Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet 04 PDF
Uploaded by
Vijay BhaskarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 04 PDF
Uploaded by
Vijay BhaskarCopyright:
Available Formats
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 1
4 Worksheet (AS)
Data needed to answer questions can be found in the Data, formulae and relationships sheet.
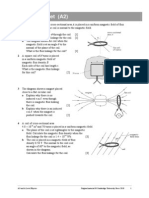
1 Two forces, each of magnitude 8 N, act on an object. The angle between the two forces is 60.
What is the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the object? [1]
A 4 N
B 7 N
C 8 N
D 14 N
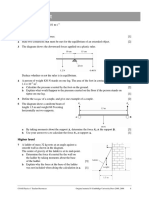
2 The object in the diagram is in equilibrium.
Which equation is correct about the forces? [1]
A 15 = 20 cos
B 20 = F cos
C F = 15 sin
D F = 15 tan
3 A force of 10 N is resolved into two components at right angles to each other.
One of the components is 8 N. What is the other component? [1]
A 2 N
B 4 N
C 6 N
D 12 N
4 A man of weight 600 N stands at
the end of a uniform wooden
plank, which is pivoted as shown
in the diagram.
What is the weight of the wooden
plank? [1]
A 100 N
B 200 N
C 300 N
D 400 N
5 A uniform square block is pushed along a
rough surface at constant speed by a force of
100 N. A horizontal force of friction acts
between the surface and the block.
What is the moment of the force of friction
about the centre of gravity? [1]
A 80 N m clockwise
B 80 N m anticlockwise
C 160 N m clockwise
D 160 N m anticlockwise
20 N
15 N
F
0.5 m
3.0 m
direction of movement
1.6 m
centre of
gravity
4 Worksheet (AS)
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 2
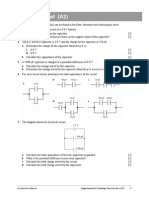
6 Calculate the magnitude of the resultant force in each case below.
a
b
[2] [3]
7 In each case below, resolve the vector into two perpendicular components in the x and y directions.
a
b
[2] [2]
8 a Define the moment of a force. [1]
b State two conditions that must be met for the equilibrium of an extended object. [2]
9 The diagram shows a uniform beam of
length 1.5 m and weight 60 N resting
horizontally on two supports.
a By taking moments about the support A, determine the force R
B
at the support B. [3]
b Use your answer to a to calculate the force R
A
at support A. [1]
10 A child of mass 35 kg on a swing is pulled to one side.
The diagram shows the forces acting on the seat of the
swing when it is in equilibrium.
a What is the net force on the seat? [1]
b Draw a triangle of forces. Hence determine:
i the tension T in the rope [4]
ii the angle made by the rope with the vertical. [2]
4 Worksheet (AS)
AS and A Level Physics Original material Cambridge University Press 2010 3
11 A gardener pulls a 50 kg roller along level
ground, as shown in the diagram.
The roller moves at a steady speed along
the level ground when the handle makes an
angle of 30 to the horizontal ground and
the gardener pulls with a force of 300 N
along the handle.
a Calculate the horizontal component of the force 300 N. [2]
b What is the net force in the horizontal direction? Hence determine the magnitude of the
resistive force acting on the roller. [2]
c Determine the vertical contact force acting on the roller due to the ground. [3]
12 A ladder of mass 32 kg rests at an angle against a smooth
wall as shown in the diagram. The centre of gravity of the
ladder is at its mid-point.
a Determine the force R exerted by the wall on
the ladder by taking moments about the base
of the ladder. [3]
b Explain why the force at the base of the ladder
was not included when doing the calculation in a. [1]
13 A 62 kg person lies flat on a uniform plank of mass 15 kg. The plank, with the person lying on it,
is placed on a brick and some bathroom scales, as shown in the diagram below.
The persons toe-to-head distance is 1.56 m. The length of the plank is also 1.56 m.
a Sketch the diagram above. On your sketch, show all the forces acting on the plank. [2]
b The reading on the bathroom scales is 30 kg. Use this information to determine how far
the centre of gravity of the person is from the toes. [4]
Total:
45
Score: %
You might also like
- 04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..Document3 pages04 Forces Vectors and Moments 04..Ashani0001100% (1)
- Physics First Term Mid Exam Preparation QuestionsDocument8 pagesPhysics First Term Mid Exam Preparation QuestionsEnju ChipepeNo ratings yet
- Moments WorksheetDocument2 pagesMoments Worksheetarieljuwo75% (4)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Worksheet 05 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 05 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- M Schemes 01Document2 pagesM Schemes 01Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Mass, Weight and Density IGCSEDocument2 pagesMass, Weight and Density IGCSEsapini100% (1)
- Worksheet 12 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 12 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- As Student WorksheetsDocument54 pagesAs Student WorksheetsHiyahiyahiya HuhahuhahuhaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 13Document4 pagesWorksheet 13Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Physics Pressure WorksheetDocument5 pagesYear 9 Physics Pressure Worksheetaswata NarayanNo ratings yet
- Moments QuestionsDocument12 pagesMoments Questionsmuxadey100% (1)
- Worksheet 18Document4 pagesWorksheet 18Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 10 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 24 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 24 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Usman Public School System: Pressure WorksheetDocument2 pagesUsman Public School System: Pressure Worksheetmarium khanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet (AS) PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet (AS) PDFMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- 6 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Document3 pages6 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Ruby Chong67% (3)
- Worksheet AUGUST 2021 CH 5: Force and Matter Grade: 9 Subject: PhysicsDocument1 pageWorksheet AUGUST 2021 CH 5: Force and Matter Grade: 9 Subject: PhysicsAnish KanthetiNo ratings yet
- G Field PDFDocument25 pagesG Field PDFmughees_itcompNo ratings yet
- WorkEnergy P2Document26 pagesWorkEnergy P2dhairya gandhi100% (1)
- Gravitational Forces and FieldsDocument3 pagesGravitational Forces and FieldsPathmanathan Nadeson0% (2)
- Momentum WorksheetDocument2 pagesMomentum Worksheetkjnero100% (1)
- Lesson 1-A2 Physics - ADocument14 pagesLesson 1-A2 Physics - ACheng WLNo ratings yet
- KS3 Physics: Worksheet TwoDocument4 pagesKS3 Physics: Worksheet TwoAsif AyazNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 28 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- IGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 26 - Motion in The UniverseDocument2 pagesIGCSE - Physics - Worksheet 26 - Motion in The UniverseAishath Waheeda0% (1)
- Turning Effect of ForceDocument4 pagesTurning Effect of ForceIbrahim Khurram100% (1)
- Worksheet 20 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Flemings Left RuleDocument5 pagesFlemings Left RuleZaina A LeeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 07 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 07 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 23 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 23 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- CH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersDocument1 pageCH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersAmberNo ratings yet
- Phys 191 Worksheet Uncertainty CalculationsDocument4 pagesPhys 191 Worksheet Uncertainty CalculationsJanett Sánchez MuñozNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 15Document5 pagesWorksheet 15Vijay Bhaskar33% (3)
- 5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorDocument2 pages5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorRuby Chong100% (2)
- 9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MDocument2 pages9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MRuby ChongNo ratings yet
- Waves - Worksheet 2Document7 pagesWaves - Worksheet 2Ricardo Johnson0% (2)
- Worksheet 11 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 11 PDFVijay Bhaskar50% (2)
- 15 Superposition of Waves 15Document5 pages15 Superposition of Waves 15Ashani0001100% (1)
- Worksheet 08Document4 pagesWorksheet 08Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22jad obaidNo ratings yet
- Fully Ab Initio Finite-Size Corrections for Charged-Defect Supercell CalculationsDocument4 pagesFully Ab Initio Finite-Size Corrections for Charged-Defect Supercell Calculationshoehoe1234No ratings yet
- A Level: Circular Motion - AnswerDocument3 pagesA Level: Circular Motion - AnswerAnn OthmanNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Topic-7 Astrophysics and Cosmology Answers (End-Of-Chapter & Examzone)Document8 pagesUnit-5 Topic-7 Astrophysics and Cosmology Answers (End-Of-Chapter & Examzone)Avrinox100% (3)
- Worksheet 26Document3 pagesWorksheet 26Subarna Lamsal100% (1)
- Worksheet (AS) PDFDocument1 pageWorksheet (AS) PDFMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- 8 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : X F K K K F X XDocument3 pages8 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : X F K K K F X XRuby Chong0% (1)
- 7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : A F P A Decreases, Therefore The Pressure Exerted On The Floor Will IncreaseDocument2 pages7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : A F P A Decreases, Therefore The Pressure Exerted On The Floor Will IncreaseRuby Chong100% (1)
- Core 625 2003-2008 PDFDocument107 pagesCore 625 2003-2008 PDFal_helu26No ratings yet
- Electric Fields and Circuits Study GuideDocument22 pagesElectric Fields and Circuits Study GuideLawrence Onthuga100% (1)
- Potential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet: Name: . DateDocument4 pagesPotential and Kinetic Energy Worksheet: Name: . DateJamar FraserNo ratings yet
- Waves MCQDocument45 pagesWaves MCQkoeliaNo ratings yet
- 14 Worksheet (AS) : 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveDocument4 pages14 Worksheet (AS) : 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveNolawitNo ratings yet
- P G7 Turning Effect of ForceDocument2 pagesP G7 Turning Effect of ForceD'ferti Anggraeni100% (1)
- Transformationsclassifieds PDFDocument35 pagesTransformationsclassifieds PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 33Document3 pagesWorksheet 33Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 30 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 30 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 29Document4 pagesWorksheet 29Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 32Document2 pagesWorksheet 32Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 28Document2 pagesWorksheet 28Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 31Document3 pagesWorksheet 31Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 33A LevelDocument3 pagesWorksheet 33A LevelVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 32Document2 pagesWorksheet 32Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 31 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 31 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 29 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 29 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 30Document4 pagesWorksheet 30Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages27 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Syed Abdul Rehman ShahNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 28 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 28 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (3)
- Worksheet 26Document3 pagesWorksheet 26Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 26 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 26 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 25 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 25 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (2)
- Worksheet 27Document3 pagesWorksheet 27Vijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 25Document3 pagesWorksheet 25Vijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 24 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 24 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- 22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages22 Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 24Document3 pagesWorksheet 24Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 21Document3 pagesWorksheet 21Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 23 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 23 PDFVijay Bhaskar100% (1)
- Worksheet 22Document3 pagesWorksheet 22Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 19Document2 pagesWorksheet 19etud3cl100% (1)
- Worksheet 23Document2 pagesWorksheet 23Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 21 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 21 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Worksheet 20 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 20 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 20Document3 pagesWorksheet 20Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- The Twisting Tennis RacketDocument19 pagesThe Twisting Tennis RacketCarlos Daniel ArmentaNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicsihllhmNo ratings yet
- TOS GRADE 7 3rd GRADINGDocument1 pageTOS GRADE 7 3rd GRADINGMELISSA MORENONo ratings yet
- IB Lab - 09 Projectile Motion (DCP CE)Document3 pagesIB Lab - 09 Projectile Motion (DCP CE)ringo_tigerNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 9 - Module 1Document23 pagesQ4 Science 9 - Module 1Danilo Saliog67% (6)
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceandraeNo ratings yet
- CHM092 Chapter 2 Atoms-Ions-PeriodicDocument240 pagesCHM092 Chapter 2 Atoms-Ions-PeriodicNUrLinaNo ratings yet
- Turbomachinery Chapter: Pump and Turbine DesignDocument26 pagesTurbomachinery Chapter: Pump and Turbine DesignfauzNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics ManualDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics ManualHarold Taylor100% (1)
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment 3Document3 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment 3Vishal kumar SawNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices: Betty Lise Anderson - Richard L. AndersonDocument52 pagesFundamentals of Semiconductor Devices: Betty Lise Anderson - Richard L. Andersonfourier76No ratings yet
- F3-Flow Through A NozzleDocument21 pagesF3-Flow Through A NozzleTAN PANG ZORNo ratings yet
- Design and Application of FeederDocument32 pagesDesign and Application of FeederJason SorianoNo ratings yet
- Start Download: Euler's Column FormulaDocument2 pagesStart Download: Euler's Column FormulaTrushar GhosalkarNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (4th Year)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics (4th Year)Jaypee Calamba100% (1)
- TWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2Document4 pagesTWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2HassanSobohNo ratings yet
- Project in ScienceDocument4 pagesProject in ScienceEpejema Tagarao AmaroNo ratings yet
- Concept: Defining ConstraintsDocument3 pagesConcept: Defining ConstraintsPraveen SreedharanNo ratings yet
- Twin Paradox: What's The Paradox?Document2 pagesTwin Paradox: What's The Paradox?Harshank NimonkarNo ratings yet
- Turbine: The Effect of Friction On The Joule CycleDocument13 pagesTurbine: The Effect of Friction On The Joule CycleGeorge AniborNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of A Human BodyDocument13 pagesThermodynamics of A Human BodyJuan Carlos Cahuasquí IntriagoNo ratings yet
- ADocument2 pagesAsardarsndi96No ratings yet
- Typical Vibration Signatures AnalysisDocument8 pagesTypical Vibration Signatures Analysisdfz138100% (1)
- Numerical Quantum DynamicsDocument281 pagesNumerical Quantum DynamicsDontu MariaNo ratings yet
- Slab reinforcement design calculationsDocument34 pagesSlab reinforcement design calculationsGayan IndunilNo ratings yet
- Wellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsDocument85 pagesWellbore Hydraulics, Pressure Drop CalculationsNikhil ShahaneNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies ProblemsDocument9 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies ProblemsZie Agustin67% (3)
- Applied Thermodynamics by Onkar Singh.0001 PDFDocument330 pagesApplied Thermodynamics by Onkar Singh.0001 PDFImran TahirNo ratings yet
- AS Physics Specifications 2024Document10 pagesAS Physics Specifications 2024Malik Ammad AnjumNo ratings yet
- Bridge Deck Analysis Through The Use of Grillage ModelsDocument7 pagesBridge Deck Analysis Through The Use of Grillage ModelslucasgambiNo ratings yet