Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit6 - No Man Is An Island - Discovering Language
Uploaded by
kamtecOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit6 - No Man Is An Island - Discovering Language
Uploaded by
kamtecCopyright:
Available Formats
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.
Kais
K. Benleulmi
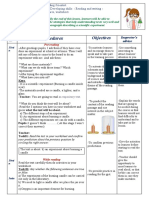
Unit 06 : No Man is an Island
Time Allotted : 6 hours
Rubric: Discovering the language
Lesson contents:
Lexical:
- Vocabulary relevant to disasters.
- Reporting verbs.
Grammatical:
- Reported speech with the present perfect and past simple .
Phonological :
- Prnunciation of the final ed- Silent letters .
Aims :
Time
To elicit information from a report .
To practise / recycle the language forms useful in a report .
To transfer information from a pie chart into a written report ..
To work out vocabulary items in suitable contexts .
T tasks and lessons steps
Lesson One :
Step One : Think it over
( Brain storming )
Aim : To introduce the topic
and some vocabulary items
related to disasters .
Methodology
- What does the picture represent?
- What does the map represent?
- What is there on this map?
- When was the photo taken? Why?
- They flashed news on TV whenever
there was something new.
Learners' tasks
Flood.
A map of Algeria.
A sign of an
earthquake.
On November 10th, 01.
To use theme in their
reports.
- What do people in other places do ?
How ? They donate.
-
They help .
They give money ,
blood , food , clothes
They are worried .
They think that these
disasters might happen
again/they might be the
victims next time .
Pps do .
- What about people affected in these
kinds of disasters ? Why ? .
Step two : Discovering the
language .
Before you read .
Act 1:
Aim : to make the learners
know the symbols and their
significance.
Picture page 120 .
- T asks Pps to read the words in the
green column to master the
pronunciation of the final ed
-.
They may use their
native language .
Others may say a
- T asks the first question :
- What does the first symbol represent ? crescent .
It is a cross .
.
Pps may give different
- Yes , it is a Red Crescent .
answers .
- What does the second symbol
Pps listen and take
represent ?
notes
- Yes , it is a Red Cross .
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
K. Benleulmi
They help people in
cases of natural
disasters .
Some Pps say : yes ,
others say : no , they
are volunteers .
- In what situations in people's lives do Whenever people need
help in cases of natural
they operate ? .
disasters .
- Which of the duties below do they for Pps listen and choose .
fulfill ? .
Fund raising .
1. Fund raising
Collecting food aids
2. Collecting food aids .
3. Preventing man made disasters Helping with medical
care .
Providing assistance in
4. Cleaning affected areas .
emergency situations .
5. Helping with medical care .
6. Providing assistance in
emergency situation .
- What is their task in common ?
- Do people working in these charities
get paid ? .
Lesson Two :
As you read
Act 2 :
Aim : to give the learners a
reason for a careful reading .
Read the report and answer the
following questions .
1. What is the report about ? .
2. In which paragraph does the
author speak about the
findings / results , and in which
one does he give the
interpretation ?
3. Why does the reporter use
interestingly in the second
paragraph? .
4. Does the report confirm the
older generations worry about
society or not ? Why ? .
Class discussion :
Ts reading :
Collective correction on BB .
1. The report is about youth
charity.
2. the author writes about the
findings or the results in the
2nd and his interpretation in
the 3rd .
3. Because of the unexpected
results , the author used the
word to show his surprise .
4. No , it doesn't .Because
according to the data 2010
gathered , people ( young ) are
more charitable than their
parents thought.
Pp read the act .
Then read the report .
Pps try to answer on
their ex-copy books .
Give their own answers
Collective correction
on BB .
Writing phase Pps
write down on their
copy books
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
K. Benleulmi
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
After you read
Aim : to get learners elicit the
rule through comparison and
discussion
Lesson Three :
Practice :
Aim: to practise the reported
speech.
Activity one page 122 .
K. Benleulmi
Read the following examples and
compare
1. Have you ever experienced an
emergency situation ? .
2. Youth 2010 asked the teenagers
if they had ever experienced an
emergency situation .
3. Did you contribute anything to
help ? .
4. youth 2010 reporter asked them
whether they had contributed
anything to help them during
emergency situation .
- What about the tenses ? .
- What about the question mark?
- Then as a rule : what do we
have ? .
- When we report a question ,
changes must happen .
1. We introduce the reporting
verb.
2. We omit the inverted commas .
3. We change the tense of verbs if
the introductory verb is not in
the present .
4. We omit question mark .
5. We change the word order .
6. When we report yes/no
questions , the reporting verb is
followed by if or whether .
The 1st and the 3rd
sentences are direct
speech sentences .
The 2nd and the 4th are
indirect speech stces .
There are differences
between tenses in the
direct questions and the
reported ones .
We use "asked" in the
indirect speech
sentences.
It is called a reporting
verb like: said, told,
informed, announced
We use first the present
perfect then it is turned
into past perfect.
We used in the 3rd
example the simple
past, then turned into
past perfect.
The question make is
omitted in the indirect
speech stces.
Now, let's practise this rule:
Read the interview in the box, then ask * PP read the
instruction, read the
and answer questions: as in the
example then do the
dialogue below: Eg: P: 122.
activity.
* PP ask whenever they
* T. explains the example.
need help.
* T. turns round, checks and helps.
* PP are asked to give
Collective correction on BB.
their answers.
You: What did the interview ask Bill
Gates?
Your partner: He asked him where he
had grown up.
You: And what did he answer?
Your partner: He said that he had
grown up in Seattle, Washington.
You: What did the interviewer ask
him?
Your partner: He asked him where he
had discovered his interest in
Software.
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
K. Benleulmi
Your partner: He answered that he had
discovered his interest in Software at the
Private Lakeside school.
You: What did the interviewer ask him?
Your partner: He asked him when had
begun computer programming .
You: And what did he answer?
Your partner: He answered that he had
begun computer programming at the age
of 13.
Your partner: He asked him when he
had entered Harvard University.
Your partner: He said that he had
entered Harvard University in 1973.
Your partner : He asked him whether
he had developed the first computer
there.
Your partner: He answered that he
developed it there.
Your partner: He asked him how long
he had been head of Microsoft.
Your partner: He said that he had been
head of Microsoft for more than 20
years.
Your partner: He asked him why he
had set up Bill Gates Foundation.
Your partner: He answered that he had
been always thoughtful about others.
That's why he had done it.
Your partner: He asked him how much
money he had donated that year.
Your partner: He said that he donated
3.2 million $.
Your partner: He asked him which
charities he had supported so far.
Your partner: He answered that he had
supported organizations working in the
field of Health and Learning.
Your partner: He asked him if his wife
had helped him.
Your partner: He said that she helped
him
Activity two:
*Turn the quotes into reported speech
using the verbs given to you.
*T. explains the instruction.
T. turns round, checks and helps.
T. reminds them of the rule of the
introductory.
*What happens if the introductory verb
is in the simple present or present
perfect?
Remark:
For "you" the same
question are repeated.
We focus only on:" your
partner, "report.
PP. read the instruction
Read the exercise
Do the task
PP. the tense of the verb
do not change when
reporting.
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
K. Benleulmi
Collective correction on BB.
a: 1- Albert Einstein doubts whether
present day Americans have become any
happier since their grand parents settled
in the country.
2- Albert Einstein doubted whether
present day Americans had become any
happier since their grand parents had
settled in the country.
b: 1- John Donne writes that no man is
an island.
2- John Donne wrote that no man is an
island.
c: 1- Bertrand Russel says that three
passions had governed his life longing
for love, the search for knowledge and
an unbearable pity for the sufferings of
mankind.
2- Beitrand Russel says that three
passions had governed his life: the
longing for love, the search for
knowledge and an unbearable pity for
the sufferings of mankind.
Lesson four:
Write it wright
Aim:
To transfer a visual form into a
written report.
T. asks PP to use information in the pie
chart and the lay out to write a report
about:
*Why Americans elected Bill Gates
Man of the year 2005.
Use verbs from the yellow box to write
sentences using the given percentages.
T. use these sentences to write your
report starting as follows:
Why was Bill Gates elected the Man of
the year.
PP. listen to the teacher
- Read the instruction
again.
- Study the pie chart.
30% of our informants
believed that because he
sponsored vaccination
campaigns.
25% regarded him as a
self made man .
20% thought that
because he donated
money to improve
learning opportunities.
15% reckoned that he
had made the PC
available for everyone.
10% stated that he wrote
Business @ the speed of
thought which had
helped to solve business
problems.
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
K. Benleulmi
Introduction :
Bill Gates was elected Man of the year
2005. we have carried out a public
Opinions survey to find out about the
reasons why he was so elected.
Here are our findings:
30% of our informants.
Lesson five:
Say it loud and clear:
Aim: to learn about silent letters
in contrast with other sounds.
*observe these examples :
knife, know, honest, wring, white,
knock, column, listen, often,
1Say them loudly.
2Contrast them with other
sounds.
PP. observe the
examples.
Read them loudly
Key, look, worried, flower,
a: What are the differences?
PP. (K)in knife is not
pronounced, but (K) in
key is pronounced.
(W) in wring is not
pronounced, and (W) is
pronounced in worried.
Silent letters
*These kinds of letters are called.
Listen to your teacher reading the poem -honest, serving
and the dialogue and cross out the letters -taught, knew
which are not pronounced.
-what why when
-where who
st
1 : the poem
some PP read
*your what
2nd : the dialogue.
one autumn. Column
condemned. Prisoners.
Solemnly marched
Singing hymns
*your what
knights knocked. Knave
knuckles. Knotted
knew. When. Knelt
knees. Knife. Knitted
knikers.
*T. asks pupils to read again slowly.
*Class discussion.
*Correction on BB.
Some pupils read the
poem again.
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
K. Benleulmi
Activity 2: p: 124
Find the spelling form of the transcribed
words in the box :
T. gives an example: how do we
transcribe the word : know?.
-Know is the spelling word
-/n
/ is the transcribed form
*what about the letter (K)
*Correction on BB.
Spelling
Listen
report
Famine
Doctor
cupboard
-It is not pronounced.
-it is a silent letter.
PP do the task
Spelling
Writing
Wednesday
Starve
Cut
cute
*Can you give other examples
Lesson six:
Working with words:
Work out reporting verbs in
suitable contexts.
Activity one:
/n
1-Remark: it is a class work (group) (not
a homework)
*T brings at least 5 dictionaries from the
library to be used by pps in checking the
meaning of words :
T. Check the meaning of the verbs in
your dictionary. Then report each of the
quotes using some of them:
T.turns round checks and helps.
a: A thief speaking to a police officer "I
have stolen her bag".
the thief admitted that he had stolen
her bag .
b: A mother speaking to a doctor."
Please, doctor save my son!"
the mother prayed / begged/ the
doctor to save her son.
C: A school girl speaking to her teacher:
"sorry, I am late".
she apologized for being late.
d: a mother speaking to her child:
"Come here".
she ordered him to go there.
e: A boy friend speaking to another boy
friend: "Let's go out for a walk".
He suggested to go out for a walk.
PP thinks of other
examples.
PP. must work in
groups. They make their
groups of 5 pupils at
least.
- Each group looks for a
number of words.
-admit: /
/ allow to
enter, let in. agree that
(s.th) is true.
-beg: ask for (money,
food) ask seriously
and with feeling.
-request: act of politely
asking for sth.
-Report:/
/ give an
account of (sth) heard,
done
-refuse: not give accept
or do (sth).
-pray: speak to God
hope very strongly.
- promise: make a
written or a spoken
statement to do sth.
-persuade: cause (s.b) to
do some thing by
Soufi A/Hafid Secondary School.Kais
K. Benleulmi
discussion reasoning
f: A girl friend speaking to an other girl
to convince.
friend: "If I were you, I would consult a - order: command ask
doctor"
for (s.b) to supply sth.
she advised her girl friend to consult a - apologize: say that one
doctor.
is sorry.
g: "The vase is broken. It's your fault".
-threaten: give
she blamed him / her for breaking the warning. /
/.
vase.
h: "You're right. The flowers are really
beautiful".
Leila agreed that the flowers were
really beautiful.
*Class discussion.
*Correction on BB.
Activity two:
Go through the rest of the reporting
verbs in act one. Then get students to
use the remaining verbs.
-blame: consider (s.b/
sth) to be responsible for
(sth).
-agree: have the same
opinion as somebody.
- suggest: /
/
bring an idea into the
mind.
- insist: demand
strongly.
-deny:
-advise:
PP. use the remaining
verbs in full sentences.
You might also like
- Unit Exam-House On Mango StreetDocument6 pagesUnit Exam-House On Mango StreetJean Paul Colon Rivera100% (1)
- The Lottery Lesson TestDocument2 pagesThe Lottery Lesson TestSIMPLEJGNo ratings yet
- جميع حلول تمارين كتاب اللغة الانجليزية سنة ثانية ثانويDocument56 pagesجميع حلول تمارين كتاب اللغة الانجليزية سنة ثانية ثانويATMMOBILIS66% (59)
- How To Take Notes From A Textbook - HACK MY STUDYDocument5 pagesHow To Take Notes From A Textbook - HACK MY STUDYebenashNo ratings yet
- Streaming 3rd Year StudentsDocument53 pagesStreaming 3rd Year StudentsKADDOUR95% (20)
- Budding Scientis Unit PlanDocument27 pagesBudding Scientis Unit PlanBelhadj Nasreddine50% (4)
- 2nd Year Lesson Plans - Waste Not Want Not - NEWDocument17 pages2nd Year Lesson Plans - Waste Not Want Not - NEWdidia96% (26)
- Unit Three Planning Waste Not Want NotDocument31 pagesUnit Three Planning Waste Not Want NotLamri Bey80% (10)
- Best of South AfricaDocument224 pagesBest of South Africasven67% (3)
- Waste Not Want Not (Tests & Exams)Document15 pagesWaste Not Want Not (Tests & Exams)sara wilson100% (3)
- Safety First 3rd YearDocument13 pagesSafety First 3rd Yeardaloulasud3092% (12)
- 1as - Unit 1 - Getting ThroughDocument34 pages1as - Unit 1 - Getting Throughsabahsousou74% (34)
- CreateSpace ArduinoDocument57 pagesCreateSpace ArduinoMichel MüllerNo ratings yet
- كل مذكرات السنة الأولى في الانجليزيةDocument33 pagesكل مذكرات السنة الأولى في الانجليزيةasmasamsouma92% (26)
- I Wander LonelyDocument4 pagesI Wander LonelysoskahobbaNo ratings yet
- TSOS Project Self-Study CourseDocument2 pagesTSOS Project Self-Study CourseAvery CloverNo ratings yet
- Unit 03 Our Findings ShowDocument19 pagesUnit 03 Our Findings ShowChakerhamdi100% (1)
- Unit Plan 1AS Unit 2 Communication The Press Our Findings Show 1Document23 pagesUnit Plan 1AS Unit 2 Communication The Press Our Findings Show 1Bilal Serg57% (7)
- 2as Files'Document105 pages2as Files'Śŋŏw Wĥíțě86% (79)
- Explore Science Through ExperimentsDocument13 pagesExplore Science Through Experimentsnouna86% (22)
- Waste Not Want NotDocument14 pagesWaste Not Want NotMouhamed Choukal76% (25)
- Unit 4 Back To Nature)Document21 pagesUnit 4 Back To Nature)daloulasud3075% (64)
- Make Peace (Assessment, Revision)Document3 pagesMake Peace (Assessment, Revision)Abdechakour Hadji92% (12)
- First Year Communication Unit on The Press and ReportingDocument29 pagesFirst Year Communication Unit on The Press and ReportingImad Ossama100% (1)
- 1 As Unit One Getting Through Lesson PlanDocument26 pages1 As Unit One Getting Through Lesson PlanRihabSallam83% (6)
- Continental - Dry - Temperate - TropicalDocument10 pagesContinental - Dry - Temperate - TropicalDiza San100% (1)
- Unit Two Making Peace Unit Planning.Document34 pagesUnit Two Making Peace Unit Planning.scytheer544785% (75)
- Waste Not Want NotDocument11 pagesWaste Not Want NotKhelif AhmedNo ratings yet
- Budding Scientist (R, W) CAPESDocument4 pagesBudding Scientist (R, W) CAPESSelma Ouchaou100% (2)
- 2AS - Unit 1 - DiversityDocument14 pages2AS - Unit 1 - Diversityarmy ka100% (1)
- Dirah high school lesson on business lettersDocument17 pagesDirah high school lesson on business lettersAiluro PhileNo ratings yet
- Budding Unit Plan, LessonDocument20 pagesBudding Unit Plan, Lessonsara wilson100% (1)
- Make Peace ExamDocument3 pagesMake Peace ExamBelhadj Nasreddine100% (9)
- Unit Plan - 1AS (Unit 2 - Communication - The Press Our Findings Show) - 1Document23 pagesUnit Plan - 1AS (Unit 2 - Communication - The Press Our Findings Show) - 1yamami452088% (40)
- 106 Unit THREE - Our Findings ShowDocument2 pages106 Unit THREE - Our Findings ShowFayçal Serhani33% (3)
- Waste Want Resources Sustainable: Not Not World AND DevelopmentDocument28 pagesWaste Want Resources Sustainable: Not Not World AND Developmentcharfi abdelhamid100% (1)
- Mohamed Ben Teftifa HS Group Makes PeaceDocument3 pagesMohamed Ben Teftifa HS Group Makes Peacenouna80% (25)
- 2as 1st Term Test Make PeaceDocument3 pages2as 1st Term Test Make Peacesabrina's world100% (5)
- Budding Scientist 2ASDocument48 pagesBudding Scientist 2ASسدن آرما100% (1)
- Budding Scientist: Technology and InnovationDocument13 pagesBudding Scientist: Technology and InnovationKhalil HassaniNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Waste Not Want Not 2asDocument27 pagesUnit 3 Waste Not Want Not 2assofianeNo ratings yet
- Once Upon A Time Unit AssessmentDocument1 pageOnce Upon A Time Unit AssessmentAmel75% (4)
- First Term Test of English 2nd Year Literary StreamDocument2 pagesFirst Term Test of English 2nd Year Literary Streammoufida50% (2)
- 1AS Unit One Getting Through. First Lesson PlaningDocument4 pages1AS Unit One Getting Through. First Lesson PlaningIhsane Dz100% (2)
- World Resources Unit Focuses on Sustainable Waste ManagementDocument10 pagesWorld Resources Unit Focuses on Sustainable Waste Managementfatiha100% (3)
- The New Lesson Plan Science and FictionDocument20 pagesThe New Lesson Plan Science and Fictionbouaroura100% (1)
- 1st Year Lesson Comparing Email and Snail MailDocument4 pages1st Year Lesson Comparing Email and Snail MailAZZOUZ OMARNo ratings yet
- Writing A Reply To Kirsi's Email: Unit: Getting Through SequenceDocument1 pageWriting A Reply To Kirsi's Email: Unit: Getting Through Sequenceaya brahimi100% (2)
- Reading & Writing Make PeaceDocument3 pagesReading & Writing Make PeaceMadani KhayraNo ratings yet
- 1AS - Unit 1 - Getting Through 1Document20 pages1AS - Unit 1 - Getting Through 1Khadidja Belaskri69% (150)
- Unit Four Planning Budding ScientistDocument27 pagesUnit Four Planning Budding ScientistNina NounaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Back To Nature (Lesson 0)Document7 pagesUnit 3 - Back To Nature (Lesson 0)Djaafar MessaoudiNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Make PeaceDocument23 pagesLESSON PLAN Make PeaceSalem ZemaliNo ratings yet
- Effects Deforestation Cutting TreesDocument23 pagesEffects Deforestation Cutting Treestatto50% (2)
- Unit 1 Signs of The The Time - Level 2Document2 pagesUnit 1 Signs of The The Time - Level 2api-29370123375% (8)
- Our Findings Show 1st LessonDocument3 pagesOur Findings Show 1st Lessonسليمان تايبي100% (1)
- 2 As Exam No Man Is An IslandDocument3 pages2 As Exam No Man Is An Islandmaian saja67% (3)
- UNIT 1 Signs of The TimeDocument18 pagesUNIT 1 Signs of The TimeSofiane Zaoui100% (1)
- Ill-Gotten Needs Never Prosper: Teaching WorksheetsDocument50 pagesIll-Gotten Needs Never Prosper: Teaching WorksheetsImene Mïmî100% (3)
- Unit Plan Two 3 RD Year ConsumersDocument11 pagesUnit Plan Two 3 RD Year Consumersdaloulasud30100% (2)
- Unit 1 Say It Clear Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Say It Clear Lesson PlanbeatrixNo ratings yet
- Expressing Purpose 2as Waste Not Want NotDocument1 pageExpressing Purpose 2as Waste Not Want NotEnglish Teacher100% (4)
- Expressing Purpose Waste NotDocument2 pagesExpressing Purpose Waste Nottarik sadouki100% (1)
- Class: 2nd Year Scientific Stream Diagnostic TestDocument1 pageClass: 2nd Year Scientific Stream Diagnostic TestPrincess OtakuNo ratings yet
- 284 SpeakUp2Document2 pages284 SpeakUp2Vitório AflaloNo ratings yet
- Celebrites and MediaDocument2 pagesCelebrites and Mediaalfredo.gonzgomNo ratings yet
- Drill-Direct and Indirect SpeechDocument10 pagesDrill-Direct and Indirect SpeechJean Claudine MandayNo ratings yet
- Deformance and InterpretationDocument21 pagesDeformance and InterpretationRajamanitiNo ratings yet
- Job Application Letter Format PakistanDocument7 pagesJob Application Letter Format Pakistanvyp0bog1w1m3100% (2)
- TKT CLIL Handbook For TeachersDocument31 pagesTKT CLIL Handbook For TeacherscherryNo ratings yet
- 2024 GKS-U University Available Departments (Hankuk University of Foreign Studies - U)Document3 pages2024 GKS-U University Available Departments (Hankuk University of Foreign Studies - U)thitiwanngoenthongNo ratings yet
- World EnglishesDocument2 pagesWorld EnglishesXuan Mai ĐàmNo ratings yet
- Phrases To Use To Confirm InformationDocument3 pagesPhrases To Use To Confirm InformationZita JeremiásNo ratings yet
- The Most Common English IdiomsDocument19 pagesThe Most Common English IdiomsNino TskitishviliNo ratings yet
- Question #20Document12 pagesQuestion #20Елена ХалимоноваNo ratings yet
- Kalinga CharacteristicsDocument3 pagesKalinga CharacteristicsHeleeneNo ratings yet
- ADifferentGuidedTour KEYDocument2 pagesADifferentGuidedTour KEYACADEMIA POSÍO / GEMANo ratings yet
- Lif Vis Pol Int Short 0-1bDocument2 pagesLif Vis Pol Int Short 0-1bmarcinfast1No ratings yet
- Introduction To Java ProgrammingDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Java ProgrammingChike ChukudebeluNo ratings yet
- Resume WizardDocument1 pageResume WizardSinbad SaNo ratings yet
- We LikeDocument48 pagesWe LikeRahul H.No ratings yet
- IRREGULAR VERB CONJUGATIONSDocument7 pagesIRREGULAR VERB CONJUGATIONSPROF - David LaparraNo ratings yet
- Syllubs 1567484677Document3 pagesSyllubs 1567484677Savithri MurthyNo ratings yet
- Does EFL Readers Lexical and Grammatical Knowledge Predict Their Reading Ability Insights From A Perceptron Artificial Neural Network StudyDocument23 pagesDoes EFL Readers Lexical and Grammatical Knowledge Predict Their Reading Ability Insights From A Perceptron Artificial Neural Network StudyHeinous Hy43naNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Aplicativo Ingles.Document10 pagesTrabajo Aplicativo Ingles.Ronal Espinoza PachecoNo ratings yet
- Adv. English SSLM. Magdadaro.Q1-Module4Document7 pagesAdv. English SSLM. Magdadaro.Q1-Module4Maria Rica Ramirez MagdadaroNo ratings yet
- Basic Phonetics and English Phonology Week 12 The SyllableDocument38 pagesBasic Phonetics and English Phonology Week 12 The SyllableHashem A. al-ShukriNo ratings yet
- From Inis Fraoigh To Innisfree... and Back Again - Sense of Place in Poetry in Irish Since 1950 - Gearoid DenvirDocument25 pagesFrom Inis Fraoigh To Innisfree... and Back Again - Sense of Place in Poetry in Irish Since 1950 - Gearoid DenvirSoumili MoitraNo ratings yet
- C++ Interview Questions and Answers - TypesDocument7 pagesC++ Interview Questions and Answers - TypesAmritaRupiniNo ratings yet
- LEsson Plan For 16th Week EnglishDocument9 pagesLEsson Plan For 16th Week EnglishMUHAMAD AZRI BIN JOHARI KPM-GuruNo ratings yet