Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Droughts Overview
Uploaded by
Shrey ShekharCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Droughts Overview
Uploaded by
Shrey ShekharCopyright:
Available Formats
Droughts
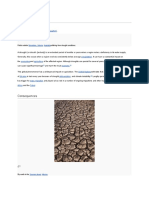
Drought is an extended period when a region receives a deficiency in its water supply, whether
atmospheric, surface or ground water. A drought can last for months or years, or may be declared after as
few as 15 days.
[1]
Generally, this occurs when a region receives consistently below average precipitation. It
can have a substantial impact on the ecosystem and agriculture of the affected region. Although droughts
can persist for several years, even a short, intense drought can cause significant damage
[2]
and harm to the
local economy.
[3]
Prolonged droughts have caused mass migrations and humanitarian crises.
types
1. Meteorological drought is brought about when there is a prolonged period with less than average
precipitation. Meteorological drought usually precedes the other kinds of drought.
2. Agricultural droughts are droughts that affect crop production or the ecology of the range. This
condition can also arise independently from any change in precipitation levels
when soil conditions and erosion triggered by poorly planned agricultural endeavors cause a
shortfall in water available to the crops. However, in a traditional drought, it is caused by an
extended period of below average precipitation.
3. Hydrological drought is brought about when the water reserves available in sources such
as aquifers, lakes and reservoirs fall below the statistical average. Hydrological drought tends to
show up more slowly because it involves stored water that is used but not replenished. Like an
agricultural drought, this can be triggered by more than just a loss of rainfall. For
instance, Kazakhstan was recently awarded a large amount of money by the World Bank to
restore water that had been diverted to other nations from the Aral
Sea under Soviet rule.
[44]
Similar circumstances also place their largest lake, Balkhash, at risk of
completely drying out.
[45]
causes
Generally, rainfall is related to the amount (determined by air temperature) of water vapour carried by
regional atmosphere, combined with the upward forcing of the air mass containing that water vapour. If
these combined factors do not support precipitation volumes sufficient to reach the surface, the result is a
drought. This can be triggered by high level of reflected sunlight and above average prevalence of
highpressure systems, winds carrying continental, rather than oceanic air masses, and ridges of high
pressure areas from behaviors which prevent or restrict the developing of thunderstorm activity or rainfall
over one certain region. Oceanic and atmospheric weather cycles such as the make drought a regular
recurring feature of the Americas along the Midwest and Australia.
Human activity can directly trigger exacerbating factors such as over farming, excessive
irrigation,
[35]
deforestation, and erosion adversely impact the ability of the land to capture and hold
water.
[36]
While these tend to be relatively isolated in their scope, activities resulting in global climate
change are expected to trigger droughts with a substantial impact on agriculture
[37]
throughout the world,
and especially indeveloping nations.
[38][39][40]
Overall, global warming will result in increased world
rainfall.
[41]
Along with drought in some areas, flooding and erosion will increase in others. Paradoxically,
some proposed solutions to global warming that focus on more active techniques, solar radiation
management through the use of a space sunshade for one, may also carry with them increased chances of
drought.
Consequences
Diminished crop growth or yield productions and carrying capacity for livestock
Dust bowls, themselves a sign of erosion, which further erode the landscape
Dust storms, when drought hits an area suffering from desertification and erosion
Famine due to lack of water for irrigation
Habitat damage, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic wildlife
[5]
Hunger, drought provides too little water to support food crops.
Malnutrition, dehydration and related diseases
Mass migration, resulting in internal displacement and international refugees
Reduced electricity production due to reduced water flow through hydroelectric dams
[6]
Shortages of water for industrial users
[7][8]
Snake migration, which results in snakebites
[9]
Social unrest
War over natural resources, including water and food
Wildfires, such as Australian bushfires, are more common during times of drought and even death of
people.
[
You might also like
- DroughtDocument4 pagesDroughtSarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- DroughtDocument2 pagesDroughtFer MartinezNo ratings yet
- DroughtDocument6 pagesDroughtSameer_1985No ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument12 pagesDisaster ManagementMeenaNo ratings yet
- Drought: Precipitation Surface Water Ground Water Ecosystem Agriculture Economy Tropics Water VapourDocument25 pagesDrought: Precipitation Surface Water Ground Water Ecosystem Agriculture Economy Tropics Water VapourSRIDEVI QUEEN RECIPESNo ratings yet
- Drought, Causes and ConsequencesDocument5 pagesDrought, Causes and ConsequencesVijesh CormatyNo ratings yet
- Types of DroughtDocument7 pagesTypes of DroughtSakshi JainNo ratings yet
- 1Document35 pages1Megha Gupta100% (1)
- Dai2010 Drought Under Global WarmingDocument21 pagesDai2010 Drought Under Global WarmingWaqar UlNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Drought Management & Water HarvestingDocument7 pagesModule 5 Drought Management & Water HarvestingOxygen LiveNo ratings yet
- Natural HazardsDocument22 pagesNatural HazardsBriana-j MartinNo ratings yet
- CropsDocument7 pagesCropsArzoo GodaraNo ratings yet
- Drought Group 2Document3 pagesDrought Group 2etwinningNo ratings yet
- Types of DroughtDocument6 pagesTypes of DroughtDanielle DeeCee CampbellNo ratings yet
- Drought Management & Water HarvestingDocument6 pagesDrought Management & Water HarvestingEvans AsensoNo ratings yet
- Well-Known Historical Droughts IncludeDocument6 pagesWell-Known Historical Droughts IncludeJavedNo ratings yet
- Drought)Document4 pagesDrought)Arjun SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. DroughtDocument30 pagesChapter 6. DroughtkamagaraNo ratings yet
- The DroughtDocument11 pagesThe DroughtEngineer 1122100% (1)
- 18CEO307T DMM Unit-II Lecture NotesDocument18 pages18CEO307T DMM Unit-II Lecture Notespratham sainiNo ratings yet
- HDM-Lec-02-Part IIIDocument90 pagesHDM-Lec-02-Part IIIWaqas Muneer KhanNo ratings yet
- Geography ProjectDocument12 pagesGeography ProjectVaibhav BharwardNo ratings yet
- Droughts PDFDocument4 pagesDroughts PDFMaria346 ButtNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentRishabh Mittal0% (1)
- Environmental Degradation: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Degradation: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaConstance BandaNo ratings yet
- What Causes Droughts?: What Is A Drought?Document3 pagesWhat Causes Droughts?: What Is A Drought?Rohan AtrawalkarNo ratings yet
- Partido State University: Module 13: Drought and FloodDocument7 pagesPartido State University: Module 13: Drought and FloodRalph NavelinoNo ratings yet
- Brendon 3509Document5 pagesBrendon 3509geoboom12No ratings yet
- Drought Is An Extended Period When A Region Receives A Deficiency in Its Water Supply, Whether AtmosphericDocument2 pagesDrought Is An Extended Period When A Region Receives A Deficiency in Its Water Supply, Whether Atmosphericmina579623No ratings yet
- Droughts, Main Types Recognized in IndiaDocument3 pagesDroughts, Main Types Recognized in IndiaBetter guggNo ratings yet
- What Is DroughtDocument6 pagesWhat Is DroughtBhakti AdiNo ratings yet
- Floods & DroughtsDocument6 pagesFloods & DroughtssheshasriNo ratings yet
- Source: InternetDocument2 pagesSource: Internetnayan dhawalNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Harmeet Kaur Ashmita Mondal Bba-Mba 2 Sem Section-B Regn - No - 3020070020Document36 pagesSubmitted To: Submitted By: Mrs. Harmeet Kaur Ashmita Mondal Bba-Mba 2 Sem Section-B Regn - No - 3020070020Ashmita MondalNo ratings yet
- Drought Prone SoilDocument48 pagesDrought Prone SoilNasmin NaherNo ratings yet
- MappingDocument7 pagesMappinglizalise0kNo ratings yet
- The Impacts of Drought in South AfricaDocument10 pagesThe Impacts of Drought in South AfricaadelaidekegaogetsweNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Poor Rain FallDocument13 pagesCause and Effect Poor Rain FallJohn AjishNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Geo Notes New Curriculum - To Be EditedDocument120 pagesForm 2 Geo Notes New Curriculum - To Be EditedLemarNo ratings yet
- LessonDocument1 pageLessonNeña Bautista PagalNo ratings yet
- Floods in IndiaDocument13 pagesFloods in IndiaMoksh Jain100% (1)
- DROUGHT: All You Need To KnowDocument2 pagesDROUGHT: All You Need To KnowAngel Anne AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Climate Change ReviewerDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Climate Change ReviewerGARCIA, KYLA MAE A.No ratings yet
- DP - PM Unit - 2Document101 pagesDP - PM Unit - 2pooja.amanchiNo ratings yet
- DroughtDocument20 pagesDroughtJaire100% (1)
- FloodDocument12 pagesFloodgoons7777No ratings yet
- Cause and EffectDocument2 pagesCause and EffectKyle Hilary MatundingNo ratings yet
- Consenquences of The Natural DisastersDocument10 pagesConsenquences of The Natural Disastersrajkamal singhNo ratings yet
- Droughts: Types of DroughtDocument3 pagesDroughts: Types of DroughtShumaila MajeedNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Potential Threat From Climate Change in MalaysiaDocument8 pages2.0 Potential Threat From Climate Change in MalaysiaDayang Suzica Ahmad SafuanNo ratings yet
- 1 1 FloodsDocument34 pages1 1 FloodsjyotiangelNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Drought TypesDocument3 pagesAgriculture Drought Typeslovedeep singhNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document14 pagesUnit 5Jack PNo ratings yet
- Dean's Group (Envi Sci)Document9 pagesDean's Group (Envi Sci)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- Tide River Lake Levees: About FloodDocument4 pagesTide River Lake Levees: About FloodarifcahyagumelarNo ratings yet
- PM 211 Module 6Document19 pagesPM 211 Module 6Louray JeanNo ratings yet
- Drought (Xi Yuan)Document7 pagesDrought (Xi Yuan)xzsim25No ratings yet
- Floods and DroughtsDocument37 pagesFloods and DroughtsVernon90% (10)
- The Main Effects of Tropical Cyclones Include Heavy RainDocument8 pagesThe Main Effects of Tropical Cyclones Include Heavy Rainabirami sNo ratings yet
- Dry Lands, Fading Hopes: Aridification and Our Future: Global Collapse, #10From EverandDry Lands, Fading Hopes: Aridification and Our Future: Global Collapse, #10No ratings yet
- Badjao HouseDocument2 pagesBadjao HouseApple Empalmado Llarena100% (2)
- A Three Level Framework For Multi Risk AssessmentDocument17 pagesA Three Level Framework For Multi Risk AssessmentSanda RoșcaNo ratings yet
- Daeling With Hazards and RisksDocument121 pagesDaeling With Hazards and RisksprinceNo ratings yet
- Guideline of RiskDocument48 pagesGuideline of RiskFelipe Ignacio Campos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Asignación Final InglésDocument2 pagesAsignación Final InglésMarcela GonzálezNo ratings yet
- On Corals of AndamanDocument20 pagesOn Corals of AndamanRajesh NayakNo ratings yet
- English - DPP Haor Risk Management Main PartDocument10 pagesEnglish - DPP Haor Risk Management Main PartShadman ShakibNo ratings yet
- SEC6010 - Planning For Information SecurityDocument9 pagesSEC6010 - Planning For Information SecurityVenkata Pathi JaligamaNo ratings yet
- Masteral GeoDocument5 pagesMasteral GeoMhelody VioNo ratings yet
- Antigone - Background Info ActivityDocument5 pagesAntigone - Background Info Activityapi-298255419No ratings yet
- Guardia LombardiDocument16 pagesGuardia LombardiCyrus Yu Shing ChanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE - Q1 - W7 - Mod16 - Earth and Life Science (Geologic Hazards)Document11 pagesSCIENCE - Q1 - W7 - Mod16 - Earth and Life Science (Geologic Hazards)Liesel0% (1)
- 1st Quarter NSED Monitoring Reporting Template 2023Document12 pages1st Quarter NSED Monitoring Reporting Template 2023Janeth CondesNo ratings yet
- Deadliest Earthquake in The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDeadliest Earthquake in The PhilippinescollenedesilvaNo ratings yet
- Minimum Six Elements Must Be Included in The PlanDocument4 pagesMinimum Six Elements Must Be Included in The PlanGlenn Vincent Octaviano GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Mat 107 Understanding Braced Wall Lines 2018 IrcDocument95 pagesMat 107 Understanding Braced Wall Lines 2018 IrcAbdurrahman CinarNo ratings yet
- Is 13920Document47 pagesIs 13920Ravinder KumarNo ratings yet
- Times Leader 10-07-2011Document38 pagesTimes Leader 10-07-2011The Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- MB Lal ReportDocument130 pagesMB Lal ReportVasant Kumar VarmaNo ratings yet
- 2020 5% BDRRMFDocument14 pages2020 5% BDRRMFJeyren Bala-anNo ratings yet
- Torrential Monsoon Rains and Rising River Levels Have Caused FloodingDocument3 pagesTorrential Monsoon Rains and Rising River Levels Have Caused Floodingywon nay chi lwinNo ratings yet
- Medical Emergency Response PlanDocument16 pagesMedical Emergency Response PlanMurtadda MohammedNo ratings yet
- +1EngSolvedQP - March 2016Document11 pages+1EngSolvedQP - March 2016Siva PrakashNo ratings yet
- Bu-Cbem Students Teaching and Non-TeachiDocument64 pagesBu-Cbem Students Teaching and Non-TeachiJace RiveraNo ratings yet
- Urethane Foam MSDSDocument3 pagesUrethane Foam MSDSSIZ1400No ratings yet
- Dokumen List Re - SkpiDocument2 pagesDokumen List Re - SkpiarisNo ratings yet
- Iv. Learning Phases and Learning ActivitiesDocument4 pagesIv. Learning Phases and Learning ActivitiesBRENT LOUIS COMETANo ratings yet
- Cagayan Valley Flood Mitigation Master Plan 2005 2030Document59 pagesCagayan Valley Flood Mitigation Master Plan 2005 2030Beverly A. Cannu100% (3)
- News Item Text: Purpose: Inform Readers, Listeners or Viewers About Events of The Day Which Are ConsideredDocument3 pagesNews Item Text: Purpose: Inform Readers, Listeners or Viewers About Events of The Day Which Are ConsideredSean Owen SoerjohadiNo ratings yet
- Nuclear PlantDocument74 pagesNuclear PlantNafis TahmidNo ratings yet