Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 16
Uploaded by
Vijay Bhaskar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
385 views4 pagesDiagram shows the fundamental mode of vibration on a string. The string is vibrating with a frequency of! "#. Which diagram shows the second harmonic$ with the correct frequency of vibration? diagram shows the a%%aratus used to measure the wavelength of microwaves. As a detector is moved from the transmitter to the metal %late$ maxima are found at %oints P$ Q$ R$ S and T.
Original Description:
Original Title
worksheet_16.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiagram shows the fundamental mode of vibration on a string. The string is vibrating with a frequency of! "#. Which diagram shows the second harmonic$ with the correct frequency of vibration? diagram shows the a%%aratus used to measure the wavelength of microwaves. As a detector is moved from the transmitter to the metal %late$ maxima are found at %oints P$ Q$ R$ S and T.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
385 views4 pagesWorksheet 16
Uploaded by
Vijay BhaskarDiagram shows the fundamental mode of vibration on a string. The string is vibrating with a frequency of! "#. Which diagram shows the second harmonic$ with the correct frequency of vibration? diagram shows the a%%aratus used to measure the wavelength of microwaves. As a detector is moved from the transmitter to the metal %late$ maxima are found at %oints P$ Q$ R$ S and T.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
16 Worksheet (AS)
1 Which of the statements about stationary waves is true? [1]
A A node occurs where the vibration is at a maximum.
B An antinode occurs where the vibration is at a maximum.
C The distance between consecutive antinodes is one wavelength.
D The distance between consecutive nodes is one wavelength.
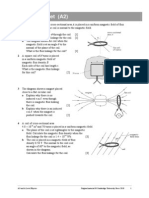
2 The diagram shows the fundamental mode of vibration on a string. The string is vibrating with a
frequency of ! "#.
Which diagram shows the second harmonic$ with the correct frequency of vibration? [1]
3 The diagram shows the a%%aratus used to measure the wavelength of microwaves.
As a detector is moved from the transmitter to the metal %late$ maxima are found at %oints
P$ Q$ R$ S and T. What is the wavelength of the microwaves? [1]
A & cm
B ' cm
C 1! cm
D &! cm
A( and A )evel *hysics +riginal material , -ambridge .niversity *ress /!1! 1
frequency 0 1! "#
frequency 0 /! "#
frequency 0 1/! "#
frequency 0 12! "#
A B
C D
16 Worksheet (AS)
4 Which diagram shows the fundamental mode of vibration in an o%en %i%e? [1]
5 A vibrating tuning for3$ held above a tube$ sets u% a standing wave in the air in the tube.
Which of the following statements is correct? [1]
A At the antinodes the %articles vibrate bac3 and forth$ %arallel to the length of the tube.
B At the antinodes the %articles vibrate from side to side$ %er%endicular to the length of the tube.
C At the nodes the %articles vibrate bac3 and forth$ %arallel to the length of the tube.
D At the nodes the %articles vibrate from side to side$ %er%endicular to the length of the tube.
6 +ne end of a ro%e is fixed and the other end is sha3en rhythmically. A stationary 4standing5
wave is formed on the ro%e. 6x%lain how such a wave is formed on the ro%e. [/]
7 The diagram shows a stationary wave on a string.
a 7ar3 the %ositions of the nodes 485 and the antinodes 4A5. [/]
b 6x%lain what is meant by a node and an antinode. [/]
c 9etermine the wavelength of the %rogressive waves on the string. [/]
8 A string of length 2! cm is fixed at both ends. The middle of the string is %luc3ed. This creates
a stationary wave %attern on the string with one com%lete :loo%;. The string is vibrating in
fundamental mode with a frequency of /! "#. -alculate<
a the wavelength of the %rogressive wave on the string [/]
b the s%eed of the %rogressive wave on the string. [1]
A( and A )evel *hysics +riginal material , -ambridge .niversity *ress /!1! /
=' cm
A B
C
D
16 Worksheet (AS)
9 A tuning for3 vibrating at a frequency of &>! "# is held above the o%en end of an em%ty bottle.
When the length of the air column within the bottle is 1= cm$ a fundamental mode of vibration
is set u% in the air within the bottle and a loud sound is heard.
a (3etch a diagram of the stationary wave %attern. 4Assume the air within the bottle is a
uniform cylinder of air.5 [/]
b 9etermine the wavelength of the sound waves. [/]
c "ence determine the s%eed of sound in air. [1]
10 A string of length 1. m is held under tension. When the string is made to vibrate at a frequency
of &!! "#$ three antinodes are formed along this length of the string. 9etermine the s%eed of the
%rogressive waves that form the stationary wave %attern. [']
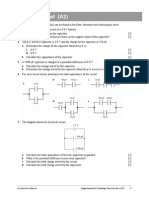
11 The diagram below shows a stationary wave %attern formed in the air between the o%en ends
of a tube when a vibrating louds%ea3er is held at one end. The %ositions of the nodes 485 and
antinodes 4A5 are also shown.
The length L of the tube is ! cm. The s%eed of sound is 1&! m s
?1
.
9etermine the frequency of sound from the louds%ea3er. [']
A( and A )evel *hysics +riginal material , -ambridge .niversity *ress /!1! 1
16 Worksheet (AS)
12 @n a resonanceAtube ex%eriment$ a tuning for3 vibrating at
a frequency of /' "# is held over the o%en end of a tube
4as shown in the diagram5.
A stationary wave can form in the air between the o%en end of
the tube and the surface of the water. The antinode at the o%en
end of the tube does not occur exactly at the end but at a small
distance c from this end. The distance c is 3nown as the :endA
correction;. The value of c for a %articular tube does not
de%end on the harmonic.
This ex%eriment ta3es into account any errors that may occur
due to the endAcorrection. The tube is fully immersed into the
water. The o%en end of the tube is slowly raised. A loud
sound is first heard when the to% of the tube is 1! cm above
the surface of the water. The next loud sound is heard when the
to% of the tube is >' cm above the water surface.
.se this information to determine the s%eed of sound in air.
[]
Total<
&1
(core< B
A( and A )evel *hysics +riginal material , -ambridge .niversity *ress /!1! &
You might also like
- Worksheet 16 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 16 PDFAlina Smagutta0% (1)
- Standing Waves WorksheetDocument4 pagesStanding Waves WorksheetMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Worksheet PhysicsDocument42 pagesWorksheet Physicsinfinite onlineNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 16 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 16 PDFVijay Bhaskar33% (6)
- Standing WavesDocument14 pagesStanding WavesNo IdeaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 14Document4 pagesWorksheet 14Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 1 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : S M 7 - 2 S M 66 - 2Document2 pages1 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : S M 7 - 2 S M 66 - 2alyhamad50No ratings yet
- Worksheet 31Document3 pagesWorksheet 31Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 09Document3 pagesWorksheet 09Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 11 Worksheet (AS) : What Is The Current X ?Document4 pages11 Worksheet (AS) : What Is The Current X ?Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 12Document3 pagesWorksheet 12Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 23Document2 pagesWorksheet 23Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 07 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 07 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 13Document4 pagesWorksheet 13Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MDocument2 pages9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MRuby ChongNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 18Document4 pagesWorksheet 18Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (AS) PDFDocument1 pageWorksheet (AS) PDFMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Topic - 1 Measurement and UncertaintiesDocument11 pagesTopic - 1 Measurement and UncertaintiesKevin OktaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 26Document3 pagesWorksheet 26Subarna Lamsal100% (1)
- Ch04 HWDocument2 pagesCh04 HWDilini Wijesinghe100% (1)
- 22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 15 Superposition of Waves 15Document5 pages15 Superposition of Waves 15Ashani0001100% (1)
- Worksheet 21 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 21 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 28 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- CH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersDocument1 pageCH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersAmberNo ratings yet
- 12 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : R I V RDocument1 page12 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : R I V RRuby ChongNo ratings yet
- R2019 49P1MSDocument29 pagesR2019 49P1MSSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 05 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 05 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- The effects of light waves and their propertiesDocument148 pagesThe effects of light waves and their propertiesAhmed KhalilNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 27Document3 pagesWorksheet 27Vijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- 9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MDocument2 pages9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MRuby ChongNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Waves AllDocument17 pages9702 p1 Waves AllNushanKhan100% (1)
- Calculating bearings, distances and speeds from maps and diagramsDocument19 pagesCalculating bearings, distances and speeds from maps and diagramsAhmed ElmoghazyNo ratings yet
- 23 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : D V E VDocument3 pages23 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : D V E Vajay100% (1)
- Worksheet 23 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 23 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 08Document4 pagesWorksheet 08Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 9&10 Phases of Matter & Deformation of SolidsDocument4 pages9&10 Phases of Matter & Deformation of SolidsShanielNo ratings yet
- Physics WavesDocument10 pagesPhysics WavesJerry GJNo ratings yet
- II IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 15 Waves Q+SolnDocument12 pagesII IIT IRP Physics Worksheet - 15 Waves Q+SolnAshwin Kumar100% (2)
- Worksheet 24 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 24 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Compiled By: Sir Sumair: DynamicsDocument6 pagesCompiled By: Sir Sumair: DynamicsAleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-13 Electric Current PAPER-1 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-13 Electric Current PAPER-1 Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- Waves & OscillationsDocument10 pagesWaves & OscillationsDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- M Schemes 01Document2 pagesM Schemes 01Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 17Document2 pagesWorksheet 17Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 30 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 30 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- 2021 Physics - MCQ & EssayDocument15 pages2021 Physics - MCQ & Essaynkwochaephraim100% (1)
- A Level: Circular Motion - AnswerDocument3 pagesA Level: Circular Motion - AnswerAnn OthmanNo ratings yet
- Expr Waves TidyDocument34 pagesExpr Waves TidyMohamed ElaminNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20Document3 pagesWorksheet 20Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty Review: Calculating Errors in MeasurementsDocument5 pagesUncertainty Review: Calculating Errors in MeasurementsAmelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Physics - MCQ & EssayDocument18 pages2015 Physics - MCQ & EssayIzundu VictorNo ratings yet
- As Student WorksheetsDocument54 pagesAs Student WorksheetsHiyahiyahiya HuhahuhahuhaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 09 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 09 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Momentum Edexcel WorksheetDocument3 pagesMomentum Edexcel WorksheetWilliam100% (1)
- 5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorDocument2 pages5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorRuby Chong100% (2)
- COAS TR P1 18ws1Document2 pagesCOAS TR P1 18ws1Mahmud RahmanNo ratings yet
- Exp 11-Standing Sound Waves in Air ColumnsDocument4 pagesExp 11-Standing Sound Waves in Air Columnsthe_truth_94No ratings yet
- Wave Properties MCQs and QuestionsDocument2 pagesWave Properties MCQs and QuestionsdreamydamselNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 33A LevelDocument3 pagesWorksheet 33A LevelVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 33Document3 pagesWorksheet 33Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 32Document2 pagesWorksheet 32Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Transformationsclassifieds PDFDocument35 pagesTransformationsclassifieds PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 31Document3 pagesWorksheet 31Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 29Document4 pagesWorksheet 29Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 30 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 30 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 31 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 31 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 28 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 32Document2 pagesWorksheet 32Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 29 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 29 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 30Document4 pagesWorksheet 30Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 28Document2 pagesWorksheet 28Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 26Document3 pagesWorksheet 26Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 27Document3 pagesWorksheet 27Vijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 26 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 26 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 21 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 21 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- 27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Syed Abdul Rehman ShahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 24Document3 pagesWorksheet 24Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 25Document3 pagesWorksheet 25Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 25 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 25 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (2)
- Worksheet 22Document3 pagesWorksheet 22Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 21Document3 pagesWorksheet 21Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 24 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 24 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 23 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 23 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- 22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 23Document2 pagesWorksheet 23Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 19Document2 pagesWorksheet 19etud3cl100% (1)
- Worksheet 20Document3 pagesWorksheet 20Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Atributele lui Dumnezeu din teologia creștinăDocument8 pagesAtributele lui Dumnezeu din teologia creștinăMAMBOSENKO100% (1)
- Geometrical Optics: ExplanationDocument2 pagesGeometrical Optics: ExplanationAniket SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physical Quantities and SI UnitsDocument15 pagesPhysical Quantities and SI UnitsNur SyahirahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Basics of Heat TransferDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Basics of Heat Transfermunyah778No ratings yet
- 6th Grade Vocabulary List IDocument7 pages6th Grade Vocabulary List IM MNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula Sheet Unit 2Document1 pagePhysics Formula Sheet Unit 2sadika sabaNo ratings yet
- Spectral Reflectance Curve: - Ratio of Energy Reflected by The Surface To The Energy Incident On The SurfaceDocument38 pagesSpectral Reflectance Curve: - Ratio of Energy Reflected by The Surface To The Energy Incident On The Surfaceruchi100% (1)
- Ionospheric Modification and Its Potencial To Enhance or Degrade The Performance of Military Systems PDFDocument474 pagesIonospheric Modification and Its Potencial To Enhance or Degrade The Performance of Military Systems PDFRyanADNo ratings yet
- Types of PowersDocument4 pagesTypes of PowersAnusha SinghNo ratings yet
- Microwave Path Design ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesMicrowave Path Design Considerationssayys1390No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Heat TransferDocument40 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Heat TransferEjad AfifiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics - TocDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics - TocNguyễn Hồng Quân100% (2)
- Signal degradation and distortion in optical fibersDocument16 pagesSignal degradation and distortion in optical fibersBianNo ratings yet
- A General Velocity Profile For A Laminar Boundary Layer Over Flat Plate With Zero IncidenceDocument1 pageA General Velocity Profile For A Laminar Boundary Layer Over Flat Plate With Zero Incidenceemadsaad77No ratings yet
- Tadamun Social Society Imamu-Nawawi Secondary Schools Bosaso-Puntland-Somalia Assignment: Subject Physics Classes: Form FourDocument13 pagesTadamun Social Society Imamu-Nawawi Secondary Schools Bosaso-Puntland-Somalia Assignment: Subject Physics Classes: Form FourIbrahim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Forced convection heat transfer experimentDocument3 pagesForced convection heat transfer experimentangela yuNo ratings yet
- HT304 Draft Report PDFDocument7 pagesHT304 Draft Report PDFUmesh JangidNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Heat and Mass TransferDocument6 pagesLesson Plan: Heat and Mass TransferNithyanandmNo ratings yet
- Rate Gyro Application Note TheoryDocument4 pagesRate Gyro Application Note TheoryPhạm Ngọc HòaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Week 1 and 2Document11 pagesModule 1 Week 1 and 2Princess Charisse BautistaNo ratings yet
- Channel Flow RoutingDocument21 pagesChannel Flow RoutingKhurram SherazNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/21Nisha zehraNo ratings yet
- PhET Simulation - Color VisionDocument3 pagesPhET Simulation - Color VisionDanikaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Practical RevisionDocument6 pagesGrade 8 Practical RevisionIncognito UntraceableNo ratings yet
- Lecon 1Document52 pagesLecon 1Radu SNo ratings yet
- A Matlab GUI For Calculating The Solar Radiation On EarthDocument12 pagesA Matlab GUI For Calculating The Solar Radiation On EarthRicardo Mayorga Paredes100% (3)
- Science 7 q3 Summative TestDocument2 pagesScience 7 q3 Summative TestThelma Bajo82% (11)
- ANSI-ANS 8.23-2007 Nuclear Criticality Accident Emergency Planning and ResponseDocument31 pagesANSI-ANS 8.23-2007 Nuclear Criticality Accident Emergency Planning and ResponseDJSeidelNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula SheetAMINA SARFRAZNo ratings yet