Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 08 PDF
Uploaded by
Vijay BhaskarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 08 PDF
Uploaded by
Vijay BhaskarCopyright:
Available Formats
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 1
8 Worksheet (AS)
Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet.
1 Two springs X and Y have spring constants k and 2k respectively.
Spring X is stretched by a force F and spring Y is stretched by a force 2F. Each spring obeys
Hookes law during the extension.
The work done in stretching spring X is W
X
and the work done in stretching spring Y is W
Y
.
What is the relationship between W
X
and W
Y
? [1]
A W
Y
=
2
1
W
X
B W
Y
= W
X
C W
Y
= 2W
X
D W
Y
= 4W
X
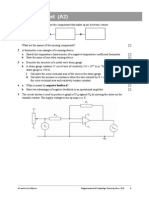
2 Four wires A, B, C and D have diameters, lengths and are stretched by forces as shown. All the
wires are made of the same material.
Which wire has the smallest extension? [1]
3 The force on a sample of a material is slowly increased and then slowly decreased. The
forceextension graph is shown in the diagram.
Which area represents the net work done on the sample during the complete process? [1]
A P + Q B Q + R C P + Q R D P + Q + R
F
A B C D
d
l
2d d 2d
2l
2F
F 2F
8 Worksheet
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 2
4 Which statement is true about rubber, a polymeric material? [1]
A A normal rubber band breaks when the strain is greater than 1.
B A normal rubber band breaks when the strain is less than 10%.
C When a small amount of sulfur is added, to provide cross-links between molecules in
rubber, the elastic limit is reduced.
D When a small amount of sulfur is added, to provide cross-links between molecules in
rubber, the ultimate tensile stress is reduced.
5 What is equal to the Young modulus? [1]
A The area between a forceextension graph and the extension axis.
B The area between a stressstrain graph and the stress axis.
C The gradient of a forceextension graph.
D The gradient of a stressstrain graph.
6 Springs and wires obey Hookes law. State Hookes law. [1]
7 A spring has a natural length of 2.5 cm. A force of 4.0 N extends the spring to a length
of 6.2 cm.
a What is the extension of the spring? [1]
b Determine the force (spring) constant k for the spring in N m
1
. [3]
c Calculate the extension of the spring when a tensile force of 6.0 N is applied. You may
assume that the spring has not exceeded its elastic limit. [2]
8 The diagram shows the stressstrain graphs for two wires A and B made from different materials.
The wires have the same length and cross-sectional area. Explain which of the materials is:
a brittle [1]
b stiffer [1]
c stronger. [1]
8 Worksheet
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 3
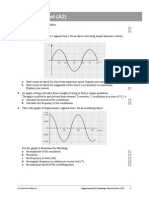
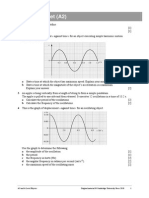
9 A graph of force F against extension x is shown for a spring.
a Use the graph to determine the force (spring) constant k of the spring. [2]
b Calculate the energy stored (elastic potential energy) in the spring when its extension is
5.0 cm. [3]
10 A length of cable of diameter 1.2 mm is under a tension of 150 N. Calculate the stress in the
cable. [3]
11 A metal wire of diameter 0.68 mm and natural length 1.5 m is fixed firmly to the ceiling at one
end. When a 6.8 kg mass is hung from the free end, the wire extends by 2.8 mm. Calculate:
a the stress in the wire [3]
b the Young modulus of the material of the wire. [4]
12 The diagram shows two springs X and Y connected
in series and supporting a weight of 8.0 N. The force
constants of the springs are shown on the diagram.
a Calculate the extension of each spring. [2]
b Determine the force (spring) constant for the
combination. [2]
c According to a student, the force constant for the
springs in series is the sum of the force constants
of the individual springs. Is the student correct? [1]
8 Worksheet
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 4
13 A 180 g trolley is placed on a frictionless air track. One end of the trolley is attached to a spring
of force constant 50 N m
1
. The trolley is pushed against a fixed support so that the compression
of the spring is 8.0 cm. The trolley is then released.
a What is the initial acceleration of the trolley when it is released? [3]
b What is the initial energy stored in the spring? [3]
c Calculate the final speed of the trolley along the air track. You may assume that there is
100% transfer of energy from the spring to the trolley. [2]
14 The forceextension graph for a length of metal wire is shown below.
a The gradient of the graph is equal to the
force constant k of the wire. Show that
the force constant k is given by:
k =
l
EA
where E is the Young modulus of the metal,
A is the cross-sectional area of the wire and
l is the natural length of the wire. [4]
b Explain how the gradient of the forceextension
graph would change for a wire of
the same material but:
i twice the length [1]
ii twice the radius. [1]
Total:
49
Score: %
You might also like
- Worksheet 33Document3 pagesWorksheet 33Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 32Document2 pagesWorksheet 32Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 31 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 31 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 32Document2 pagesWorksheet 32Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 31Document3 pagesWorksheet 31Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 33A LevelDocument3 pagesWorksheet 33A LevelVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Transformationsclassifieds PDFDocument35 pagesTransformationsclassifieds PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 30 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 30 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 29Document4 pagesWorksheet 29Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 28Document2 pagesWorksheet 28Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 30Document4 pagesWorksheet 30Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 28 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 29 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 29 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 27Document3 pagesWorksheet 27Vijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 24Document3 pagesWorksheet 24Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Syed Abdul Rehman ShahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 26Document3 pagesWorksheet 26Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 25 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 25 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (2)
- 22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 26 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 26 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 25Document3 pagesWorksheet 25Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 23 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 23 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 24 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 24 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 23Document2 pagesWorksheet 23Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 21Document3 pagesWorksheet 21Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20Document3 pagesWorksheet 20Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 21 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 21 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 22Document3 pagesWorksheet 22Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 19Document2 pagesWorksheet 19etud3cl100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter 1 - Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Matter in Our SurroundingsTara SinghNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Fabrication-6 PDFDocument1 page5.0 Fabrication-6 PDFRohit KambleNo ratings yet
- Nabakem PCB Insulating Coating AgentDocument4 pagesNabakem PCB Insulating Coating Agentsutrisno00No ratings yet
- Dex La Fontaine CJ98Document12 pagesDex La Fontaine CJ98jatan aminNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Rock MechanicsDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Rock Mechanicsmaomao_vt890% (1)
- Main Oxidation Number of Common ElementsDocument2 pagesMain Oxidation Number of Common Elementsvanerie manumbale100% (1)
- Indian & International STDDocument8 pagesIndian & International STDMirza Sameer Ali BaigNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Major Reaction WDocument102 pagesChapter 4 Major Reaction Wsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Unit III: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: E. D. Gloria Ust - Faculty of Pharmacy Chem200 - Organic ChemistryDocument19 pagesUnit III: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: E. D. Gloria Ust - Faculty of Pharmacy Chem200 - Organic ChemistryLyra LasangreNo ratings yet
- 15 PDFDocument28 pages15 PDFNathanNo ratings yet
- SDFDSEFDocument3 pagesSDFDSEFpppppp5No ratings yet
- Distillation Column Design MethodsDocument4 pagesDistillation Column Design Methodsramu karriNo ratings yet
- Scheil EquationDocument2 pagesScheil EquationsiswoutNo ratings yet
- B - SC - Chemistry (I To VI Semesters) W - e - F - 2014-15 in Phased MannerDocument30 pagesB - SC - Chemistry (I To VI Semesters) W - e - F - 2014-15 in Phased MannerNatish JaglanNo ratings yet
- Raw Material Index For Passives April 31, 2012Document6 pagesRaw Material Index For Passives April 31, 2012Dennis ZogbiNo ratings yet
- (10th Grade Science) Brief Introduction of Gamma RaysDocument14 pages(10th Grade Science) Brief Introduction of Gamma RaysVinceRaymundRamaGonatoNo ratings yet
- Q DT /DX:) ) Rsub (X) ( (W) Over ( (M) (2) )Document8 pagesQ DT /DX:) ) Rsub (X) ( (W) Over ( (M) (2) )Aiza AlbuferaNo ratings yet
- CHEM 135 Exam 2 F15 KeyDocument7 pagesCHEM 135 Exam 2 F15 KeyMikeNo ratings yet
- Catalog Biocraft Electronic Test InstrumentDocument2 pagesCatalog Biocraft Electronic Test InstrumentHmmNo ratings yet
- G200Document4 pagesG200Gul Hassan Akhunzada100% (2)
- Experiment 1Document17 pagesExperiment 1Kelvin Lim100% (3)
- ASTM-F1941-F1941M Standard Specification For Electrodeposited Coatings On Mechanical Fasteners, Inch and MetricDocument14 pagesASTM-F1941-F1941M Standard Specification For Electrodeposited Coatings On Mechanical Fasteners, Inch and MetricSinan Chen100% (1)
- US20110189056A1 - Microwave ReactorDocument19 pagesUS20110189056A1 - Microwave ReactorKhaledAhmedNo ratings yet
- Smart Choices Grades 7-8Document15 pagesSmart Choices Grades 7-8Tan TaylorNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Soils in The Environment, Volume 2 PDFDocument585 pagesEncyclopedia of Soils in The Environment, Volume 2 PDFFer NúñezNo ratings yet
- Chemsys Training Program IntroductionDocument5 pagesChemsys Training Program Introductionnaam2105_996631495No ratings yet
- Completion Practices in Deep Sour Tuscaloosa Wells: SPE, Amoco Production CoDocument10 pagesCompletion Practices in Deep Sour Tuscaloosa Wells: SPE, Amoco Production CoAnonymous VNu3ODGavNo ratings yet
- Aspen Exchanger Design and Rating Shell & Tube V9Document1 pageAspen Exchanger Design and Rating Shell & Tube V9MAYANK AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- APV Paraflow Plate HX ManualDocument31 pagesAPV Paraflow Plate HX ManualAnonymous gwldee5100% (2)
- Pyrolytic Syn EliminationsDocument20 pagesPyrolytic Syn EliminationsSulagna DasNo ratings yet