Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN CHANGKAT LADA CHEMISTRY MONTHLY TEST 2009
Uploaded by
MarziahAsmawi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views5 pagesThis document contains a chemistry monthly test for a secondary school in Malaysia. It has multiple choice and structured questions testing concepts related to rates of chemical reactions. Specifically, it tests the ability to: 1) determine rates from data provided; 2) identify factors that affect rates; and 3) calculate average rates from time and volume data. The test contains questions on concepts like the measurements that can indicate reaction rates, the effects of concentration, catalysts, and temperature on rates, and using data to calculate rates.
Original Description:
Chemistry
Original Title
SMKCL Chemistry Monthly Test 1 F5 2009
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains a chemistry monthly test for a secondary school in Malaysia. It has multiple choice and structured questions testing concepts related to rates of chemical reactions. Specifically, it tests the ability to: 1) determine rates from data provided; 2) identify factors that affect rates; and 3) calculate average rates from time and volume data. The test contains questions on concepts like the measurements that can indicate reaction rates, the effects of concentration, catalysts, and temperature on rates, and using data to calculate rates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
79 views5 pagesSEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN CHANGKAT LADA CHEMISTRY MONTHLY TEST 2009
Uploaded by
MarziahAsmawiThis document contains a chemistry monthly test for a secondary school in Malaysia. It has multiple choice and structured questions testing concepts related to rates of chemical reactions. Specifically, it tests the ability to: 1) determine rates from data provided; 2) identify factors that affect rates; and 3) calculate average rates from time and volume data. The test contains questions on concepts like the measurements that can indicate reaction rates, the effects of concentration, catalysts, and temperature on rates, and using data to calculate rates.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
SEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN CHANGKAT LADA
CHEMISTRY MONTHLY TEST 2009
FORM 5
Name : .. Form :
1. The rate of a chemical reaction cannot be determined by measuring
A the volume of gas liberated per unit time
B the formation of precipitate per unit time
C the change of colour per unit time
D the change of size of solid per unit time
2. Which of the folloing reaction is the sloest!
A "usting of iron
B #recipitation
C Neutralisation
D $ombustion
%. & student ants to study the relationship beteen the concentration of hydrochloric acid and time of
reaction by reacting the acid ith magnesium ribbon. What should be the responding variable!
A $oncentration of acid
B Time ta'en for reaction
C &mount of magnesium ribbon
D (ength of magnesium ribbon
). &luminium poder reacts faster ith hydrochloric acid than an aluminium strip because
A the particles in the aluminium strip are pac'ed closely
B the particles of aluminium poder have more 'inetic energy
C the aluminium poder has a larger total surface area
D there is a layer of aluminium o*ide on the aluminium
+. The table shos the total volume of gas collected at regular intervals in a reaction. What is the average
rate of reaction in this e*periment !
A ,.,)1 cm
%
-s
B ,.,). cm
%
-s
C ,.,)/ cm
%
-s
D ,.,+% cm
%
-s
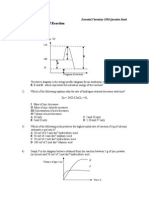
0. The graph shos the volume of carbon dio*ide gas produced against time for the reaction of calcium
carbonate and sulphuric acid.
Time (s) , %, 0, /, 12, 1+, 1., 21,
Volume of gas (cm
3
) , 2., %.1 +.2 0.) 1.% ..0 ..0
Volume of
CO
2
gas / cm
3
Time / second
The gradient of the graph decreases ith time because
A catalyst is not used
B volume of mi*ture decreases
C temperature of reaction decreases
D concentration of sulphuric acid decreases
1. 2iagram ) shos the graph of volume of carbon dio*ide gas against time hen + g of marble chips is
added to +, cm
%
of ,.2 mol dm
3%
hydrochloric acid
&t hat time the rate of reaction the highest!
At1
B t2
C t%
D t)
.. Which of the folloing statements is correct about the rate of reaction!
A The rate of reaction decreases ith time
B The rate of reaction depends on the total volume of the reactants
C The rate of reaction is constant if the reaction is carried out at very high temperature
D The rate of reaction doubles hen the temperature is doubled
/.
& group of students carried out an e*periment to determine the rate of reaction of zinc metal ith dilute
hydrochloric acid. The diagram above shos the graph for the total volume of gas collected against time.
The average rate of reaction for the hole e*periment is :
A ,.% cm
%
-s
B ,.2+ cm
%
-s
C ,.11 cm
%
-s
D ,.1% cm
%
-s
1,. 4ydrogen gas is liberated hen magnesium reacts ith sulphuric acid. Which of the folloing pairs of
reactants ill give the fastest initial rate of reaction!
A ,.1 mol dm
3%
of sulphuric acid and magnesium ribbon
B ,.1 mol dm
3%
of sulphuric acid and magnesium poder
C ,.2 mol dm
3%
of sulphuric acid and magnesium ribbon
D ,.2 mol dm
3%
of sulphuric acid and magnesium poder
0 60 120 180 240 300 time / s
Volume of H
2
gas / cm
3
4
0
3
6
3
0
2
0
1
8
1
0
11. When + g of zinc metal reacts ith an e*cess of hydrochloric acid5 the rate of reaction is faster using fine
zinc poder instead of using granulated zinc. Which of the folloing statements e*plain hy this occurs!
A The fine zinc poder is more reactive than granulated zinc
B The activation energy level is loered hen the fine zinc poder is used
C The fine zinc poder has a greater surface area in contact ith hydrochloric acid
D The particles in the fine zinc poder collide faster than that in the granulated zinc
12. 2iagram belo shos curve W obtained from the decomposition of 2, cm
%
of ,.), mol dm
3%
hydrogen
pero*ide solution5 42625 using ,.2 g of manganese 789: o*ide as catalyst at a temperature of %,
,
$.
Which of the folloing e*periments ill
produce curve ;!
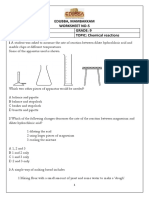
1%. The diagram shos the apparatus set3up used to study the rate of reaction of calcium carbonate and
hydrochloric acid.
The rate of the
above reaction can
be increased by
A grinding the marble chips
B loering the temperature of hydrochloric acid
C using a larger flas'
D adding ater to hydrochloric acid
1). $atalysts speed up chemical reactions. Which industry uses enzymes as a catalyst!
A #roduction of ammonia from hydrogen and nitrogen
B #roduction of sulphuric acid from sulphur
C #roduction of ethanol from sugar
D #roduction of ethane from al'ene
1+. & catalyst is use in manufacturing industries because it can
A increase the <uantity of the products
B reduce the <uantity of ra materials used
C reduce the time of production
9olume of 4262 -cm
%
$oncentration of 4262 -mol dm
3%
Temperature -
,
$
A 1, ,.0, %,
B 1+ ,.2, %,
C 2, ,.0, ),
D %, ,.%, ),
D increase the <uality of the product
STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
1. $lassify the folloing reactions into fast and slo reactions in the folloing table.
a: Neutralisation beteen potassium hydro*ide and hydrochloric acid solutions
b: #hotosynthesis
c: "eaction beteen sodium thiosulphate 798: and hydrochloric acid solutions
d: #recipitation reaction beteen silver nitrate and sodium chloride solutions
e: "usting of an iron nail
f: =urning of a magnesium ribbon
(6 marks)
2. What can be measured to determine the rate of reaction beteen marble chips and hydrochloric acid!
>ive a tic' 7 : for the correct anser in the folloing table.
(4 marks)
%. 1.. g of magnesium ribbon is added to e*cess dilute hydrochloric acid in a bea'er. The reaction stops
after ,.+ minutes. 12.,cm
%
of hydrogen gas is collected.
a:
$alculate the average rate of reaction5 in g s
31
(1 mark)
b:
$alculate the average rate of reaction5 in cm
%
s
31
(1 mark)
). ?tate five factors hich affect the rate of reaction.
i: . ii: .
iii: iv:.
v:.
(5 marks)
+. Name to variables hich are constant in e*periment to study:
!ast "eaction Slo# "eaction
$easu"a%le &isi%le c'anges Tic( )
The change in mass at regular time intervals
Formation of precipitate
$olour changes
The volume of gas liberated at regular time intervals
a: the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction.
i:... ii:..
(2 marks)
b: the effect of catalyst on rate of reaction.
i:... ii:..
(2 marks)
c: the temperature on the rate of reaction.
i:... ii:..
(2 marks)
0. The folloing table shos the volume of gas collected from e*periment
$alculate the average rate of reaction for
a: the first 0, seconds
(1 mark)
b: the overall reaction
(1 mark)
Time (s) , %, 0, 12, 1+,
Volume of gas (cm
3
) , 11 2/ %0 %0
You might also like
- Naskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionDocument14 pagesNaskah Murid Modul 1-Rate of ReactionIza MohdSabriNo ratings yet
- IT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (E)Document8 pagesIT Chem F5 Topical Test 1 (E)Norzawati NoordinNo ratings yet
- Reactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsFrom EverandReactive Transport Modeling: Applications in Subsurface Energy and Environmental ProblemsYitian XiaoNo ratings yet
- 1Document19 pages1Anonymous UwOENfNo ratings yet
- Application of Rate ReactionDocument10 pagesApplication of Rate ReactionRahmawati PutrianasariNo ratings yet
- Energetic Chemistry TestDocument10 pagesEnergetic Chemistry Testmuhammad naufalNo ratings yet
- Test 1 2011 Kimia MarchDocument7 pagesTest 1 2011 Kimia MarchMaryati KematNo ratings yet
- Transition Metal-Catalyzed Pyridine Synthesis: Transition Metal-Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesFrom EverandTransition Metal-Catalyzed Pyridine Synthesis: Transition Metal-Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNo ratings yet
- GCE O Levels (Singapore) - Speed of ReactionDocument3 pagesGCE O Levels (Singapore) - Speed of ReactionChong56No ratings yet
- Rate NotesDocument16 pagesRate NotesMegan GohNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Document75 pages1.3 Rate of Reaction (1.2c)Sha Tasha Natasha0% (1)
- AS Edexcel Chemistry Formulae and EquationsDocument23 pagesAS Edexcel Chemistry Formulae and EquationsTheMagicCarpet100% (1)
- Tonmo y Roy: Unit 3 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesTonmo y Roy: Unit 3 Multiple Choice QuestionsjenifaNo ratings yet
- Saturday X-Tra X-Sheet: 16 Rates of Reaction: Key ConceptsDocument6 pagesSaturday X-Tra X-Sheet: 16 Rates of Reaction: Key ConceptsKingford MwesoNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry - SL Topic 6 Questions 1Document21 pagesIB Chemistry - SL Topic 6 Questions 1Jonathon Hart100% (1)
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDocument71 pages1.1 Rate of ReactionyiosahhNo ratings yet
- Surface Area: Experiment 1.1: To Investigate The Effect of The of A Reactant On The Rate of ReactionDocument75 pagesSurface Area: Experiment 1.1: To Investigate The Effect of The of A Reactant On The Rate of ReactionRakesh NairNo ratings yet
- Chem Form 5Document37 pagesChem Form 5Ashwin Boy Ash100% (1)
- UJIAN PRA 7 TG. 5Document13 pagesUJIAN PRA 7 TG. 5Nik ZharifNo ratings yet
- RTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10Document8 pagesRTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10Scorched ZenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Report (Size of Reactant)Document3 pagesChemistry Report (Size of Reactant)Ain NajwaNo ratings yet
- 10 Rate of ReactionDocument36 pages10 Rate of ReactionMuhammad MustaqimNo ratings yet
- Gabrielle Robinson - 601 Labs 2021Document13 pagesGabrielle Robinson - 601 Labs 2021Gabrielle RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Assessment 1 Form 5Document12 pagesAssessment 1 Form 5Masitah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Kinetics MCQDocument57 pagesKinetics MCQNg Swee Loong Steven100% (2)
- Chemistry F5C1Document9 pagesChemistry F5C1Mohammad Nur SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Chem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionDocument24 pagesChem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionKarim WaelNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument7 pagesRate of ReactionNubar MammadovaNo ratings yet
- EXP7-Rate (MG and HCLDocument5 pagesEXP7-Rate (MG and HCLNor Ashikin Ismail100% (10)
- RTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10Document8 pagesRTS Chemistry SPM Question Bank Chapter 10dobbybibiNo ratings yet
- The Molar Volume of A Gas: Go To TopDocument11 pagesThe Molar Volume of A Gas: Go To TopZu LiyaNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry QuestionDocument6 pagesSPM Chemistry QuestionSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction f5 (Worksheet)Document35 pagesRate of Reaction f5 (Worksheet)Derek Ma67% (3)
- 4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsDocument18 pages4.3 Reaction Rates and Reversible ReactionsVictor VC100% (5)
- Chemistry Student CD IBID PRESS CH 06 AnswersDocument4 pagesChemistry Student CD IBID PRESS CH 06 AnswersFranklin garryNo ratings yet
- Class Test 1 Rate of Reaction For Edexcel A2 ChemistryDocument7 pagesClass Test 1 Rate of Reaction For Edexcel A2 Chemistryjeffydaniel1972No ratings yet
- IA - Metals and AcidsDocument3 pagesIA - Metals and Acids14nganhc1No ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Trial 2021 Key PointsDocument10 pagesSTPM Chemistry Trial 2021 Key PointsChong Jie OhNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Chemical KineticsDocument37 pagesUnit 5 Chemical KineticsSanjay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Page@Rate of Reactions Module JujDocument45 pagesPage@Rate of Reactions Module JujmawarhanifNo ratings yet
- Topik 10 Rate of ReactionDocument33 pagesTopik 10 Rate of ReactionJaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Rate of ReactionDocument23 pages1.1 Rate of ReactionAnonymous uK5JEjNo ratings yet
- 4.chemistry by DesignDocument84 pages4.chemistry by DesignThrinath KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Rate of Reaction: Larning Task 1.2 Problem SolvingDocument29 pagesChapter 1: Rate of Reaction: Larning Task 1.2 Problem Solvingamin_zamanNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics Study Guide - Multiple ChoiceDocument21 pagesReaction Kinetics Study Guide - Multiple ChoiceNidhi SisodiaNo ratings yet
- 2004 U. S. National Chemistry Olympiad: National Exam-Part IiDocument8 pages2004 U. S. National Chemistry Olympiad: National Exam-Part IiihappyscribdNo ratings yet
- MCH 05 2020 April Final Exam Option OneDocument20 pagesMCH 05 2020 April Final Exam Option Onepaul kapambweNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry Answers ToolDocument19 pagesIb Chemistry Answers ToolGeorges FarahNo ratings yet
- 64edf0f4e41caDocument6 pages64edf0f4e41caDanzell JonathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Rate of ReactionsDocument21 pagesChapter 1: Rate of ReactionsMasitah Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Effect of Surface Area on Magnesium-HCl Reaction RateDocument4 pagesEffect of Surface Area on Magnesium-HCl Reaction RateNor Ashikin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chemistry Chapter 1: Rate of ReactionsDocument101 pagesForm 5 Chemistry Chapter 1: Rate of ReactionscikgufiezaNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet - 5 Grade 9Document7 pagesWork Sheet - 5 Grade 9SOLONo ratings yet
- MYE 2018 CHEM S3A QP FinalDocument17 pagesMYE 2018 CHEM S3A QP FinalVina Octavia AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Kinetics: 6.1 Rates of ReactionDocument20 pagesKinetics: 6.1 Rates of ReactionSeung Hee KimNo ratings yet
- Excretion OrgansDocument1 pageExcretion OrgansMarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- Science Word PuzzleDocument3 pagesScience Word PuzzleMarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- Test On CationsDocument2 pagesTest On CationsmarziahNo ratings yet
- Science Word PuzzleDocument3 pagesScience Word PuzzleMarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2011 - Science Form 2Document1 pageRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2011 - Science Form 2MarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- OrgansDocument1 pageOrgansMarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- Science Word PuzzleDocument3 pagesScience Word PuzzleMarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2011 - Chemistry Form 5Document2 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2011 - Chemistry Form 5MarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2011 - Chemistry Form 5Document2 pagesRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2011 - Chemistry Form 5MarziahAsmawiNo ratings yet
- Interhalogen Compounds Structure and PropertiesDocument14 pagesInterhalogen Compounds Structure and PropertiesAndriati RahayuNo ratings yet
- Acid Leachability Copper Species PDFDocument10 pagesAcid Leachability Copper Species PDFJeyson Cornejo100% (1)
- Deet1-2 - Lab2 GRP3Document6 pagesDeet1-2 - Lab2 GRP3Jhay lambert MercadoNo ratings yet
- Water Testing Quotation of R.v.briggsDocument1 pageWater Testing Quotation of R.v.briggsSuvojit DasNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesAtomic Structureneetisharma2010No ratings yet
- Astm A510 6 PDFDocument7 pagesAstm A510 6 PDFNafiou KamelNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts in ChemistryDocument19 pagesSome Basic Concepts in Chemistryg_ayyanarNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Half Life LabDocument2 pagesUnit 7 Half Life Labapi-331085450No ratings yet
- Uses of MetalloidsDocument3 pagesUses of MetalloidsSeema SinghalNo ratings yet
- Nonferrous MetalsDocument26 pagesNonferrous MetalsKaushik SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 3 EdexcelDocument2 pagesChemistry Unit 3 EdexcelMywhole OtherworldNo ratings yet
- STOICHIOMETRYDocument22 pagesSTOICHIOMETRYCacey Daiwey CalixtoNo ratings yet
- MSE 2010 Homework #1 Thermodynamics ProblemsDocument4 pagesMSE 2010 Homework #1 Thermodynamics Problemsblvckops890No ratings yet
- WCH13 - 01 - MS - May - 2021 (Unseen)Document23 pagesWCH13 - 01 - MS - May - 2021 (Unseen)Defaults rulezNo ratings yet
- 060 Half Life WorksheetDocument3 pages060 Half Life WorksheetLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- Specimen QP - Paper 1 OCR Chemistry As-LevelDocument27 pagesSpecimen QP - Paper 1 OCR Chemistry As-Levelboonboon124No ratings yet
- Refractory metals and alloys industrial lectureDocument16 pagesRefractory metals and alloys industrial lectureMalik Nazim ChannarNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/42Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/42septinNo ratings yet
- AP 015 900.zincDocument4 pagesAP 015 900.zincjcortezcNo ratings yet
- Metals & Non-Metals ClassificationDocument4 pagesMetals & Non-Metals ClassificationHitesh Alwadhi0% (1)
- FMDS0785 Metals and AlloysDocument14 pagesFMDS0785 Metals and AlloysAlif GhazaliNo ratings yet
- IGCSE energy changes and bonding questionsDocument18 pagesIGCSE energy changes and bonding questionsFatema KhatunNo ratings yet
- SW 347 CoredDocument1 pageSW 347 CoredDanut RusNo ratings yet
- Transmission Accessories for Demountable and Semi-Demountable CellsDocument1 pageTransmission Accessories for Demountable and Semi-Demountable CellsSorinNo ratings yet
- Names of Ores - Alloys AsdfghDocument2 pagesNames of Ores - Alloys AsdfghJyotiraditya Singh Rathore100% (1)
- List of Compound SemiconductorsDocument8 pagesList of Compound Semiconductorsravi+jigarNo ratings yet
- Sulphuric Acid AceDocument2 pagesSulphuric Acid AceLam Wen HongNo ratings yet
- High-performance Anode Material for Li-ion BatteriesDocument10 pagesHigh-performance Anode Material for Li-ion Batteriesmigman99No ratings yet
- List of Monovalent IonsDocument7 pagesList of Monovalent IonsJaishree & JothishreeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02 A1Document4 pagesAssignment 02 A1sundusNo ratings yet