Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study 5 Electrical Connectors
Uploaded by
Sunil BaliOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study 5 Electrical Connectors
Uploaded by
Sunil BaliCopyright:
Available Formats
Falex Tribology Case Study 5
Quality
Knowledge
Partner Solutions
Falex Tribology nv
Wingepark 23b | 3110 Rotselaar Belgium
T +32 (0)16 40 79 65 | F +32 (0)16 40 51 28 | office@falex.eu | www.falex.eu
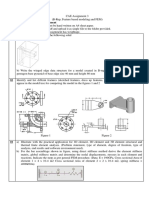
Electrical Connectors
Reliability in Fretting Conditions
Electrical connections in moving
equipment may fail from fretting
damage
Compare different solutions to the
problem by a Falex Fretting Wear
test
Today, electrical connectors are present in many products from cars to mobile phones and
other portable electronics. Because the product moves, the connectors slide over very small
displacements and generate damage that blocks the electrical connection. Such small
displacements are hard to lubricate and damage must be avoided in another way. The
geometry of the connector can be changed, to reduce mechanical pressure, or wear
resistant coatings can be applied, or a suitable grease can be used to avoid the fatal fretting
damage. The different approaches can be tested by a Falex fretting wear test Falex fretting wear test Falex fretting wear test Falex fretting wear test.
Simulate the fretting wear motion on
the real components (or models)
Less than 100 m displacement
Compare useful lifetime of the
electrical contact or low electrical
contact resistance
Compare designs or materials, or the
effect of lubrication or coatings
0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000
0,0
0,5
1,0
1,5
2,0
Test Geometry A
Fretting at 1 Hz, 50 m displacement, 100000 cycles
C
o
n
t
a
c
t
r
e
s
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
(
)
Test duration (s)
0 20000 40000 60000 80000 100000
0,0
0,4
0,8
1,2
1,6
2,0
Test Geometry B
Fretting at 1 Hz, 50 m displacement, 100000 cycles
C
o
n
t
a
c
t
r
e
s
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
(
)
Test duration (s)
Falex Tribology Case Study 5
Quality
Knowledge
Partner Solutions
Falex Tribology nv
Wingepark 23b | 3110 Rotselaar Belgium
T +32 (0)16 40 79 65 | F +32 (0)16 40 51 28 | office@falex.eu | www.falex.eu
Introduction Introduction Introduction Introduction
The reliability of electrical contacts is essential
in many
applications
but the
mechanical
parts are
often
subjected to vibrations and small
displacements during their use.
This may cause fretting damage and this
damage in turn may create wear particles that
isolate the electrical contact, or damage an
electrically conductive coating, like gold.
To ensure correlation between the lab
simulation and the application, we use the real
components (small electrical
connectors) in our test equipment.
Objective Objective Objective Objective
In an unlubricated contact, fretting in
ambient conditions leads to severe fretting
corrosion which ultimately results in connector
electrical failure.
By applying the right grease, this can be
avoided or delayed. To test the durability of the
electrical contact, we combine a Falex high
frequency fretting wear test with an electrical
conductivity measurement of the contact.
We also evaluate the effect on the friction
force, by performing insertion tests and friction
tests with the Falex MUST microtribometer.
Results Results Results Results
Without lubrication, electrical resistance
increases due to the fretting damage.
Greases A, B and C prevent this increase.
Further distinction is visible in the wear
tracks : grease C is more effective in
reducing the total wear than grease A.
CONTACT CONTACT CONTACT CONTACT PROJECTED AREA (m) PROJECTED AREA (m) PROJECTED AREA (m) PROJECTED AREA (m)
Unlubricated 296.753
With Grease A 159.326
With Grease C 46.783
This way, a relative comparison can
easily be made of the anti-wear
properties of the greases.
The insertion force and sliding friction
force of the electrical connectors can be
measured with a MUST Micro
Tribometer.
Conclusion Conclusion Conclusion Conclusion
The anti-wear and friction reducing
properties of special greases for
electrical contacts can be quantitatively
evaluated by laboratory simulations.
0,0 5,0x10
5
1,0x10
6
1,5x10
6
2,0x10
6
2,5x10
6
0,08
0,09
0,10
0,11
0,12
0,13
0,14
0,15
C
o
n
ta
c
t r
e
s
is
ta
n
c
e
(O
h
m
)
Number of fretting cycles
GreaseA GreaseB GreaseC
0,0 5,0x10
5
1,0x10
6
1,5x10
6
2,0x10
6
2,5x10
6
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
C
o
n
ta
c
t
r
e
s
is
t
a
n
c
e
(
O
h
m
)
Number of fretting cycles
Unlubricated Unlubricated Unlubricated Unlubricated A A A A C CC C
You might also like
- A Primer On Dense Phase Pneumatic Conveying SystemsDocument7 pagesA Primer On Dense Phase Pneumatic Conveying Systemspneucon100% (1)
- Composites REVOLUTIONISE AEDocument3 pagesComposites REVOLUTIONISE AEmachit_xNo ratings yet
- Review On Electrical Wiring (Types, Sizes and Installation) : December 2019Document11 pagesReview On Electrical Wiring (Types, Sizes and Installation) : December 2019Vinayak JenaNo ratings yet
- Composite Material 1 2Document1 pageComposite Material 1 2Sudhakar KarnanNo ratings yet
- Pro Sheetmetal LESSONDocument125 pagesPro Sheetmetal LESSONEwerson PalucoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Cable GuideDocument19 pagesElectrical Cable GuideatramanathanNo ratings yet
- Ai For AutomotivesDocument18 pagesAi For AutomotivesAbhishek SoundaleNo ratings yet
- Fotovoltaic ImprovementsDocument5 pagesFotovoltaic Improvements3dfelixNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD Electrical 2017 Quick Reference GuideDocument14 pagesAutoCAD Electrical 2017 Quick Reference GuideElizabeth ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool Awt 5060Document14 pagesWhirlpool Awt 5060Vally ValyNo ratings yet
- Relay Pin Configuration and Implementation in The CircuitsDocument3 pagesRelay Pin Configuration and Implementation in The CircuitsSandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- MetroDocument36 pagesMetroBhuvanes WaranNo ratings yet
- Understanding RelaysDocument20 pagesUnderstanding RelaysrhloaizaNo ratings yet
- Electric Bus June 19, 2019Document12 pagesElectric Bus June 19, 2019Jon WillingNo ratings yet
- List of Regulated Electrical Equipment - Revised25mac2013Document11 pagesList of Regulated Electrical Equipment - Revised25mac2013viethuong96No ratings yet
- Tata Starbus Ultra Electric 9 - 12 EV Bus - Price, Features & SpecificationsDocument3 pagesTata Starbus Ultra Electric 9 - 12 EV Bus - Price, Features & SpecificationsmayankNo ratings yet
- Household AppliancesDocument32 pagesHousehold Appliancesbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- Mizuho Sugita 2 Titanium ClipDocument12 pagesMizuho Sugita 2 Titanium ClipsigmakarsaNo ratings yet
- Main Embedded + SoftwareDocument33 pagesMain Embedded + SoftwareChimbhu SubramaniyamNo ratings yet
- BN-DS-E03 Electrical Design Direct Burial of CablesDocument12 pagesBN-DS-E03 Electrical Design Direct Burial of Cablesvineets0580% (1)
- IC615 Embedded Systems - 23 - 09 - 2020 PDFDocument154 pagesIC615 Embedded Systems - 23 - 09 - 2020 PDFHussainNo ratings yet
- Six Eyes of A DesignerDocument45 pagesSix Eyes of A DesignerSriram100% (3)
- Course FileDocument36 pagesCourse FileElakkiya N.SNo ratings yet
- Automatic Solar Tracker-2Document17 pagesAutomatic Solar Tracker-2ShahnawazNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool Awt 2288 3 sm2 PDFDocument18 pagesWhirlpool Awt 2288 3 sm2 PDFSudrigian Augustin SorinNo ratings yet
- Component of ElectricsDocument13 pagesComponent of ElectricsRam Kishore RoyNo ratings yet
- Wire Drawing Process - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument11 pagesWire Drawing Process - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz AmeenNo ratings yet
- Embedded System DesignDocument22 pagesEmbedded System Designtrail meNo ratings yet
- Interface For CATIA V5 Creo1.0 RevHDocument17 pagesInterface For CATIA V5 Creo1.0 RevHLawrence MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Embed SystemDocument4 pagesEmbed SystemMohan RajNo ratings yet
- IT1353 Embedded SystemDocument6 pagesIT1353 Embedded SystemReeshma ApNo ratings yet
- Electrical Overview PresentationDocument31 pagesElectrical Overview PresentationSomnath DasNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines Ignition System: Rahul Deharkar Lecturer School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarDocument11 pagesInternal Combustion Engines Ignition System: Rahul Deharkar Lecturer School of Technology, PDPU, GandhinagarAdityasinh DesaiNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool Awt 2284Document9 pagesWhirlpool Awt 2284th_gabNo ratings yet
- EmbededsystemDocument31 pagesEmbededsystemsonalNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool AWT2084Document9 pagesWhirlpool AWT2084jjchristy34100% (1)
- Sheet Metalworking Analysis: DFM Concurrent Costing DfmaDocument8 pagesSheet Metalworking Analysis: DFM Concurrent Costing DfmaSharun JacobNo ratings yet
- Electrical WiringDomest 8310585Document20 pagesElectrical WiringDomest 8310585Berry KasanNo ratings yet
- AkiraDocument28 pagesAkiraRoby Surya100% (1)
- ET7104-Design of Embedded SystemsDocument5 pagesET7104-Design of Embedded SystemsAnonymous zQOH5ikNo ratings yet
- Autocad ElectricalDocument2 pagesAutocad ElectricalcontgautamNo ratings yet
- Solar Panel Maintenance SystemDocument5 pagesSolar Panel Maintenance SystemSikhiva Publishing HouseNo ratings yet
- Plastic OmniumDocument2 pagesPlastic Omniumgsravan_23No ratings yet
- CATIA Generative Part Structural DatasheetDocument2 pagesCATIA Generative Part Structural DatasheetburakbariskanNo ratings yet
- GpsDocument5 pagesGpstanhuyhcmutNo ratings yet
- Electric Plugs Per CountryDocument4 pagesElectric Plugs Per Countryandrei_bertea7771No ratings yet
- Embedded SystemsDocument24 pagesEmbedded Systemspavi1402No ratings yet
- Prototyping: Presented by Pradeep PandeyDocument16 pagesPrototyping: Presented by Pradeep PandeyPradeep Kumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- List of Case ExamplesDocument2 pagesList of Case ExamplesvinulalNo ratings yet
- Wires and Cables Used For Residential Electrical SystemsDocument3 pagesWires and Cables Used For Residential Electrical SystemsNurul ShathirahNo ratings yet
- Washing Machine Motor Wiring BasicsDocument3 pagesWashing Machine Motor Wiring BasicsSamorai Kaza100% (1)
- Final Report Godrej Sagar VermaDocument36 pagesFinal Report Godrej Sagar VermaSagarNo ratings yet
- 2020 CAE Assignment 3Document1 page2020 CAE Assignment 3Important Not importantNo ratings yet
- AircraftDocument254 pagesAircraftpodolskaya100% (1)
- Presentation: Coefficient of Friction On Threaded Fasteners in The Automotive IndustryDocument20 pagesPresentation: Coefficient of Friction On Threaded Fasteners in The Automotive IndustryAvinashRaiNo ratings yet
- Loctite 243™: Technical Data SheetDocument4 pagesLoctite 243™: Technical Data SheetRadu_ISNo ratings yet
- Tratos Flex000Document64 pagesTratos Flex000twinvbooksNo ratings yet
- Vibration TransducerDocument13 pagesVibration TransducerLawren IgnatiusNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument6 pagesData SheetcornolioNo ratings yet
- WHP Nema Iec Cont ActorsDocument4 pagesWHP Nema Iec Cont ActorsJimmy Tacca ApazaNo ratings yet
- HF2100 enDocument4 pagesHF2100 enBhakti PermanaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications With Special Reference To Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate)Document18 pagesPlastic Degradation and Its Environmental Implications With Special Reference To Poly (Ethylene Terephthalate)Anonymous Wcj4C3jNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis and Evaluation of A Rectangular Pressure VesselDocument10 pagesStress Analysis and Evaluation of A Rectangular Pressure Vesselmatodelanus100% (1)
- Ethanol Blended Fuel in India: An Overview: July 2010Document12 pagesEthanol Blended Fuel in India: An Overview: July 2010Sunil BaliNo ratings yet
- BS VI Fuel Spec Working Paper VFDocument4 pagesBS VI Fuel Spec Working Paper VFYajuvendra JhalaNo ratings yet
- Ineos Polypropylene Processing GuideDocument18 pagesIneos Polypropylene Processing GuideLe Toan100% (1)
- Paper - Ethanol Blend Fuel Performance On Evaporative Emission of Motorcycle in Thailand (Thummarat-Thai Speaker PDFDocument22 pagesPaper - Ethanol Blend Fuel Performance On Evaporative Emission of Motorcycle in Thailand (Thummarat-Thai Speaker PDFSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- Case Study 5 Electrical ConnectorsDocument2 pagesCase Study 5 Electrical ConnectorsSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- Mohyals-Bali Mohyal BrahmansDocument2 pagesMohyals-Bali Mohyal BrahmansSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- Lambda Sensor2Document180 pagesLambda Sensor2Sunil Bali100% (4)
- FLENDERDocument79 pagesFLENDERekin100% (4)
- 1DIN 6921-10.9 Hex Flange Bo.Document2 pages1DIN 6921-10.9 Hex Flange Bo.Sunil BaliNo ratings yet
- GD&T Hierarachy PyramidDocument1 pageGD&T Hierarachy PyramidSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- DSM Engineering Plastics - Annealing-001Document1 pageDSM Engineering Plastics - Annealing-001Sunil BaliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Plastics AnealingDocument1 pageEngineering Plastics AnealingSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- GD&T Reference ChartDocument1 pageGD&T Reference ChartChinna ThiruNo ratings yet
- Engineering Plastics AnealingDocument1 pageEngineering Plastics AnealingSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Plastics AnealingDocument1 pageEngineering Plastics AnealingSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Plastics AnealingDocument1 pageEngineering Plastics AnealingSunil BaliNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower TroubleshootingDocument4 pagesCooling Tower TroubleshootingTobaNo ratings yet
- TI Manual Side ElevatorDocument18 pagesTI Manual Side ElevatorMANUFACTURA PETROLERA SERVICES (ADMINISTRACIÓN)No ratings yet
- 3050 System Seals Failure HandbookDocument22 pages3050 System Seals Failure HandbookShaufiq RashidNo ratings yet
- Mechanical SealsDocument49 pagesMechanical Sealsglazetm100% (2)
- Wear Protection Conveyor TechnologyDocument12 pagesWear Protection Conveyor TechnologyFernando MilmanNo ratings yet
- High Speed Hard Turning of Aisi S1 (60Wcrv8) Cold Work Tool SteelDocument18 pagesHigh Speed Hard Turning of Aisi S1 (60Wcrv8) Cold Work Tool Steelnovkovic1984No ratings yet
- On-Road Tyres: Product Range 2020Document11 pagesOn-Road Tyres: Product Range 2020sgdgdsgsdgNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Failure Analysis of Various ImplantDocument7 pagesMetallurgical Failure Analysis of Various Implantdiegomez84100% (1)
- Kluber-Brochure Lubrication of Various ComponentsDocument17 pagesKluber-Brochure Lubrication of Various ComponentsjalalNo ratings yet
- Wear of Teeth and RestorationsDocument7 pagesWear of Teeth and RestorationsAya Ibrahim YassinNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument28 pagesInternship ReportCH.H.AWAIS RASOOLNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Roadmap To Reliability: Our ConsultantDocument10 pagesMaintenance Roadmap To Reliability: Our Consultantmaintenance cwaNo ratings yet
- FQ MeterDocument2 pagesFQ MeterJJNo ratings yet
- Triton Cupper Manual 4-23-15Document118 pagesTriton Cupper Manual 4-23-15Marcelo BarrosNo ratings yet
- 4in Chain-Vey - ManualDocument29 pages4in Chain-Vey - ManualRonald Barcia100% (1)
- b02 Wiethoff VosslohDocument28 pagesb02 Wiethoff Vosslohcheikh ahmedNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Nano3 PDFDocument5 pagesJurnal Nano3 PDFamaliaNo ratings yet
- 212 12e PDFDocument20 pages212 12e PDFMiguel Angel Vargas LeónNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Modelling in Super Duplex Stainless Steel TurningDocument16 pagesSurface Roughness Modelling in Super Duplex Stainless Steel TurningfatinNo ratings yet
- Wear Maps and Statistical Approach of AISI 316L Alloy Under Dry Sliding ConditionsDocument16 pagesWear Maps and Statistical Approach of AISI 316L Alloy Under Dry Sliding ConditionsRicardo Andrés García LeónNo ratings yet
- Applying Higher C-Values in API RP 14E Erosion Velocity Calculations For Gas Condensate Wells ΠA Case StudyDocument12 pagesApplying Higher C-Values in API RP 14E Erosion Velocity Calculations For Gas Condensate Wells ΠA Case StudyKamal HamzahNo ratings yet
- Propeler Shaft Survey Extension - Preventive Maintenance (1) 4Document8 pagesPropeler Shaft Survey Extension - Preventive Maintenance (1) 4Frano GrifiNo ratings yet
- Bearing Failure AnalisisDocument2 pagesBearing Failure AnalisischasestarNo ratings yet
- Abrasive Agents in DentistryDocument38 pagesAbrasive Agents in Dentistryjohn mwambu100% (1)
- 13 Ways To Kill A Mechanical Seal FINALDocument16 pages13 Ways To Kill A Mechanical Seal FINALRanjit Koshy AlexanderNo ratings yet
- ABB-DMI Type DC Machines Operating and Maintenance InstructionsDocument48 pagesABB-DMI Type DC Machines Operating and Maintenance InstructionsElafanNo ratings yet
- HonningDocument13 pagesHonningSyed Danish FayazNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Condition Monitoring: Why The Lubricants MonitoringDocument14 pagesLubricant Condition Monitoring: Why The Lubricants Monitoringrbdubey2020No ratings yet
- Euclid Wheel Attatching Tech TipsDocument12 pagesEuclid Wheel Attatching Tech Tipstim winkelmanNo ratings yet