Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cfmeu Health and Safety Audit
Uploaded by
suhanisingh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views12 pagesreport
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentreport
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views12 pagesCfmeu Health and Safety Audit
Uploaded by
suhanisinghreport
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Environmental & Occupational
Health and Safety Unit
HEALTH SAFETY &
ENVIRONMENTAL
WORKSITE AUDIT
This health and safety audit report is advisory only. This information is not
intended to be relied upon to meet any legal standards of care. This safety audit is
for the recipient only and is not a substitute for professional advice in relation to all
matters of occupational health and safety. The CFMEU disclaims all liability for
any loss or damage whether foreseeable or not suffered by any person acting
upon any information, representation or statement in this document.
1
CFMEU HEALTH AND SAFETY AUDIT
CONTENTS:
1. Management responsibilities
2. Amenities
3. First aid
4. Traffic Management
5. Training and consultation
6. Electrical
7. Scaffolding
8. Hazardous Materials
9. Cranes and Rigging
10. Plant and Equipment
11. Excavation and trenching
12. Oxy-acetylene cutting and welding
13. Confined space
14. Work at heights
15. Environmental
2
CFMEU HEALTH AND SAFETY AUDIT
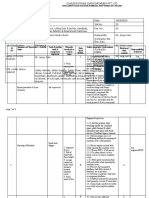
1. MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITIES
YES NO COMMENT
1.1 Is there an Environmental, Health and Safety
Management Plan developed for this project?
1.2 Is the Health and Safety Policy displayed and
signed by management?
1.3 Are emergency response procedures developed
and displayed at appropriate locations?
1.4 Is there safe access in and out of the site?
1.5 Is there suitable public protection where building
works are next to, or over public access ways?
ie gantries, hoardings
1.6 Does site management consult with OH&S
representatives?
1.7 Are site personnel kept informed on
incident/accident data?
1.8 Are personnel records, certificates of competency
and induction records kept on site?
1.9 Are contractor/sub contractor method statements
& J SAs provided before commencing each major
task?
1.10 Is the management involved in regular, formal
site inspections?
1.11 Are appropriate signs posted at entrance ie hard
hats, report to site office?
1.12 Are necessary permits developed and retained
on site?
2. AMMENITIES
2.1 Is there covered access from inclement weather?
2.2 Is crib hut seating adequate for the numbers on
site?
2.3 Are crib huts hygienic, tidy bins with bin liners?
2.4 Are there adequate numbers of toilet cubicles
with clean tidy washing facilities?
3
2.5 Are there notice boards in crib huts?
2.6 Cool clean drinking water available at appropriate
locations?
2.7 Are there toilets for women?
3. EMERGENCY RESPONSE/FIRST AID
3.1 Are site personnel aware of the first aid location
and is it clearly identified?
3.2 Is the first aid box adequately stocked?
3.3 Are there adequate first aid personnel clearly
identified for contact.
3.4 Are first aid treatment records kept on site?
3.5 Are emergency response personnel trained in site
emergency procedures? Last test date of emergency
procedure ___/___/_________
3.6 Emergency siren and equipment ie stretcher,
trauma kit, oxy viva.
4. TRAFFIC MANAGEMENT
4.1 Has a traffic management plan been selected or
provided?
4.2 Are all roadwork signs and devices installed
according to the plan?
4.3 Have safety barriers been installed correctly?
4.4 Have the needs of other road users, pedestrians
and pedestrian support vehicles been provided for?
5. TRAINING AND CONSULTATION
5.1 Is there a site induction for new starters to
project?
5.2 Are induction records maintained on site?
5.3 Do all site personnel hold a current industry
induction card?
5.4 Is emergency response and evacuation training
conducted?
4
5.5 Are personnel trained in fire precautions and use
of fire extinguishers?
5.6 Is training for identified hazardous work
processes conducted? i.e. confined spaces.
5.7 Are visitors inducted as to site hazards and
procedures?
5.8 Have managers and supervisors attended a
health and safety course?
5.9 Are hazards, incidents, and accidents reported to
site personnel at toolbox meetings?
5.10 Do supervisors conduct regular toolbox
meetings?
5.11 Do supervisors carry out risk assessments, and
incident reports?
5.12 Are health and safety committees established
on site?
5.13 Are health and safety committee meetings held
regularly?
5.14 Are health and safety committee meeting
minutes discussed at toolbox meetings and displayed
in the crib hut?
5.15 Where subcontractors collaborate, interface, co-
operate or work together, is everybody involved
inducted together by the builder?
6. ELECTRICAL
6.1 Does a licensed electrician test portable electrical
equipment every quarter?
6.2 Are all electrical leads supported above the
ground with insulated hooks or stands?
6.3 Are extension leads correctly connected to
temporary power boards?
6.4 Are temporary power boards weatherproof?
6.5 Is the electrical testing register maintained on
site?
6.6 Are temporary power boards installed 30 meters
from all work areas?
6.7 Is all electrical equipment in good condition?
5
7. SCAFFOLDING
7.1 Scaffold types in use
7.2 Are standards on solid foundations with adequate
soul boards?
7.3 Is there adequate bracing in all directions?
7.4 Are the ties correctly positioned and fixed? (Every
3 bays, 2 lifts)
7.5 Are there working platforms at required locations?
7.6 Are handrails and kickboards installed on
scaffolds over 2mts?
7.7 Are mesh guards installed where a risk of
material falling may occur? i.e. bricks.
7.8 Is there access to and from all working platforms?
7.9 Are working platforms the correct distance from
the working face?
7.10 Are ladders of an industrial grade?
7.11 Are ladders secured top and bottom and
exceeding platform 1 meter at a 4:1 pitch?
7.12 Are scaffold boards secured to prevent uplift
from winds?
7.14 When completed, are scaffolds tagged with
scaftag system or similar?
7.15 Are signs or barriers erected for incomplete
scaffolds?
7.16 Are scaffolds regularly inspected and records
kept of details?
8. HAZARDOUS MATERIALS
8.1 Are Material Safety Data Sheets available for all
hazardous substances?
8.2 Is a chemical register kept on site?
8.3 Do site personnel understand MSDSs ?
6
8.4 Are appropriate signs posted at storage areas on
site?
8.5 Are containers appropriately labeled?
8.6 Are chemical storage facilities provided with
appropriate containment area? i.e. bunds and
containment medium
8.7 Is appropriate PPE supplied when using
hazardous materials.
9. CRANES AND RIGGING
9.1 Crane certificates of inspection provided and kept
on record at site.
9.2 Crane drivers certificate of competency and
licenses. Intermediate riggers for concrete panel
erection.
9.3 Is the manufacturers instruction book and cranes
log book in crane and completed daily?
9.4 Cranes set up on firm level ground; engineers
specification details where applicable? ie suspended
floors & near excavations
9.5 Riggers and dogmen certified and recorded and
used for crane operations?
9.6 Is there a safe working zone established for crane
operation?
9.7 Is all rigging equipment in good condition with
inspection records kept on site?
10. PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
10.1 Are excavators used as cranes fitted with
velocity valves and SWL stamped on boom?
10.2 Are manufacturers instructions for lifting
capacities in all directions in excavator cabins?
10.3 Are roll over protection systems on all
earthmoving equipment?
10.4 Where applicable, are reverse and visual alarms
operating and audible?
7
10.5 Are isolation procedures developed for
maintenance and repair work on plant?
10.6 Are Elevated Work Platform logbooks and daily
inspections completed, recorded and kept on the
machine?
10.7 Do only licensed operators operate Elevated
Work Platform?
10.8 Are Elevated Work Platforms used on a firm
level surface?
10.9 Are hoists erected on stable ground and tied into
the structure?
10.10 Is overhead protection provided for operator
with material hoist?
10.11 Are limit switches correctly installed?
10.12 Is the operators manual readily accessible?
10.13 Are all combustion type engines only operated
outdoors or with extra ventilation?
eg portable welders, generators etc.
10.14 Are seatbelts installed in the forklift and used
by the operators?
11. EXCAVATION AND TRENCHING
11.1 Are excavation permits developed and
implemented on site?
11.2 Is a site plan available for existing and new
services?
11.3 Are new and existing services identified on site
and controls implemented to prevent accidental
contact?
11.4 Are procedures in place to avoid isolated
personnel working in excavations?
11.5 Is air quality testing carried out to ensure toxic
gas build up does not occur?
11.6 Is signage and barricading used to reduce
erosion or collapse?
11.7 Are excavations regularly inspected for erosion
or collapse?
8
11.8 Are excavations battered or benched to prevent
collapse?
11.9 Has safe access/egress been provided for deep
excavations?
11.10 Has spoil material and equipment been stored
away from excavation edges?
11.11 Are dust control measures in place?
12. OXY-ACETYLENE CUTTING &
WELDING
12.1 Are hot work permits developed for site?
12.2 Are permits completed and signed by
supervisors and kept on site?
12.3 Are bottles stored upright in a lockable trolley?
12.4 Fire fighting equipment is located with bottles or
at work area?
12.5 Flash back arresters fitted to both the hand
piece and at the bottles?
12.6 Correct personnel protective equipment for
oxy/acetylene works?
12.7 Is lifting box or cradle used for crane lifting of
bottles?
12.8 Are hoses and fittings in good condition?
12.9 Is welding equipment in good working order?
12.10 Are screens and ventilation provided for
welding works?
12.11 Is there any risk of dust exploding?
13. CONFINED SPACE
13.1 Are permits developed for confined space
works?
13.2 Are emergency procedures developed for
confined space works?
13.3 Is emergency rescue equipment available? i.e.
radios, RPD, air monitors.
13.4 Are personnel trained for confined space works
including sentries?
9
14. WORK AT HEIGHTS
14.1 Are procedures developed for working at
heights?
14.2 Are emergency procedures developed for
retrieval of a fallen or injured person?
14.3 Are personnel trained for working at heights?
14.4 Is safe access and egress provided for
personnel?
14.5 Are harnesses inspected and inspection records
kept on site?
14.6 Are anchorage points assessed by a qualified
engineer?
14.7 Are barriers, barricades and signs erected to
delineate restricted areas?
15. ENVIRONMENTAL
15.1 Is water or other means used to prevent dust
generation?
15.2 Are roadways defined and used by site
personnel?
15.3 Is there adequate watering equipment when
cutting and chasing?
15.4 Are noisy work tasks defined, controls used to
reduce noise levels and signage utilised?
15.5 Is sound pressure level testing performed to
ensure compliance?
15.6 Are signs posted to alert personnel?
15.7 Is hearing protection provided and used where
required?
16. PERSONNEL PROTECTIVE
EQUIPMENT (PPE)
16.1 Are signs displayed to identify the required
PPE?
16.2 Is PPE readily available and complying with the
relevant Australian standards?
16.3 Are personnel trained in the use of the specific
PPE?
10
16.4 Are facilities provided for the maintenance and
storage of PPE?
Whats a Site Audit and What Does it Mean?
Many workers have been exposed to hazardous substances in the past because
people didnt know they were there. Employers have an obligation under the
Victorian Occupational Health & Safety (Asbestos) Regulations 2003. (Part 5
Asbestos in workplace and Part 6 demolition including refurbishment to ensure
that a site audit is done before your job starts. Its better for all parties if this is
done properly because it avoids any exposures or other problems and its usually
cheaper to do it when theres not other people wanting to work in the same area).
What to look for When Reading Site Audits:
Check that the audit is up to date.
Make sure its a full hazard audit and not just and asbestos audit. The
audit should identify anything and everything that may be hazardous to the
people working on the site or the general public. This could include
chemicals, PCBs (in light fittings or elsewhere), lead paints, synthetic
mineral fibres or asbestos.
When reading an audit, make sure that it has
a) A register of all hazardous materials that may be present
b) An asbestos register identifying all possible asbestos containing
materials
c) The condition the material is in
d) The friability the material is in
e) The friability of any asbestos
f) Areas where access could not be obtained during the auditing process.
No access should be allowed in those areas until they are opened
and assessed for any hazardous materials.
Ensure that all different coloured floor tiles have been analysed for
asbestos content. Asbestos floor tiles re non-homogenous, that is the
asbestos content is not evenly distributed throughout the tile. The content in
floor tiles is usually about 2% - 3%. It is very common for one consultant to
obtain a clear result and for another to find asbestos.
Asbestos can be presented in the form of: White Chrysotile
Brown Amosite
Blue Crocidolite
11
PCBs can be found in capacitors and electrical equipment. Paper insulated
capacitors manufactured by DUCON between 1960 and 1974, operated on
AC voltages, mainly 250V, 330V, 370V, 400V and 600V, contained PCBs.
Capacitors are usually enclosed in an oval shaped aluminium tin can
approximately 40mm x 25mm (long and short axis) and an overall length of
112mm. There is usually a model number beginning with letters APA, APB,
APC, APD or APF. There is also a 4 digit number which indicates the week
and year manufacturing, eg 2264 means the 22
nd
week in 1964.
Other capacitors manufactured in the same period are rectangular in shape
with a painted or unpainted tin plate can and have model numbers
beginning with the letters GPA, GPB or GPM.
Capacitors are also found in electrical control circuits, usually in a grey
coloured time plated enclosure manufactured in the same period with model
numbers being with GP will also contain PCBs.
Before any work starts make sure that hazardous materials have been
stripped and removed. If any are to remain onsite they must be clearly
labelled and identifiable, to ensure that everyone knows that hazardous
materials are present.
12
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- HIRADocument57 pagesHIRAAnonymous Uc25fP83% (6)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- JSA-Site Survey and Downloading of Relay ConfigurationDocument4 pagesJSA-Site Survey and Downloading of Relay Configurationfrancis_e_tan100% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- OHS Policies and Procedures ManualDocument13 pagesOHS Policies and Procedures Manualismailines100% (2)
- Attachment 16. Site HSSE PlanDocument79 pagesAttachment 16. Site HSSE PlanCristianMontoyaMujica100% (1)
- KCC DATASHEET Technical Data Sheet Thinner-024 EngDocument2 pagesKCC DATASHEET Technical Data Sheet Thinner-024 EngIsabelo AbaoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Installation and Maintenance ActivityDocument11 pagesElectrical Installation and Maintenance ActivityAlle Eiram Padillo100% (1)
- Plant Manual IOM S PDFDocument829 pagesPlant Manual IOM S PDFluis olivoNo ratings yet
- Ecm 367 - Project and Construction ManagementDocument84 pagesEcm 367 - Project and Construction ManagementMuhd Muqhrey50% (2)
- 010-MS For Grouting PDFDocument33 pages010-MS For Grouting PDFKöksal PatanNo ratings yet
- Construction HAZID Workshop Report PK Pipeline-FinalDocument18 pagesConstruction HAZID Workshop Report PK Pipeline-FinalsaqibNo ratings yet
- Work OrderDocument9 pagesWork Orderiyappa civil100% (1)
- Accura Operation Manual Version 2.0 20160621Document64 pagesAccura Operation Manual Version 2.0 20160621Duy DangNo ratings yet
- Health, Safety & WellbeingDocument13 pagesHealth, Safety & WellbeingImran ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MST For Roof Slab WaterproofingDocument6 pagesMST For Roof Slab Waterproofingdina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Hacking Work & Patch BackDocument4 pagesHacking Work & Patch BackJamruz JamilNo ratings yet
- PI - Standard - Feed Mill Standard - Issue 2.1 - 23-May-2017 PDFDocument29 pagesPI - Standard - Feed Mill Standard - Issue 2.1 - 23-May-2017 PDFRomy Bennouli TambunanNo ratings yet
- 6 Common TesdaDocument28 pages6 Common TesdaStevenNo ratings yet
- Qhse Prequalification QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesQhse Prequalification QuestionnaireaymenmoatazNo ratings yet
- JSA Format Erection of Column 901-C-01Document9 pagesJSA Format Erection of Column 901-C-01sakthi venkatNo ratings yet
- Kristal Violet PDFDocument4 pagesKristal Violet PDFGanjar Tri Gita AzhariNo ratings yet
- Jurnal K3 Terbit EnglishDocument6 pagesJurnal K3 Terbit Englishadhan efendiNo ratings yet
- Elvex Is Committed To Innovative SolutionsDocument48 pagesElvex Is Committed To Innovative SolutionssanpkaruNo ratings yet
- Msds Shell Thermia BDocument7 pagesMsds Shell Thermia BMuhammad Nurul AminNo ratings yet
- TPC-HOMO02 - (No FDA)Document5 pagesTPC-HOMO02 - (No FDA)Nicky AfrilliaNo ratings yet
- COVID Handbook and Outbreak Management Plan (4974)Document32 pagesCOVID Handbook and Outbreak Management Plan (4974)Rachit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Final ReportDocument28 pagesIndustrial Training Final ReportMuhammad Harith Hilmi Zen AzharNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGEAR 600 XP 220Document12 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Product Name: MOBILGEAR 600 XP 220muhammad imtiazNo ratings yet
- Group # 28-Introduction To ISO 45001-Mini-ProjectDocument14 pagesGroup # 28-Introduction To ISO 45001-Mini-ProjectA to z type videosNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingDocument20 pagesSafety Data Sheet: SECTION 1: Identification of The Substance/mixture and of The Company/undertakingsantiagoNo ratings yet
- Diesel SDS enDocument10 pagesDiesel SDS enfidan muradovaNo ratings yet