Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ce383 Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Mark FernandezCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ce383 Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Mark FernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
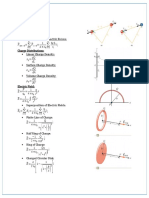
Open Channel Flow Rectangular Channels
1
Steady Flow: Vel = constant @ a given point q2
Uniform Flow: Vel = constant over a given length
2
yc=
g( ) q=unit flow
3
1
1.49 Rh3 √ S Q2
v=
n
yc= (
g∗widt h 2 )
3
2 Trapezoidal Channels
1.49 √ S A 3 2 3
v= 2
Q 2 (by+ m y )
=
n P3 g b+2 my
2 All Channels (yc embedded in A)
2 3
1.49 √ S ( by +m y ) lb
v= Q2 A 3
2 = TW =TopWidthτ =γ∗y∗s γ water =62.4 3
n ( b +2 y √ 1+m 2 3
) g TW ft
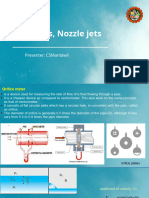
n concrete=0.013 Orifice Equation
Q=C d A √ 2 gh
5 C d π D 2 √ 2 gh
2
3 Q=
Q=VA Q= 1.49 A R
3
h √ s Q= 1.49 √ s2 A 576
n h = f/ CL of pipe to WL
n P3
HW = Head Waters = f/ bottom of pipe to WL
5
Weir Equation
1.49 √ s ( by+ m y 2 ) 3
Q= 2 Atrap =by +m y 2 Q=C w L H 1.5
2 3
n ( b+2 y √ 1+ m ) H=Height above weir
A Area For Circular Pipes:
Rh = = Head> 0.4 D=Orifice Flow
P Wetted Pe rimeter
Head< 0.4 D=Weir Flow
Ptrap =b+2 y √1+m 2m=run [H :V ]b=BottomWidth
Hydrologic Cycle (consistent units)
drop Δ S=( P−ET )+ ( R¿ −Rout ) + ( B¿ −Bout )
y=Water Depth s=
run
8 P = Precipitation
√S s D
Q= ( 16 )
n
3
ET = Evapotranspiration
R = Runoff
3
Qn
D=16 (
√s )
8 B = Groundwater/Seepage
Conversions
Half-Filled Pipes 2
43,560 f t 449 gpm 1.55 cfs
Multiply Qhalf by 2 for Qfull, then solve as usual. acre cfs MGD
If Q (discharge) is constant: Q= A 1 V 1= A 2 V 2 ft 3
ac∗¿ mph
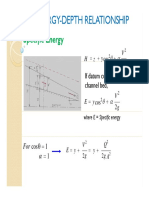
Energy Equation (E = ft) cfs ≈
7.481 gal hr 1.467 fps
2
v
E= y +
2g Probability
Q2 Water Year: October 1 – September 30
E= y +
2 g A2 1
P X < x =1− Probability
Eminimum @ y c T
Critical Depth 1 1 n
y > y c Subcritical (slower flow) P X > x=
T
Probability of exceedence Risk=1− 1− ( T )
y < y c Supercritical (faster flow) 1
T= n!
1 P x=? ,n , p = (1−p )x p n−x
1−( 1−R )n x ! ( n−x ) !
1
“25% of the time I get 3 out of 5 correct”:
¿ gauges= A [ A=mi 2 ]
3
P = 0.25 x=3 n=5
Weibull Arithmetic mean
m 1 Thiessen Method
P X > x= = Draw & extend ⊥bisectors of lines
n+ 1 T
Gringorten Isohyetal Method
m−a Equally divide lines w/ tick marks
P X > x= a =0.4
n+ 1−2 a default <Cum depth → Incremental depth → Intensity>
m=rank (1=largest ) Infiltration
F R
= NRCS assumption
Log Normal Distribution S P−I a
Take ln of data. ( P−0.2 S )2 ( P−0.04 )2 S= 1000 −10
x ln−( x́ ln ) R= [ P>0.2 S ] R98=
P+ 0.8 S P+0.16 CN
z=
s ln Group A soil = Sandy
x=e z∗s + x́
ln ln
Group D soil = Clayey
Table Entries=P X <x Antecedent Moisture Condition (AMC)
Gumbel Distribution (Rainfall) 4.2∗CN 23∗CN
C N I= C N III =
g = +1.14 = Constant skewness 10−0.058∗CN 10+ 0.13∗CN
Don’t transform data. Horton Method – use Solver, f=in/hr
1 x −x́+ 0.45 s f ( t )=f c + ( f 0−f c ) e−kt
−b
P X > x =1−e−e b=−ln −ln 1− ( ( )) T
b=
0.7797 s f 0=initial F
x=0.7797∗s∗b+ x́−0.45 s f c =ultimate F
Log Pearson 3 Distribution k + t=same time units !
Take ln of data. g
i=
G=skew coef (n>100) h+duration
G m =Territorial skew coef (n<30)
( n−25 ) G n−25 Rational Method
Gw =
75
+ 1−
75 (Gm ) [time= min]
x ln − x́ ln Q p=Ci A ac A<25 ac
K= 0.385
sln L3
x=e K∗s ln + x́ ln
t c=
( )H
Kirpich
Constants 128
n concrete=0.013 NRCS:
lb t c =t overland +t shall owconcentrated +t channel
γ water =62.4 3
ft 0.42 ( n L )0.8
lb t o= L< 100 ft , P 2=2 yr , 24 hr
g=32.174 2 √ P2 s 0.4
s
C w =3.3 sharp L L
t sc = f paved =1220 f unpaved =968t c = v=4 fps
f √s v
C w =3.0 broad
t c =5 min if watershed < 1ac
C d=0.6
1 ¿ t c → i→Q> ¿
per foot=0.020
4 Storm Pipe Routing
Precipitation Start upstream
Rain gauges located (2*height) away f/ object Use largest tc
<Node, C, A, C*A, ∑(C*A), ∑tc, I, Q, tp>
Q 3=i 3 ( C1 A 1 +C2 A 2 +C 3 A3 ) [t ¿ ¿ c 3 → i3 ]¿
Unit Hydrograph
[time= hr]
Q3 +Q4
∗Δt
2
Incr R depth= [ sincunits ]
A
To construct a UH f/ observed flow, divide all
observed ordinates by the event’s cum R
<Observed flow → Inc R →Cum R → UH>
0.7
1000
t c=
1.67∗L0.8 (
CN
−9 )
Δ D=0.133∗t c
1900 √Y %
ΔD
t p= + 0.6∗t c
2
tr 484∗A∗Rcum m i2∗¿
t p=3 q p=
5 tp hr
qp 180∗t
q (t)=
2 (
∗ 1−cos
tp (t< 1.25∗t p
))
−1.3∗t
tp
q ( t )=4.34∗q p e t >1.25∗t p
V =1.39∗Q p∗t p
Reservoir Routing
Storage=V =k∗stag e b
A=K∗b∗stag eb −1
ΔV =Δt ( Qinflow−Q outflow )
( Qinflowpeak −Qoutflowpeak ) t p
V=
2
Total Runoff Volume
V =R cum∗A
V =Σ ( UH ordinates ) ( Δ t ) R cum
V =Σ ( Hydro ordinates ) Rcum
V =Σ ( Rainfall Excesses ) =R cum
V =1.39∗Q p∗t p
Convert Observed Hydrograph to Unit Hydrograph by
div OH ordinates by total R_cum
“Find the flow discharge @ time = _____”, use
convolution
i∗Δ D→ Pcum → R cum → EX 1
You might also like
- Midterm 02-Solutions PDFDocument7 pagesMidterm 02-Solutions PDFElizabeth DouglasNo ratings yet
- Schematic of a cylindrical body falling through oil in a tubeDocument4 pagesSchematic of a cylindrical body falling through oil in a tubegambitNo ratings yet
- Statistical Physics SolutionsDocument2 pagesStatistical Physics SolutionsPrince Mensah100% (2)
- 4211 Sheet 3Document2 pages4211 Sheet 3Roy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Conduction AnalysisDocument30 pagesObjectives of Conduction AnalysisnachappaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2020Document14 pagesFiitjee All India Test Series: JEE (Advanced) - 2020yashjhan2017No ratings yet
- Streamline EquationsDocument108 pagesStreamline Equationstoligado27No ratings yet
- Uhf Tec - CT 1 (2015-2016)Document11 pagesUhf Tec - CT 1 (2015-2016)nameNo ratings yet
- SBC Calculation PDFDocument4 pagesSBC Calculation PDFMcKen FloresNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Applications in ProbabilityDocument2 pagesWorksheet Applications in ProbabilityVanessa HardjadinataNo ratings yet
- F Q Q R R F QDQ R R Q Q R R: (Document Title)Document8 pagesF Q Q R R F QDQ R R Q Q R R: (Document Title)kashawna fujiwaraNo ratings yet
- Clement's and Desormes' ExperimentDocument3 pagesClement's and Desormes' Experimentkanchankonwar50% (2)
- DC5e ErrataDocument6 pagesDC5e ErrataNihar KuchrooNo ratings yet
- Homework 02-Solutions PDFDocument10 pagesHomework 02-Solutions PDFElizabeth DouglasNo ratings yet
- Final: CS 188 Fall 2013 Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument23 pagesFinal: CS 188 Fall 2013 Introduction To Artificial IntelligenceTryerNo ratings yet
- Mechanics, thermal physics, waves & optics, electricity & magentism, modern physicsDocument11 pagesMechanics, thermal physics, waves & optics, electricity & magentism, modern physicsTibra ArkaNo ratings yet
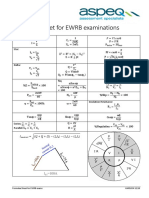
- Formulae Sheet For EWRB Examinations: For Examination Use OnlyDocument1 pageFormulae Sheet For EWRB Examinations: For Examination Use OnlyJason JiaNo ratings yet
- Errata Digital Communications: John G. Proakis and Masoud Salehi Fifth Edition, Mcgraw-Hill, 2008Document3 pagesErrata Digital Communications: John G. Proakis and Masoud Salehi Fifth Edition, Mcgraw-Hill, 2008Rasha ZiyadNo ratings yet
- An Algorithm To Compute Generalized Padé-Hermite Forms, by Harm DerksenDocument6 pagesAn Algorithm To Compute Generalized Padé-Hermite Forms, by Harm DerksenNikolay IkonomovNo ratings yet
- Griffith's Quantum Mechanics Problem 2.51Document3 pagesGriffith's Quantum Mechanics Problem 2.51palisonNo ratings yet
- ProblemDocument2 pagesProblemJishnuNo ratings yet
- Koutecky-Levich Plots in Charge-Transfer Mechanism DiagnosesDocument7 pagesKoutecky-Levich Plots in Charge-Transfer Mechanism DiagnosesAnonymous hkDxd8LNo ratings yet
- EMTLDocument40 pagesEMTLBharat_Reddy_N100% (1)
- M01 Hibb0000 00 Se C16Document153 pagesM01 Hibb0000 00 Se C16luisloredoperez156No ratings yet
- 2006 JC 1 H2 JCT & Promo - Differential EquationsDocument3 pages2006 JC 1 H2 JCT & Promo - Differential EquationsOccamsRazorNo ratings yet
- 2843 Solutions Chap9Document10 pages2843 Solutions Chap9Thomas LiuNo ratings yet
- Green TheoremDocument1 pageGreen TheoremBrian chunguliNo ratings yet
- EMH5020 Mate1 PDFDocument1 pageEMH5020 Mate1 PDFpubekasNo ratings yet
- Language Modeling: Introduction To N-GramsDocument79 pagesLanguage Modeling: Introduction To N-GramsMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture35 Ch12 CoherenceDocument25 pagesLecture35 Ch12 Coherencepavan457No ratings yet
- Question Paper Format and InstructionsDocument38 pagesQuestion Paper Format and Instructionsanon020202No ratings yet
- Here are the solutions:(a) v1 = 0 V, vdiff = -4 mV, vcm = -2 mV(b) v1 = 2.001 V, vdiff = -10 mV, vcm = 2.005 V (c) v3 = -4 V, vdiff = -4 mV, vcm = 2 V(d) vdiff = 0 V, vcm = -1.2 VDocument88 pagesHere are the solutions:(a) v1 = 0 V, vdiff = -4 mV, vcm = -2 mV(b) v1 = 2.001 V, vdiff = -10 mV, vcm = 2.005 V (c) v3 = -4 V, vdiff = -4 mV, vcm = 2 V(d) vdiff = 0 V, vcm = -1.2 V鄭又嘉No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Discrete Time Fourier Transform Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Discrete Time Fourier Transform Questions and Answers - Sanfoundry PDFzohaibNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Lect3Document16 pagesNonlinear Lect3win alfalahNo ratings yet
- ExpertTA AnswersDocument25 pagesExpertTA AnswersJohn Ndambuki0% (1)
- Mechanics of Materials Formula - SheetDocument14 pagesMechanics of Materials Formula - SheetFrancesNo ratings yet
- IIT-JAM-PH-2020 Answer Key Career Endeavor PDFDocument11 pagesIIT-JAM-PH-2020 Answer Key Career Endeavor PDFCosmk1ng Zero-1No ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps 8 B PDFDocument14 pagesCentrifugal Pumps 8 B PDFGeorge OparNo ratings yet
- Univalent Harmonic FunctionsDocument4 pagesUnivalent Harmonic FunctionsAdvanced Research Publications100% (2)
- Matrices Practice Sheet Solution HSC FRB 24Document45 pagesMatrices Practice Sheet Solution HSC FRB 24ruinedfuture858No ratings yet
- Spyridon Stamatopoulos School AdviserDocument12 pagesSpyridon Stamatopoulos School AdviserSpyros StamatopoulosNo ratings yet
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 pagesChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaNo ratings yet
- Application of CalculusDocument36 pagesApplication of CalculusTAPAS KUMAR JANANo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Constants and Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument20 pagesEquilibrium Constants and Le Chatelier's Principlekrishna100% (1)
- 026 Ahmed IntegralDocument9 pages026 Ahmed Integraljuniotor2023No ratings yet
- JNTUA B Tech 2018 1 2 May R15 ECE 15A54201 Mathematics IIDocument2 pagesJNTUA B Tech 2018 1 2 May R15 ECE 15A54201 Mathematics IIMRUDULA KULAKARNINo ratings yet
- Solutions 8: Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas Ihn Fall 2017Document2 pagesSolutions 8: Semiconductor Nanostructures Thomas Ihn Fall 2017ApuNo ratings yet
- Exam 2 Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesExam 2 Cheat SheetAmyNo ratings yet
- Homework 08-Solutions PDFDocument11 pagesHomework 08-Solutions PDFElizabeth DouglasNo ratings yet
- PH4211 Statistical Mechanics: Problem Sheet 2 - AnswersDocument14 pagesPH4211 Statistical Mechanics: Problem Sheet 2 - AnswersRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- Liquid Solutions Jee ModuleDocument49 pagesLiquid Solutions Jee ModuleAfsheen TahiraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (Hydrodynamics)Document9 pagesFluid Mechanics (Hydrodynamics)Derrick Ramos100% (1)
- Flow in Open ChannelsDocument14 pagesFlow in Open ChannelsAurora VillalunaNo ratings yet
- ENERGY--DEPTH RELATIONSHIPDocument13 pagesENERGY--DEPTH RELATIONSHIPHd MuluNo ratings yet
- Rumus Head Loss BernoulliDocument2 pagesRumus Head Loss BernoulliZmique AzmiNo ratings yet
- Study of Standing Wave FlumeDocument5 pagesStudy of Standing Wave FlumeAyon SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Lec3b-Orifice JetsDocument16 pagesLec3b-Orifice JetsRANDOM VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- Lec3b Orifice JetsDocument16 pagesLec3b Orifice JetsJesselyn EstopitoNo ratings yet
- AC Chapter 1Document17 pagesAC Chapter 1Muhammed BahaaNo ratings yet
- Process Dynamics and Control Seborg 2nd Ch02 PDFDocument20 pagesProcess Dynamics and Control Seborg 2nd Ch02 PDFsdrtfgNo ratings yet
- How Racing Defined The Automobile ParadigmDocument7 pagesHow Racing Defined The Automobile ParadigmMark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Leadership's Fulcrum v2Document5 pagesLeadership's Fulcrum v2Mark FernandezNo ratings yet
- NCSU Py208n Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesNCSU Py208n Cheat SheetMark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Wordsworth's Appreciation of Time in "Tintern Abbey"Document4 pagesWordsworth's Appreciation of Time in "Tintern Abbey"Mark Fernandez75% (4)
- Leadership's FulcrumDocument6 pagesLeadership's FulcrumMark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Right To BelieveDocument7 pagesRight To BelieveMark Fernandez100% (1)
- IndulgencesDocument8 pagesIndulgencesMark Fernandez100% (1)
- Causes of Homosexuality: The Ultimate AuthorityDocument7 pagesCauses of Homosexuality: The Ultimate AuthorityMark Fernandez100% (6)
- The Segmentation of Language in Heart of DarknessDocument8 pagesThe Segmentation of Language in Heart of DarknessMark Fernandez100% (17)
- 05wknm15 Week05 2015Document119 pages05wknm15 Week05 2015Hung le VanNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physical OcenographyDocument13 pagesFundamentals of Physical OcenographyvenuNo ratings yet
- Delta Deposits Morphology and EvolutionDocument49 pagesDelta Deposits Morphology and EvolutionMelissa2305No ratings yet
- S-44 Edition 6.0.0: International Hydrographic Organization Standards For Hydrographic SurveysDocument50 pagesS-44 Edition 6.0.0: International Hydrographic Organization Standards For Hydrographic SurveysNabil Amirul HaqNo ratings yet
- AirmassDocument22 pagesAirmassVaishnavi SwamiNo ratings yet
- OceanographyDocument94 pagesOceanographyKokila AmbigaeNo ratings yet
- Factors That Influence ClimateDocument2 pagesFactors That Influence ClimateGino R. MonteloyolaNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle ExplainedDocument3 pagesThe Water Cycle ExplainedLeliNo ratings yet
- Weekly State of SA ReservoirsDocument8 pagesWeekly State of SA ReservoirsivaldeztNo ratings yet
- DRRR - ToS and Test Question - 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesDRRR - ToS and Test Question - 2nd QuarterCP Yttrep91% (11)
- River Patterns and Their MeaningDocument60 pagesRiver Patterns and Their Meaninggeology1No ratings yet
- Elements of WeatherDocument11 pagesElements of WeatherAngel BalayongNo ratings yet
- Tsunamis: Presented By: Palak Arora 9 CDocument17 pagesTsunamis: Presented By: Palak Arora 9 CVanita KhungerNo ratings yet
- HydrologyDocument50 pagesHydrologyArvind JainNo ratings yet
- Understanding Floods: Causes, Impacts and TypesDocument34 pagesUnderstanding Floods: Causes, Impacts and TypesjyotiangelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Mass Balance Questions and Answers: B. The Concentration Does Not Change With TimeDocument4 pagesLecture 6 - Mass Balance Questions and Answers: B. The Concentration Does Not Change With TimeAndrew SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Inundation EriksdaleDocument1 pageInundation EriksdaleKoert OosterhuisNo ratings yet
- The Biology of the Southern OceanDocument107 pagesThe Biology of the Southern OceanEllie M.100% (1)
- MSC Zoology PaperDocument5 pagesMSC Zoology PaperkamranNo ratings yet
- DGCA Meteorology Question PaperDocument4 pagesDGCA Meteorology Question PaperKrithika R68% (28)
- Endorheic Basin: Éndon 'Within') andDocument8 pagesEndorheic Basin: Éndon 'Within') andForty 106.9 fm radioNo ratings yet
- 9 - ATPL Questions MeteorologyDocument99 pages9 - ATPL Questions MeteorologyRitwik Chowdhury100% (1)
- SINTLAW UnclosDocument20 pagesSINTLAW UnclossujeeNo ratings yet
- Surface Water and Ground Water Interaction: Ohio Department of Natural Resources Division of Water Fact SheetDocument2 pagesSurface Water and Ground Water Interaction: Ohio Department of Natural Resources Division of Water Fact SheetAzwanAliNo ratings yet
- Corals CabaitanDocument20 pagesCorals CabaitanNiño Jess Mar MechaNo ratings yet
- CE378 Chapter3 Hydrograph Final 6Document25 pagesCE378 Chapter3 Hydrograph Final 6Mahmoud MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Disputed South China Sea shoal claimed by China, Taiwan, and the PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDisputed South China Sea shoal claimed by China, Taiwan, and the PhilippinesGrace Angelie C. Asio-SalihNo ratings yet
- AMOC Weakening May Be Delayed by Warming Indian OceanDocument4 pagesAMOC Weakening May Be Delayed by Warming Indian Oceanmojo xoxoNo ratings yet
- Catch The Fundy Action: AttractionsDocument10 pagesCatch The Fundy Action: AttractionsgeoformNo ratings yet