Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acceleration 2 ωV dW dW 2 2 0.75 1 dt dt 2 2 0.75 1 2 5 rad/s
Uploaded by
AvinashGauravOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acceleration 2 ωV dW dW 2 2 0.75 1 dt dt 2 2 0.75 1 2 5 rad/s
Uploaded by
AvinashGauravCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
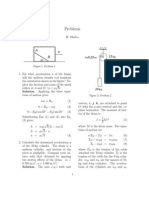
A link OB is rotating with a constant angular velocity of 2 rad/s in counter clockwise
direction and a block is sliding radially outward on it with an uniform velocity of 0.75 m/s
with respect to the rod, as shown in the figure below. If O A = 1 m, the magnitude of the
absolute acceleration of the block at location A in m/s
2
is
O
A
B
a. 3
b. 4
c. 5
d. 6
[2013 : 1 mark]
Ans. (C)
}
Acceleration
2 V
dW dW
2 2 0.75 1
dt dt
2 2 0.75 1 2
5 rad/s
= + o
| |
= + o =
|
\ .
= +
=
2. A planar closed kinematic chain is formed with rigid links PQ = 2.0 Q, QR = 3.0 m, RS = 2.5 m
and SP = 2.7 m with all revolute joints. The link to be fixed to obtain rocker (rocker-rocker)
mechanism is
a. PQ
b. QR
c. RS
d. SP
[2013 : 1 mark]
Ans. (C)
PQ 2.0 m. QR 3.0 m, RS 2.5 m, SP 2.7 m = = = =
a. If shortest line PQ = 2.0 m is fixed, then we will give double crank.
b. If link adjacent to shortest is fixed, then we will get crank-rocker mechanism.
c. If we fix coupler RS, we will get double rocker mechanism.
3. If two nodes are observed at a frequency of 1800 rpm during whirling of simply supported
long slender rotating shaft, the first critical speed of the shaft in rpm is
a. 200
b. 450
c. 600
d. 900
[2013 : 1 mark]
Ans. (B)
1
2
4
3
n
n
n
n
n
First frequency f
Second frequency 4f
Third frequency 9f
1800 4f
1800
f 450 rpm
4
=
=
=
=
= =
4. A compound gear train with gears P, Q, R and S has number of teeth 20, 40, 15 and 20
respectively. Gears Q and R are mounted on the same shaft as shown in the figure below.
The diameter of the gear Q is twice that of the gear R. IF the module of the gear R is 2 mm,
the centre distance in mm between gears P and S is
+ + +
R
Q
P
S
a. 40
b. 80
c. 120
d. 160
[2013 : 2 mark]
Ans. (B)
P Q R S
Q R
R
Given : T 20; T 40; T 15; T 20
Q and R are compound gear
D 2D
m 2mm
centre distance (CD) between 'P' and 'S' ?
= = = =
=
=
=
( )
R
R
S R
R S
S
S
Q R
D
Modulem
T
D 2 15 30 mm
D D
T T
D 30
15 20
D 40 mm
D 2D given
=
= =
=
=
=
=
Q
Q
P
'
Q
P
P
P Q
Q
D 2 30 00 mm
D
D
T
T
T 20
D D 60 30 mm
T 40
= =
=
= = =
P P
D 30 mm r 15 mm = =
( ) ( )
P P
Q Q
R R
S S
P Q R S
D 30 mm r 15 mm
D 60 mm r 15 mm
D 30 mm r 15 mm
D 40 mm r 20 mm
Centre distance
CD r r r r
80 mm
= =
= =
= =
= =
= + + +
=
5. A flywheel connected to a punching machine has to supply energy of 400 Nm while running
at a mean angular speed of 20 rad/s. If the total fluctuation of speed is not to exceed 2%
the mass moment of inertia of the flywheel in kg-m
2
is
a. 25
b. 50
c. 100
d. 125
[2013 : 2 mark]
Ans (A)
( )
s
2
s
2
2
Given : E 400 Nm
20 rad/s
C 2% 0.04
I ?
As we know
E l C
400 l 20 0.04
l 25 kg-m
=
e=
= =
=
A = e
=
=
6. In the mechanism given below, if the angular velocity of the eccentric circular disc is 1 rad/s,
the angular velocity (rad/s) of the follower link for the instant shown in the figure is
[Note : All dimensions are in mm.]
5 45
25
a. 0.05
b. 0.1
c. 5.0
d. 10.0
[2012 : 1 mark]
Ans. (B)
7. The following are the data for two crossed helical gears used for speed reduction:
Gear 1 : Pitch circle diameter in the plane of rotation 80 mm and helix angle 30
0
Gear 2 : Pitch circle diameter in the plane of rotation 120 mm and helix angle 22.5
0
if the
input speed is 1440 rpm, the output speed in rpm is
a. 1200
b. 900
c. 875
d. 720
[2012 : 1 mark]
Ans. (B)
2 1
1 2
0
0
2
2
For helical gear
N D cos
Velocity ratio
N D cos
80cos 30
120cos 22.5
N 1440 0.625
N 900 rpm
|
= =
|
=
=
=
8. A concentrated mass m is attached at the centre of a rod of length 2L as shown in the figure.
The rod is kept in a horizontal equilibrium position by a spring of stiffness k. For very small
amplitude of vibration, neglecting the weights of the rod and spring, the undamped natural
frequency of the system is
m
k
L L
a.
k
m
b.
2k
m
c.
k
2m
d.
4k
m
[2012 : 2 mark]
Ans. (D)
Taking moments about 0
O
kx x
mg
L L
d
( )
n
kx 2L mg L
mg
x
2k
x
now from similar triangles
2L L
x
2
Using static deflection of mass
g 4k
m
=
=
o
=
o =
e = =
o
9. A double parallelogram mechanism is shown in the figure. Note that PQ is a single link. The
mobility of the mechanism is
P
Q
a. 1
b. 0
c. 1
d. 2
[2011 : 1 mark]
Ans. (C)
2.1 For the four-bar linkage shown in the figure, the angular velocity of link AB is 1 rad/s. The
length of link CD is 1.5 times the length of link AB. In the configuration shown, the angular
velocity of link CD in rad/s is
B
1 rad/s
C
A
D
a. 3
b. 3/2
c. 1
d. 2/3
[2011 : 2 mark]
Ans. (D)
10. A mass of 1 kg is attached to two identical springs each with stiffness k = 20 kN/m as shown
in the figure. Under frictionless condition, the natural frequency of the system in Hz is close
to
1 kg
x
k
k
a. 32
b. 23
c. 16
d. 11
[2011 : 2 mark]
Ans. (A)
equivalent
3
Since springs are in parallel hence
K K K 2K
1 2K
Frequency
2 m
1 2 20 10
2 1
31.83
= + =
=
t
=
t
=
11. A disc of mass m is attached to a spring of stiffness k as shown in the fig. The disc rolls
without slipping on a horizontal surface. The natural frequency of vibration of the system is
k
m
a.
1 k
2 m t
b.
1 2k
2 m t
c.
1 2k
2 3m t
d.
1 3k
2 2m t
[2011 : 2 mark]
Ans. (C)
( )
2
2
2 2
l Kxr 0
mr
mr K r. r 0
2
3
mr Kr 0
2
2K
0
3m
1 2K
Natural frequency
2 3m
u + =
| |
+ u + u =
|
|
\ .
u + u =
u + u =
=
t
12. Mobility of a statically indeterminate structure is
a. 1 s
b. 0
c. 1
d. 2 >
[2010 : 1 mark]
Ans. (A)
Mobility of degree of freedom for a statically indeterminate structure is always less then
zero.
( )
i.e. F 0
only option A is negative value
F 1
<
s
13. There are two points P and Q on a planar rigid body. The relative velocity between the two
points
a. Should always be along PQ
b. Can be oriented along any direction
c. Should always be perpendicular to PQ
d. Should be along QP when the body undergoes pure translation
[2010 : 1 mark]
Ans. (C)
O
V
P
V
Q
Q
P
Planar rigid body.
PQ
PQ P Q
V Relative velocity between P and Q.
V V V Always perpendicular to PQ.
=
=
14. Which of the following statement is INCORRECT
a. Grashofs rule states that for a planar crank-rocker four bar mechanism, the sum of the
shortest and longest link lengths cannot be less than the sum of the remaining two link
lengths.
b. Inversions of a mechanism are created by fixing different links one at a time.
c. Geneva mechanism is an intermittent motion device.
d. Grueblers criterion assumes mobility of a planer mechanism to be one.
[2010 : 1 mark]
Ans. (A)
Grashofs rule states that for a planar crank rocker four bar mechanism, the sum of shortest
and longest link length is less than the sum of remaining two link length i.e.
s p q + s +
15. Tooth interference in an external involute spur gear pair can be reduced by
a. Decreasing center distance between gear pair
b. Decreasing module
c. Decreasing pressure angle
d. Increasing number of gear teeth
[2010 : 1 mark]
Ans. (D)
16. The natural frequency of a spring-mass system on earth is
n
. e The natural frequency of this
system on the moon
( )
/6
moon earth
g g = is
a. D
b. D
c. D
d. D
e. D
[2010 : 1 mark]
Ans. (A)
n
K
m
e =
17. For the configuration shown, the angular velocity of link AB is 10 rad/s counter clockwise.
The magnitude of the relative sliding velocity (in ms
-1
) of slider B with respect to rigid link CD
is
AB 250
BC 250 3
AC 500
=
=
=
a. 0
b. 0.86
c. 1.25
d. 2.50
[2010 : 2 mark]
Ans. (D)
As AB is perpendicular to slider for given condition, so sliding velocity of slider equals to
velocity of link AB
AB
10 0.25
2.5 m/s
= e
=
=
18. For the epicyclic gear arrangement shown in the figure,
2
100 e = rad/s clockwise (CW) and
arm
80 e = rad/s counter clockwise (CCW). The angular velocity
5
e (in rad/s) is
2
3 4
5
arm Shaft axis
N = Number of teeth for gear I
i
N = 20
2
N = 24
N = 32
N = 80
3
4
5
D
B
C
60
0
A
a. 0
b. 70 CW
c. 140 CCW
d. 140 CW
[2010 : 2 mark]
Ans. (C)
2
arm
2 3 4 5
Given, 100 rad/s
80 rad/s
teeth denoted by N,
N 20, N 24, N 32, N 80
e =
e =
= = = =
Action
3
a 2 5
4
Arm a is fixed and
Gear 2 is given +1 rev.
Arm a fixed Gear 2 + x
Rev. 4s given
Add x + y
20 20 32 1
0 1
24 24 80 3
5x x
0 x
6 3
5x x
y x y y y
6 3
=
+
2
arm
5
x y 100
and y 80
x 100 y 180 rad/s
x 180
y 80
3 3
140 rad/s 140 CCW
e = + =
e = =
= =
e = =
= =
19. A mass m attached to a spring is subjected to a harmonic force as shown in figure. The
amplitude of the forced motion is observed to be 50 mm. The value of m (in kg) is
m
k = 3000 N m
-1
F(t) = 100 cos(100 t)N
a. 0.1
b. 1.0
c. 0.3
d. 0.5
[2010 : 2 mark]
Ans. (A)
( )
0
0
2
Given, F(t) 100 cos (100 t) N
F 100 N
100 rad/s
K 3000 N/m
F
and amplitude, X
K m
=
=
e=
=
=
e
( )
2
3
2
2
as damping is zero.
100
K m 2000
50 10
m 3000 2000
1000
m 0.1 kg
100
e = =
e =
= =
You might also like
- Theory of Machines PDFDocument53 pagesTheory of Machines PDFShanmukha SundaramNo ratings yet
- MECH1230 Exam Paper v4 2013 2014 SolutionsDocument18 pagesMECH1230 Exam Paper v4 2013 2014 SolutionssebNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22Document62 pagesLecture 22adilafzalkhan4264No ratings yet
- SolutionsTests MEbDocument53 pagesSolutionsTests MEbmayur_lanjewarNo ratings yet
- 07 - Rotational Kinematics and MechanicsDocument9 pages07 - Rotational Kinematics and MechanicsBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Theory of MachinesDocument27 pagesTheory of MachinesbalameckNo ratings yet
- HW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationDocument8 pagesHW09 - Angular Momentum Conservation and GravitationBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and BrakesDocument17 pagesPower Transmission: Components Used To Transmit Power: Gears, Belt, Clutch and Brakesrip111176No ratings yet
- This Checks With A Computer SolutionDocument2 pagesThis Checks With A Computer SolutiondearsaswatNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion SDocument13 pagesCircular Motion SRamchandra MurthyNo ratings yet
- School of Computing, Engineering and Mathematics Semester 2 Examinations 2011/2012Document9 pagesSchool of Computing, Engineering and Mathematics Semester 2 Examinations 2011/2012Kish ShenoyNo ratings yet
- (20 Points: 5 Points For Each Force) Determine The Force in Members BC, JK, HI, and HJDocument6 pages(20 Points: 5 Points For Each Force) Determine The Force in Members BC, JK, HI, and HJAlexd10 TNo ratings yet
- Target JEE (Main + Advanced) 2017 PreparationDocument21 pagesTarget JEE (Main + Advanced) 2017 PreparationAnonymous H8TylnrHNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam: Topic VII: StaticsDocument6 pagesDiagnostic Exam: Topic VII: StaticsAnonymous dntnvrKO2100% (1)
- Vibration EngineeringDocument37 pagesVibration EngineeringAlen Benguit II0% (1)
- GATE Mechanical Engineering 2010 question paperDocument8 pagesGATE Mechanical Engineering 2010 question paperaeroherozNo ratings yet
- MechanicsDocument21 pagesMechanicsJett MaunahanNo ratings yet
- Unisa MOM3602 Theory of Machines III Mock Exam 2015 - Preparation Practice ProblemsDocument9 pagesUnisa MOM3602 Theory of Machines III Mock Exam 2015 - Preparation Practice ProblemsDaniel MabengoNo ratings yet
- Solution Collins Cap 8Document460 pagesSolution Collins Cap 8Hamid MasoodNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2010 Question Paper With SolutionDocument50 pagesWBJEE 2010 Question Paper With SolutionLokesh Kumar67% (3)
- WBJEE 2012 Physics and Chemistry Question Paper With SolutionDocument53 pagesWBJEE 2012 Physics and Chemistry Question Paper With SolutionPremKumarKalikiri100% (1)
- Examples - PhysicsDocument8 pagesExamples - Physicslaila1001No ratings yet
- Three Cylinder Engine Turning Moment Diagram AnalysisDocument57 pagesThree Cylinder Engine Turning Moment Diagram AnalysisRasikaPereraNo ratings yet
- Wbjee 2009 Paper With SolutionsDocument53 pagesWbjee 2009 Paper With SolutionsMichelle RobertsNo ratings yet
- WBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsDocument14 pagesWBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution-For-Wb-Jee-2012 Phy - Chem (Page 21 - 35)Document15 pagesSolution-For-Wb-Jee-2012 Phy - Chem (Page 21 - 35)Anupam MNo ratings yet
- Jipmer 2015 Solved QPDocument67 pagesJipmer 2015 Solved QPS Balagopal Sivaprakasam67% (3)
- Ch09 SSM 070904Document26 pagesCh09 SSM 070904VinhTranNo ratings yet
- NSEP Solved Paper 2012Document33 pagesNSEP Solved Paper 2012siteid123No ratings yet
- Sample Exam 1 Phys 213Document7 pagesSample Exam 1 Phys 213Julio César Macías ZamoraNo ratings yet
- R (Ax) 30 KipsDocument9 pagesR (Ax) 30 KipsRey Kevin OrtuosteNo ratings yet
- Gear Trains ProblemsDocument9 pagesGear Trains Problemsa c s Kumar100% (1)
- 15-Chapter Problems SHM Frequency Period AmplitudeDocument4 pages15-Chapter Problems SHM Frequency Period AmplitudeBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Final Exam 2010 Mcg3130Document12 pagesFinal Exam 2010 Mcg3130Brian Pham Vu100% (1)
- Me Year WisebnDocument517 pagesMe Year WisebnShashank PathakNo ratings yet
- 171 390 2 PBDocument23 pages171 390 2 PBCamilaAndreaGrijalbaNo ratings yet
- Calculate torque on square plate due to three forcesDocument5 pagesCalculate torque on square plate due to three forcessnyderbl2100% (1)
- Ejercicios DinamicaDocument36 pagesEjercicios Dinamicajohnfcortes100% (1)
- NSEP Solved Paper 2011Document31 pagesNSEP Solved Paper 2011ShubhamKhannaNo ratings yet
- DOM Unit-IDocument48 pagesDOM Unit-IRamanathan DuraiNo ratings yet
- NSEP Solved Paper 2007Document10 pagesNSEP Solved Paper 2007ShubhamKhannaNo ratings yet
- Adaptive State Controller Swings Up and Balances Inverted PendulumDocument6 pagesAdaptive State Controller Swings Up and Balances Inverted PendulumNeagu AdrianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NoteDocument67 pagesChapter 1 NoteMuhd AzhamNo ratings yet
- ch10 PDFDocument18 pagesch10 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- Machine Design HomeworkDocument9 pagesMachine Design HomeworkTimothy's SpaceshipNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document15 pagesCH 13xperia30100% (1)
- Circular Motion CET Test 8-3-2020 - 1 PDFDocument5 pagesCircular Motion CET Test 8-3-2020 - 1 PDFशिवाजी राख बीडकरNo ratings yet
- Resoluções de Exercícios - Cap. 24 - Princípios de Física Vol. 3Document17 pagesResoluções de Exercícios - Cap. 24 - Princípios de Física Vol. 3HDExtremeNo ratings yet
- JEE Advanced 2015 Physics Paper 1 SolutionsDocument11 pagesJEE Advanced 2015 Physics Paper 1 Solutionsrult007No ratings yet
- p11 AnsDocument8 pagesp11 AnsAnonymous ncBe0B9bNo ratings yet
- 325 - 12-07 - Elasticity - 43-51Document7 pages325 - 12-07 - Elasticity - 43-51Bradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- BCPL Recruitment 2016 Apply Online (30 Vacancies)Document4 pagesBCPL Recruitment 2016 Apply Online (30 Vacancies)AvinashGauravNo ratings yet
- Layouts and Lettering - Technical Drawing Questions and AnswersDocument2 pagesLayouts and Lettering - Technical Drawing Questions and AnswersAvinashGauravNo ratings yet
- Maxicon MechDocument3 pagesMaxicon MechIsmail MswNo ratings yet
- S K Mondal: IES Officer (Railway) Teaching Experience (12 Years)Document9 pagesS K Mondal: IES Officer (Railway) Teaching Experience (12 Years)sayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics P K Nag Exercise Unsolved Problems SolvedDocument265 pagesThermodynamics P K Nag Exercise Unsolved Problems SolvedRavinder Antil90% (40)
- RRB TemplateDocument1 pageRRB TemplateKhushiAgrawalNo ratings yet
- AKU Recruitment for Faculty and Staff PositionsDocument6 pagesAKU Recruitment for Faculty and Staff PositionsAvinashGauravNo ratings yet
- TrussDocument17 pagesTrussNote SuwansomphongNo ratings yet
- Materials Science & Engineering Introductory E-BookDocument13 pagesMaterials Science & Engineering Introductory E-BookSmitha KollerahithluNo ratings yet
- Bank's Seal: Visakhapatnam Steel PlantDocument1 pageBank's Seal: Visakhapatnam Steel PlantAvinashGauravNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Teacher SlidesDocument40 pagesModule 6 Teacher SlidesAvinashGauravNo ratings yet
- ME - GATE 2015 Online Test Series Schedule - ACE Engineering AcademyDocument4 pagesME - GATE 2015 Online Test Series Schedule - ACE Engineering AcademyAvinashGauravNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument21 pagesStrength of MaterialsrssdpmNo ratings yet
- Final Year ProjectsDocument1 pageFinal Year ProjectsSaitejaTallapellyNo ratings yet
- ME - GATE 2015 Online Test Series Schedule - ACE Engineering AcademyDocument4 pagesME - GATE 2015 Online Test Series Schedule - ACE Engineering AcademyAvinashGauravNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument21 pagesStrength of MaterialsrssdpmNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument21 pagesStrength of MaterialsrssdpmNo ratings yet
- Restructuring Egypt's Railways - Augst 05 PDFDocument28 pagesRestructuring Egypt's Railways - Augst 05 PDFMahmoud Abo-hashemNo ratings yet
- Finance at Iim Kashipur: Group 9Document8 pagesFinance at Iim Kashipur: Group 9Rajat SinghNo ratings yet
- Vidura College Marketing AnalysisDocument24 pagesVidura College Marketing Analysiskingcoconut kingcoconutNo ratings yet
- Janome DC6030 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDocument56 pagesJanome DC6030 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian HistoryDocument146 pagesModern Indian HistoryJohn BoscoNo ratings yet
- FALL PROTECTION ON SCISSOR LIFTS PDF 2 PDFDocument3 pagesFALL PROTECTION ON SCISSOR LIFTS PDF 2 PDFJISHNU TKNo ratings yet
- Deluxe Force Gauge: Instruction ManualDocument12 pagesDeluxe Force Gauge: Instruction ManualThomas Ramirez CastilloNo ratings yet
- IMT Ghaziabad PGDM Timetable Term II 2020Document22 pagesIMT Ghaziabad PGDM Timetable Term II 2020Ved JhingranNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document25 pagesLecture 4ptnyagortey91No ratings yet
- Application D2 WS2023Document11 pagesApplication D2 WS2023María Camila AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- WhatsoldDocument141 pagesWhatsoldLuciana KarajalloNo ratings yet
- IMM Indian Oil Case Group 3Document13 pagesIMM Indian Oil Case Group 3Soniya AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesFailure Analysis Case Study PDFScott50% (2)
- Standard Deviation IntroductionDocument3 pagesStandard Deviation IntroductionShyam ShresthaNo ratings yet
- ME6404 Thermal EngineeringDocument18 pagesME6404 Thermal EngineeringAnonymous mRBbdopMKfNo ratings yet
- PCSE_WorkbookDocument70 pagesPCSE_WorkbookWilliam Ribeiro da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Calibration Motion Control System-Part2 PDFDocument6 pagesCalibration Motion Control System-Part2 PDFnurhazwaniNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument1 pageTransistorXhaNo ratings yet
- Cianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogDocument1 pageCianura Pentru Un Suras de Rodica OjogMaier MariaNo ratings yet
- For Coin & Blood (2nd Edition) - SicknessDocument16 pagesFor Coin & Blood (2nd Edition) - SicknessMyriam Poveda50% (2)
- Diemberger CV 2015Document6 pagesDiemberger CV 2015TimNo ratings yet
- How To Check PC Full Specs Windows 10 in 5 Ways (Minitool News)Document19 pagesHow To Check PC Full Specs Windows 10 in 5 Ways (Minitool News)hiwot kebedeNo ratings yet
- Factsheet B2B PunchOut en 140623Document2 pagesFactsheet B2B PunchOut en 140623Curtis GibsonNo ratings yet
- Assessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyDocument4 pagesAssessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Dodd-Frank On Divorcing Citizens 1Document5 pagesThe Effect of Dodd-Frank On Divorcing Citizens 1Noel CookmanNo ratings yet
- AVANTIZ 2021 LNR125 (B927) EngineDocument16 pagesAVANTIZ 2021 LNR125 (B927) EngineNg Chor TeckNo ratings yet
- Amar Sonar BanglaDocument4 pagesAmar Sonar BanglaAliNo ratings yet
- Feasibility StudyDocument47 pagesFeasibility StudyCyril Fragata100% (1)
- IP68 Rating ExplainedDocument12 pagesIP68 Rating ExplainedAdhi ErlanggaNo ratings yet
- SD-SCD-QF75 - Factory Audit Checklist - Rev.1 - 16 Sept.2019Document6 pagesSD-SCD-QF75 - Factory Audit Checklist - Rev.1 - 16 Sept.2019Lawrence PeNo ratings yet