Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SSC Je Syllabus
Uploaded by
Prabhakar Kumar Barnwal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagegud
Original Title
Ssc Je Syllabus
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentgud
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageSSC Je Syllabus
Uploaded by
Prabhakar Kumar Barnwalgud
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
2.
General Engineering (Civil and Structural)
Civil Engineering:
Building Materials: Physical and Chemical properties, classification, standard tests, uses and
manufacture/quarrying of materials e.g. building stones, silicate based materials, cement (Portland),
Asbestos products, Timber and Wood based Products, laminates, bituminous materials, paints, varnishes.
Surveying: Principles of surveying, working of properties, compass and bearing, plane table surveying,
theodolite traverse, adjustment of theodolite, levelling and contouring, curvature, refraction, permanent
adjustment of dumpy level, methods of contouring and uses of a control map, tachometric survey.
Soil Mechanics: Origin of soil phase diagram, definitions of void ratio, porosity, degree of saturation, water
content, specific gravity of soil grains and unit weights, grain size distribution curves for different solid and
their uses. Atterjergs limits, ISI soil classification, plasticity chart, coefficient of permeability, effective
stress, consolidation of soils.
Calculation of shear strength of soils, direct shear test, vane shear test, triaxial test, soil compaction, Lab
compaction, Lab compaction test, moisture content and bearing capacity of soils, plate load test, standard
penetration test.
Hydraulics: Fluid properties, hydrostatics, measurements of flow, Bernoullis theorem and its application,
flow through pipes, flow in open channels, weirs, flumes, spillways, pumps and turbines.
Environmental Engineering: Quality of water, source of water supply, purification of water, distribution of
water, need of sanitation, sewerage system, circular sewers, oval sewer, sewer appurtenances, surface water
drainage, sewage treatments.
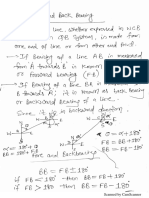
Structural Engineering : Theory of structures: Elasticity constants, type of beams, determinate and
indeterminate, bending moment and shear force diagrams of simply supported, cantilever and over hanging
beams. Moment of area and moment of inertia for rect. & circular section, bending moment and shear stress
for tee, channel and compound sections, chimneys, dams and retaining walls, eccentric loads, slope
deflection of simply supported and cantilever beams, critical load and columns, torsion of circular section.
Concrete Technology : Properties, Advantages and uses of concrete, cement aggregates quality, water
cement ratio, workability, mix design, storage, batching, mixing, placement, compaction, finishing and curing
of concrete, quality control of concrete, hot weather and cold weather concreting, repair and maintenance of
concrete structure.
RCC Design:
RCC beams: flexural strength, shear strength, bond strength, design of single reinforced beans, lintels,
cantilever beams, double reinforced beams, one way slabs, two way slabs, isolated footings, reinforced brick
work. T-beams, columns, staircases, retaining walls, water tanks (RCC design questions may be based on
both Limit State method and Working Stress method).
Steel Design: Steel design and construction of steel columns, beams, roof trusses, plate girders.
You might also like
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Deriving Accident Costs Using Willingness-to-Pay Approaches - A Case Study For SingaporeDocument17 pagesDeriving Accident Costs Using Willingness-to-Pay Approaches - A Case Study For SingaporePrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Sl. No. Name of Faculty M/F PAN. No. Designation DOBDocument7 pagesSl. No. Name of Faculty M/F PAN. No. Designation DOBPrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- CE-III Sem TIME TABLEDocument1 pageCE-III Sem TIME TABLEPrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- FB & BBDocument18 pagesFB & BBPrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Willingness-To-Pay For Road Safety Improvement: Mohamed Mouloud Haddak, Nathalie Havet, Marie LefèvreDocument18 pagesWillingness-To-Pay For Road Safety Improvement: Mohamed Mouloud Haddak, Nathalie Havet, Marie LefèvrePrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic ControlDocument24 pagesAir Traffic ControlPrabhakar Kumar Barnwal100% (1)
- HydroGraphic SurveyingDocument7 pagesHydroGraphic SurveyingPrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Social Cost of Road Traffic Crashes in India PDFDocument10 pagesSocial Cost of Road Traffic Crashes in India PDFPrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- MCQ TestDocument4 pagesMCQ TestPrabhakar Kumar Barnwal0% (1)
- Previous Paper HPPSC Assistant Engineer Civil 1 PDFDocument38 pagesPrevious Paper HPPSC Assistant Engineer Civil 1 PDFabhishek vatsiNo ratings yet
- RepairDocument3 pagesRepairPrabhakar Kumar BarnwalNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Lec 6Document16 pagesLec 6shahid aliNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundations For River Bridges According To Ec 7-1: Manfred Fross, Dietmar Adam, Robert HofmannDocument2 pagesPile Foundations For River Bridges According To Ec 7-1: Manfred Fross, Dietmar Adam, Robert HofmannharshaNo ratings yet
- Evaluasi Serta Perancangan Aplikasi Emergency Response Plan (Erp) Dan Sistem Proteksi Kebakaran Aktif Di Perusahaan Fabrikasi Boiler Berbasis AndroidDocument6 pagesEvaluasi Serta Perancangan Aplikasi Emergency Response Plan (Erp) Dan Sistem Proteksi Kebakaran Aktif Di Perusahaan Fabrikasi Boiler Berbasis AndroidYoga NurwansyahNo ratings yet
- Technictehal Data TN0 - SSDocument4 pagesTechnictehal Data TN0 - SSMihai ApostoliuNo ratings yet
- Technical Data - CABLE 2P X 1 SQMMDocument1 pageTechnical Data - CABLE 2P X 1 SQMMManoj AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Culvert (1x3.0x3.0)Document19 pagesCulvert (1x3.0x3.0)Shashank SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- RC5 Data Sheet MGS40 DN100-150 @enDocument2 pagesRC5 Data Sheet MGS40 DN100-150 @enAmeneh KhajehaliNo ratings yet
- Library Technical Furniture SpecificationsDocument8 pagesLibrary Technical Furniture SpecificationsModernLibraryDesignNo ratings yet
- Cheng WentaoDocument289 pagesCheng WentaorodofgodNo ratings yet
- ASTM StandardsDocument4 pagesASTM StandardsBalaji Lubricants & ChemicalsNo ratings yet
- CBPM Portfolio HeritageDocument1 pageCBPM Portfolio Heritageapi-241367179No ratings yet
- API2000 Tank Venting CalcsDocument5 pagesAPI2000 Tank Venting Calcsruhul01No ratings yet
- Handrail Code AnalysisDocument1 pageHandrail Code AnalysisSivadol VongmongkolNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Designing Plumbing SystemsDocument13 pagesUnderstanding and Designing Plumbing SystemsGowtham PNo ratings yet
- Self Cooling BuildingDocument41 pagesSelf Cooling BuildingSubham PaulNo ratings yet
- Timesaving Design Aids-Part 2Document28 pagesTimesaving Design Aids-Part 2Ahmet TükenNo ratings yet
- Business Name: Solanki Plastic Business Address: 72/2, Khatipura, Near ElectronicDocument3 pagesBusiness Name: Solanki Plastic Business Address: 72/2, Khatipura, Near ElectronicShelendraSinghNo ratings yet
- PAM Advisory Note Covid-19 MCO PDFDocument1 pagePAM Advisory Note Covid-19 MCO PDFkjfNo ratings yet
- Sistema Monolitico DOKA One GoDocument50 pagesSistema Monolitico DOKA One GoPeter MarvinNo ratings yet
- Concrete Making MaterialsDocument55 pagesConcrete Making Materialsjaffna100% (1)
- Kathmandu Engineering College Kalimati 2075 FalgunDocument3 pagesKathmandu Engineering College Kalimati 2075 Falgunविशाल पुडासैनीNo ratings yet
- Literature Study of Hotel: School of Architecture SBSSTC, FerozepurDocument7 pagesLiterature Study of Hotel: School of Architecture SBSSTC, FerozepuranasNo ratings yet
- Porch Stairs Section Detail Lintel Beam Section Detail: H (H Depth of Beam)Document1 pagePorch Stairs Section Detail Lintel Beam Section Detail: H (H Depth of Beam)Lourdjeth AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- API 5l Practice Questions Doc r2Document4 pagesAPI 5l Practice Questions Doc r2Anonymous SLI4aGNo ratings yet
- Managing Building Moisture PDFDocument53 pagesManaging Building Moisture PDFengmec04No ratings yet
- Yc 108 GDocument72 pagesYc 108 Gyewlim100% (1)
- Wall Chart Linings VESUVIUS FOSECODocument1 pageWall Chart Linings VESUVIUS FOSECOGermano BissonNo ratings yet
- Wickes Laying PatioDocument8 pagesWickes Laying PatiofiachduhNo ratings yet
- Controllable Pitch Propellers and Reduction Gear: Key Features Kongsberg Propulsion SystemsDocument4 pagesControllable Pitch Propellers and Reduction Gear: Key Features Kongsberg Propulsion SystemsVighnesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Fosroc Dekguard AC: Constructive SolutionsDocument4 pagesFosroc Dekguard AC: Constructive SolutionsVJ QatarNo ratings yet