Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Probability and Stochastic Processes (PTSP
Uploaded by
Bnr GoudOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Probability and Stochastic Processes (PTSP
Uploaded by
Bnr GoudCopyright:
Available Formats
(53019) PROBABILITY THEORY AND STOCHASTIC PROCESSESUnit I: Probability
Probability introduced through Sets and Relative Frequency, Experiments and Sample Spaces, Discrete
andContinuous Sample Spaces, Events, Probability Definitions and Axioms, Mathematical Model of
Experiments,Probability as a Relative Frequency, Joint Prob
ability, Conditional Probability, Total Probability, Bayes Theorem,
Independent Events.
Unit II: Random Variable
Definition of a Random Variable, Conditions for a Function to be a Random Variable, Discrete, Continuous andMixed
Random Variables, Distribution and Density functions and their Properties - Binomial, Poisson, Uniform,Gaussian,
Exponential, Rayleigh and Conditional Distribution, Methods of defining Conditional Event,Conditional Density,
Properties.
Unit III: Operation on One Random Variable
Expectations
Introduction, Expected Value of a Random Variable, Function of a Random Variable, Moments about the Origin,
Central Moments, Variance and Skew, Chebychevs Inequality, Characteristic Function, Moment Generating
Function, Transformations of a Random Variable: Monotonic Transformations for a Continuous RandomVariable,
Nonmonotonic Transformations of Continuous Random Variable, Transformation of a Discrete RandomVariable.
Unit IV: Multiple Random Variables
Vector Random Variables, Joint Distribution Function, Properties of Joint Distribution, Marginal DistributionFunctions,
Conditional Distribution and Density
Point Conditioning, Conditional Distribution and Density
Interval conditioning, Statistical Independence, Sum of Two Random Variables, Sum of Several RandomVariables,
Central Limit Theorem (Proof not expected), Unequal Distribution, Equal Distributions.
Unit V: Operations on Multiple Random Variables
Expected Value of a Function of Random Variables: Joint Moments about the Origin, Joint Central Moments,Joint
Characteristic Functions, Jointly Gaussian Random Variables: Two Random Variables case, N RandomVariable
case, Properties, Transformations of Multiple Random Variables, Linear Transformations of GaussianRandom
Variables.
Unit VI: Stochastic Processes
Temporal Characteristics
The Stochastic Process Concept, Classification of Processes, Deterministic and Nondeterministic
Processes,Distribution and Density Functions, Concept of Stationarity and Statistical Independence, First-Order
StationaryProcesses, Second-Order and Wide-Sense Stationarity, Nth Order and Strict-Sense Stationarity, Time
Averagesand Ergodicity, Mean-Ergodic Processes, Correlation-Ergodic Processes, Autocorrelation Function and
itsProperties, Cross-Correlation Function and its Properties, Covariance and its Properties, Linear SystemResponse
of Mean and Mean-squared Value, Autocorrelation Function, Cross-Correlation Functions, GaussianRandom
Processes, Poisson Random Process.
Unit VII: Stochastic Processes
Spectral Characteristics
Power Spectrum: Properties, Relationship between Power Spectrum and Autocorrelation Function, Cross-
Power Density Spectrum, Properties, Relationship between Cross-Power Spectrum and Cross-Correlation
Function,Spectral Characteristics of System Response: Power Density Spectrum of Response, Cross-Power
SpectralDensity of Input and Output of a Linear System.
Unit VIII: Noise
Types of Noise: Resistive (Thermal) Noise Source, Shot noise, Extra terrestrial Noise, Arbitrary Noise Sources,White
Noise, Narrowband Noise : In phase and quadrature phase components and its Properties, Modeling of Noise
Sources, Average Noise Bandwidth, Effective Noise Temperature, Average Noise Figures, Average NoiseFigure of
cascaded networks
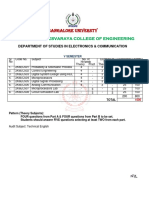
LESSON PLAN
YEAR & SEM : II-I SUBJECT: PTSP
BRANCH: ECE(A&B) FACULTY: Mythii Sharan
UNIT 1: Probability
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 I
Probability introduced through Sets and Relative
Frequency
2
2 I
Experiments and Sample Spaces, Discrete and
Continuous Sample Spaces
1
3 I
Events, Probability Definitions and Axioms,
Mathematical Model of Experiments
2
4 I
Probability as a Relative Frequency
1
5 I
Joint Probability
2
6 I
Conditional Probability, Total Probability, Bayes
Theorem,
2
7 I
Independent Events.
1
Total no of classes: 11
UNIT 2: Random Variable
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 II
Definition of a Random Variable, Conditions for a
Function to be a Random Variable
1
2 II
Discrete, Continuous andMixed Random
Variables
1
3 II
Distribution functions and their Properties
2
4 II
Density functions and their Properties
2
5 II
Binomial Poisson distribution
3
6 II
Uniform, Gaussian, Exponential, Rayleigh
and Conditional Distribution
3
7 II
Methods of defining Conditional
Event,Conditional Density, Properties
2
8 II Revision 1
Total no of classes: 15
UNIT 3: Operation on One Random VariableExpectations
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 III
Introduction, Expected Value of a Random
Variable
, ,
1
2 III
Function of a Random Variable,
1
3 III
Moments about the Origin,
Central Moments, Variance and Skew, Chebychevs
Inequality
3
4 III
Characteristic Function, Moment Generating
Function,
1
5 III
Transformations of a Random Variable:
Monotonic Transformations for a Continuous
RandomVariable, Nonmonotonic
Transformations of Continuous Random
Variable, Transformation of a Discrete
RandomVariable
2
Total no of classes: 08
UNIT 4 Multiple Random Variables
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 IV
Vector Random Variables, Joint Distribution
Function
2
2 IV
Properties of Joint Distribution, Marginal
DistributionFunctions
2
3 IV
Conditional Distribution and Density
2
4 IV
Statistical Independence, Sum of Two Random
Variables, Sum of Several RandomVariables,
2
5 IV
Central Limit Theorem (Proof not expected),
Unequal Distribution, Equal Distributions.
2
Total no of classes: 10
UNIT 5 Operations on Multiple Random Variables
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 V
Expected Value of a Function of Random
Variables
1
2 V
Joint Moments about the Origin, Joint Central
Moments,Joint Characteristic Functions
3
3 V
Jointly Gaussian Random Variables: Two
Random Variables case
2
4 V
N RandomVariable case, Properties,
Transformations of Multiple Random Variables
2
5 V
Linear Transformations of GaussianRandom
Variables
1
7 V Revision 1
Total no of classes: 10
UNIT 6: Stochastic Processes Temporal Characteristics
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 VI
The Stochastic Process Concept, Classification
of Processes
1
2 VI
Deterministic and Nondeterministic
Processes,Distribution and Density Functions
1
3 VI
Concept of Stationarity and Statistical
Independence, First-Order StationaryProcesses,
Second-Order and Wide-Sense Stationarity, Nth
Order and Strict-Sense Stationarity,
2
4 VI
Time Averagesand Ergodicity, Mean-Ergodic
Processes, Correlation-Ergodic Processes,
Autocorrelation Function and itsProperties
2
5 VI
Cross-Correlation Function and its Properties,
Covariance and its Properties
2
6 VI
Linear SystemResponse of Mean and Mean-
squared Value, Autocorrelation Function, Cross-
Correlation Functions,
2
7 VI
GaussianRandom Processes, Poisson Random
Process
1
Total no of classes: 11
UNIT 7: Stochastic Processes Spectral Characteristics
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 VII
Power Spectrum: Properties,
2
2 VII
Relationship between Power Spectrum and
Autocorrelation Function
2
3 VII
Cross-Power Density Spectrum, Properties,
1
4 VII
Relationship between Cross-Power Spectrum
and Cross-Correlation Function
2
5 VII
Characteristics of System Response: Power
Density Spectrum of Response
2
6 VII
Spectral, Cross-Power SpectralDensity of Input
and Output of a Linear System.
2
Total no of classes: 11
UNIT 8: Noise
S.NO UNIT TOPIC NO.OF
CLASSES
1 VIII
Types of Noise: Resistive (Thermal) Noise
Source, Shot noise, Extra terrestrial Noise,
1
2 VIII
Arbitrary Noise Sources,White Noise
1
3 VIII
Narrowband Noise : In phase and quadrature
phase components and its Properties, Modeling
of Noise Sources
1
4 VIII
Average Noise Bandwidth
1
5 VIII
Effective Noise Temperature, Average Noise
Figures
1
6 VIII
Average NoiseFigure of cascaded networks
1
Total no of classes: 06
HOD PRINCIPAL
TEACHING SCHEDULE
III YEAR II SEMESTER
SUBJECT: DSP
BRANCH: ECE(A&B) FACULTY: B.RAVINDRA NAIK
S.NO UNIT TOTAL CLASSES
1 1 11
2 II 14
3 III 10
4 IV 10
5 V 10
6 VI 11
7 VII 11
8 VIII 06
Total classes 80
HOD PRINCIPAL
You might also like
- Conditional Variance Conditional Expectation Iterated Expectations Independent Random VariablesDocument1 pageConditional Variance Conditional Expectation Iterated Expectations Independent Random VariablesKenosNo ratings yet
- PTSP Jntu SyllabusDocument2 pagesPTSP Jntu SyllabusGS Naveen Kumar100% (1)
- Probability Theory and Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pagesProbability Theory and Stochastic ProcessesLaxmi KumariNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pagesProbability Theory and Stochastic Processessmyle_nag100% (1)
- Syllabus-1Document17 pagesSyllabus-1ECE N.V.Satyanarayana MurthyNo ratings yet
- PTSP SyllabusDocument2 pagesPTSP SyllabusTayyabunnissa BegumNo ratings yet
- EceDocument11 pagesEceparrotpanduNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationDocument73 pagesAnalog CommunicationMelaku DinkuNo ratings yet
- 5th Sem SyllabusDocument11 pages5th Sem SyllabusC MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- PTSP - MLRS - R22 - II - I - ECE - SyllabusDocument2 pagesPTSP - MLRS - R22 - II - I - ECE - Syllabusrupa kumar dhanavathNo ratings yet
- Unit-I:: Year & Sem: E1S2 Course Code: EC1301 Course Name: Probability No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0Document1 pageUnit-I:: Year & Sem: E1S2 Course Code: EC1301 Course Name: Probability No. of Credits: 4 L T&Ps P 2 2 0ANKALA HARINADHNo ratings yet
- Random Vibrations & Failure Analysis CourseDocument14 pagesRandom Vibrations & Failure Analysis CourseHarshit AgrahariNo ratings yet
- Random Variables & Stochastic ProcessesDocument2 pagesRandom Variables & Stochastic ProcessesAnonymous WL0eWCeNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes: Course Description and ObjectivesDocument3 pagesProbability Theory and Stochastic Processes: Course Description and ObjectivesD JNo ratings yet
- MA202 Probability Distributions, Transforms and Numerical MethodsDocument3 pagesMA202 Probability Distributions, Transforms and Numerical MethodsSáçhìñDêvNo ratings yet
- MA202 Probability Distributions, Transforms and Numerical Methods SyllabusDocument3 pagesMA202 Probability Distributions, Transforms and Numerical Methods SyllabusPMNo ratings yet
- BTech S4 Probability DistributionDocument3 pagesBTech S4 Probability DistributionJohn RoyNo ratings yet
- Compiled by Birhan Fetene: Stat 276: Introductory Probability Lecture NotesDocument77 pagesCompiled by Birhan Fetene: Stat 276: Introductory Probability Lecture NotesAbdu HailuNo ratings yet
- Allied 3 - Mathematical Statistics I - Semester IIIDocument3 pagesAllied 3 - Mathematical Statistics I - Semester IIISwethaNo ratings yet
- MA202 Probability Distributions Transforms and Numerical MethodsDocument3 pagesMA202 Probability Distributions Transforms and Numerical Methodsaranuraj999_85222309No ratings yet
- Esla Mod1 5@azdocuments - inDocument151 pagesEsla Mod1 5@azdocuments - inKrupanand KiranNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument20 pagesStatisticsEconomic TruthNo ratings yet
- Kerala Technological University Master of Technology - Curriculum, Syllabus & Course PlanDocument2 pagesKerala Technological University Master of Technology - Curriculum, Syllabus & Course Planmanjunath nNo ratings yet
- Random Process SyllabusDocument2 pagesRandom Process Syllabusmanjunath nNo ratings yet
- Probability & Stochastic Processes Course HandoutDocument3 pagesProbability & Stochastic Processes Course HandoutkattaswamyNo ratings yet
- Te - Extc - Sem 5 (Rev)Document29 pagesTe - Extc - Sem 5 (Rev)siddhantmishra007No ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument112 pagesProbability and StatisticsBiraj GhimireNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument127 pagesProbability and StatisticsproursNo ratings yet
- 1.PTSP SyllabusDocument2 pages1.PTSP SyllabusSaivenkat BingiNo ratings yet
- Program: Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence: Section 1. Linear Algebra and Analytic GeometryDocument49 pagesProgram: Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence: Section 1. Linear Algebra and Analytic GeometryTameneNo ratings yet
- Semester IIIDocument2 pagesSemester IIIAakarshak NandwaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engg - SE (SEM IV)Document17 pagesMechanical Engg - SE (SEM IV)Vallabh MehtreNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Stochastic Process-18Document195 pagesProbability Theory and Stochastic Process-18Bighnaraj PatiNo ratings yet
- Ece201 Probability Theory and Random Process TH 1.10 Ac29Document2 pagesEce201 Probability Theory and Random Process TH 1.10 Ac29netgalaxy2010No ratings yet
- PDFDocument3 pagesPDFBharathi SelvamNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and StatisticsDocument2 pagesProbability Theory and StatisticsVishnuvardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Jntuk 2-1 and 2-2 ECE Syllabus R10Document30 pagesJntuk 2-1 and 2-2 ECE Syllabus R10anushkaaaaaaaaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering 3rd&4th Semester SyllabusDocument10 pagesChemical Engineering 3rd&4th Semester Syllabusadityakushwaha371No ratings yet
- Mathematical Techniques of Applied Probability: Discrete Time Models: Basic TheoryFrom EverandMathematical Techniques of Applied Probability: Discrete Time Models: Basic TheoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PTSP Lecture NotesDocument19 pagesPTSP Lecture NotesshandilyaNo ratings yet
- 1-2 Syllabus 2010-2011Document42 pages1-2 Syllabus 2010-2011kiranbondNo ratings yet
- Engineering Maths 4 SyllabusDocument3 pagesEngineering Maths 4 SyllabusRanjan NayakNo ratings yet
- S.Y.B.SC (I.T) Applied Mathematics: Semester - Iii (CBCS)Document271 pagesS.Y.B.SC (I.T) Applied Mathematics: Semester - Iii (CBCS)Monisha MudaliarNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem SyllabusDocument3 pages4th Sem SyllabusRaimond RosarioNo ratings yet
- PHY 212-QuantumMechanics-I PHY 513 Quantum Theory-I-Muhammad Sabieh AnwarDocument4 pagesPHY 212-QuantumMechanics-I PHY 513 Quantum Theory-I-Muhammad Sabieh AnwarMuhammadTahaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus IV Semester Engineering Mathematics - Iii 08.401 Probability & Random Processes (Ta)Document8 pagesSyllabus IV Semester Engineering Mathematics - Iii 08.401 Probability & Random Processes (Ta)Renjith R NairNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 1st Year VtuDocument0 pagesSyllabus 1st Year Vtuapi-238188038No ratings yet
- Syllabus 8th SemesterDocument4 pagesSyllabus 8th SemesterChittaranjan satapathyNo ratings yet
- DSE Syllabus - Semester IIIDocument4 pagesDSE Syllabus - Semester IIIRhutuja AmbatkarNo ratings yet
- National University: Third Year Syllabus Depart Ment of PhysicsDocument10 pagesNational University: Third Year Syllabus Depart Ment of PhysicsmasudNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory: Measure, Integration and Random VariablesDocument151 pagesProbability Theory: Measure, Integration and Random VariablesRocApplyNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory: STAT310/MATH230 September 12, 2010Document151 pagesProbability Theory: STAT310/MATH230 September 12, 2010RocApplyNo ratings yet
- (CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics) Roger Temam - Navier-Stokes Equations and Nonlinear Functional Analysis-Society For Industrial Mathematics (1987)Document160 pages(CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics) Roger Temam - Navier-Stokes Equations and Nonlinear Functional Analysis-Society For Industrial Mathematics (1987)natanael quintinoNo ratings yet
- Probability and Random ProcessesDocument2 pagesProbability and Random ProcessesTanishq BhedaNo ratings yet
- Probability and Random Processes PDFDocument2 pagesProbability and Random Processes PDFTanishq BhedaNo ratings yet
- EC 622 Statistical Signal Processing SyllabusDocument135 pagesEC 622 Statistical Signal Processing Syllabusakash130791No ratings yet
- MathematicsDocument13 pagesMathematicsJeevan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Contents Basic Probability and Inference DiplomaDocument3 pagesContents Basic Probability and Inference DiplomaJuan David PNo ratings yet
- Syllabus (Linear System Theory) 2019 SPRINGDocument3 pagesSyllabus (Linear System Theory) 2019 SPRINGKavi Ya100% (1)
- Bhel Enginner 11112022Document8 pagesBhel Enginner 11112022Bnr GoudNo ratings yet
- 3453Document7 pages3453Bnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Osmania University Ph.D. Entrance Test InfoDocument7 pagesOsmania University Ph.D. Entrance Test InfoBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Hyd Notification 03 11 2022Document2 pagesHyd Notification 03 11 2022Bnr GoudNo ratings yet
- EDC NotesDocument377 pagesEDC NotesBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Static GA Refresher For IBPS PO Main PDFDocument18 pagesStatic GA Refresher For IBPS PO Main PDFBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- 02 - WAG12 - Loco Pilot Handbook - (English)Document71 pages02 - WAG12 - Loco Pilot Handbook - (English)Bnr Goud100% (2)
- Subject Wise Technical & General Mock TestsDocument2 pagesSubject Wise Technical & General Mock TestsBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Auxiliary Motors in WAG7Document18 pages3 Phase Auxiliary Motors in WAG7Bnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Solar Tracking System Project ReportDocument12 pagesSolar Tracking System Project ReportSrinivas MudhirajNo ratings yet
- Important Days Exclusively For IBPS PO MainDocument2 pagesImportant Days Exclusively For IBPS PO MainBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Dr. B. VictorDocument29 pagesDr. B. VictorBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- BSC - Computer Objectives PDFDocument72 pagesBSC - Computer Objectives PDFAnirudh Singha75% (4)
- Solar Tracking System Project ReportDocument12 pagesSolar Tracking System Project ReportSrinivas MudhirajNo ratings yet
- Pee 40 QueDocument6 pagesPee 40 QueBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- SKP 1Document6 pagesSKP 1Bnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Motor Drives Recent Progress and PerspectiveDocument12 pagesPower Electronics and Motor Drives Recent Progress and PerspectiveBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- 10 252Document12 pages10 252Bnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Dr. B. VictorDocument29 pagesDr. B. VictorBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Nano-Composite Paper Battery: Working, Features & ApplicationsDocument14 pagesNano-Composite Paper Battery: Working, Features & ApplicationsBnr Goud50% (2)
- 79 e 4150 e 6 F 95 D 35 C 30Document4 pages79 e 4150 e 6 F 95 D 35 C 30Bnr GoudNo ratings yet
- BNR BLDCDocument12 pagesBNR BLDCBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Nano-Composite Paper Battery: Working, Features & ApplicationsDocument14 pagesNano-Composite Paper Battery: Working, Features & ApplicationsBnr Goud50% (2)
- Power System Loss MinimisationDocument31 pagesPower System Loss MinimisationBnr GoudNo ratings yet
- Reduce Power Losses Distribution MethodsDocument27 pagesReduce Power Losses Distribution MethodssayedmhNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of Induction Motor Using AnnDocument67 pagesSpeed Control of Induction Motor Using AnnBnr Goud50% (6)
- Sta 242 Bivariate AnalysisDocument46 pagesSta 242 Bivariate AnalysisJared MutindaNo ratings yet
- Stat 130 Module 1 B SlidesDocument16 pagesStat 130 Module 1 B SlidesambonulanNo ratings yet
- STA 5325 HW 3 Ramin ShamshiriDocument20 pagesSTA 5325 HW 3 Ramin ShamshiriRedmond R. Shamshiri93% (15)
- SimVoi 311 GuideDocument44 pagesSimVoi 311 GuideMessy CoolNo ratings yet
- ST2133 Advanced Statistics TheoryDocument2 pagesST2133 Advanced Statistics TheoryAlex ZhangNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics PDFDocument93 pagesProbability and Statistics PDFsiddhant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Mansci - Chapter 3Document2 pagesMansci - Chapter 3Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- R19 B.Tech ECE II, III & IV Year Syllabus at MLRS-R19Document91 pagesR19 B.Tech ECE II, III & IV Year Syllabus at MLRS-R19rupa kumar dhanavathNo ratings yet
- Analyzing M&E Data: Chapter at A GlanceDocument18 pagesAnalyzing M&E Data: Chapter at A GlanceRoqueNo ratings yet
- STA642 Short Notes Written by Mahar Afaq Safdar MuhammadiDocument13 pagesSTA642 Short Notes Written by Mahar Afaq Safdar MuhammadiMuhammad AlamNo ratings yet
- HW 02Document4 pagesHW 02Abdullah WasfiNo ratings yet
- Iriga City: School of Graduate Studies and ResearchDocument11 pagesIriga City: School of Graduate Studies and ResearchKim NoblezaNo ratings yet
- STA301 Formulas Definitions 01 To 45Document28 pagesSTA301 Formulas Definitions 01 To 45M Fahad Irshad0% (1)
- Bayesian Methods For Dealing With Missing Data Problems: Journal of The Korean Statistical Society April 2018Document18 pagesBayesian Methods For Dealing With Missing Data Problems: Journal of The Korean Statistical Society April 2018Andra ComanNo ratings yet
- Probability Rules ExplainedDocument24 pagesProbability Rules ExplainedCarbidemanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of A Wind Turbine Blade Cross SectionDocument11 pagesAnalysis of A Wind Turbine Blade Cross Sectionkim seok jinNo ratings yet
- Sit Cse PG - Big Data SyllabusDocument96 pagesSit Cse PG - Big Data SyllabusSelvaNo ratings yet
- Bivariate Probability FunctionsDocument12 pagesBivariate Probability Functionshardadi nur azizNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. StatisticsDocument62 pagesB.Sc. StatisticsksathieshrNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Random Variables and Probability DistributionsDocument37 pagesChapter 3: Random Variables and Probability DistributionsMert SEPETOĞLUNo ratings yet
- MA6451 Probability and Random ProcessDocument59 pagesMA6451 Probability and Random ProcessPrajwal BirwadkarNo ratings yet
- 3-Random Variables-04-01-2023Document54 pages3-Random Variables-04-01-2023SARTHAK GOYALNo ratings yet
- 42 Revisions WithFAT QP 10 Apr 2020material V 10 Apr 2020 MAT2001 FAT 10Document3 pages42 Revisions WithFAT QP 10 Apr 2020material V 10 Apr 2020 MAT2001 FAT 10Ahmed Shmels MuheNo ratings yet
- Probability Concepts for Engineering Data AnalysisDocument16 pagesProbability Concepts for Engineering Data AnalysisKim - Gabriel TanNo ratings yet
- Revised Brochure BStat (2016)Document36 pagesRevised Brochure BStat (2016)ManishKumarNo ratings yet
- ISO 3534 Statistical TerminologyDocument10 pagesISO 3534 Statistical TerminologyLeo TsaoNo ratings yet
- m4 Simp (1) PDFDocument4 pagesm4 Simp (1) PDFManoj MNo ratings yet
- PTU-K Probability & Random Variables SyllabusDocument2 pagesPTU-K Probability & Random Variables SyllabusFares H. AbualiNo ratings yet
- Joint Distribution of Two Random VariablesDocument5 pagesJoint Distribution of Two Random VariablesmarielleramosNo ratings yet