Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Electronics Question Bank
Uploaded by
Harish Sudhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
371 views3 pagesPower Electronics Question Bank
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPower Electronics Question Bank
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
371 views3 pagesPower Electronics Question Bank
Uploaded by
Harish SudhanPower Electronics Question Bank
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
EE 1353 POWER ELECTRONICS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, PUNALKULAM 1
KINGS
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
QUESTION BANK
NAME OF THE SUBJECT: EE 1353 POWER ELECTRONICS
YEAR / SEM : III / VI
UNIT-I
POWER SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
PART-A
1. What are the different methods to turn on the thyristor?
2. Define latching current.
3. Define holding current.
4. What is a snubber circuit?
5. Why IGBT is very popular nowadays?
6. What is the difference between power diode and signal diode?
7. What are the advantages of GTO over SCR?
8. What losses occur in a thyristor during working conditions?
PART-B
1. Draw the two transistor model of SCR and derive an expression for anode current. (8)
2. Explain the characteristics of SCR (8)
3. Describe the various methods of thyristor turn on. (16)
4. Explain the operation of MOSFET and IGBT (16)
UNIT II
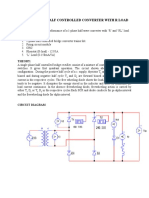
PHASE-CONTROLLED CONVERTERS
PART-A
1. What is the function of freewheeling diodes in controlled rectifier?
2. What is commutation angle or overlap angle?
3. What are the advantages of six pulse converter?
4. What is meant by commutation?
5. What are the types of commutation?
6. Mention some of the applications of controlled rectifier.
7. What are the different methods of firing circuits for line commutated converter?
EE 1353 POWER ELECTRONICS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, PUNALKULAM 2
8. What is meant by natural commutation?
9. What is meant by forced commutation? In this commutation, the current flowing through
PART-B
1. Describe the working of 1 _ fully controlled bridge converter in the Rectifying mode and
inversion mode. And derive the expressions for average output voltage and rms output
voltage. (16)
2. Describe the working of 3 _ fully controlled bridge converter in the Rectifying mode and
inversion mode. And derive the expressions for average output voltage and rms output
voltage. (16)
3. Describe the working of Dual converter. (16)
4. Derive the expressions for average output voltage and rms output voltage of 1 _
semiconverter. (16)
UNIT III
DC TO DC CONVERTERS
PART-A
1. What is meant by dc chopper?
2. What are the applications of dc chopper?
3. What are the advantages of dc chopper?
4. What is meant by step-up and step-down chopper?
5. What is meant by duty-cycle?
6. What are the two types of control strategies?
7. What is meant by TRC?
8. What are the two types of TRC?
9. What is meant by PWM control in dc chopper?
PART-B
1. Describe the principle of step-up chopper. Derive an expression for the average output ]
voltage in terms of input dc voltage & duty cycle. (16)
2. Describe the working of four quadrant chopper. (16)
3. Explain the working of current commutated chopper with aid of circuit diagram and
necessary waveforms. Derive an expression for its output voltage. (16)
4. Explain the working of voltage commutated chopper with aid of circuit diagram and
necessary waveforms. Derive an expression for its output voltage. (16)
UNIT IV
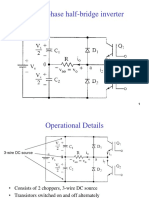
INVERTERS
PART-A
1. What is meant by inverter?
2. What are the applications of an inverter?
3. What are the main classification of inverter?
4. Why thyristors are not preferred for inverters?
EE 1353 POWER ELECTRONICS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, PUNALKULAM 3
5. Give two advantages of CSI.
6. What is meant a series inverter?
7. What is meant a parallel inverter?
8. What are the applications of a series inverter?
9. What is meant by McMurray inverter?
10. What are the applications of a CSI?
11. What is meant by PWM control?
12. What are the advantages of PWM control?
PART-B
1. Describe the operation of series inverter with aid of diagrams. Describe an expression for
output frequency, current and voltages. What are the disadvantages of basic series
inverter? (16)
2. State different methods of voltage control inverters. Describe about PWM control in
inverter. (16)
3. Explain the operation of 3 _ bridge inverter for 180 degree mode of operation with aid of
relevant phase and line voltage waveforms. (16)
UNIT V
AC VOLTAGE CONTROLLER
PART-A
1. What does ac voltage controller mean?
2. What are the applications of ac voltage controllers?
3. What are the advantages of ac voltage controllers?
4. What are the disadvantages of ac voltage controllers?
5. What are the two methods of control in ac voltage controllers?
6. What is the difference between ON-OFF control and phase control?
7. What is meant by cyclo-converter?
8. What are the two types of cyclo-converters?
9. What is meant by step-up cyclo-converters?
10. What is meant by step-down cyclo-converters?
11. What are the applications of cyclo-converter?
PART-B
1. Explain the operation of multistage control of AC voltage controllers with neat diagram. (16)
2. Explain the operation of 1_ AC voltage controller with RL load. (16)
3. Explain the operation of 1_ sinusoidal AC voltage controller. (16)
4. For a 1 _ voltage controller, feeding a resistive load, draw the waveforms of source voltage,
gating signals, output voltage and voltage across the SCR. Describe the working with
reference to waveforms drawn. (16)
You might also like
- Short Answer Type Questions: Unit Ii Voltage Source ConvertersDocument7 pagesShort Answer Type Questions: Unit Ii Voltage Source ConvertersBhanu Ganesh LukkaNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument2 pagesFinalgobinathNo ratings yet
- PS7202-Flexible AC Transmission Systems PDFDocument5 pagesPS7202-Flexible AC Transmission Systems PDF1balamanianNo ratings yet
- Important Questions - APS - IDocument3 pagesImportant Questions - APS - IAakash MehtaNo ratings yet
- Ee2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit IDocument38 pagesEe2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit INavneethNo ratings yet
- Subject Code/name: EE 2306-Flexible AC Transmission Systems: Facts 8 Kce/Eee/Qb/Ivyr/FactsDocument26 pagesSubject Code/name: EE 2306-Flexible AC Transmission Systems: Facts 8 Kce/Eee/Qb/Ivyr/FactssivakumarsarvananNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument29 pagesMCQsSuhaib QaisarNo ratings yet
- 161EE54 Question BankDocument5 pages161EE54 Question BankRajeshNo ratings yet
- PSOC 2 Marks With AnswerDocument10 pagesPSOC 2 Marks With AnswerAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- Power Quality 2 Marks and 16 MarksDocument6 pagesPower Quality 2 Marks and 16 MarksBala MuruganNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Series and Parallel Inverter FinalDocument19 pagesSingle Phase Series and Parallel Inverter Finalmazza23467% (3)
- Experiment - 12: Power Angle Curve of Syncronous MachineDocument3 pagesExperiment - 12: Power Angle Curve of Syncronous MachinesanjuNo ratings yet
- Power System Reactance Diagram Questions PDFDocument22 pagesPower System Reactance Diagram Questions PDFHota bNo ratings yet
- 200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Question Bank 3Document119 pages200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Question Bank 3NiteshNarukaNo ratings yet
- 2 Synchronous Generator WithansDocument19 pages2 Synchronous Generator WithansIncst Bhai0% (1)
- Viva QuestionsDocument5 pagesViva QuestionsKalyan RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chopper Notes1Document7 pagesChopper Notes1Ruthra DeviNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Efficiency and Voltage RegulationDocument18 pagesQuestions & Answers On Efficiency and Voltage Regulationkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- EE6702 2marksDocument21 pagesEE6702 2marksVISWA VikNo ratings yet
- Question Bank: Flexible Ac Transmission SystemsDocument20 pagesQuestion Bank: Flexible Ac Transmission SystemsGnanaseharan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Facts 2 MarksDocument14 pagesFacts 2 MarksBharath Raj100% (1)
- FACTS Question PapersDocument3 pagesFACTS Question PapersyelhankaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines-III Question BankDocument9 pagesElectrical Machines-III Question BanksanthiNo ratings yet
- Objective Question Protection and SwitchgearDocument20 pagesObjective Question Protection and SwitchgearRaja Desingu100% (1)
- Bee Viva QueDocument3 pagesBee Viva QueVijayramraj Mocherla40% (5)
- Power Electronics Chapter#06Document34 pagesPower Electronics Chapter#06Bilal HussainNo ratings yet
- Ee8004 Modern Power Converters SyllabusDocument2 pagesEe8004 Modern Power Converters SyllabussignjpcoeNo ratings yet
- Single Phase InverterDocument29 pagesSingle Phase InverterEla ResearchNo ratings yet
- EE 2402 - QB ProtectionDocument7 pagesEE 2402 - QB ProtectionArun Bharath RajaNo ratings yet
- EE 8602 - Protection and Switchgear Unit I - MCQ BankDocument11 pagesEE 8602 - Protection and Switchgear Unit I - MCQ Bankpoonam yadavNo ratings yet
- SUBJECT: Elective-I Flexible A.C. Transmission Systems (FACTS) Question Bank Unit-I:Introduction To FactsDocument4 pagesSUBJECT: Elective-I Flexible A.C. Transmission Systems (FACTS) Question Bank Unit-I:Introduction To FactsJagadish Babu KondraguntaNo ratings yet
- Facts QuestionsbankDocument7 pagesFacts Questionsbankjaackson10No ratings yet
- Generation of High D.C. Voltages & AC VoltagesDocument14 pagesGeneration of High D.C. Voltages & AC VoltagesSumaira SaifNo ratings yet
- Ee2351 Question BankDocument59 pagesEe2351 Question Banksaran_0666100% (1)
- Unit-6 Circuit Breakers (Switchgear and Protection)Document84 pagesUnit-6 Circuit Breakers (Switchgear and Protection)sujithNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadDocument3 pagesSingle Phase Half Controlled Converter With R LoadB ANIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- Hopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesHopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorVarun VadluriNo ratings yet
- Industrial Drives Lab File PDFDocument19 pagesIndustrial Drives Lab File PDFMayankJainNo ratings yet
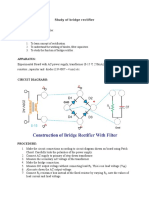
- Study of Bridge Rectifier: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesStudy of Bridge Rectifier: ObjectivesDeepak KumbharNo ratings yet
- Praharsh PPT (Modelling of Unified Power Flow Controller) GGDocument16 pagesPraharsh PPT (Modelling of Unified Power Flow Controller) GGPraharsh MishraNo ratings yet
- EE2351 PSA Answers PDFDocument58 pagesEE2351 PSA Answers PDFkrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- DCMTDocument37 pagesDCMTGloria HolcombNo ratings yet
- Parallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesDocument9 pagesParallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesJayant Kirpekar100% (1)
- Four Quadrant Operation of DC Drives: - Dual ConvertersDocument12 pagesFour Quadrant Operation of DC Drives: - Dual ConvertersDr.K.Krishna Veni ProfessorNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA MethodDocument6 pagesExperiment No.3-Voltage Regulation of A 3-Phase Alternator by ZPF and ASA Method61EEPrabhat Pal100% (1)
- Question and AnswersDocument46 pagesQuestion and AnswersKumaranNo ratings yet
- Generation of WaveformsDocument9 pagesGeneration of WaveformsNivas Kumar SureshNo ratings yet
- Ee 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesEe 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswerssukeshsrkNo ratings yet
- Ee 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersDocument7 pagesEe 1352 Power System Analysis Question and AnswersSandhosh RajaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 2 MarkDocument5 pagesPower Electronics 2 MarkPrakash Mahendran100% (2)
- Swinburne S Test On DC Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesSwinburne S Test On DC Shunt Motortamann2004No ratings yet
- Drives and Control Lab ManualDocument36 pagesDrives and Control Lab ManualKabilanNo ratings yet
- Investigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsFrom EverandInvestigation of the Usefulness of the PowerWorld Simulator Program: Developed by "Glover, Overbye & Sarma" in the Solution of Power System ProblemsNo ratings yet
- WWW Universityquestions inDocument8 pagesWWW Universityquestions inagreykatoNo ratings yet
- EE2301 Power ElectronicsDocument12 pagesEE2301 Power ElectronicsMuniyasamy BalaNo ratings yet
- Mlp-Ee 51Document11 pagesMlp-Ee 51prasad357No ratings yet
- PE Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesPE Lesson PlanAnbalagan GuruNo ratings yet
- EE6503 Power ElectronicsDocument8 pagesEE6503 Power ElectronicscoolrajeeeNo ratings yet
- 4hana 1909Document60 pages4hana 1909ddharNo ratings yet
- ONDULEUR APC Easy UPS 3S 1-10 KVADocument7 pagesONDULEUR APC Easy UPS 3S 1-10 KVAouattara yaya katiaNo ratings yet
- Recon2015 14 Christopher Domas The MovfuscatorDocument158 pagesRecon2015 14 Christopher Domas The Movfuscatorjames wrightNo ratings yet
- Pascal Ehimare,: Popm, AsmDocument2 pagesPascal Ehimare,: Popm, AsmharshNo ratings yet
- Lecture0 720p enDocument19 pagesLecture0 720p enanupathi mamatha deen dayalNo ratings yet
- Book2 20231108011717Document137 pagesBook2 20231108011717oindrila dasguptaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Supply Chain Integration On Information Sharing Enhancing The Supply Chain PerformanceDocument20 pagesThe Effect of Supply Chain Integration On Information Sharing Enhancing The Supply Chain PerformanceOsama MazharNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Basic Printing Education For Human Resource Development in Printing IndustryDocument12 pagesThe Importance of Basic Printing Education For Human Resource Development in Printing IndustryAries Chandra AnandithaNo ratings yet
- Gaia Reference v8p4Document57 pagesGaia Reference v8p4De Jesus, AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Test Class MethodsDocument7 pagesTest Class Methodsvarun.chintatiNo ratings yet
- Sans 1231Document1 pageSans 1231Sandro MeloNo ratings yet
- Soc BookDocument19 pagesSoc BookmuraliNo ratings yet
- Philips FWC170Document54 pagesPhilips FWC170Luis Nava CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mphasis Data 10.4.19Document5 pagesMphasis Data 10.4.19Vyshnavi ThottempudiNo ratings yet
- For The Full Manual, Refer To The CD Inside The Rear Cover: Avcount2 Particle Counters SA1000-2 & SA1250-2Document8 pagesFor The Full Manual, Refer To The CD Inside The Rear Cover: Avcount2 Particle Counters SA1000-2 & SA1250-2Renzo Jaime Gabriel BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Precious - Resume-232Document2 pagesPrecious - Resume-232PreciousNo ratings yet
- Mamoolat e YoumiaDocument49 pagesMamoolat e YoumiaSheraz Ali RajNo ratings yet
- OneDrive For BusinessDocument29 pagesOneDrive For BusinessJohann NeethlingNo ratings yet
- Extreme Privacy: Personal Data Removal Workbook & Credit Freeze GuideDocument36 pagesExtreme Privacy: Personal Data Removal Workbook & Credit Freeze Guideblacksun_moon100% (2)
- Seatupjee Poly Jan1316Document63 pagesSeatupjee Poly Jan1316Arshdeep YadavNo ratings yet
- Class Activity - Identify Running Processes: ObjectivesDocument2 pagesClass Activity - Identify Running Processes: Objectivestinod18399No ratings yet
- Mto, Bom & BoqDocument3 pagesMto, Bom & BoqDayo IdowuNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions Converter 801Document26 pagesOperating Instructions Converter 801Vu Duc TuNo ratings yet
- Job Description PharmacistDocument4 pagesJob Description PharmacistAbdiNo ratings yet
- CCNP Switching LAB Preparation TestDocument2 pagesCCNP Switching LAB Preparation TestGiannisDemetriouNo ratings yet
- Part List - Piston & Rod Group PDFDocument2 pagesPart List - Piston & Rod Group PDFRahulNo ratings yet
- Discussion Assignment 5Document5 pagesDiscussion Assignment 5Nothando MkhwanaziNo ratings yet
- Soldering TutorialDocument15 pagesSoldering Tutorialyrikki100% (1)
- Zella Pro Tech Specs - March 2021Document16 pagesZella Pro Tech Specs - March 2021Yusuf ShunanNo ratings yet
- Concept of ERS in SAP MMDocument9 pagesConcept of ERS in SAP MMARABINDA CHAKRAVARTYNo ratings yet