physics Energy and MomentumAmira SarzhanovaNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument17 pagesCircular MotionElaaf AnzarNo ratings yet
- NMAT 17 Crash Course Review - PhysicsDocument64 pagesNMAT 17 Crash Course Review - PhysicsMikaela Rome BigayNo ratings yet
- Q4 M1-9Science 9Document23 pagesQ4 M1-9Science 9Allen AlabaNo ratings yet
- Freely Falling BodiesDocument10 pagesFreely Falling BodiesarvinfaviaNo ratings yet
- Phy 101 Lecture Note 5Document10 pagesPhy 101 Lecture Note 5bukolaesan48No ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocument16 pagesDynamics of Rigid BodiesFernando Alcala Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- DLR-Fizik Konu AnlatımıDocument18 pagesDLR-Fizik Konu Anlatımıugurhan96No ratings yet
- Experiment 07: Momentum and CollisionsDocument32 pagesExperiment 07: Momentum and CollisionseviroyerNo ratings yet
- 09 Rotational MotionDocument10 pages09 Rotational MotionBalaram MullapudiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Rotational MotionDocument29 pagesLesson 6 - Rotational MotionJonathan VillapanaNo ratings yet
- Start-Up: Estimate Using Linear Approximation: Cos 62Document9 pagesStart-Up: Estimate Using Linear Approximation: Cos 62dietcoke093No ratings yet
- More Applications of Newton's LawsDocument40 pagesMore Applications of Newton's LawsTina NguyenNo ratings yet
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDocument9 pagesGce o Level Physics MatterirmaNo ratings yet
- Coffee Filter LabDocument2 pagesCoffee Filter LabEdward_Zhou_380050% (2)
- Angular MomentumDocument24 pagesAngular MomentumPepc MaNo ratings yet
- Momentum & CollisionsDocument40 pagesMomentum & CollisionsMona Mohamed SafwatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Rot Motion GravityDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Rot Motion Gravityjoe termNo ratings yet
- Projectile and Circulatory Motion NotesDocument6 pagesProjectile and Circulatory Motion NotesAditya MauriyaNo ratings yet
- Course Handout on Angular Momentum and the Spinning TopDocument15 pagesCourse Handout on Angular Momentum and the Spinning TopAtif ImamNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Revision NotesDocument34 pagesIGCSE Physics Revision NotesCoolman Poon88% (17)
- DLL - Science 9 - Q4Document32 pagesDLL - Science 9 - Q4Nazer M. LacaboNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Table of ContentsDocument154 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Table of Contentsgood17100% (3)
- z198 201Document4 pagesz198 201mikiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits and Magnetic Fields MCQDocument44 pagesElectrical Circuits and Magnetic Fields MCQdinesh kumarNo ratings yet
- 2017 HKDSE Physics Paper 1A SolDocument32 pages2017 HKDSE Physics Paper 1A SolAlex KongNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4.1Document5 pagesAssignment 4.1Khanur AysahNo ratings yet
- Experimental Skills AssignmentDocument18 pagesExperimental Skills AssignmentGayathri cnNo ratings yet
- ECE 476 Exam #1 Thursday, October 6, 2016: Name: - AnswersDocument8 pagesECE 476 Exam #1 Thursday, October 6, 2016: Name: - AnswersTaher JebreelNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Manual Tcm44-1249312Document8 pagesCompressed Air Manual Tcm44-1249312Osama Kamel ElghitanyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Questions MCqsDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Questions MCqsGoverdhan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- PDF Compiled DLDocument477 pagesPDF Compiled DLrickyNo ratings yet
- 30V P-Channel MOSFET SummaryDocument5 pages30V P-Channel MOSFET SummaryBsm GwapuNo ratings yet
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical Handbook: February 2022Document5 pagesSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical Handbook: February 2022Wolfy gacha elamparoNo ratings yet
- Trochoidal Wave TheoryDocument12 pagesTrochoidal Wave TheorycaptnathanNo ratings yet
- On The Definition of Propellant Force: SciencedirectDocument4 pagesOn The Definition of Propellant Force: SciencedirectMarcelo MartinezNo ratings yet
- AREVA The Testing of TransformerDocument49 pagesAREVA The Testing of TransformerOsman Ahmed100% (2)
- Compression Process CalculationsDocument2 pagesCompression Process CalculationsRahul ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Flow Through Notches & Bernoulli's Theorem LabDocument22 pagesFlow Through Notches & Bernoulli's Theorem LabGautam GunjanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/41minionhead1936No ratings yet
- Motion Graphs Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesMotion Graphs Lesson PlanEmmanuel RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Boyle'S Law Module 10Document12 pagesBoyle'S Law Module 10Greth NuevaNo ratings yet
- Static Equilibrium (Problems)Document5 pagesStatic Equilibrium (Problems)E-m FunaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Physical Quantities & Units PDFDocument53 pages1 - Physical Quantities & Units PDFMazinNo ratings yet
- Inductance Meter AdapterDocument3 pagesInductance Meter AdapterioanNo ratings yet
- Particle Kinematics Rect Motion 1Document10 pagesParticle Kinematics Rect Motion 1Dídimo GomesNo ratings yet
- Chap. 3: First Law of ThermodynamicsDocument33 pagesChap. 3: First Law of ThermodynamicsYeshan JuberiNo ratings yet
- 15EEE401 - II Ass - Aug 2018Document2 pages15EEE401 - II Ass - Aug 2018sriharshitha vegesnaNo ratings yet
- Review of Fundamental Vibration TheoryDocument34 pagesReview of Fundamental Vibration TheoryMohamed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Our Own High School, Al Warqa'A Grade: Xii E Worksheet - PhysicsDocument2 pagesOur Own High School, Al Warqa'A Grade: Xii E Worksheet - PhysicsAniruddha KadamNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Learning Activity Sheet (Week 3)Document2 pagesScience 8 Learning Activity Sheet (Week 3)Rosita CayananNo ratings yet