Professional Documents
Culture Documents
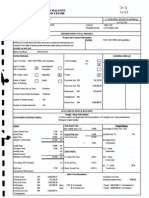
MEP Light Calculation
Uploaded by
Amit JhaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MEP Light Calculation
Uploaded by
Amit JhaCopyright:
Available Formats
MEP light calculation
Basic
Design of lighting system
Direct lighting
90% of light fall into floor example ceiling light
Semi direct lighting
60% to 90% light fall into floor remaining waste or into wall face
Semi Indirect lighting
60% to 90% light fall into wall face like wall mounted light
Indirect lighting
90% light fall into wall face
Depends on our architectural purpose we fix the light.
So the factors are
1. Where the reflected light goes?
2. Efficiency of light, power, and so on
3. No of lights
4. Height of the lamp
5. How much light fall into floor(working plan in revit)
Lighting calculation methods by practical
Watts per square metre method
Lumen or light flux method (revit MEP USES THIS METHOD)
Formula = No of lamps x watts of each x effi. Of each per watt x (coefficient of
utilization / depreciation factor)
Point to point or inverse square law method
In software how the average illumination calculated.
we need to calculate each light illumination and calculate average by the
AEI(Average estimate illumination) formula.
Consider I placed 2 light with 50lux, at a elevation height of 6 feet
Room Cavity Height
RCH = LP - LCW
RCH = Room Cavity Height
LP = Lighting Calculation Luminaire Plane (The height of the light sources in the space)
LCW = Lighting Calculation Workplane for example school class room the light should fall on
table so the table height.
In this example: RCH = 9' 6" - 3' 0" = 6' 6" (If there are multiple light sources at varying heights,
the lowest height is used).
Room Cavity Ratio
Room Cavity Ratio is calculated as: RCR = 2.5 * RCH * P / A
RCR = Room Cavity Ratio
P = Room Perimeter
A = Room Area
In this example: RCR = 2.5 * 6.5 * 97.3333 / 567.11 = 2.788989
This green value is compared with the photometric web file in the software as per our given
wall, ceiling, floor reflect percentage in space properties.
It will get some values. This is called co efficient of utilization (Each light has different web file
check with light properties)
WL = II * LLF * CU
WL = Lumens at work plane
II = Initial Intensity (check with light properties )
LLF = Light Loss Factor (check with light properties )
CU = Coefficient of Utilization
Apply the above formula you get one light average value calculate for all light and apply to the
AEI.
That why the reason we are not getting the exact (50 lux +50 lux = 100lux) value. The lights are
wasted or affected by other elements.
Note:
1 lux = 0.0929030436 footcandles
Illumination is defined as the luminous flux received by the surface per unit area.
1 lux = one lumen per sq.metre
1 fc = one lumen per sq. foot.
You might also like
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesFrom EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Types of Artificial Lighting: Architectural Acoustics and LightingDocument12 pagesTypes of Artificial Lighting: Architectural Acoustics and LightingRashid MujahidNo ratings yet
- Electrical Notes & Articles: Calculate No of Lighting Fixtures / Lumen For Indoor LightingDocument10 pagesElectrical Notes & Articles: Calculate No of Lighting Fixtures / Lumen For Indoor Lightingerson1981No ratings yet
- Electric LightingDocument10 pagesElectric LightingSarah FrazierNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 - Artificial - Lighting - CalculationDocument40 pagesLecture - 4 - Artificial - Lighting - Calculationsamuel seyoumNo ratings yet
- Cotoh LIGHTING CALCULATIONDocument12 pagesCotoh LIGHTING CALCULATIONAhmad HarisNo ratings yet
- BIM DiaLux SoftwareDocument17 pagesBIM DiaLux SoftwarenhatvpNo ratings yet
- Lighting Calculation (Zonal Cavity Method)Document2 pagesLighting Calculation (Zonal Cavity Method)Catrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- Lighting Calculation-Flurcent LightsDocument4 pagesLighting Calculation-Flurcent Lightsganesh_dgNo ratings yet
- Electrical Panel Load Calculation-22!8!12-1Document33 pagesElectrical Panel Load Calculation-22!8!12-1micaziv4786No ratings yet
- Lighting Calculations Is Available On Most FittingsDocument2 pagesLighting Calculations Is Available On Most FittingsMind of BeautyNo ratings yet
- Lighting REV 0Document24 pagesLighting REV 0كرم عمروNo ratings yet
- Load CalculationDocument1 pageLoad CalculationMichele PriceNo ratings yet
- CV - MEP Architects GharibDocument5 pagesCV - MEP Architects GharibSHEIKH100% (1)
- Selection of Main - Branch CB As Per NEC-210 (1.1.19)Document9 pagesSelection of Main - Branch CB As Per NEC-210 (1.1.19)jiguparmar1516No ratings yet
- Mep Design Engineering and Drafting Consist of Hvac Design EngineeringDocument4 pagesMep Design Engineering and Drafting Consist of Hvac Design EngineeringVineeth MuraleedharanNo ratings yet
- Instructions To Users: A Run 500 M Sq. MM 3 Allow V DropDocument26 pagesInstructions To Users: A Run 500 M Sq. MM 3 Allow V DropjjspenceNo ratings yet
- A Roadmap For The MEP EngineerDocument8 pagesA Roadmap For The MEP EngineerAlbert ArominNo ratings yet
- Load Estimation of A Building: EEG205 Electrical InstallationDocument29 pagesLoad Estimation of A Building: EEG205 Electrical InstallationLoay MohammedNo ratings yet
- Design CriteriaDocument4 pagesDesign CriteriamansidaughtNo ratings yet
- Design of Lighting SchemesDocument39 pagesDesign of Lighting Schemesg3v5No ratings yet
- Lampiran: Proyek: Jakarta International StadionDocument2 pagesLampiran: Proyek: Jakarta International StadionJoseph AnthonyNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL DESIGN InternDocument35 pagesELECTRICAL DESIGN Internomair sirajNo ratings yet
- Electrical CalculationsDocument48 pagesElectrical CalculationsRaymond Neil BarajanNo ratings yet
- Annexure E2 - Electrical Load Details-R3 - (09!09!2011)Document10 pagesAnnexure E2 - Electrical Load Details-R3 - (09!09!2011)vinesh_viswanathan_3No ratings yet
- Mep SyllabusDocument20 pagesMep SyllabusMunavir KNo ratings yet
- Electrical Load Estimation r1 29.01.2013Document9 pagesElectrical Load Estimation r1 29.01.2013PrasadNo ratings yet
- Lighting Design PrintDocument3 pagesLighting Design PrintChristy JosephNo ratings yet
- BMC - Electrical DBRDocument19 pagesBMC - Electrical DBRAmit Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Extron Ceiling Speaker Calculator Coverage Map - ExtronDocument2 pagesExtron Ceiling Speaker Calculator Coverage Map - ExtronMHEP_DANIELNo ratings yet
- MEP Testing and Commissioning ManagementDocument6 pagesMEP Testing and Commissioning ManagementJon TyackeNo ratings yet
- MepDocument3 pagesMepGiftson ImmanuelNo ratings yet
- Sizing A Generator For Electric Motor LoadsDocument2 pagesSizing A Generator For Electric Motor Loadsjob_pNo ratings yet
- Electrical Work Procedure - Building, Testing, Checklist, SafetyDocument34 pagesElectrical Work Procedure - Building, Testing, Checklist, SafetyRITAM CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- Electrical Unpriced BOQ-23 07 2019Document13 pagesElectrical Unpriced BOQ-23 07 2019Mitesh KhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design IndexDocument11 pagesElectrical Design IndexjitendraNo ratings yet
- Blue Star Catalogue 2018 ChillerDocument20 pagesBlue Star Catalogue 2018 Chiller3nadhNo ratings yet
- BE-WI-248-01-F03 Work Hour Estimate Electrical and InstrumentationDocument3 pagesBE-WI-248-01-F03 Work Hour Estimate Electrical and Instrumentationmika cabelloNo ratings yet
- FINALDocument21 pagesFINALRajesh ShingreNo ratings yet
- Electrical BasicsDocument24 pagesElectrical BasicsSnehal Mane100% (1)
- Installation AllDocument45 pagesInstallation AllDaaniyyee AbdiisaaNo ratings yet
- Essentials Electrical Quality Control Plan Sample PDFDocument13 pagesEssentials Electrical Quality Control Plan Sample PDFSalman HameedNo ratings yet
- 3.GS03 General Specs For ElectricalDocument25 pages3.GS03 General Specs For ElectricalSHAAM ENG100% (1)
- How To Find The Suitable Size of CableDocument9 pagesHow To Find The Suitable Size of CableMajid GhaffarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Layout Design in BuildingDocument15 pagesElectrical Layout Design in BuildingIlam ShresthaNo ratings yet
- LV Board SpecsDocument21 pagesLV Board SpecsVignesh BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Cost EstimationDocument30 pagesElectrical Cost EstimationLeo KhkNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Installation of Electric Water Heater - Method Statement HQDocument5 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Electric Water Heater - Method Statement HQGwenn AsprerNo ratings yet
- Installation Check ListDocument4 pagesInstallation Check ListAbdul Hakkim0% (1)
- Panel Board ScheduleDocument12 pagesPanel Board ScheduleSantosh Vardhan100% (1)
- Sample Template - Branch Circuit Panel Board ScheduleDocument1 pageSample Template - Branch Circuit Panel Board Schedulemusleh19No ratings yet
- 16139-Cable TraysDocument4 pages16139-Cable TraysNATHANNo ratings yet
- Lighting Calculation FormulaDocument5 pagesLighting Calculation FormulaPramod B.WankhadeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Notes: Electrical Design of Residential, Commercial and Industrial BuildingsDocument5 pagesElectrical Notes: Electrical Design of Residential, Commercial and Industrial BuildingsIrish ArapocNo ratings yet
- Selecting An Automatic Capacitor Size 480V System To ADocument5 pagesSelecting An Automatic Capacitor Size 480V System To Arafe788No ratings yet
- Lecture (3d) - Calculating Illuminance LevelsDocument19 pagesLecture (3d) - Calculating Illuminance LevelsNuno HenriquesNo ratings yet
- VejigDocument2 pagesVejigMiner TPNo ratings yet
- Zonal Cavity Method: Laguna State Polytechnic University Sta Cruz, LagunaDocument12 pagesZonal Cavity Method: Laguna State Polytechnic University Sta Cruz, LagunaEeeeeeNo ratings yet
- LUMINARIESDocument9 pagesLUMINARIESMuhammad Sadiq Syamir HasnanNo ratings yet
- Artificial Lighting CalculationDocument40 pagesArtificial Lighting CalculationSonisha Aryal100% (1)
- Catia Tips & TricksDocument3 pagesCatia Tips & TrickschuranjitNo ratings yet
- How To Acess CATIA V5 R18 As Admin - CATIA Tutorial CADDocument5 pagesHow To Acess CATIA V5 R18 As Admin - CATIA Tutorial CADAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- 3dlive For Enovia and Catia: Ibm Product Lifecycle ManagementDocument8 pages3dlive For Enovia and Catia: Ibm Product Lifecycle ManagementAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Composer FAQDocument8 pagesComposer FAQAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Top Ten CATIA V5 Macros WeightDocument20 pagesTop Ten CATIA V5 Macros WeightAnonymous rhbWnv100% (1)
- Enovia 3dlive: Key BenefitsDocument6 pagesEnovia 3dlive: Key BenefitsAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Starting A School Makerspace From Scratch - EdutopiaDocument4 pagesStarting A School Makerspace From Scratch - EdutopiaAmit Jha100% (1)
- Project-Based Learning Through A Maker's Lens - EdutopiaDocument3 pagesProject-Based Learning Through A Maker's Lens - EdutopiaAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Top Ten CATIA V5 Macros WeightDocument20 pagesTop Ten CATIA V5 Macros WeightAnonymous rhbWnv100% (1)
- What Is Kerning - The Importance of Space Between Letter PairsDocument6 pagesWhat Is Kerning - The Importance of Space Between Letter PairsAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Aveva l18 Cabledesign FinalDocument2 pagesAveva l18 Cabledesign FinalAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Evolution of CreoDocument9 pagesExploring The Evolution of CreoAlan BelniakNo ratings yet
- 7 Reasons Why You Will Never Do Anything Amazing With Your Life - Life Learning - MediumDocument11 pages7 Reasons Why You Will Never Do Anything Amazing With Your Life - Life Learning - MediumAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Pdms Main ModulesDocument16 pagesPdms Main ModulesAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Creo Certification Test - Part 1 Flashcards - QuizletDocument2 pagesCreo Certification Test - Part 1 Flashcards - QuizletAmit Jha100% (2)
- Presentation 1Document2 pagesPresentation 1Amit JhaNo ratings yet
- These Posters Explain The Difference Between Being Smart and Oversmart at A Job InterviewDocument10 pagesThese Posters Explain The Difference Between Being Smart and Oversmart at A Job InterviewAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With PDMSDocument92 pagesGetting Started With PDMSsridharj_2No ratings yet
- MSSSDocument2 pagesMSSSAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Creo2 Adv PrimerDocument174 pagesCreo2 Adv PrimerAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- CADD Centre - ProfileDocument2 pagesCADD Centre - ProfileAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of CAMDocument71 pagesFundamentals of CAMAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- International Grad ChecklistDocument2 pagesInternational Grad ChecklistAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- IGCC For Power Generation: N.T.P.C Gas Plant DadriDocument25 pagesIGCC For Power Generation: N.T.P.C Gas Plant DadriAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- 24022011030538VSA App Form 230211 Ad2Document1 page24022011030538VSA App Form 230211 Ad2Ravindra Singh TomerNo ratings yet
- Creo ElementsDocument2 pagesCreo ElementsAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Rocket ProjectDocument21 pagesHybrid Rocket ProjectAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic RefrigerationDocument19 pagesMagnetic RefrigerationAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Race Car AerodynamicsDocument7 pagesRace Car AerodynamicsejjLi100% (1)
- VaastuDocument1 pageVaastuRiti RajNo ratings yet
- Burj KhalifaDocument15 pagesBurj KhalifaSanand KarwaNo ratings yet
- E SF 400 PDFDocument98 pagesE SF 400 PDFAmirhosein605334No ratings yet
- Electrical ConstructionDocument41 pagesElectrical ConstructionMuhammad Tanveer SattiNo ratings yet
- Mech-Elecl - 1 Electrical SystemsDocument102 pagesMech-Elecl - 1 Electrical SystemsGellaii Aquino QuinsaatNo ratings yet
- Ax3000 Sfs enDocument200 pagesAx3000 Sfs enVejsNo ratings yet
- RC Design PDFDocument58 pagesRC Design PDFZerihun IbrahimNo ratings yet
- RCC Principles - Construction ProcessDocument44 pagesRCC Principles - Construction ProcessDharatiSote100% (1)
- Roffing Sample Pictures - MalaysiaDocument87 pagesRoffing Sample Pictures - Malaysiasimbua72No ratings yet
- Maryland Historical Trust: Inventory No. 15-71Document24 pagesMaryland Historical Trust: Inventory No. 15-71M-NCPPCNo ratings yet
- Erection and User Manual HRZDocument4 pagesErection and User Manual HRZsmartcad60No ratings yet
- Tabel HoneycombDocument2 pagesTabel HoneycombAzwar HalimNo ratings yet
- BT4 Sir TavsDocument7 pagesBT4 Sir Tavsuapsaua.rubiteNo ratings yet
- Designing Stairs and Laying Out Stair StringersDocument13 pagesDesigning Stairs and Laying Out Stair StringersJessicalba LouNo ratings yet
- TWS Sec - GDocument60 pagesTWS Sec - GWilmer Huaman PasaperaNo ratings yet
- OPCM Chaper 8, 11Document31 pagesOPCM Chaper 8, 11sandiluluNo ratings yet
- Sound-Proofing A DoorDocument4 pagesSound-Proofing A Doorgrimer_wongNo ratings yet
- I I I I I: Institution of Surveyors MalaysiaDocument9 pagesI I I I I: Institution of Surveyors MalaysiarokiahhassanNo ratings yet
- Thesis CompleteDocument80 pagesThesis Complete4God50% (2)
- CocreteDocument62 pagesCocretesandhya rani bindhaniNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1 - Cleanroom HVAC Design - KarachiDocument25 pagesSeminar 1 - Cleanroom HVAC Design - KarachituzlucayirNo ratings yet
- Residential - Waterfront GardensDocument1 pageResidential - Waterfront GardensPoppe MusaNo ratings yet
- Physics 06-06 ConductionDocument2 pagesPhysics 06-06 ConductionLetmiDwiridalNo ratings yet
- Erection Programme For 500Mw Boiler - NTPC Korba: Pressure PartsDocument8 pagesErection Programme For 500Mw Boiler - NTPC Korba: Pressure PartskmbkrisNo ratings yet
- Back For Christmas - John Collier (1939)Document7 pagesBack For Christmas - John Collier (1939)nastynate800No ratings yet
- Models 180-LD 181-LDDocument2 pagesModels 180-LD 181-LDEddie SantillánNo ratings yet
- SobhabazarDocument6 pagesSobhabazarsuhani patelNo ratings yet
- 2012/CU2 Information of The Following Places of Interest. 1. I-CityDocument7 pages2012/CU2 Information of The Following Places of Interest. 1. I-CityPushpa RaniNo ratings yet
- Fire Resistant Fiber CablesDocument43 pagesFire Resistant Fiber Cablesrose chenNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide: Non-Programmable Digital ThermostatDocument16 pagesInstallation Guide: Non-Programmable Digital ThermostatBojan BjelajacNo ratings yet
- Solar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsFrom EverandSolar Power Demystified: The Beginners Guide To Solar Power, Energy Independence And Lower BillsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Shorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridFrom EverandShorting the Grid: The Hidden Fragility of Our Electric GridRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- The Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialFrom EverandThe Complete HVAC BIBLE for Beginners: The Most Practical & Updated Guide to Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems | Installation, Troubleshooting and Repair | Residential & CommercialNo ratings yet
- Idaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentFrom EverandIdaho Falls: The Untold Story of America's First Nuclear AccidentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Power of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesFrom EverandPower of Habit: The Ultimate Guide to Forming Positive Daily Habits, Learn How to Effectively Break Your Bad Habits For Good and Start Creating Good OnesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Heat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesFrom EverandHeat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Asphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsFrom EverandAsphaltene Deposition Control by Chemical Inhibitors: Theoretical and Practical ProspectsNo ratings yet
- Well Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsFrom EverandWell Integrity for Workovers and RecompletionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Electric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsFrom EverandElectric Motors and Drives: Fundamentals, Types and ApplicationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Handbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemFrom EverandHandbook on Battery Energy Storage SystemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Air Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&AFrom EverandAir Cooled Heat Exchanger Handbook: Fundamentals, Calculations, Design and Q&ANo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsFrom EverandOffshore Wind Energy Generation: Control, Protection, and Integration to Electrical SystemsNo ratings yet
- The Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceFrom EverandThe Permaculture City: Regenerative Design for Urban, Suburban, and Town ResilienceNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsFrom EverandPhotovoltaic Solar Energy: From Fundamentals to ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Live Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerFrom EverandLive Off Grid: Escape The City, Learn How To Travel Intelligently Using Solar PowerNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsFrom EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Smart Power Distribution Systems: Control, Communication, and OptimizationFrom EverandSmart Power Distribution Systems: Control, Communication, and OptimizationNo ratings yet
- The New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successFrom EverandThe New 3D Layout for Oil & Gas Offshore Projects: How to ensure successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Electrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977From EverandElectrical Load-Curve Coverage: Proceedings of the Symposium on Load-Curve Coverage in Future Electric Power Generating Systems, Organized by the Committee on Electric Power, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, Rome, Italy, 24 – 28 October 1977No ratings yet
- A Pathway to Decarbonise the Shipping Sector by 2050From EverandA Pathway to Decarbonise the Shipping Sector by 2050No ratings yet