Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cocon Law Flow Chartn Law II Final Flow Chart
Uploaded by
poppy_de_poopy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
120 views5 pagessuper useful for final
Original Title
Cocon law flow chartn Law II Final Flow Chart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsuper useful for final
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
120 views5 pagesCocon Law Flow Chartn Law II Final Flow Chart
Uploaded by
poppy_de_poopysuper useful for final
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
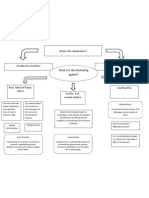
Comparing Levels of Scrutiny
Scrutiny Rational Basis Rational Basis
Plus
Strict Scrutiny
for race, not claimed
to be benign
Strict Scrutiny
for Affirmative
Action
Intermediate
Scrutiny
Intermediate
Scrutiny:
Real Sex
Diffs.
State Interest legitimate
almost anything will
do, even if imagined
by the Court
legitimate but
cannot be driven
by bare desire to
harm group or
animus
compelling
-Risk of imminent
death/violence
-National security
compelling
-Diversity
-Past
discrimination
-National
security
important important-
ish
Fit rationally related;
Court is highly
deferential, will
invent argument for
state
rationally
related but Ct
carefully
scrutinizes fit, in
under/over
inclusive, Ct.
may infer animus
necessary; non-
racial alternatives
exhausted
Fit so close that
little or no
possibility that
illegitimate
racial prejudice
or stereotypes
motivate
substantially
related
substantial
Who bears
the burden of
establishing?
Challenger: Heavy
Presumption of
constitutionality.
Demonstrate
scheme is not
rationally related to
any legit. State
interest
State: either
triggered by some
social groups or
by s prima
facie showing of
animus. Must
establish the
REAL reason
State: Heavy
presumption of
unconstitutionality
State: some
deference to state
regarding the
importance of
state interest and
fit (See Grutter
& Adarand).
State; and the
Court will
pick it out
piece by piece
State,
nominally.
Court defers
to states
conclusions
Purpose Prevent truly
arbitrary exercise of
state power
Protect
disfavored groups
from attempts to
restrict their
rights/liberties by
hostile majorities
Comparing Classifications
Immutable
characteristic
Historically disadvantaged
group
Stigma Discrete/
Insular
Numerical
minority
Stereotypes
Racial Minority X X X X X X
Sex X X X
Alienage ? X X X X
Disability X X X X? X X
Age X
Wealth ? X X X X X
Sexual
Orientation
X X X X
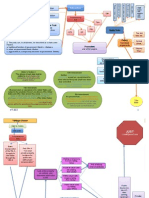
Final Exam Flow Chart
State Action
There is state action if:
1. private actors performing public functions (democratic party excludes Asians from voting in primary)
2. Entanglement (Fashion Valley leases land from city and city provides free parking and Marsh is arrested for trespass when
handing out leaflets)
EPC or SDP/Fundamental Right??
Does the law classify on the basis of a suspect class?
EPC: If classifies on the basis on National Origin, Ethnicity, Alienage, or Race, then subject to Strict Scrutiny
SDP: if restricts a fundamental right (either in Constitution or named by Court)
To determine if something is a fundamental right, must do History & Tradition Analysis
Strict Scrutiny Test:
A law that classifies people on the basis of race fails unless, the government has a compelling state interest (that is a non-racial and
permissible state interest) and the law is necessary to achieve that state interest.
State interest (ends): Does the state have a compelling state interest?
FIT (means): Is the use of race as a classification necessary to achieving that interest and are there no non-racial means available to
achieve that interest?
Affirmative Action: legitimate state interests can be remedying past discrimination or diversity in higher education
If classifies on the basis of gender or legitimacy, then subject to Intermediate Scrutiny.
Intermediate Scrutiny Test
A law that classifies on the basis of gender must have an important state interest and the law must be substantially related to that
state interest.
State Interest
According to VMI, these are NOT valid, important state interests
-no invented or post hoc justifications
-hypothesized effects
-justifications based on stereotyped differences
-State interests pursued just for one sex
Court never says it uses strict scrutiny, but it will strike down laws that
Deny women opportunities that men have
Deny men opportunities or liberties that men have if based on archaic views of men and women roles or gross statistical
generalizations
Court will uphold laws that benefit women if truly remedial & not based on stereotypes
Real Sex Differences
Ct will uphold sex differentiations if
1. Plausibly tied to "real (biological) differences"
Pregnancy, child rearing (get rest from PP)
2. St has institutional reasons to defer to judgment of another branch of govt
Military, immigration
3. Law doesnt advantage or disadvantage men or women and just has a classification in it
**Compromised position
Race is artificial classification is artificial and irrelevant
Most ppl think there are some differences based on sex in ways that are relevant to law making
-Craig v. boren- looks like Ct is ahead of where nation is(ERA never ratified)
Ppl are uncomfortable with idea that men and women are the same
-ct in real sex differences cases comes into line with general population American moderate position
Real Sex differences cases are a big exception to Ct's intermediate scrutiny
Rational Basis is the rule and almost all classifications receive rational basis scrutiny (heightened scrutiny are exceptions)
Rational Basis Test
Laws classification is rationally related to a legitimate state interest.
The asserted state interest doesnt need to the state interest that actually motivated the law. The Court will often imagine
possible state interests: advocates can invent possible rationales.
In some circumstances, the Court says it is applying Rational Basis Scrutiny, but it is more critical in its review.
Rational Basis Plus
Laws classification is rationally related to a legitimate state interest.
but cannot be driven by bare desire to harm group or animus
Must establish the REAL reason behind the law
Ct carefully scrutinizes fit, in under/over inclusive, Ct. may infer animus
If the law is facially neutral, then the must prove that the state purposely discriminated
Facially discriminatory:
No blacks on juries
Whites and Blacks must attend separate schools
Whites may only marry whites
Facially Neutral
Ban on wooden laundries
Changed city boundaries
Test 21: reading comprehension and vocabulary test for police officers
For a facially neutral law to violate the EPC, must have discriminatory results and discriminatory intent
Arlington Heights factors to show Discriminatory Purpose (B/C of not in spite of discriminatory effect)
1. A clear pattern of racially disparate impact that is inexplicable on other grounds
2. Historical background of decision reveals evidence of racial invidiousness
3. Sequence of events leading up to decisions (what events sparked the action)
4. Departures from normal procedure
5. Substantive departures from prior policy-making standards
6. Legislative History contemporary statements by decision makers, minutes and/or reports
If there is are discriminatory results and discriminatory purpose, then use heightened scrutiny (depending on the
classification)
Under-inclusivity: The law does not restrict persons or activities that pose the same or similar risk of harm as those that are restricted.
Over-inclusivity: Some members of the restricted class pose no risk of harm at all.
State Interest
Classification
Classification
State
Interest
You might also like
- Equal Protection Flow ChartDocument1 pageEqual Protection Flow ChartLaurie Smith100% (2)
- Scrutiny Categorization ChartDocument1 pageScrutiny Categorization Chartsuperxl2009No ratings yet
- Conlaw Rights Outline - CODY HOCKDocument49 pagesConlaw Rights Outline - CODY HOCKNoah Jacoby LewisNo ratings yet
- Con Law II NotesDocument190 pagesCon Law II NotesBNo ratings yet
- Con Law Cheat Sheet (Judicial Tests)Document4 pagesCon Law Cheat Sheet (Judicial Tests)Rachel CraneNo ratings yet
- Clear and Present Danger Test: Advocacy of Illegal ActionDocument98 pagesClear and Present Danger Test: Advocacy of Illegal ActionDavid YergeeNo ratings yet
- Con Law Short OutlineDocument17 pagesCon Law Short OutlineJennifer IsaacsNo ratings yet
- Criminal Procedure Epstein Fall 2009-1Document16 pagesCriminal Procedure Epstein Fall 2009-1dicleverNo ratings yet
- Parties. ALIENAGE If One Party Is Citizen of Foreign State, Alienage Jdx. Satisfied, Except WhenDocument2 pagesParties. ALIENAGE If One Party Is Citizen of Foreign State, Alienage Jdx. Satisfied, Except WhenCory BakerNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Preclusion DoctrineDocument11 pagesCivil Procedure Preclusion DoctrinePegah AfsharNo ratings yet
- Con Law II - Final OutlineDocument27 pagesCon Law II - Final OutlineKeiara Pather100% (1)
- Civil Procedure SkeletonDocument8 pagesCivil Procedure SkeletonTOny AwadallaNo ratings yet
- Erie Doctrine ChartDocument3 pagesErie Doctrine ChartAlexis R GaryNo ratings yet
- Con Law II OutlineDocument29 pagesCon Law II OutlineLangdon SouthworthNo ratings yet
- Crim Pro OutlineDocument22 pagesCrim Pro Outlinemichael bradfordNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Key Points on Judicial Power and StandingDocument36 pagesConstitutional Law Key Points on Judicial Power and StandingRebekahNo ratings yet
- Con Law PracticeDocument10 pagesCon Law PracticeNick ArensteinNo ratings yet
- Property Law Outline-Spring 2011Document60 pagesProperty Law Outline-Spring 2011cooperjd88No ratings yet
- Sample Student Family Law Final Exam AnswersDocument6 pagesSample Student Family Law Final Exam Answersfish100% (1)
- Evidence Mini OutlineDocument18 pagesEvidence Mini OutlineAdam GreerNo ratings yet
- Con Law I Final Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesCon Law I Final Cheat SheetKathryn CzekalskiNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure Outline (Detailed)Document91 pagesCivil Procedure Outline (Detailed)par halNo ratings yet
- Charts Due Process and Equal Protection AnalysisDocument3 pagesCharts Due Process and Equal Protection Analysisdsay88No ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesConstitutional Law Cheat Sheet: by ViaMartin LaiNo ratings yet
- Evidence Outline (1) (1) - OkayDocument58 pagesEvidence Outline (1) (1) - OkayTybNo ratings yet
- Equal Protection Clause: LucidchartDocument1 pageEqual Protection Clause: LucidchartJheelGosainNo ratings yet
- Antitrust Kesselman Fall 2020Document101 pagesAntitrust Kesselman Fall 2020Rhyzan CroomesNo ratings yet
- Criminal Procedure-Final OutlineDocument37 pagesCriminal Procedure-Final Outlineeric berns100% (2)
- Crim Pro Outline Kroeber Summer 2009 FINALDocument13 pagesCrim Pro Outline Kroeber Summer 2009 FINALNeel VakhariaNo ratings yet
- Evidence OutlineDocument13 pagesEvidence OutlineNicole WilliamsonNo ratings yet
- Con Law Equal Protection 2009Document56 pagesCon Law Equal Protection 2009The LawbraryNo ratings yet
- Outline-Civ.-pro II (Very Thorough)Document37 pagesOutline-Civ.-pro II (Very Thorough)adamNo ratings yet
- Crim Law Attack SheetDocument1 pageCrim Law Attack SheettreifelNo ratings yet
- Business Associations Outline Fall 2011Document63 pagesBusiness Associations Outline Fall 2011caro6032No ratings yet
- Flowchart - Negligence (Occupier's Liability) : Issue 1: Did The Defendant Owe The Plaintiff A Duty of Care?Document4 pagesFlowchart - Negligence (Occupier's Liability) : Issue 1: Did The Defendant Owe The Plaintiff A Duty of Care?NDNo ratings yet
- Crim Pro Attack PlanDocument14 pagesCrim Pro Attack PlanElNo ratings yet
- Business Associations Berdejo Fall 2020 MC4xNzI3NTkwMADocument105 pagesBusiness Associations Berdejo Fall 2020 MC4xNzI3NTkwMARhyzan CroomesNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Outline Spring 2010Document17 pagesCriminal Law Outline Spring 2010BUbobby24No ratings yet
- Rule 606(b): Juror Testimony on Validity of VerdictDocument74 pagesRule 606(b): Juror Testimony on Validity of VerdictJenniferHunterNo ratings yet
- TortsDocument80 pagesTortstconn8276No ratings yet
- Evidence AND: Evidence Outline W/O Hearsay I. Relevance (FRE 401 and 403)Document12 pagesEvidence AND: Evidence Outline W/O Hearsay I. Relevance (FRE 401 and 403)no contractNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument16 pagesConstitutional Law OutlineStephanieIjomaNo ratings yet
- Remedies ChillDocument4 pagesRemedies ChillgilloteenNo ratings yet
- Civil Procedure II Pre-Writes: Intervention and Class ActionsDocument24 pagesCivil Procedure II Pre-Writes: Intervention and Class ActionsMorgyn Shae Cooper50% (2)
- 2006 Personal Jurisdiction ChecklistDocument9 pages2006 Personal Jurisdiction Checklistkatiana26100% (1)
- Business Organizations OutlineDocument29 pagesBusiness Organizations OutlineMissy Meyer100% (1)
- Degroat Crim Adjudication OutlineDocument22 pagesDegroat Crim Adjudication OutlineSavana DegroatNo ratings yet
- Spring 2016 Crim Pro (Freiwald) OutlineDocument40 pagesSpring 2016 Crim Pro (Freiwald) OutlineCharles SlingluffNo ratings yet
- I. Judicial Review: Master Constitutional Law Outline Professor BurrisDocument74 pagesI. Judicial Review: Master Constitutional Law Outline Professor BurrisDavid YergeeNo ratings yet
- Crim Pro Short OutlineDocument6 pagesCrim Pro Short OutlineDenise NicoleNo ratings yet
- First Amendment: Is There State Action Regulating Speech?Document1 pageFirst Amendment: Is There State Action Regulating Speech?rhdrucker113084No ratings yet
- Constitutional Law Free Speech OutlineDocument2 pagesConstitutional Law Free Speech OutlineEl0% (1)
- Evidence CapraDocument87 pagesEvidence CapraGuillermo FrêneNo ratings yet
- Con Law Attack OLDocument11 pagesCon Law Attack OLAnonymous hyR5rKBINsNo ratings yet
- Con Law Flow ChartDocument31 pagesCon Law Flow ChartTed Miller80% (5)
- Fourth Amendment - Searches and SeizuresDocument3 pagesFourth Amendment - Searches and SeizuresHenry ManNo ratings yet
- Devlin Con Law I 2011 - Quick Sheets For ExamDocument5 pagesDevlin Con Law I 2011 - Quick Sheets For ExamJeremy100% (1)
- 14th Amendment Flow ChartDocument6 pages14th Amendment Flow Chartdmsurveysspam100% (7)
- Separation of PowerDocument17 pagesSeparation of PowerlakimhoffNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law II Prof. Marci Hamilton Fall 2002: I. Equal ProtectionDocument21 pagesConstitutional Law II Prof. Marci Hamilton Fall 2002: I. Equal ProtectionAlina LevinaNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Ethics Independence and Corporate Governance)Document76 pagesChap 3 Ethics Independence and Corporate Governance)Thùy Linh Lê ThịNo ratings yet
- Police Permit Requirements for Public Assemblies Declared UnconstitutionalDocument51 pagesPolice Permit Requirements for Public Assemblies Declared UnconstitutionalRo ElinamNo ratings yet
- PDF Non - Discrimination On The Ground of CasteDocument6 pagesPDF Non - Discrimination On The Ground of CasteShikha ManiarNo ratings yet
- Forced Evictions of The Marginalised in IndiaDocument4 pagesForced Evictions of The Marginalised in IndiaSushmanjali NuthalapatiNo ratings yet
- Cap TailDocument3 pagesCap Tailcapitalrealty01No ratings yet
- Tove PettersenDocument14 pagesTove Pettersenbenedetta arteNo ratings yet
- Conventional Morality and Ethical RelativismDocument29 pagesConventional Morality and Ethical RelativismHazel Candelaria Gascon0% (1)
- REFORMING LEGAL EDUCATION IN INDIADocument7 pagesREFORMING LEGAL EDUCATION IN INDIARimika ChauhanNo ratings yet
- War on Terror and Growing Human Rights AbusesDocument8 pagesWar on Terror and Growing Human Rights AbusesAymen Khakwani100% (3)
- Un Basic Principles On The Role of LawyersDocument5 pagesUn Basic Principles On The Role of LawyerscfurculitaNo ratings yet
- Reviewing NSTP and its importance for youthDocument2 pagesReviewing NSTP and its importance for youthVince CedricNo ratings yet
- Gender and Command Over PropertyDocument24 pagesGender and Command Over PropertyAditi AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Key developments in the history of human rightsDocument3 pagesKey developments in the history of human rightseppieseverino5No ratings yet
- Critical Social Work As Human Rights Practice in Hospital Discharge SettingsDocument4 pagesCritical Social Work As Human Rights Practice in Hospital Discharge SettingsAngela BortaNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Lesson PlansDocument18 pagesSocial Studies Lesson PlansmohllahNo ratings yet
- Profit Maximization, Shareholder Wealth Maximization and Stakeholder Value CreationDocument6 pagesProfit Maximization, Shareholder Wealth Maximization and Stakeholder Value CreationMuhammad AzeemNo ratings yet
- Https Doc 14 A0 Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument3 pagesHttps Doc 14 A0 Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ethics Semi-Final ExamDocument7 pagesEthics Semi-Final ExamJunriv RiveraNo ratings yet
- Democratic InterventionsDocument80 pagesDemocratic InterventionsRichmond Jake Almazan100% (1)
- The Principles of Justice - Richard W. Wright, 2000Document31 pagesThe Principles of Justice - Richard W. Wright, 2000zemanel3No ratings yet
- Implementing UN HRC Res 16/18: A Framework For Inclusivity, Pluralism and DiversityDocument16 pagesImplementing UN HRC Res 16/18: A Framework For Inclusivity, Pluralism and DiversityEvelyn Lusiana TobingNo ratings yet
- First Amendment StatementDocument2 pagesFirst Amendment StatementTialena EvansNo ratings yet
- 7-The Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993Document23 pages7-The Protection of Human Rights Act, 1993Prem ChopraNo ratings yet
- Adiong Vs Comelec Case DigestDocument2 pagesAdiong Vs Comelec Case DigestEbbe Dy100% (1)
- Rights of the Child in Early MarriagesDocument127 pagesRights of the Child in Early MarriagesIov Claudia AnamariaNo ratings yet
- Briefing Paper 2 - Collective ReparationsDocument24 pagesBriefing Paper 2 - Collective ReparationsRenato SoteloNo ratings yet
- Amg Option Agreement 1 - 010120Document6 pagesAmg Option Agreement 1 - 010120Mark S. BerryNo ratings yet
- Principles of Good Urban GovernanceDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Good Urban Governancelguerra73No ratings yet
- Managing Business EthicsDocument12 pagesManaging Business Ethicsokello simon peterNo ratings yet
- Human Rights QuestionsDocument6 pagesHuman Rights QuestionsifodifodfNo ratings yet