Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DuPont Analysis On JNJ
Uploaded by
viettuan91Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DuPont Analysis On JNJ
Uploaded by
viettuan91Copyright:
Available Formats
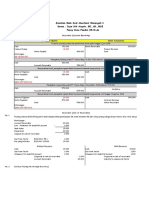
DuPont Analysis: Decomposition of ROE
Annual Data
Quarterly Data
Decomposing ROE involves expressing net income divided by shareholders' equity as the product of component ratios.
Two-Component Disaggregation of ROE
Three-Component Disaggregation of ROE
Five-Component Disaggregation of ROE
Two-Way Decomposition of ROA
Four-Way Decomposition of ROA
Decomposition of Net Profit Margin
See Also:
Novartis AG (NVS), DuPont analysis
Pfizer Inc. (PFE), DuPont analysis
Merck & Co. Inc. (MRK), DuPont analysis
Show More
Two-Component Disaggregation of ROE
Annual Data
Quarterly Data
Johnson & Johnson, decomposition of ROE
ROE
ROA
Leverage
Dec 29, 2013
18.68%
10.42%
1.79
Dec 30, 2012
16.74%
8.94%
1.87
Dec 31, 2011
16.94%
8.51%
1.99
Dec 31, 2010
23.57%
12.96%
1.82
Dec 31, 2009
24.25%
12.95%
1.87
Source: Based on data from Johnson & Johnson Annual Reports
The primary reason for the increase in Return on Equity (ROE) over 2013 year is the increase in profitability measured by Return on Assets
(ROA).
ADVERTISEMENT
Top
Three-Component Disaggregation of ROE
Annual Data
Quarterly Data
Johnson & Johnson, decomposition of ROE
ROE
Net Profit Margin
Asset Turnover
Leverage
Dec 29, 2013
18.68%
19.40%
0.54
1.79
Dec 30, 2012
16.74%
16.14%
0.55
1.87
Dec 31, 2011
16.94%
14.87%
0.57
1.99
Dec 31, 2010
23.57%
21.65%
0.60
1.82
Dec 31, 2009
24.25%
19.82%
0.65
1.87
Source: Based on data from Johnson & Johnson Annual Reports
The primary reason for the increase in Return on Equity (ROE) over 2013 year is the increase in profitability measured by Net Profit Margin.
ADVERTISEMENT
Top
Five-Component Disaggregation of ROE
Annual Data
Quarterly Data
Johnson & Johnson, decomposition of ROE
ROE
Tax Burden
Interest Burden
EBIT Margin
Asset Turnover
Leverage
Dec 29, 2013
18.68%
0.89
0.97
22.37%
0.54
1.79
Dec 30, 2012
16.74%
0.77
0.96
21.79%
0.55
1.87
Dec 31, 2011
16.94%
0.78
0.96
19.89%
0.57
1.99
Dec 31, 2010
23.57%
0.79
0.97
28.26%
0.60
1.82
Dec 31, 2009
24.25%
0.78
0.97
26.18%
0.65
1.87
Source: Based on data from Johnson & Johnson Annual Reports
The primary reason for the increase in Return on Equity (ROE) over 2013 year is the increase in effect of taxes measured by Tax Burden.
ADVERTISEMENT
Top
Two-Way Decomposition of ROA
Annual Data
Quarterly Data
Johnson & Johnson, decomposition of ROA
ROA
Net Profit Margin
Asset Turnover
Dec 29, 2013
10.42%
19.40%
0.54
Dec 30, 2012
8.94%
16.14%
0.55
Dec 31, 2011
8.51%
14.87%
0.57
Dec 31, 2010
12.96%
21.65%
0.60
Dec 31, 2009
12.95%
19.82%
0.65
Source: Based on data from Johnson & Johnson Annual Reports
The primary reason for the increase in Return on Assets (ROA) over 2013 year is the increase in profitability measured by Net Profit Margin.
ADVERTISEMENT
Top
Four-Way Decomposition of ROA
Annual Data
Quarterly Data
Johnson & Johnson, decomposition of ROA
ROA
Tax Burden
Interest Burden
EBIT Margin
Asset Turnover
Dec 29, 2013
10.42%
0.89
0.97
22.37%
0.54
Dec 30, 2012
8.94%
0.77
0.96
21.79%
0.55
Dec 31, 2011
8.51%
0.78
0.96
19.89%
0.57
Dec 31, 2010
12.96%
0.79
0.97
28.26%
0.60
Dec 31, 2009
12.95%
0.78
0.97
26.18%
0.65
Source: Based on data from Johnson & Johnson Annual Reports
The primary reason for the increase in Return on Assets (ROA) over 2013 year is the increase in effect of taxes measured by Tax Burden.
ADVERTISEMENT
Top
Decomposition of Net Profit Margin
Annual Data
Quarterly Data
Johnson & Johnson, decomposition of Net Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin
Tax Burden
Interest Burden
EBIT Margin
Dec 29, 2013
19.40%
0.89
0.97
22.37%
Dec 30, 2012
16.14%
0.77
0.96
21.79%
Dec 31, 2011
14.87%
0.78
0.96
19.89%
Dec 31, 2010
21.65%
0.79
0.97
28.26%
Dec 31, 2009
19.82%
0.78
0.97
26.18%
Source: Based on data from Johnson & Johnson Annual Reports
The primary reason for the increase in Net Profit Margin over 2013 year is the increase in effect of taxes measured by Tax Burden.
You might also like
- FAC Thomas CookDocument11 pagesFAC Thomas CookAkshay UtkarshNo ratings yet
- DuPont AnalysisDocument25 pagesDuPont AnalysisAyush100% (1)
- Profitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Document11 pagesProfitability Ratios: Return On Asset (ROA)Saddam Hossain EmonNo ratings yet
- Case 03Document9 pagesCase 03Sajieda FuadNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis With Ratio Analysis On: Glenmark Pharmaceutical LimitedDocument41 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis With Ratio Analysis On: Glenmark Pharmaceutical LimitedGovindraj PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Comparative Ratio Analysis of Three Listed Companies of ICT SectorDocument16 pagesComparative Ratio Analysis of Three Listed Companies of ICT Sectorzubair07077371100% (1)
- Financial Analysis of Askari Bank 2012Document28 pagesFinancial Analysis of Askari Bank 2012usmanrehmat100% (1)
- IV: Dupont Analysis: Return On Equity RatioDocument5 pagesIV: Dupont Analysis: Return On Equity RatioLưu Tố UyênNo ratings yet
- Feeding The Chinese Via ReutersDocument40 pagesFeeding The Chinese Via Reutersshawn2207No ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Financial Statements of Hindustan Petroleum and Bharat Petroleum.Document37 pagesRatio Analysis of Financial Statements of Hindustan Petroleum and Bharat Petroleum.Kumar RitambharNo ratings yet
- BK Adbl 030079 PDFDocument18 pagesBK Adbl 030079 PDFPatriciaFutboleraNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument10 pagesRatio AnalysisSandesha Weerasinghe0% (1)
- High Performance Tire Case Study Report 1 (Group 7)Document24 pagesHigh Performance Tire Case Study Report 1 (Group 7)AZLINDA MOHD NADZRINo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis ITCDocument15 pagesRatio Analysis ITCVivek MaheshwaryNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument27 pagesRatio AnalysisSwati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis: (Type The Document Subtitle)Document16 pagesRatio Analysis: (Type The Document Subtitle)Maliha JahanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Financial Statement AnalysisDocument7 pagesAssignment Financial Statement AnalysisNeel ManushNo ratings yet
- DuPont AnalysisDocument5 pagesDuPont Analysisআশিকুর রহমান100% (1)
- A. Liquidity Ratio: Current Assets Include Cash and Bank Balances, Marketable Securities, Debtors andDocument28 pagesA. Liquidity Ratio: Current Assets Include Cash and Bank Balances, Marketable Securities, Debtors andYugendra Babu KNo ratings yet
- Dupont Analysis ReportDocument15 pagesDupont Analysis Reportchrome.asares.keneth64No ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Indigo Airlines From Lender's PerspectiveDocument12 pagesFinancial Analysis of Indigo Airlines From Lender's PerspectiveAnil Kumar Reddy100% (1)
- Ratio Analysis of Shinepukur Ceremics Ltd.Document0 pagesRatio Analysis of Shinepukur Ceremics Ltd.Saddam HossainNo ratings yet
- Organ Oseph: Waste Industries USA, IncDocument24 pagesOrgan Oseph: Waste Industries USA, IncAlex DiazNo ratings yet
- Abellano Fria Mae A - Prelim Exam Macctngprei01Document4 pagesAbellano Fria Mae A - Prelim Exam Macctngprei01Nelia AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Profitability RatiosDocument48 pagesProfitability RatiosMohan RajNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis - LowesDocument2 pagesFinancial Analysis - Lowesanand737No ratings yet
- Case 3: BNL StoresDocument16 pagesCase 3: BNL StoresAMBWANI NAREN MAHESHNo ratings yet
- ABELLANO FRIA MAE A - PRELIM EXAM MAcctngPrEI01Document5 pagesABELLANO FRIA MAE A - PRELIM EXAM MAcctngPrEI01Nelia AbellanoNo ratings yet
- Shire PLCDocument5 pagesShire PLCIulian NanuNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Financial AccountingDocument15 pagesAssignment of Financial AccountingBhushan WadherNo ratings yet
- Abbott India: Performance HighlightsDocument11 pagesAbbott India: Performance HighlightsAngel BrokingNo ratings yet
- Namitha K Advanced Strategic ManagementDocument7 pagesNamitha K Advanced Strategic ManagementNamitha kNo ratings yet
- Thomson Reuters Company in Context Report: Baker Hughes Incorporated (Bhi-N)Document6 pagesThomson Reuters Company in Context Report: Baker Hughes Incorporated (Bhi-N)sinnlosNo ratings yet
- Article 2 Roe Breakd Dec 12 5pDocument5 pagesArticle 2 Roe Breakd Dec 12 5pRicardo Jáquez CortésNo ratings yet
- HBS Toolkit License AgreementDocument6 pagesHBS Toolkit License Agreementcool_gayathiriNo ratings yet
- Series 1: 1. Profit Margin RatioDocument10 pagesSeries 1: 1. Profit Margin RatioPooja WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument36 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementsvasuuumNo ratings yet
- Du Pont PresentationDocument20 pagesDu Pont PresentationPreetesh ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis: Year 2011-2012 - 2013 - 2014 - 2015 - Compound Annual 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Growth Rate (CAGR) %Document4 pagesEconomic Analysis: Year 2011-2012 - 2013 - 2014 - 2015 - Compound Annual 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 Growth Rate (CAGR) %ISHIKA MISHRA 20212622No ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument36 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementsHery PrambudiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument50 pagesChapter 4 - Analysis of Financial Statementsnoor_maalik100% (1)
- Du Pont Analysis: South Indian BankDocument7 pagesDu Pont Analysis: South Indian BankKashish AroraNo ratings yet
- Report On Profitability Ratios: Gross Profit MarginDocument8 pagesReport On Profitability Ratios: Gross Profit MarginakhilNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Plastic Corporation: Group Assignment Principles of Accounting CLASS SE1417Document9 pagesVietnam Plastic Corporation: Group Assignment Principles of Accounting CLASS SE1417Đông AnhNo ratings yet
- Case No. 1 BWFM5013Document8 pagesCase No. 1 BWFM5013Shashi Kumar NairNo ratings yet
- Inventory Turn Over Ratio Inventory Turnover Is A Showing How Many Times A Company's Inventory Is Sold andDocument23 pagesInventory Turn Over Ratio Inventory Turnover Is A Showing How Many Times A Company's Inventory Is Sold andrajendranSelviNo ratings yet
- Dishman Pharmaceuticals: Performance HighlightsDocument10 pagesDishman Pharmaceuticals: Performance HighlightsAngel BrokingNo ratings yet
- Glaxosmithkline Pharma: Performance HighlightsDocument11 pagesGlaxosmithkline Pharma: Performance HighlightsAngel BrokingNo ratings yet
- Oto Ar 2012Document228 pagesOto Ar 2012hakiki_nNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis (ch-6)Document38 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis (ch-6)Wares KhanNo ratings yet
- Aci Reuters BuyDocument6 pagesAci Reuters BuysinnlosNo ratings yet
- K ElectricDocument9 pagesK ElectricAyesha Bareen.No ratings yet
- JJSF Section II Revised Final 2Document4 pagesJJSF Section II Revised Final 2api-252422597No ratings yet
- Analysis of Financial StatementsDocument48 pagesAnalysis of Financial StatementsNguyễn Thùy LinhNo ratings yet
- Fiancial Analysis of Rolls RoyceDocument8 pagesFiancial Analysis of Rolls RoyceJohn Jerrin BabuNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of ASOSDocument21 pagesFinancial Analysis of ASOSDerayo Biz Amod0% (1)
- Volcan Compañía Minera S A A BVL VOLCABC1 FinancialsDocument37 pagesVolcan Compañía Minera S A A BVL VOLCABC1 FinancialsAlex ShuanNo ratings yet
- Ros, RoaDocument2 pagesRos, RoaThu Võ ThịNo ratings yet
- Term Paper - Accounting and FinanceDocument3 pagesTerm Paper - Accounting and FinanceJayNo ratings yet
- Project White - FM v2 0 (161213) - Cardiology - Onco - Neuro - Management FeeDocument1 pageProject White - FM v2 0 (161213) - Cardiology - Onco - Neuro - Management Feeviettuan91No ratings yet
- Interpret The Beta. Note That Ethwhite Is Left Out As Reference, To Used To Compare With Asian and BlackDocument4 pagesInterpret The Beta. Note That Ethwhite Is Left Out As Reference, To Used To Compare With Asian and Blackviettuan91No ratings yet
- Activity Based Costing Questions and NotesDocument11 pagesActivity Based Costing Questions and Notesviettuan9167% (3)
- Financial Market & Institutions ExamDocument7 pagesFinancial Market & Institutions Examviettuan91No ratings yet
- Intrinsic Stock Value FCFF On JNJ StockDocument6 pagesIntrinsic Stock Value FCFF On JNJ Stockviettuan91No ratings yet
- Investment Appraisal LectureDocument19 pagesInvestment Appraisal Lectureviettuan91No ratings yet
- Capital Asset Pricing Model For Johnson and JohnsonDocument6 pagesCapital Asset Pricing Model For Johnson and Johnsonviettuan91No ratings yet
- Stock-Trak Project 2013Document4 pagesStock-Trak Project 2013viettuan91No ratings yet
- Arbitrage Trading Making Money Risk FreeDocument22 pagesArbitrage Trading Making Money Risk FreeJermaine WeissNo ratings yet
- Avion Case StudyDocument5 pagesAvion Case StudyAnurag GauraitraNo ratings yet
- Non-Store Retailing, Retail Management and Trends in RetailingDocument27 pagesNon-Store Retailing, Retail Management and Trends in RetailingJay Mark T. ParacuellesNo ratings yet
- Logistics MGT (SCM U4)Document20 pagesLogistics MGT (SCM U4)Badal RoyNo ratings yet
- Consumer Perception On Green MarketingDocument14 pagesConsumer Perception On Green MarketingSWATHINo ratings yet
- Fabm 2Document2 pagesFabm 2Elijah MillerNo ratings yet
- Puja Rahangdale HR 16Document2 pagesPuja Rahangdale HR 16Luis VivasNo ratings yet
- Audit Test 1 QPDocument3 pagesAudit Test 1 QPSamarth RochwaniNo ratings yet
- Mission Aims and Objectives TNTDocument2 pagesMission Aims and Objectives TNTOmar ogiNo ratings yet
- PIZZA USA CASE STUDIES Operation Managment AssingmentDocument8 pagesPIZZA USA CASE STUDIES Operation Managment Assingmentaman KumarNo ratings yet
- Global Strategy and SustainabilityDocument21 pagesGlobal Strategy and Sustainabilityshanzayharoon786No ratings yet
- Prashant Khorana - ES1 - ZumwaldDocument3 pagesPrashant Khorana - ES1 - ZumwaldPrashant KhoranaNo ratings yet
- Bana WaxDocument25 pagesBana WaxHababes Sotelo SolomonNo ratings yet
- Chap 06 Inventory Control ModelsDocument112 pagesChap 06 Inventory Control ModelsFatma El TayebNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management AssignmentDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Management AssignmentSumit Mishra MishraNo ratings yet
- Foreign Exchange Hedging Strategies at General MotorsDocument8 pagesForeign Exchange Hedging Strategies at General MotorsMoh. Farid Adi PamujiNo ratings yet
- Kleppners Advertising Procedure 18Th Edition Lane Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument39 pagesKleppners Advertising Procedure 18Th Edition Lane Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFsiliquavexinglygmnfo100% (9)
- Jawaban Soal, Akuntansi Menengah 1Document7 pagesJawaban Soal, Akuntansi Menengah 1Mira OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Iteb G621 256Document2 pagesIteb G621 256saket reddyNo ratings yet
- Investment Options in IndiaDocument25 pagesInvestment Options in IndiaamiNo ratings yet
- Sales and Distribution Management AssignmentDocument8 pagesSales and Distribution Management AssignmentTanvi DahuleNo ratings yet
- Strategic Competitive Analysis Questionnaire 1Document2 pagesStrategic Competitive Analysis Questionnaire 1Ajay BadhayaNo ratings yet
- Design and Size of Sales TerritoriesDocument26 pagesDesign and Size of Sales TerritoriesImran Malik100% (1)
- Cash Vs Accrual Basis of AccountingDocument8 pagesCash Vs Accrual Basis of AccountingThanupa KopparapuNo ratings yet
- Operational Managment ProjectDocument191 pagesOperational Managment ProjectAamir Raza86% (14)
- Chapter-I Executive Summary: Page 1 of 63Document63 pagesChapter-I Executive Summary: Page 1 of 63Sarang MeshramNo ratings yet
- Mco 05Document8 pagesMco 05rammar147No ratings yet
- Mckesson Purchase History From June 2019 To Aug 2020Document876 pagesMckesson Purchase History From June 2019 To Aug 2020Rao Arslan RajputNo ratings yet
- Certified Business AccountantDocument11 pagesCertified Business AccountantRicky MartinNo ratings yet
- Chart of Accounts (UACS) 2015 - DescriptionsDocument115 pagesChart of Accounts (UACS) 2015 - DescriptionsCherry BepitelNo ratings yet