Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endocrine
Uploaded by
sparticuslivesCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Endocrine
Uploaded by
sparticuslivesCopyright:
Available Formats
4Anterior Pituitary
GH (Growth hormone)
- Promotes growth of all body tissue
TSH (Thyroid stimulating hormone)
- Stimulates thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone)
- Stimulates the adrenal gland to release cortisol; cortisol helps to maintain B/P and blood glucose
Hypopituitarism (Pituitary insufficiency)
- Deficiency in 1 or > hormones listed above leads to loss of function in the gland or organ that it controls
- !or e"ample# no $S% leads to loss of function in the thyroid gland
Hyperpituitarism (Gigantism or Acromegaly)
- Severe disfigurement# serious complicating conditions# and premature death if unchec&ed ' hard to diagnose in the
early stages
Posterior Pituitary
ADH (Antidiuretic hormone !asopressin)
- Promotes reabsorption of water in the &idney tubules; Stimulates smooth muscle tissue of blood vessels to constrict
Deficiency of ADH (Dia"etes #nsipidus)
- (ater metabolism problem d/t ) *D% synthesis or inability of the &idneys to respond to the *D%
- +a ,hemoconcentration-
$%cess of ADH (Syndrome of #nappropriate Antidiuretic hormone (S#ADH)
- $he body develops an e"cess of water and a decrease in sodium ,salt- concentration# as a result of improper
chemical signals
- .f there is too much *D% in the body# or if the &idneys overreact to the *D% they receive# the body retains
e"cess water and the serum sodium concentration becomes diluted and falls to abnormal levels
- ) +a ,hemodilution-
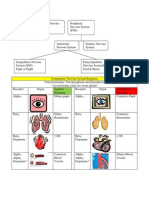
Adrenal &edulla (regulated by nerve impulses from the hypothalamus)
$pinephrine ' (orepinephrine
- / B/P ' %0; $hese two hormones are secreted in response to stimulation by sympathetic nerve# particularly during
stressful situations * lac& of hormones from the adrenal medulla produces no significant effects
Adrenal Corte% (regulated by negative feedback involving the hypothalamus)
Chemically, all the cortical hormones are steroids.
&ineralocorticoids (outermost region)
- $he principal mineralocorticoid is aldosterone# which acts to conserve sodium ions and water in the body
Glucocorticoids (middle region)
- $he principal glucocorticoid is cortisol# which increases blood glucose levels
Gonadocorticoids (se% hormones)
- Secreted by the innermost region
- +ote1 $he adrenal gland may oversecrete 1 or all adrenal hormones
Hyposecretion of adrenal corte% hormones
(Adrenocortical insufficiency ) Adrenal crisis ) Addisonian crisis or Adrenal #nsufficiency)
- ) *ldosterone ' cortisol
- ) 2lucose ,) gluconeogenesis ' ) liver ' muscle glycogen
- ) 2!0 ' gastric acid ,urea nitrogen e"cretion- 3 anore"ia ' weight loss
- 4"cessive reabsorption of potassium 3 / 5 ,hyper&alemia- ' e"cretion of +a )
ACTH(Adrenocorticotropic hormone)
- stimulates the adrenal gland to release cortisol; During steroid therapy# the hypothalamus# pituitary# '
adrenal gland are suppressed- so if stopped suddenly the client will develop s/s of adrenal insufficiency '
return of normal adrenal function can ta&e up to 6 months
Hypersecretion of adrenal corte% hormones
(Hypercortisolism ) Cushing*s disease or Cushing*s syndrome ) Hyperaldosteronism (mineralocorticoid)
or $%cessi+e Androgen)
- / 7ortisol 3 ) 8ymphocytes
- / 2lucose
- / +a ' ) 7a ' 5 ,*ldosterone / reabsorption of +a ' e"cretion of )5 ,%yperaldosterism ,.ncreased secretion of
aldosterone 3 mineralocorticoid e"cess - 7onn9s syndrome-
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- CEN Brochure SAFH InformationDocument3 pagesCEN Brochure SAFH InformationsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Today 5Document1 pageToday 5sparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Expense Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesExpense Analysis WorksheetsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Expense Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesExpense Analysis WorksheetsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- CEN Brochure SAFH InformationDocument3 pagesCEN Brochure SAFH InformationsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Neonatal Icu Skills ChecklistDocument5 pagesNeonatal Icu Skills ChecklistsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Expense Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesExpense Analysis WorksheetsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Expense Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesExpense Analysis WorksheetsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrinesparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Cardiovascular ReviewDocument8 pagesCardiovascular ReviewsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Expense Analysis WorksheetDocument2 pagesExpense Analysis WorksheetsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrinesparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument2 pagesEndocrinesparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Cardiovascular ReviewDocument8 pagesCardiovascular ReviewsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ANS ChartDocument3 pagesANS ChartsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Cardiovascular ReviewDocument8 pagesCardiovascular ReviewsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Vascular Disorders CH 38Document6 pagesVascular Disorders CH 38sparticuslives100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Vascular Disorders CH 38Document6 pagesVascular Disorders CH 38sparticuslives100% (1)
- PCA and Epidural Presentation Outline 2014Document10 pagesPCA and Epidural Presentation Outline 2014sparticuslives100% (1)
- Cardiovascular ReviewDocument8 pagesCardiovascular ReviewsparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Vascular Disorders CH 38Document6 pagesVascular Disorders CH 38sparticuslives100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- ANS ChartDocument3 pagesANS ChartKara Dawn MasonNo ratings yet
- Criteria For INACTIVE MRSA StatusDocument2 pagesCriteria For INACTIVE MRSA StatussparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- ANS ChartDocument3 pagesANS ChartKara Dawn MasonNo ratings yet
- Explanation of AbbreviationsDocument1 pageExplanation of AbbreviationssparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Explanation of AbbreviationsDocument1 pageExplanation of AbbreviationssparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Explanation of AbbreviationsDocument1 pageExplanation of AbbreviationssparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- PCA and Epidural Presentation Outline 2014Document10 pagesPCA and Epidural Presentation Outline 2014sparticuslives100% (1)
- Explanation of AbbreviationsDocument1 pageExplanation of AbbreviationssparticuslivesNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)