Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management Information System Chapter 12 Notes
Uploaded by
gut78Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Information System Chapter 12 Notes
Uploaded by
gut78Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 12: Business Intelligence and Decision Support Systems
(Prepared by Research Scholar: Amrita Patwa)
Business Intelligence is an umbrella term that includes architecture, tools, databases and
applications that have been implemented over several decades under different names by
various researchers and vendors.
Need for BI:
Provide measurable business value to smaller companies as costs declined
Increased pervasiveness
Used as a feedback mechanism
Improved data quality
Full visibility and real time excess to company data
Easy to create accurate, up to the minute report
Informed , fast decision making
The major component of BI are data ware house and marts, predictive analysis, data mining,
data visualization software and a business performance management system.
Characteristic and Objectives of Data Mining:
The data are cleared and consolidated in the data warehouse
Managing and synchronizing data to get the right result
The minors are empowered by data drill and other power query tool
Readily combined with spreadsheet and other software development tool
Massive search effort can be made for large amount of data
Data mining techniques are well suited to analyze financial time series data to find patterns,
detect anomalies and outliers recognize situation of chance and risk etc. Data mining tools are
interactive, visual and understandable and work directly on the data warehouse of the
organization.
Data Mining Applications:
There are some applications whose intend is to identify the business opportunity in order to
create a sustainable competitive advantage. Examples of such applications are retailing and
sales, banking, manufacturing and production, healthcare, broadcasting and marketing.
ISs have grown to support all managerial roles, particularly decisional role. It helps in the
identification of problem and opportunity and in the decision of what to do about them. The
two broad decision categories are problem solving and opportunity exploiting.
The need for IT support in managerial decision is basically to overcome certain issues such as
Too many alternatives , scenarios and risk to consider
Time pressure
Increased fluctuation uncertainty in the environment
Decision maker and information can be indifferent location. Bringing them all
together is difficult and costly
Need of an organization to conduct forecast
Decision making process consist of four systematic phases Intelligence, Design, Choice and
Implementation. There is a continuous flow of information from intelligent to design to
choice but at any time there may be a return of information to a prior phase. This decision
model is a simplified representation or abstraction of reality. The benefits of modeling in
decision making are as follows:
Cost of virtual experimentation is much lower
Simulated compression of time
Manipulating the model by changing variables is much easier
Cost of making mistake during experiment is much lower
Deals better with uncertainty and risk allows the analysis and comparison of a very
large number of possible alternative solutions.
Enhance reinforced learning
Decision making activities:
Structured decision( for routine and repetitive problems)
Unstructured decision (for problem having a lot of uncertainty)
Semi structured decision (falls between the two mentioned above)
Decision Support System (DSS)
Combined model and data to solve semi structure and unstructured problem with intensive
user involvement. It is an approach or philosophy rather than a precise methodology.
Characteristics of DSS:
Makes a system flexible and adaptable to changing condition and to the varying
requirement of different decision making situation
It allows user to enter their own data and to view how system will behave under
varying circumstances
It provide better understanding of sensitivity analysis model
Benefits of DSS:
1. Examine numerous alternative very quickly
2. Support forecasting
3. Provide a systematic risk analysis
4. Be integrated with communication system and databases
5. Support group work
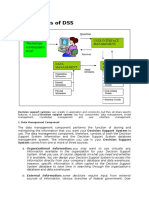
Components of DSS:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Database (contain data from multiple sources)
Model Base (contain completed models and sets of rule)
User Interface (covers all aspects of the communication between a user and the DSS)
User (the decision maker)
Knowledge base (provide the expertise to solve some part of the problem)
The DSS components are all softwares, they run on standard hardware and they can be
facilitated by additional software. One of the most popular tools for decision support is
simulation.
GDSS (Group DSS) is an interactive computer based system that facilitates the solution of
semi structure and unstructured problems when made by a group of decision maker by
concentrating on the process and procedure.
Automated Decision Support (ADS)
These systems are rule based system that automatically provides solution to repetitive
managerial problems. ADSs are closely related to BI and business analytics.
Business analytic models may be used to create and operate the business rules
Business rule can be used to trigger the automatic decision in BI application
Characteristics and Benefits of ADS:
Rapidly business rules to automate decision makers and deploy them into almost any
operating environment
Inject predictive analytics into rule based application
Combined business rules, predictive models and optimization strategy
ADS Application:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Product or service customization
Yield or price optimization
Routing or segmentation decision
Corporate regulatory compliance and fraud detection
Dynamic forecasting and SCM
Operational control
Customer selection ,loyalty and service
Human Capital
<<<>>>
You might also like
- Decision Support SystemDocument6 pagesDecision Support SystemNaveenNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Process PDFDocument8 pagesDecision Making Process PDF9827045800No ratings yet
- A NARRATIVE REPORT OF Chapter16Document22 pagesA NARRATIVE REPORT OF Chapter16Mafe Angela OrejolaNo ratings yet
- Lecture One Introduction and Basics of DSSDocument6 pagesLecture One Introduction and Basics of DSSUmmu AhmedNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems Executive Support SystemsDocument17 pagesDecision Support Systems Executive Support SystemsCR7 الظاهرةNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemsDocument36 pagesDecision Support SystemssindhujaNo ratings yet
- 10 Chapter 10 Decision Support Systems DSSDocument6 pages10 Chapter 10 Decision Support Systems DSSJobaiyerNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument19 pagesDecision Support SystemClassic WheelsNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems: Corresponds With Chapter 9Document35 pagesDecision Support Systems: Corresponds With Chapter 9Aamir RashidNo ratings yet
- DecisionDocument6 pagesDecisionSingh GurpreetNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems (DSS)Document13 pagesDecision Support Systems (DSS)wasiuddinNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument28 pagesDecision Makingvenkat1972No ratings yet
- The Architecture of An Optimizing Decision Support SystemDocument6 pagesThe Architecture of An Optimizing Decision Support SystempraveenaviNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems & Executive Support SystemsDocument17 pagesDecision Support Systems & Executive Support SystemsNabila T. Chowdhury100% (10)
- Components of A DSS: SoftwareDocument3 pagesComponents of A DSS: Softwareaisolamaddy86No ratings yet
- SCDL - Pgdba - Finance - Sem 2 - Mis-McsDocument18 pagesSCDL - Pgdba - Finance - Sem 2 - Mis-Mcsapi-3762419No ratings yet
- Compare - Dss and Bi PDFDocument6 pagesCompare - Dss and Bi PDFSharmila SaravananNo ratings yet
- DSS SummaryDocument47 pagesDSS SummarywanderaNo ratings yet
- DSS Characteristics:: Decision Support SystemDocument6 pagesDSS Characteristics:: Decision Support Systemmuddassir videosNo ratings yet
- DSS EnglDocument57 pagesDSS EnglCorina BarangaNo ratings yet
- Mis Module 3Document38 pagesMis Module 3Tinku JoyNo ratings yet
- CL585Document7 pagesCL585marcusfdm69No ratings yet
- Advantages of Business Intelligence: 1. Boost ProductivityDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Business Intelligence: 1. Boost ProductivityShivansh tomarNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument11 pagesDecision Support SystemGaurav MittalNo ratings yet
- Decision Support System: Fundamentals and Applications for The Art and Science of Smart ChoicesFrom EverandDecision Support System: Fundamentals and Applications for The Art and Science of Smart ChoicesNo ratings yet
- 3 - DSS and EISDocument27 pages3 - DSS and EISBshwas TeamllcenaNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems and Business IntelligenceDocument45 pagesDecision Support Systems and Business IntelligenceNeha Priya50% (2)
- Assingment CSE301 A60006420098 BY PIYUSH ANANDDocument8 pagesAssingment CSE301 A60006420098 BY PIYUSH ANANDPiyush AnandNo ratings yet
- Management For Innovation and Technology: Using A Dss To Determine RiskDocument12 pagesManagement For Innovation and Technology: Using A Dss To Determine RiskRomuald KinimoNo ratings yet
- Dss Class PDFDocument17 pagesDss Class PDFAkashNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems: Practical No. 3Document8 pagesDecision Support Systems: Practical No. 3Suvarna LangadeNo ratings yet
- DSS - Concepts, Structure, Function, CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesDSS - Concepts, Structure, Function, CharacteristicsSwostik RoutNo ratings yet
- Dss 3321 WWDocument5 pagesDss 3321 WWrobee.sumatraNo ratings yet
- Bcom1 Paper1 Unit4Document7 pagesBcom1 Paper1 Unit4alokpandey4555No ratings yet
- Ponents of DSSDocument7 pagesPonents of DSSDeep BhalodiaNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument55 pagesDecision Support Systemsudha_adventNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Decision Support SystemDocument5 pagesSeminar On Decision Support Systemjatin_57187No ratings yet
- Prof K.G.Muralidhra: Submitted ToDocument26 pagesProf K.G.Muralidhra: Submitted TorajendrajhaNo ratings yet
- DSS Lecture 1Document16 pagesDSS Lecture 1Sahir0% (1)
- MISDocument9 pagesMISSaurabh JoshiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Building DSSDocument8 pagesLesson 5 - Building DSSSamwelNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: AssignmentDocument7 pagesManagement Information System: AssignmentiftikharhassanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 4 Supllementary NotesDocument6 pagesModule 1 Lesson 4 Supllementary NotesMohit DaymaNo ratings yet
- MIS - Management Information SystemDocument8 pagesMIS - Management Information SystemGinu L PrakashNo ratings yet
- DSES Assignmet 3Document23 pagesDSES Assignmet 3RAHUL DEVNo ratings yet
- Management Information SystemDocument13 pagesManagement Information SystemSim Chung Ang 沈俊安No ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument6 pagesDecision Support SystemJavaid Ali ShahNo ratings yet
- Concept and Philosophy of DSSDocument10 pagesConcept and Philosophy of DSSayushiNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemDocument26 pagesDecision Support SystemamreenaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Decision Support SystemsDocument10 pagesUnit 1-Decision Support SystemsDisha Verma KalraNo ratings yet
- Group Descision Support SystemDocument15 pagesGroup Descision Support SystemBabnish JoshiNo ratings yet
- Management Information System: The Business School, University of JammuDocument10 pagesManagement Information System: The Business School, University of Jammuanon_945457258No ratings yet
- Programmed and Non-Programmed DecisionsDocument39 pagesProgrammed and Non-Programmed DecisionsHimanshiNo ratings yet
- DSS PDFDocument7 pagesDSS PDFRaktimNo ratings yet
- Nigel Gezi DDS - Assignment - 1Document6 pagesNigel Gezi DDS - Assignment - 1Troy AJ GezyNo ratings yet
- DssDocument7 pagesDssanashussainNo ratings yet
- Nigel Gezi Advanced - DDS - Assignment - 1Document6 pagesNigel Gezi Advanced - DDS - Assignment - 1Troy AJ GezyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Info SystemDocument25 pagesIntro To Info SystemRomelyn JoveroNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemsDocument9 pagesDecision Support Systemsu5999424No ratings yet
- Management Information System Chapter 10 NotesDocument5 pagesManagement Information System Chapter 10 Notesgut78No ratings yet
- Management Information System Chapter 11 NotesDocument4 pagesManagement Information System Chapter 11 Notesgut78No ratings yet
- Management Information System CHAPTER 9Document5 pagesManagement Information System CHAPTER 9gut78No ratings yet
- Management Information System CHAPTER 6Document3 pagesManagement Information System CHAPTER 6gut78No ratings yet
- Management Information System CHAPTER 4Document2 pagesManagement Information System CHAPTER 4gut78No ratings yet
- Management Information System CHAPTER 7Document3 pagesManagement Information System CHAPTER 7gut78No ratings yet
- Management Information System CHAPTER 2Document3 pagesManagement Information System CHAPTER 2gut78No ratings yet
- Smart Plant Enterprise Install ChecklistDocument54 pagesSmart Plant Enterprise Install Checklistgut78100% (1)
- Management Information System CHAPTER 1Document2 pagesManagement Information System CHAPTER 1gut78No ratings yet
- Solved ProblemsDocument75 pagesSolved Problemsgut78No ratings yet
- 08 Attachment G GLNG Emergency Response PlanDocument111 pages08 Attachment G GLNG Emergency Response PlanJupni Mulyana100% (4)
- Green HouseDocument7 pagesGreen Housegut78No ratings yet
- Z MSG Note 1723881 731 740Document66 pagesZ MSG Note 1723881 731 740xqyy1No ratings yet
- SAP User Access Request Form: New Change DeleteDocument2 pagesSAP User Access Request Form: New Change Deleteanil007rajuNo ratings yet
- Adventure Works 2012Document149 pagesAdventure Works 2012raghu_dNo ratings yet
- Inkjet Printer: Smart Handheld Printing PlatformDocument2 pagesInkjet Printer: Smart Handheld Printing PlatformMelahel Global SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Dog Breed Classificationusing Convolutional Neural NetworkDocument54 pagesDog Breed Classificationusing Convolutional Neural NetworkLike meshNo ratings yet
- GNSS Receiver Sokkia AtlasDocument3 pagesGNSS Receiver Sokkia AtlasHardy SuparmantoNo ratings yet
- Firtz Haber, Thermodynamics of Technical Gas-Reactions: Seven LecturesDocument380 pagesFirtz Haber, Thermodynamics of Technical Gas-Reactions: Seven LecturesLukaszGlinkaNo ratings yet
- News 89Document7 pagesNews 89Adrianus YogaNo ratings yet
- EASERA Installation InformationDocument1 pageEASERA Installation Informationpepeluis666No ratings yet
- 2014 Axeda Stack Image FileDocument1 page2014 Axeda Stack Image FileCasey LeeNo ratings yet
- Open Vs Traditional EdiDocument5 pagesOpen Vs Traditional EdiSaurabh2510No ratings yet
- AISG Antenna Port Color Coding Paper TP PDFDocument22 pagesAISG Antenna Port Color Coding Paper TP PDFSudipto MitraNo ratings yet
- TDH Presentation: Frantz FanonDocument19 pagesTDH Presentation: Frantz FanonHAMSE AHMED YOUSUFNo ratings yet
- Catia SymbolsDocument9 pagesCatia SymbolsAmolPagdalNo ratings yet
- NQ Series: (Ethernet/Ip)Document36 pagesNQ Series: (Ethernet/Ip)Matheus GeraldinoNo ratings yet
- Ni ElvisDocument14 pagesNi ElvisRinnoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument316 pagesUntitledJuancaNo ratings yet
- 4112-4127 Color Scan KitDocument3 pages4112-4127 Color Scan KitxcopytechNo ratings yet
- Writing PsuedoCodeDocument31 pagesWriting PsuedoCodeapi-3814408100% (3)
- Route PoisoningDocument4 pagesRoute Poisoningrosev15No ratings yet
- Numerical AnalysisDocument17 pagesNumerical Analysisateebakmal1No ratings yet
- Adobe Premiere PreciceDocument7 pagesAdobe Premiere Preciceivicans2972No ratings yet
- SAP ABAP Interview Questions Top 50Document7 pagesSAP ABAP Interview Questions Top 50pal singhNo ratings yet
- DWC2440 Quick Start GuideDocument1 pageDWC2440 Quick Start GuideSimon KorosecNo ratings yet
- Grey Card Sasha HeinDocument15 pagesGrey Card Sasha HeinIvan LiwuNo ratings yet
- TraceDocument49 pagesTraceAntoni FabricioNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10Document31 pagesMapeh 10John Thiery FedericoNo ratings yet
- Distributing and Installing RMI SoftwareDocument11 pagesDistributing and Installing RMI SoftwareKrishna VanjareNo ratings yet
- 2023 © Keymaster Poldiag - : All Rights ReservedDocument28 pages2023 © Keymaster Poldiag - : All Rights ReservedTristan CuisinierNo ratings yet
- Automotive Quality Management System Manual: Century Metal Recycling LimitedDocument7 pagesAutomotive Quality Management System Manual: Century Metal Recycling LimitedsunilNo ratings yet