Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.6 Database
Uploaded by
Rana Hassan TariqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.6 Database
Uploaded by
Rana Hassan TariqCopyright:
Available Formats
PRACTICE EXAMINATION QUESTIONS ALKANES
Introduction to Organic Chemistry)
1.
(a)
(i)
Name the process used to separate petroleum into fractions.
.......................................................................................................................
(ii)
Give the molecular formula for an alkane with nine carbon atoms.
.......................................................................................................................
(iii)
Write an equation for the complete combustion of the alkane C11H24
.......................................................................................................................
(iv)
Write an equation for the incomplete combustion of C11H24 to produce carbon
and water only.
.......................................................................................................................
(4)
(b)
Alkenes can be produced by cracking the naphtha fraction obtained from petroleum.
(i)
Write an equation for the thermal cracking of one molecule of C10 H22 to give
one molecule of propene and one molecule of an alkane only.
.......................................................................................................................
(ii)
Draw the structure of the chain isomer of but-1-ene.
(2)
(c)
The alkanes and the alkenes are examples of homologous series of compounds.
One feature of an homologous series is the gradual change in physical properties
as the relative molecular mass increases. State two other general features of an
homologous series of compounds.
Feature 1 ....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
Feature 2 ....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
2.
The fractions obtained from petroleum contain saturated hydrocarbons that belong to the
homologous series of alkanes.
(a)
Any homologous series can be represented by a general formula.
(i)
State two other characteristics of homologous series.
Characteristic 1 ................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
Characteristic 2 .................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(ii)
Name the process which is used to obtain the fractions from petroleum.
............................................................................................................................
(iii)
State what is meant by the term saturated, as applied to hydrocarbons.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(4)
(b)
Decane has the molecular formula C10H22
(i)
State what is meant by the term molecular formula.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
Give the molecular formula of the alkane which contains 14 carbon atoms.
...........................................................................................................................
(iii)
Write an equation for the incomplete combustion of decane, C10H22, to produce
carbon and water only.
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
(c)
When petrol is burned in an internal combustion engine, some nitrogen monoxide, NO,
is formed. This pollutant is removed from the exhaust gases by means of a reaction in a
catalytic converter.
(i)
Write an equation for the reaction between nitrogen and oxygen to form nitrogen
monoxide.
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
Identify a catalyst used in a catalytic converter.
...........................................................................................................................
(iii)
Write an equation to show how nitrogen monoxide is removed from the exhaust
gases as they pass through a catalytic converter.
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 10 marks)
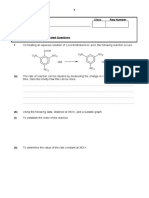
3.
(a)
Compound A (Mr = 215.8) contains 22.24% carbon, 3.71% hydrogen and 74.05% bromine
by mass. Show that the molecular formula of A is C4H8Br2.
(3)
(b)
There are nine structural isomers of molecular formula C4H8Br2, three of which have
branched carbon chains. Give the names and draw the graphical formulae for any two of
the branched chain isomers of C4H8Br2.
Name of isomer 1 .......................................................................................................
Graphical formula of isomer 1
Name of isomer 2 .......................................................................................................
Graphical formula of isomer 2
(4)
(Total 7 marks)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
4.
There are eight structural isomers with the molecular formula C5H11Br. Four of these are classed
as primary, three as secondary and one as tertiary. The graphical formula of one of the secondary
compounds, isomer A, is shown below.
CH 3 H
Br
isomer A
(a)
Give the name of isomer A.
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
Explain what is meant by the term structural isomers.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 4 marks)
5.
The table below gives some of the names and structures of isomers having the molecular formula
C4H9Br
Name
Structure
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br
CH3
H3C
CH3
2-bromo-2-methylpropane
Br
1-bromo-2-methylpropane
CH3CH2
CH
CH3
2-bromobutane
Br
Complete the table.
(Total 2 marks)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
6.
Petroleum is separated into fractions by fractional distillation.
The petrol fraction (C4 to C12) is burned in internal combustion engines and the naphtha
fraction (C7 to C14) is cracked.
(a)
Petroleum is separated into fractions when it is heated and the vapour mixture is passed into
a fractionating column.
(i)
Explain what is meant by the term fraction as applied to fractional distillation.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
State a property of the molecules in petroleum which allows the mixture to be
separated into fractions.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(iii)
Describe the temperature gradient in the column.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(b)
The fractions from petroleum contain alkane hydrocarbons.
(i)
Write an equation for the incomplete combustion of the alkane C8H18 to produce
carbon monoxide and water only.
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
One isomer of C8H18 is 2,2,3-trimethylpentane. Draw the structure of this isomer.
(2)
(c)
State one economic reason for the cracking of petroleum fractions.
.....................................................................................................................................
(1)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
(d)
Identify a catalyst used in catalytic cracking.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(e)
Identify the different type of hydrocarbon produced in a high percentage by the
thermal cracking of alkanes.
...........................................................................................................................
(1)
(Total 8 marks)
7.
Many hydrocarbon compounds burn readily in air.
(a)
Write an equation to show the complete combustion of C15H32
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(b)
One of the gaseous products of the incomplete combustion of methane in gas fires is known
to be poisonous. Identify this product and write an equation for the reaction in which it is
formed from methane.
Identity of product .......................................................................................................
Equation ......................................................................................................................
(Total 4 marks)
8.
(a)
Crude oil is separated into fractions by fractional distillation. Outline how different
fractions are obtained by this process.
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
(3)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
(b)
The table below gives details of the supply of, and demand for, some crude oil fractions.
Approximate %
Fractions
(i)
Typical supply
from crude oil
Global
demand
Gases
Petrol and naphtha
16
27
Kerosine
13
Gas oil
19
23
Fuel oil and bitumen
50
38
Use the data given above to explain why catalytic cracking of crude oil fractions is
commercially important.
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
......................................................................................................................
(ii)
Give the two main types of product obtained by catalytic cracking.
Type 1 ..........................................................................................................
Type 2 ..........................................................................................................
(4)
(c)
Name a catalyst used in catalytic cracking and outline the industrial conditions used in the
process.
Catalyst .................................................................................................................
Conditions .............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 10 marks)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
9.
(a)
The diagram below represents the industrial fractional distillation of crude oil.
gases
gasoline (petrol)
naphtha
A
gas oil (diesel)
mineral (lubricating) oil
crude oil
heater
residue
(i)
Identify fraction A.
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
What property of the fractions allows them to be separated in the column?
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
A gas oil fraction from the distillation of crude oil contains hydrocarbons in the C15 to C19
range. These hydrocarbons can be cracked by strong heating.
(i)
Write the molecular formula for the alkane with 19 carbon atoms.
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
Write an equation for one possible cracking reaction of the alkane C16H34 when the
products include ethene and propene in the molar ratio 2:1 and only one other
compound.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(Total 5 marks)
10.
Name the alkene CH3CH2CH=CH2
.....................................................................................................................................
(Total 1 mark)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
11.
The table below shows the fractions obtained from crude oil:
(a)
Name of fraction
Number of
carbon atoms
Use
Gases
1-4
bottled fuels for camping
Petrol (gasoline)
4-12
fuel for cars
Naphtha
7-14
11-15
jet fuel
Gas oil (diesel)
15-19
central heating fuel
Mineral oil
20-30
lubrication
Fuel oil
30-40
Wax
41-50
Candles
Bitumen
over 50
road surfacing
Complete the table above by writing in the empty boxes
(3)
(b)
Give one structural formula in each case for the following components of crude oil:
(i)
the isomer of C5H12 with the lowest boiling point
(ii)
a saturated compound with molecular formula C5H10
(2)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
(c)
Give a molecular formula for each of the following components of crude oil:
(i)
the alkane which, on cracking, forms, as the only products, two moles of ethene
and one mole of butane per mole of alkane.
...........................................................................................................................
(ii)
the straight chain alkane found in the petrol fraction which contains the lowest
percentage by mass of hydrogen. Refer to the table at the start of the question to
deduce your answer.
...........................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 7 marks)
12.
(a)
Central heating fuel is obtained by distillation of crude oil. An alkane present in central
heating fuel contains 16 carbon atoms per molecule. When a molecule of this alkane is
cracked, propene is formed.
(i)
Name the crude oil fraction used as central heating fuel.
............................................................................................................................
(ii)
Write an equation for the cracking of the 16-carbon alkane to form octane, propene
and ethene as the only products.
............................................................................................................................
(iii)
Give one important commercial use of propene.
............................................................................................................................
(4)
(b)
A catalytic converter in the exhaust system of a car contains a ceramic honeycomb covered
with a thin coating of the catalyst. When hot gases containing nitrogen monoxide and
unburnt octane are passed over the catalyst, they react to form nitrogen, carbon dioxide and
water.
(i)
Explain why the catalyst is coated on a honeycomb.
............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................
(ii)
Write an equation for the reaction of octane with nitrogen monoxide to form nitrogen,
carbon dioxide and water.
............................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 8 marks)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
10
13.
(a)
Gas oil (diesel), kerosine (paraffin), mineral oil (lubricating oil) and petrol (gasoline) are
four of the five fractions obtained by the fractional distillation of crude oil within the
temperature range 40400 C.
Identify the missing fraction and state the order in which the five fractions are removed as
the fractionating column is ascended. Give two reasons why the fractions collect at
different levels in the fractionating column.
(4)
(b)
Thermal cracking of large hydrocarbon molecules is used to produce alkenes. State the type
of mechanism involved in this process. Write an equation for the thermal cracking of
C21H44 in which ethene and propene are produced in a 3:2 molar ratio together with one
other product.
(3)
(c)
Write equations, where appropriate, to illustrate your answers to the questions below.
(i)
Explain why it is desirable that none of the sulphur-containing impurities naturally
found in crude oil are present in petroleum fractions.
(ii)
The pollutant gas NO is found in the exhaust gases from petrol engines. Explain why
NO is formed in petrol engines but is not readily formed when petrol burns in the
open air.
(iii)
The pollutant gas CO is also found in the exhaust gases from petrol engines. Explain
how CO and NO are removed from the exhaust gases and why the removal of each of
them is desirable.
(10)
(Total 17 marks)
14.
(a)
Petrol engines in cars produce a number of pollutants which can be removed by catalytic
converters.
Discuss this statement, indicating what the pollutants are, how they arise and how they are
removed as efficiently as possible in a catalytic converter. Write equations for any
reactions you discuss.
(11)
(b)
Petrol is obtained, not only by fractional distillation of crude oil, but also by cracking of
hydrocarbons from heavy fractions.
State why hydrocarbons from heavy fractions are cracked and explain why these
hydrocarbons are less easy to ignite than those in petrol.
(4)
(Total 15 marks)
15.
Ethene and other important hydrocarbons can be produced industrially from decane, C10H22.
Name the process involved. Write two equations for reactions in which ethene is formed from
decane by this process. Explain the economic importance of the process.
(Total 7 marks)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
11
16.
The petroleum and petrochemicals industries use a small number of processes to produce a large
number of final products. Three of these processes are fractional distillation, vacuum distillation
and cracking.
(a)
Describe briefly how fractional distillation can be used to convert crude oil into a small
number of fractions.
(4)
(b)
The residue from the fractional distillation process is usually vacuum distilled. This
process allows the compounds in the residue to boil at temperatures much lower than their
normal boiling points. State whether the sizes of the molecules of the compounds in the
residue are smaller or larger than those in the other fractions and suggest why the process of
vacuum distillation is used.
(2)
(c)
Cracking is carried out by heating long-chain hydrocarbons, often in the presence of steam
and a catalyst. Steam cracking is used to produce a mixture of alkanes and alkenes in
reactions such as the following:
C9H20 C6H14 + C3H6
(i)
Give a name for each compound produced in this reaction.
(2)
(ii)
Nonane, C9H20, can be cracked to give other products. One molecule of nonane can
give two molecules of ethene, one molecule of ethane and one molecule of another
substance. What is the molecular formula of the other substance?
(1)
(d)
Halogenoalkanes have been used for a long time as anaesthetics, for example
trichloromethane and 2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane(halothane). Give the
formulae of both trichloromethane and 2-bromo-2-chloro-1,1,1-trifluoroethane.
(2)
(Total 11 marks)
Lec.Rana Hassan Tariq
12
You might also like
- Al KanesDocument16 pagesAl KanesBrandy StoneNo ratings yet
- Al KanesDocument12 pagesAl KanessamanthaNo ratings yet
- Q1. (A) Gas Oil (Diesel), Kerosine (Paraffin), Mineral Oil (Lubricating Oil) and PetrolDocument96 pagesQ1. (A) Gas Oil (Diesel), Kerosine (Paraffin), Mineral Oil (Lubricating Oil) and Petrolwerkape1No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsDocument65 pagesBasic Concepts and Hydrocarbonsdank dankNo ratings yet
- F322 Module 1 Practice 1Document7 pagesF322 Module 1 Practice 1kingmimi24No ratings yet
- Produce Useful Fuels from Crude Oil MixturesDocument34 pagesProduce Useful Fuels from Crude Oil MixturesMohammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 2 QPDocument10 pagesAlkenes 2 QPIyad AbdallahNo ratings yet
- AS Level Chemistry Topic 7 Organic Chemistry HomeworkDocument14 pagesAS Level Chemistry Topic 7 Organic Chemistry HomeworkShirmara Pile-fordeNo ratings yet
- Practice Examination Questions For 1.6 Alkanes (Includes Some Questions From 1.5 Introduction To Organic Chemistry)Document12 pagesPractice Examination Questions For 1.6 Alkanes (Includes Some Questions From 1.5 Introduction To Organic Chemistry)Маша ЖуковскаяNo ratings yet
- Alkane and AlkeneDocument3 pagesAlkane and AlkeneNajeeb ullahNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 8Document9 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 8Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Alkanes Assessed HomeworkDocument7 pages1.6 Alkanes Assessed HomeworkSibel Halibryam ℂ⋆No ratings yet
- Revision 2 Chapter 4-5Document125 pagesRevision 2 Chapter 4-5Siti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsDocument64 pagesBasic Concepts and HydrocarbonsSiti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- Alkenes 1 QPDocument11 pagesAlkenes 1 QPasddf asdafNo ratings yet
- Isomerism 2 QPDocument9 pagesIsomerism 2 QPPragna AnanthNo ratings yet
- Topic 7 TestDocument11 pagesTopic 7 Testab9652378No ratings yet
- Shapes of Ions and Molecules AsDocument17 pagesShapes of Ions and Molecules Asalvin2282No ratings yet
- Metal p4 Ws 4Document10 pagesMetal p4 Ws 4NonnoonoNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Synthetic & Naturally Occurring Polymers 3 QPDocument13 pages7.3 Synthetic & Naturally Occurring Polymers 3 QPke poNo ratings yet
- Mixed 3Document15 pagesMixed 3Yaakkw100% (1)
- Organic Acylechloride M18 Mmmmm,.......Document60 pagesOrganic Acylechloride M18 Mmmmm,.......Muhammad HashimNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksDocument10 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- Organic Worksheet 1Document10 pagesOrganic Worksheet 1moiz.8450No ratings yet
- HW 1474 7209 IGCSEChemistryWorksheetChapters2226812OctDocument19 pagesHW 1474 7209 IGCSEChemistryWorksheetChapters2226812Octzaseel86No ratings yet
- Fermentation and Ethanol ProductionDocument184 pagesFermentation and Ethanol Productionan7li721No ratings yet
- Alkanes TestDocument7 pagesAlkanes TestmjNo ratings yet
- 2 HoursDocument18 pages2 HoursOTTO OLIMANo ratings yet
- Alcohols & Carboxylic Acids 3 QPDocument10 pagesAlcohols & Carboxylic Acids 3 QPAyca UgurluNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons, polymers and crude oil fractions identification quizDocument4 pagesHydrocarbons, polymers and crude oil fractions identification quizYee MeiNo ratings yet
- Beaconhouse School System, Mandi Bahauddin Work Sheet of Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry - Alcohols Class: XI-Cambridge Name: - Date: - Q1Document4 pagesBeaconhouse School System, Mandi Bahauddin Work Sheet of Chemistry Topic: Organic Chemistry - Alcohols Class: XI-Cambridge Name: - Date: - Q1Qurrat Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Compounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsDocument69 pagesCompounds Containing The Carbonyl Group QuestionsmarvellousadenugaNo ratings yet
- A-Level Paper 2 pp2Document16 pagesA-Level Paper 2 pp2Charlie MarstonNo ratings yet
- GCSE Style Questions Crude OilDocument19 pagesGCSE Style Questions Crude OilSteve Bishop100% (4)
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 18Document16 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 18Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Optical Isomerism 1 QPDocument8 pagesOptical Isomerism 1 QPfajrk8567No ratings yet
- Carbon Dioxide - Methane As Greenhouse Gases 1 QP PDFDocument23 pagesCarbon Dioxide - Methane As Greenhouse Gases 1 QP PDFmelissaicecream10No ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsDocument149 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes and AlcoholsFaria TahsinNo ratings yet
- Quiz - 1 - Matter & StoichiometryDocument4 pagesQuiz - 1 - Matter & StoichiometryDaniel Ngenokesho WandyaNo ratings yet
- PH - Buffers 1 QPDocument12 pagesPH - Buffers 1 QPRoshae SinclairNo ratings yet
- As Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksDocument11 pagesAs Level Chemistry: Answer All Questions Max 50 MarksAlia ShabbirNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 3 '03Document12 pagesChemistry Paper 3 '03Ghaydah L. Al-ShamiNo ratings yet
- A2 Chemistry Worksheet on Partition CoefficientDocument10 pagesA2 Chemistry Worksheet on Partition CoefficientHassaan arshadNo ratings yet
- AS LEVEL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC TOPIC TESTDocument14 pagesAS LEVEL CHEMISTRY ORGANIC TOPIC TESTBee Jay JayNo ratings yet
- Fractional Distillation Revision Questions: MinutesDocument32 pagesFractional Distillation Revision Questions: MinutesAgam HanasichulaNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Organic ChemistryDocument4 pagesExam Questions Organic Chemistrymalikimran28No ratings yet
- 13 - Organic Chemistry - P4Document72 pages13 - Organic Chemistry - P4Sulaf OmarNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rates & Equilibrium 1 QPDocument14 pagesReaction Rates & Equilibrium 1 QPLeilani Arrow-SmithNo ratings yet
- 18.1 Amino Acids WS 2021 UnlockedDocument30 pages18.1 Amino Acids WS 2021 UnlockedOnline TeachingNo ratings yet
- Equilibria AsDocument39 pagesEquilibria AsyousafNo ratings yet
- 03 0620 42 3RP - InddDocument5 pages03 0620 42 3RP - InddIzzati AnuarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Reactions of Organic Chem - Alkanes PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Reactions of Organic Chem - Alkanes PDFpretzNo ratings yet
- Catalysts 1 QPDocument12 pagesCatalysts 1 QPprettytakadiyiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC: 4.2 Equilibria: Answer All Questions Total 40 MarksDocument4 pagesTOPIC: 4.2 Equilibria: Answer All Questions Total 40 MarksrokuNo ratings yet
- Alcohol and Carboxylic Acid 1Document5 pagesAlcohol and Carboxylic Acid 1Geraldine LatupeirissaNo ratings yet
- SLG ChemistryDocument15 pagesSLG ChemistryVithuNo ratings yet
- Unusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandUnusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Translator ProgramDocument3 pagesTranslator ProgramAish PayariNo ratings yet
- Experimental Techniques in Chemistry Ist YearDocument5 pagesExperimental Techniques in Chemistry Ist YearAish PayariNo ratings yet
- 95996-2014-Syllabus Cambridge SyllabusDocument90 pages95996-2014-Syllabus Cambridge Syllabusaline_lin_2No ratings yet
- MCQ QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCQ QuestionsAish PayariNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2Aish PayariNo ratings yet
- 1st Chapter Basic Concepts McqsDocument6 pages1st Chapter Basic Concepts McqsamaraaaaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry (5070) Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Lec. Rana Muhammad Hassan TariqDocument10 pagesChemistry (5070) Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding: Lec. Rana Muhammad Hassan TariqAish PayariNo ratings yet
- MCQ QuestionsDocument5 pagesMCQ QuestionsAish PayariNo ratings yet